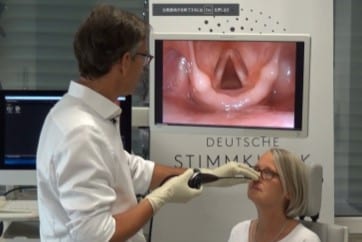
OFFICE-BASED PHONOSURGERY
In office-based phonosurgery various procedures can be performed. All of them depend on good technical imaging skills during laryngoscopy.
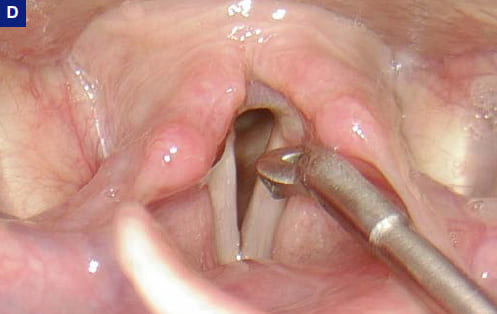
The transoral approach has been used for more than one hundred years. For excision of tiny lesions, a high level of magnification is very helpful. Here the 90° rigid endoscope with zoom has advantages. For other purposes the 70° rigid endoscope has the advantage of a good overview and does not need refocusing when changing the position during endoscopy.
With the transnasal approach, procedures such as laser treatment can be performed. Excisions or injections are also possible, but with this technique the procedure may be less precise compared to the transoral technique.
