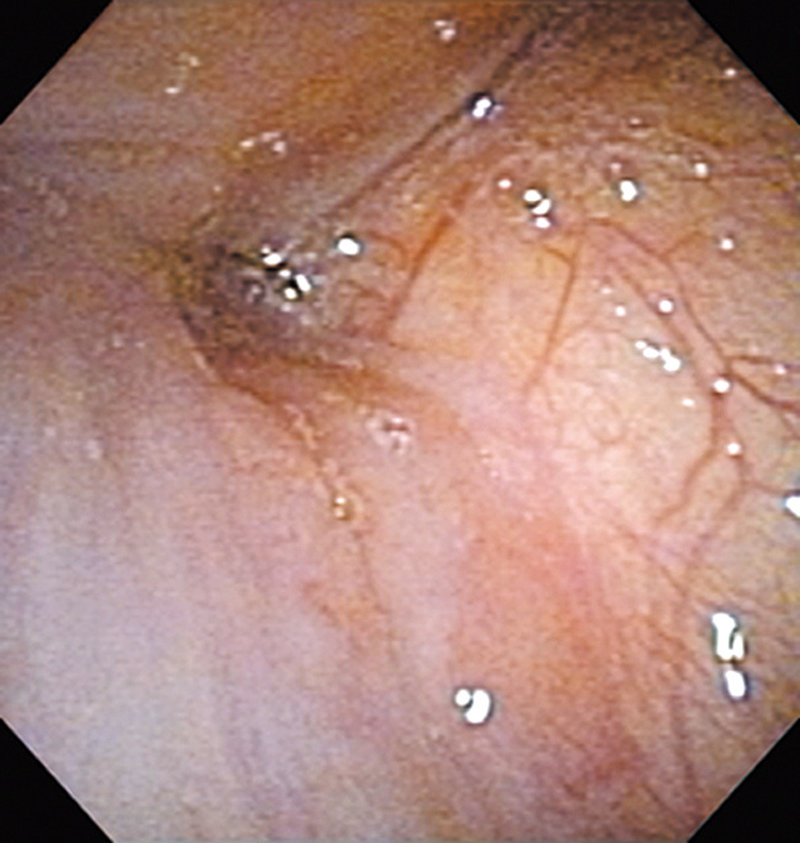
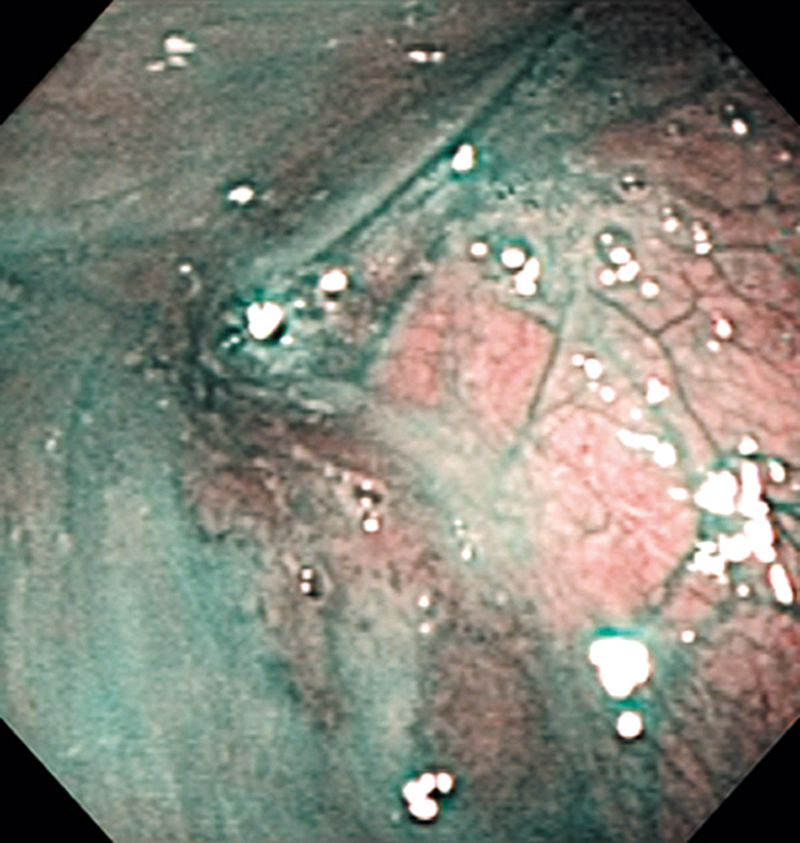
