Esophageal Case 10

Dr. Roos Pouw
Utrecht UMC, Utrecht, the Netherlands
Scope : GIF-EZ1500
Case : Barrett esophagus inspection of early neoplasia, followed by endoscopic resection that showed a well differentiated T1m3 cancer
Organ : Esophagus
Patient Information : 73-year old man, referred with a Barrett segment and low- and high-grade dysplasia in random biopsies
Medical History : During Barrett surveillance endoscopy random biopsies showed low- and high-grade dysplasia
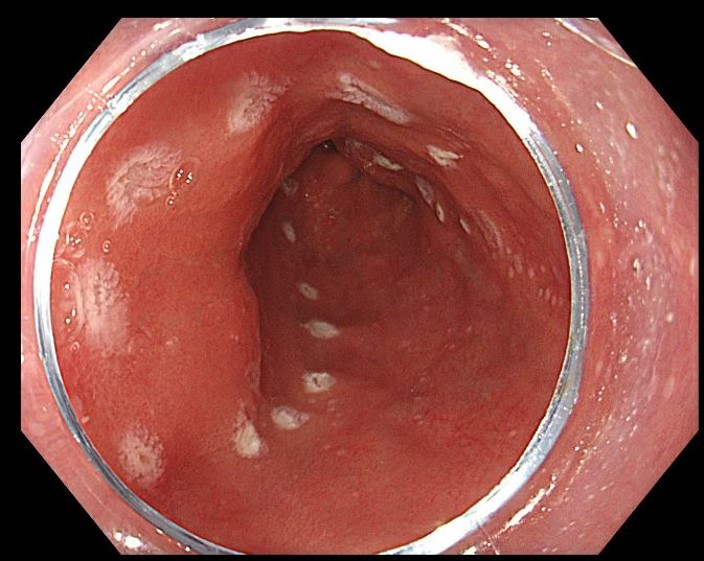
1. High-resolution white light endoscopy of the lesion, subtle demarcation line
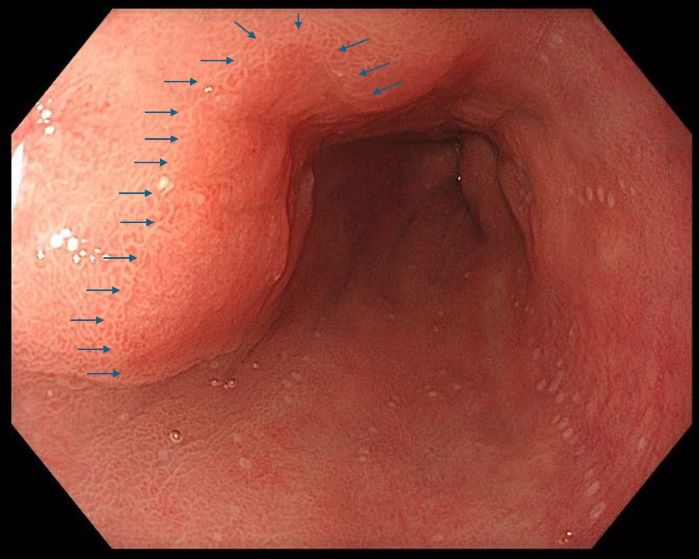
High resolution white light endoscopy demonstrated a color change in the mucosa that was indicating presence of an early neoplastic lesion. Due to the high resolution of the image, a demarcation line between normal and neoplastic tissue could be clearly identified.
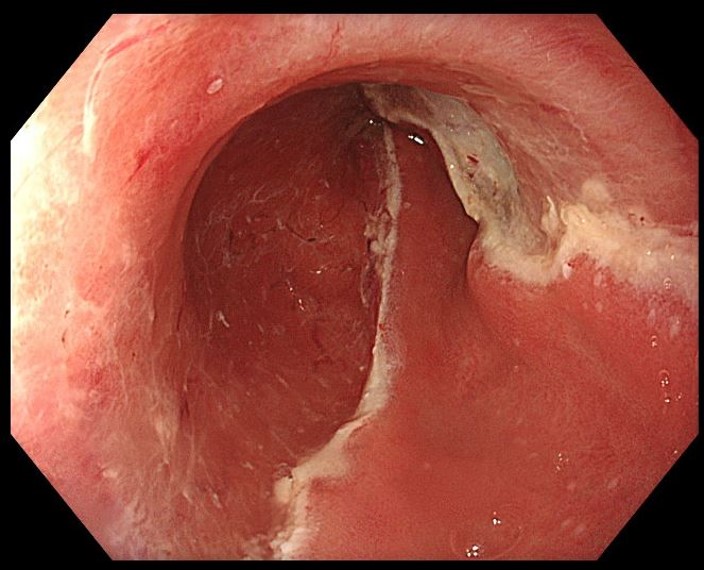
2. Demarcation line of neoplastic lesion nicely visualized with narrow-band imaging and near focus and distal attachment cap
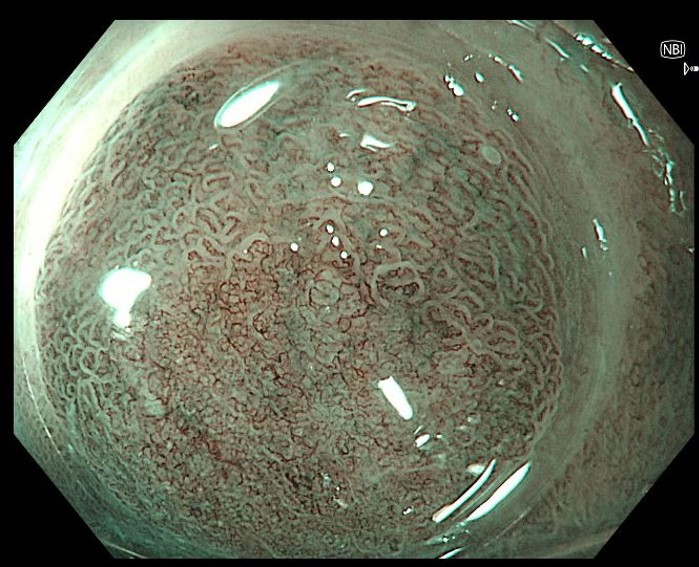
Inspection with narrow-band imaging (NBI), near focus and a distal attachment cap helps in delineating the neoplastic lesion. Inspection clearly shows a sharp demarcation line between normal versus irregular mucosal and vascular pattern.
Case video
A pullback with white light endoscopy shows a long segment Barrett esophagus, with a subtle, flat type lesion from 7-1 o’clock in the distal esophagus, recognized by slight mucosal irregularities and slightly more reddish colour
A pullback with NBI shows shows the lesion by making the subtle mucosal irregularities a bit more pronounced.
Inspection with NBI, near focus and the use of a distal attachment cap to stabilize the mucosa, helps to identify the delineation line of the neoplastic lesion by clearly showing the border between normal mucosa and irregular mucosa and irregular vascularity.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
- Keyword
- Content Type