For percutaneous vocal fold augmentation, the visualization of the glottis with transnasal flexible endoscopy is very helpful. This approach needs two surgeons.
Another possibility is splitting the surgical transoral approach and transnasal endoscopic visualization. This approach needs two surgeons.
Table 8.1 Phonosurgical Office-Based Procedures
| Rigid Transoral | Flexible Transnasal |
Percutaneous Procedure with Transnasal Visualization |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Excision | + | (+) | – |
| Biopsy | + | + | – |
| Augmentation | + | (-) | + |
| Injection (e.g. steroids, botulinum toxin) | + | + | + |
| Laser | + | + | – |
+ = suitable access for specific procedure
(+) = sometimes suitable
Phonosurgery, Rigid Transoral Procedure
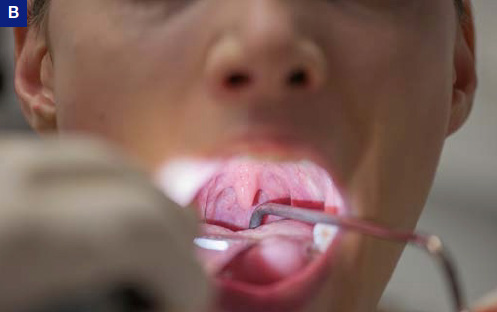
Topical anesthesia before indirect transoral intervention; A) Oro- and hypopharynx; B) Endolarynx (spatula was used in this case to expose the posterior oral cavity for didactic purposes only – otherwise it is done with tongue protruded, see C)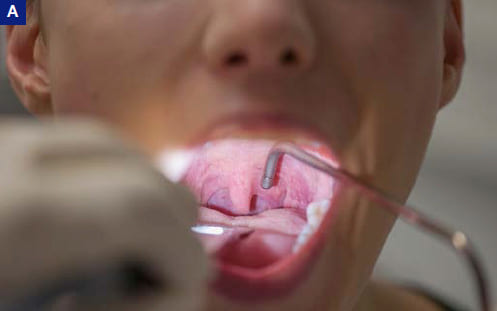