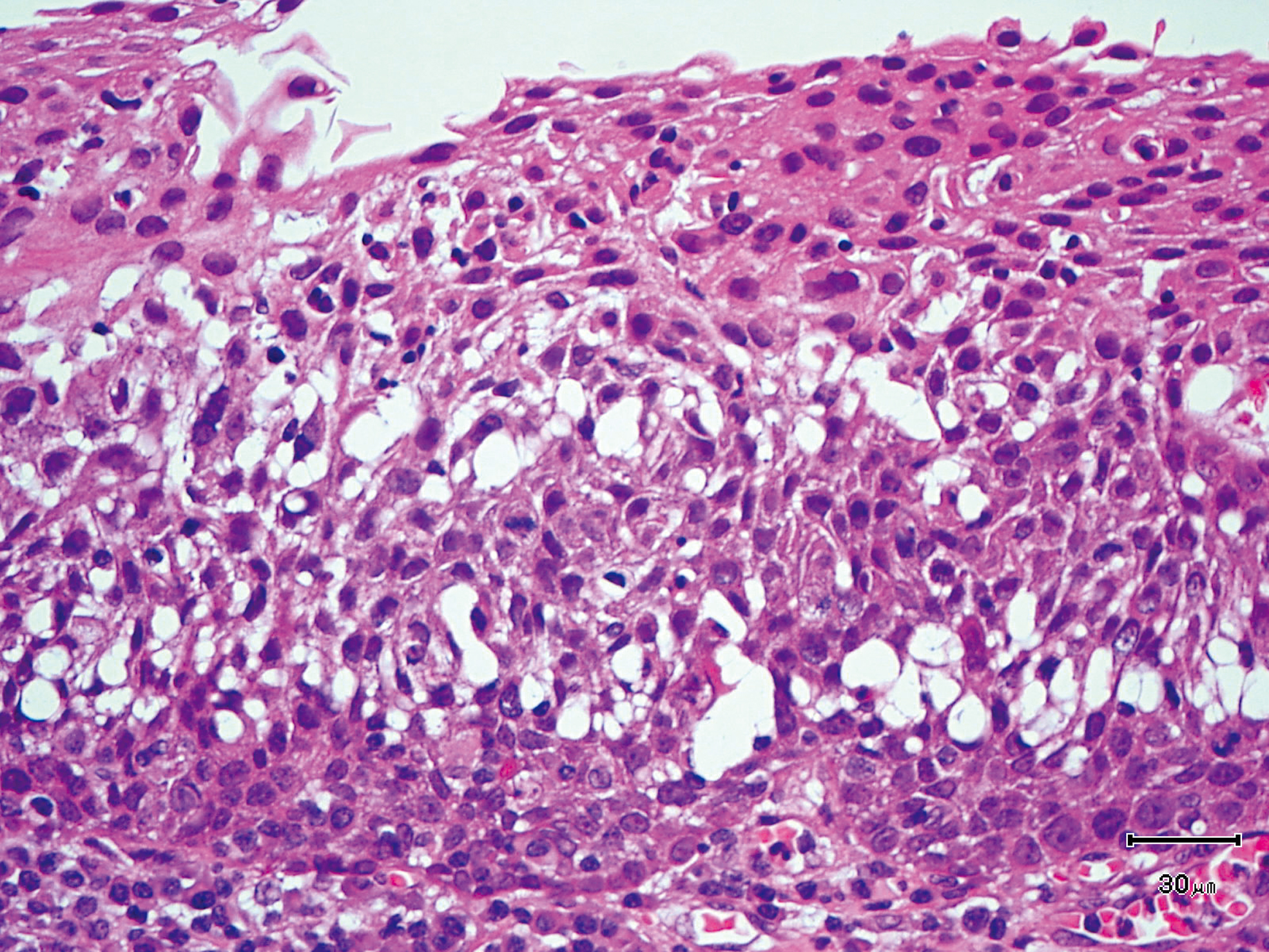
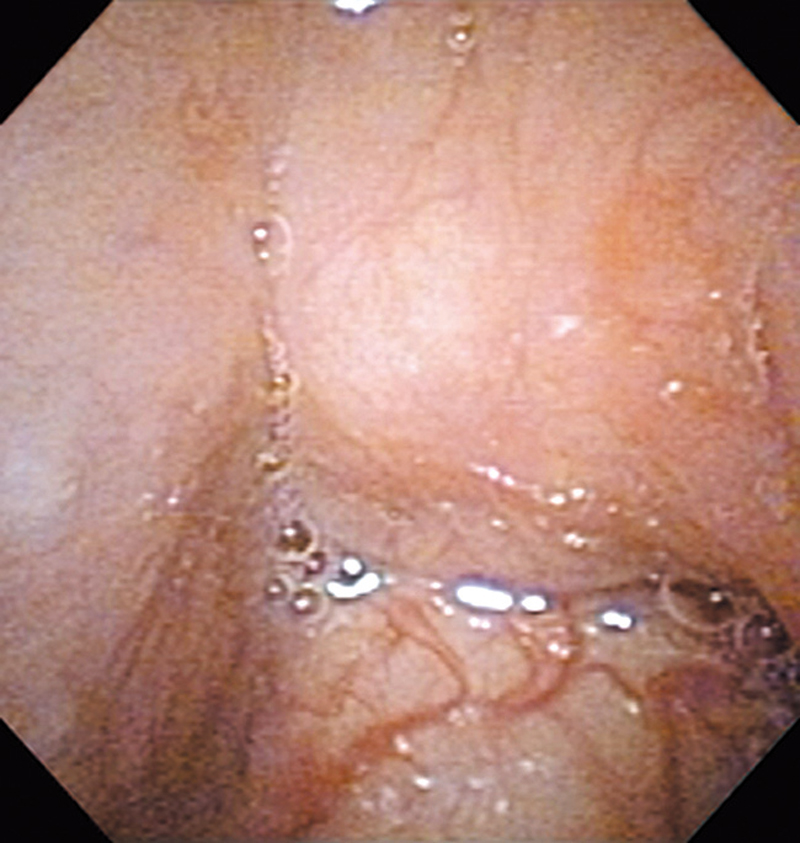
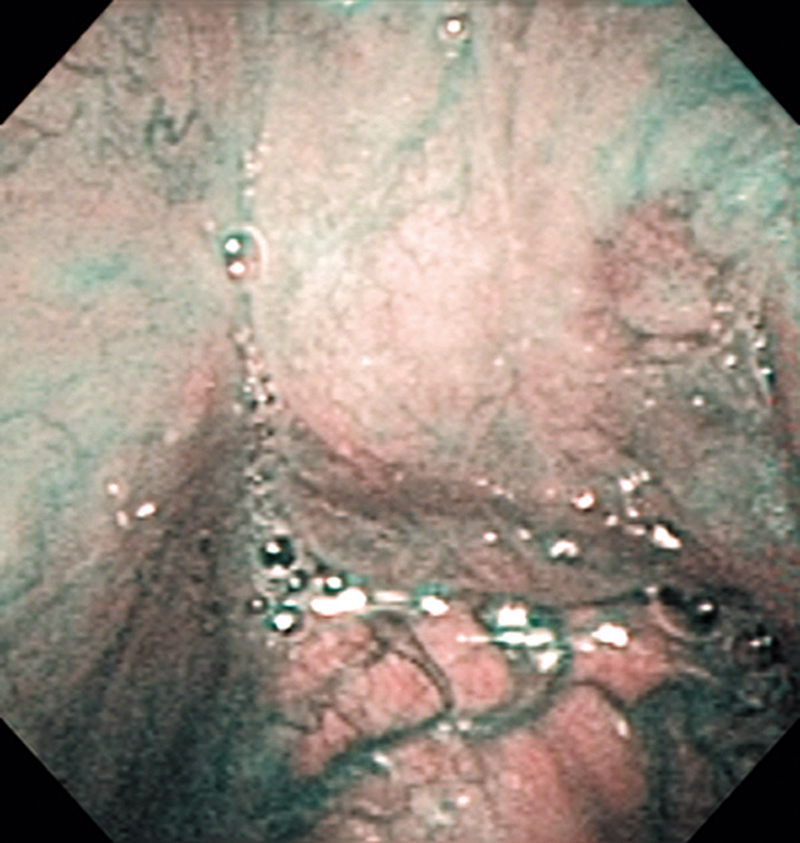