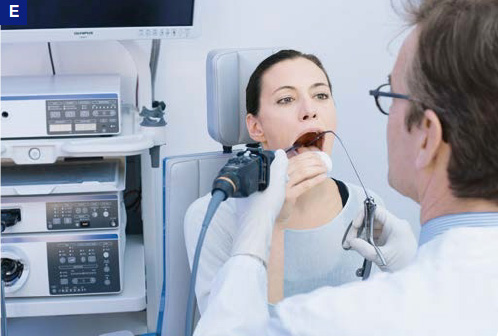
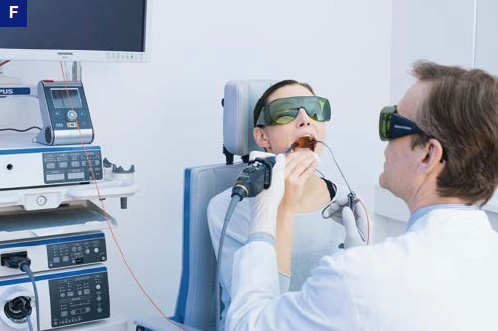
Phonosurgery, Flexible Transnasal Procedure
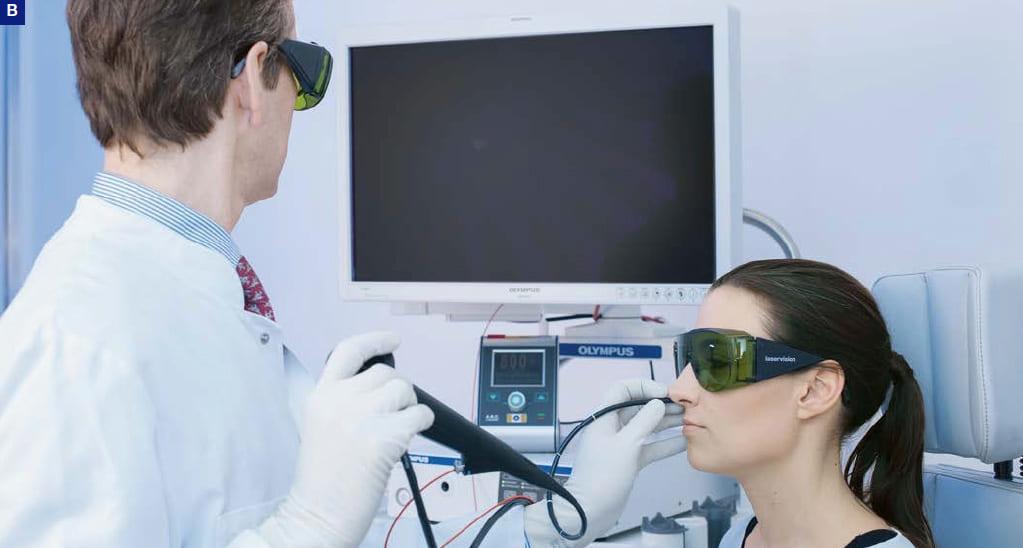
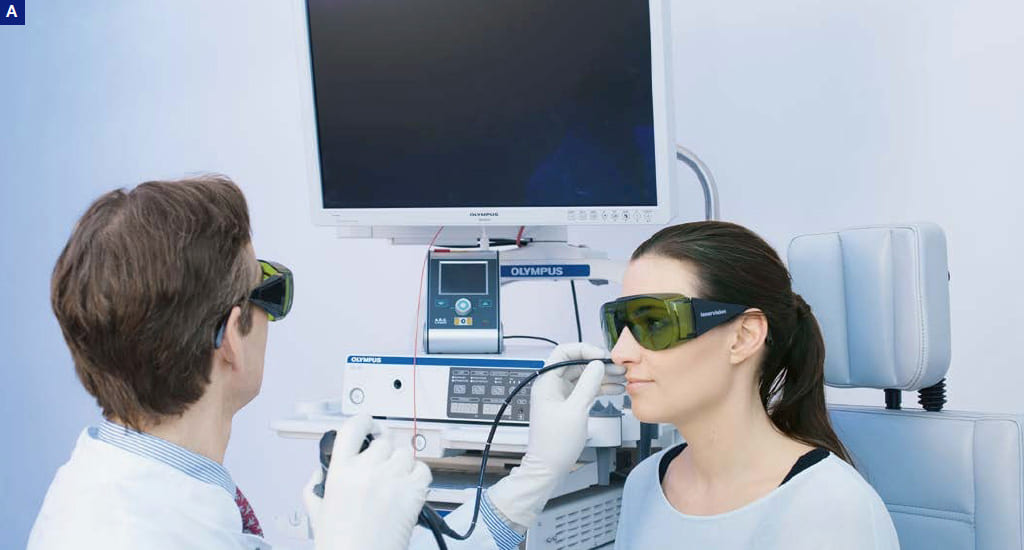

Phonosurgery, Percutaneous Procedure with Transnasal Visualization
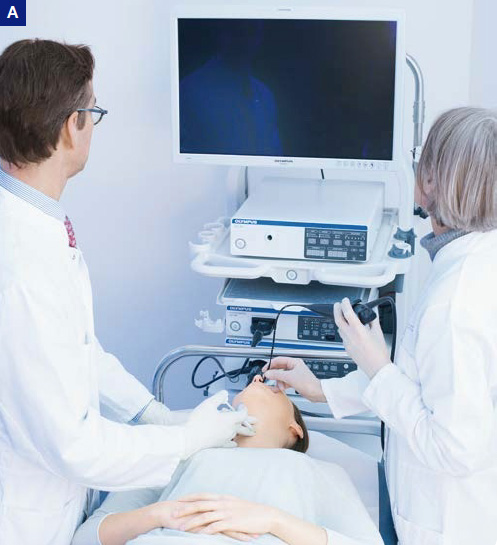
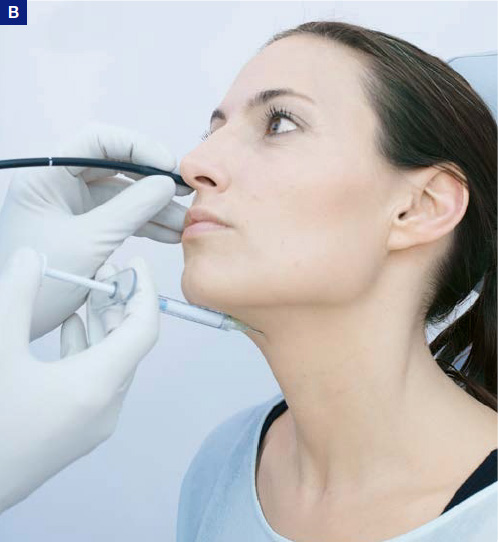
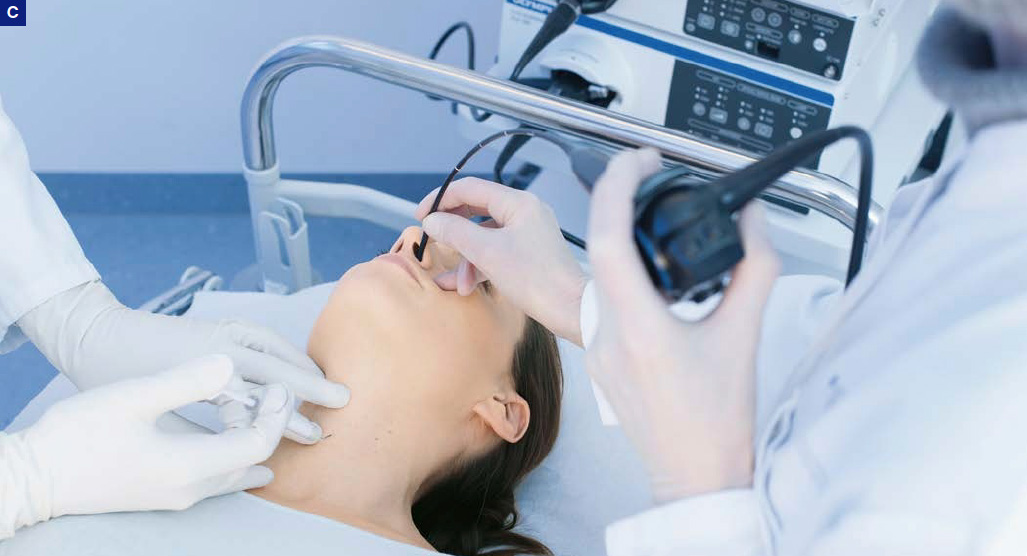
A–C) Percutaneous augmentation.
A, C) Surgeon (left) injects (here: Cricothyroid approach). Positioning of needle is monitored with the help of an endoscopist (right).
B) Demonstration of needle position and angulation for thyrohyoid approach. Here, surgeon supports advancement of endoscope. Nevertheless, this procedure needs an endoscopist (not displayed in B).
- Content Type