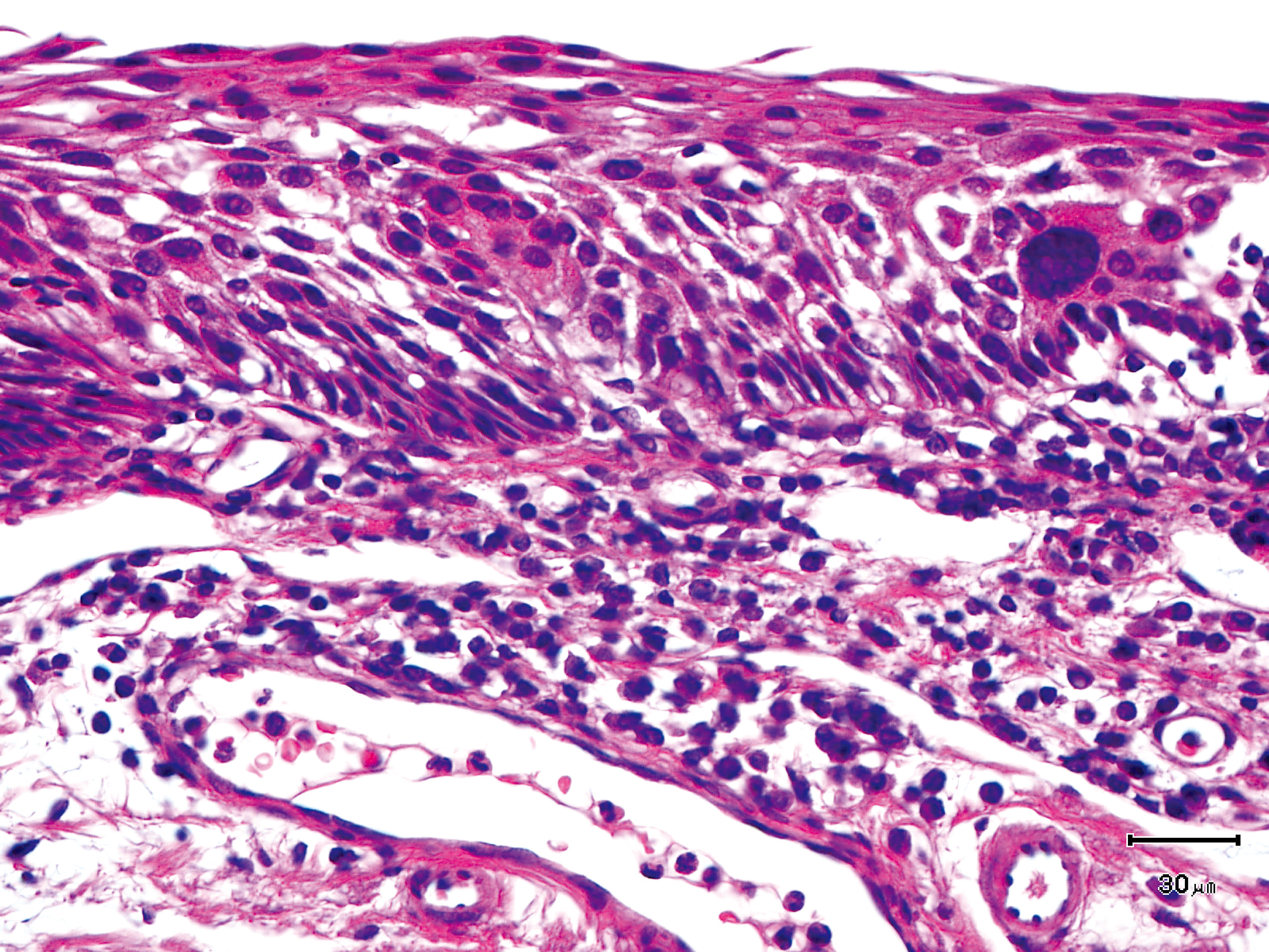
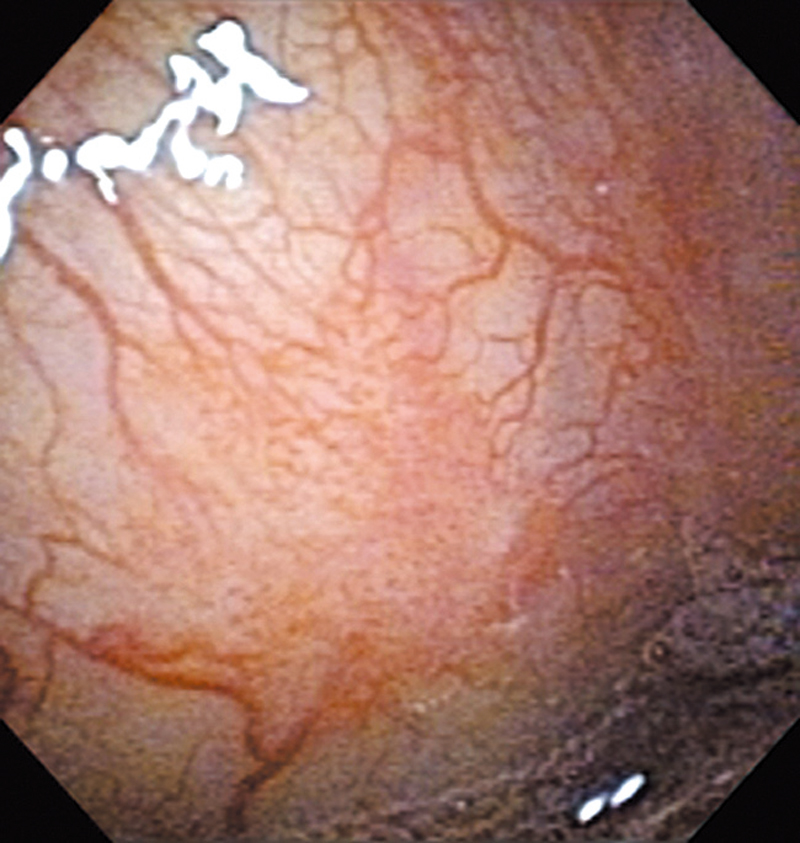
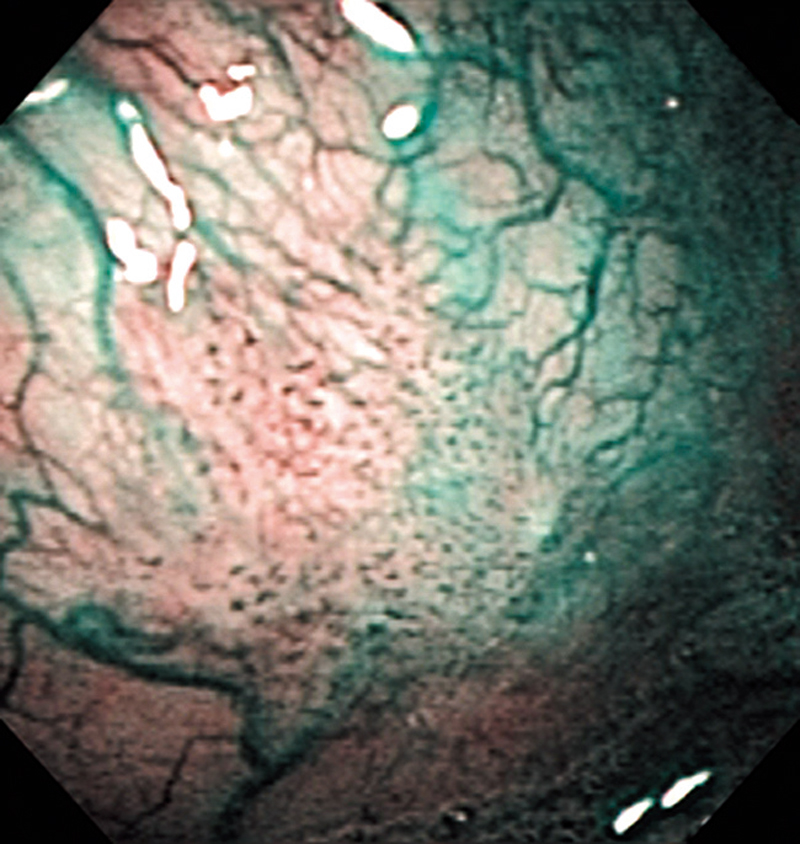
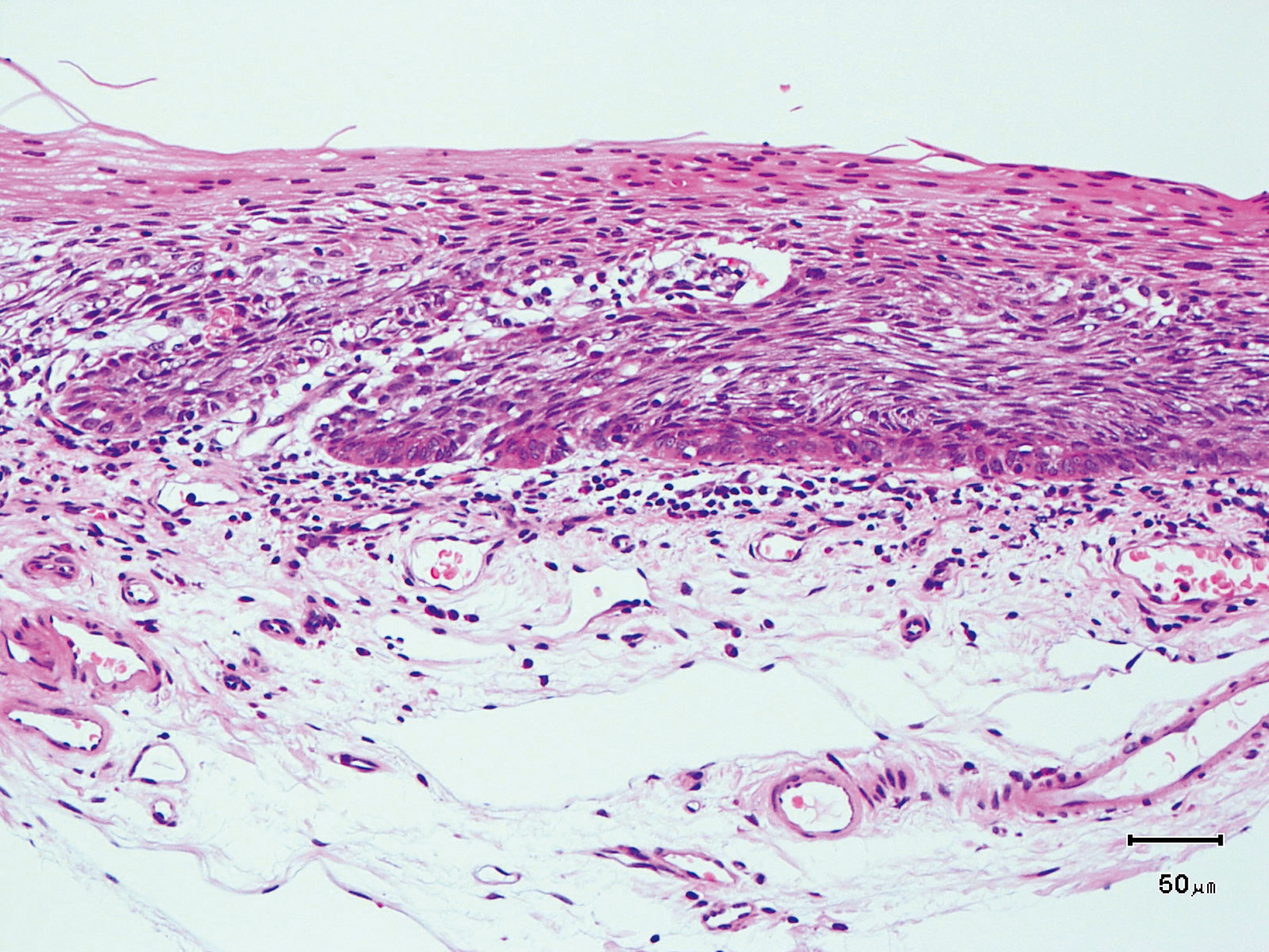
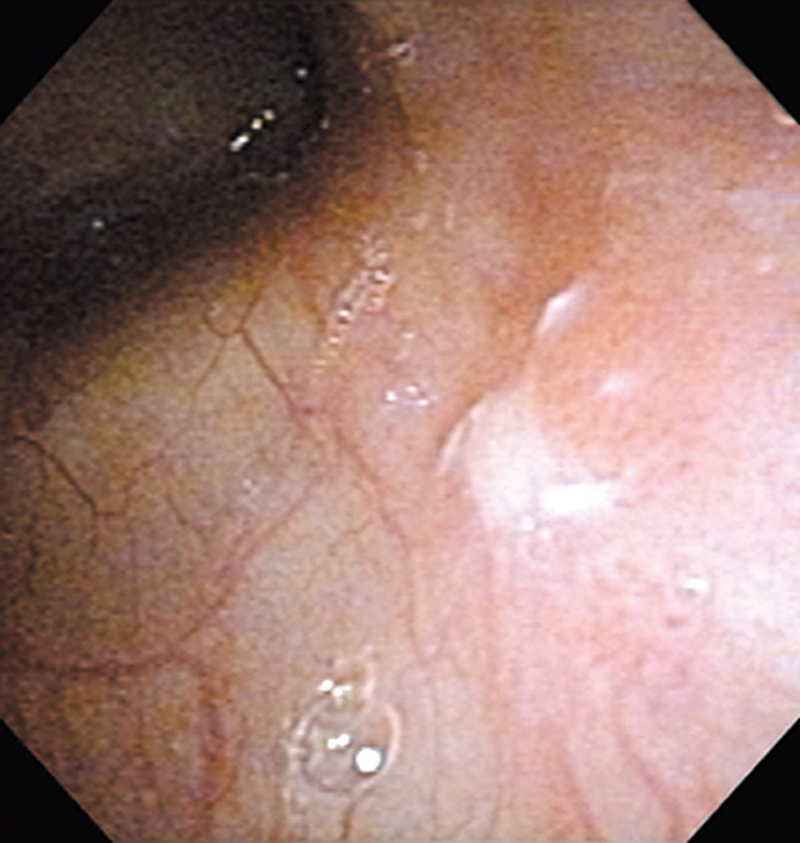
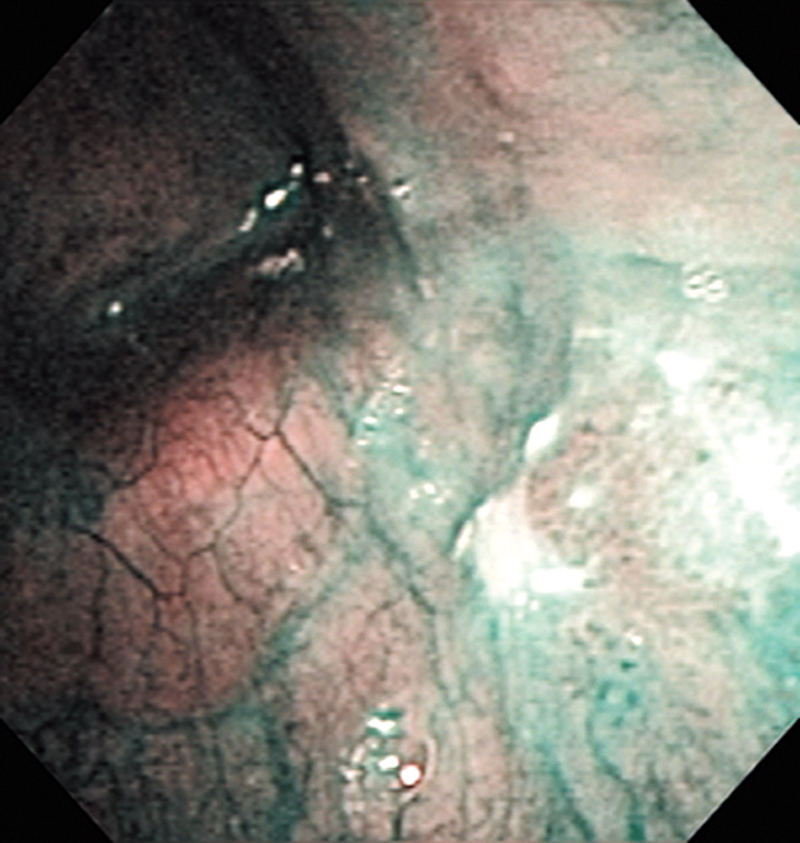
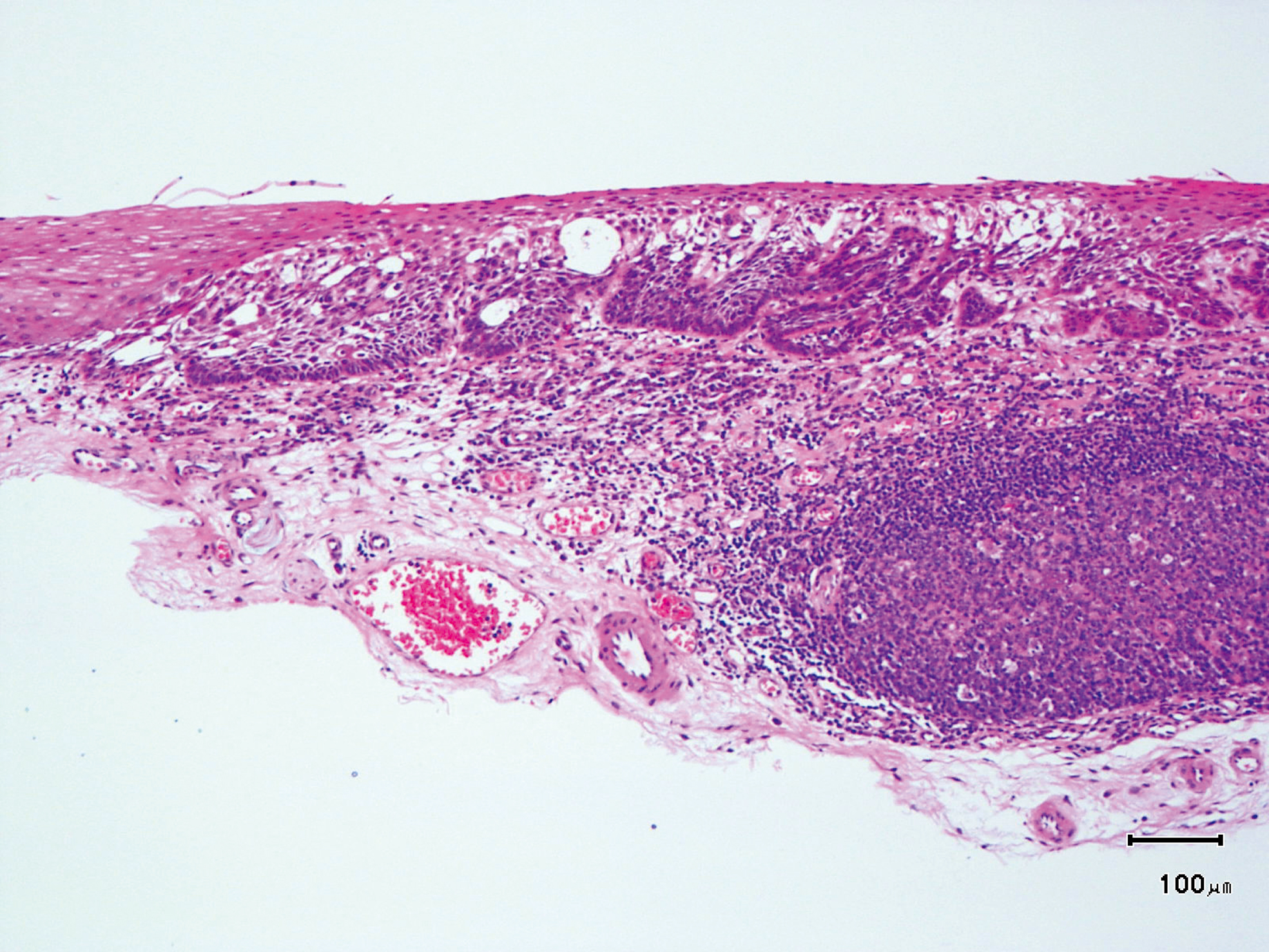
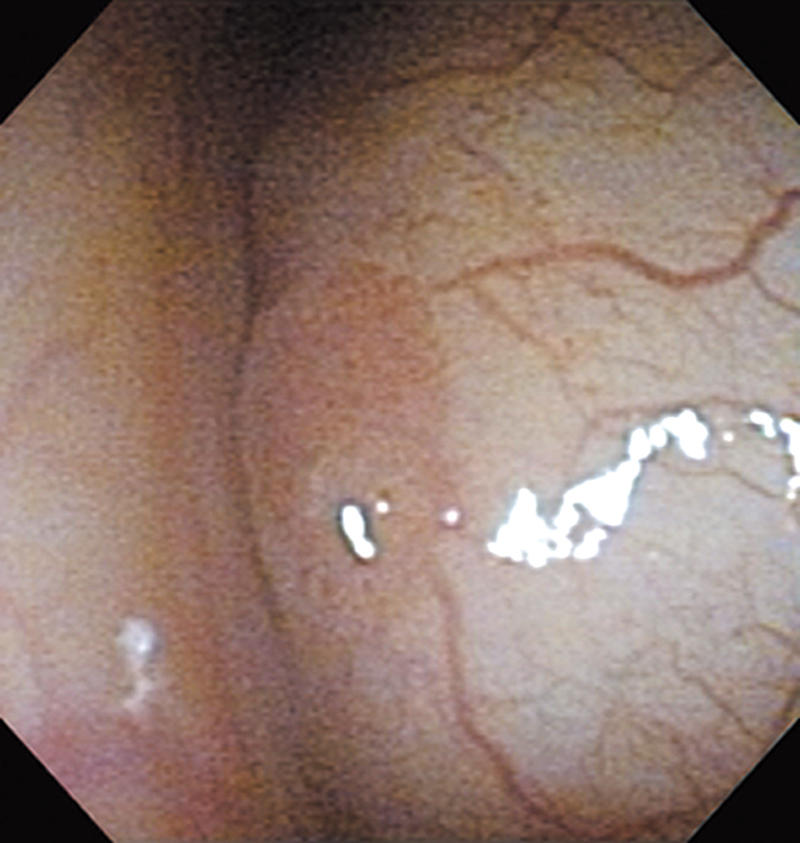
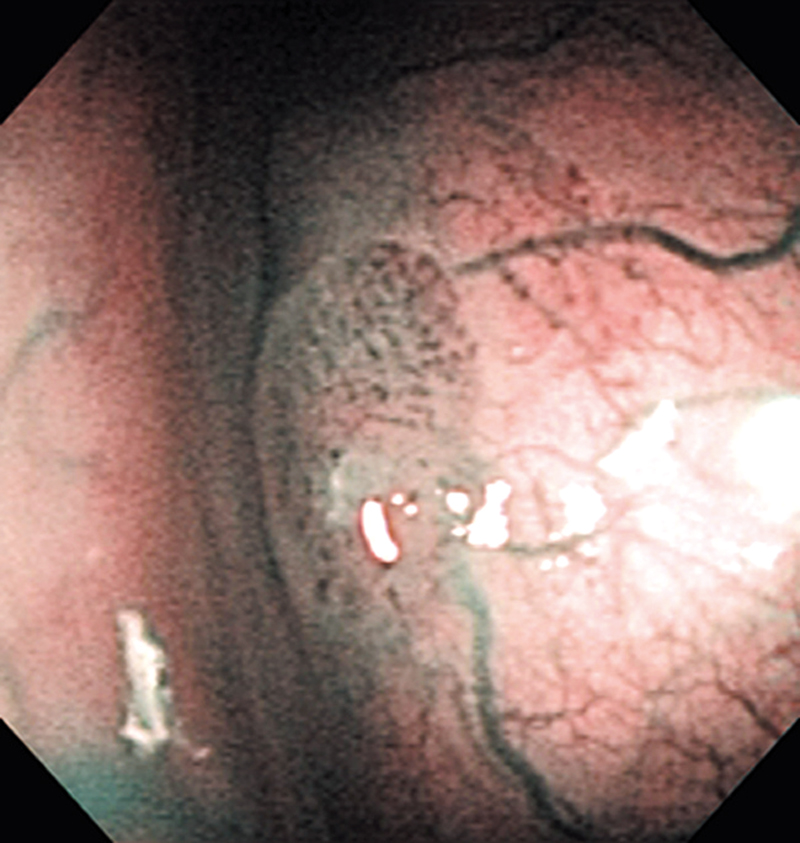
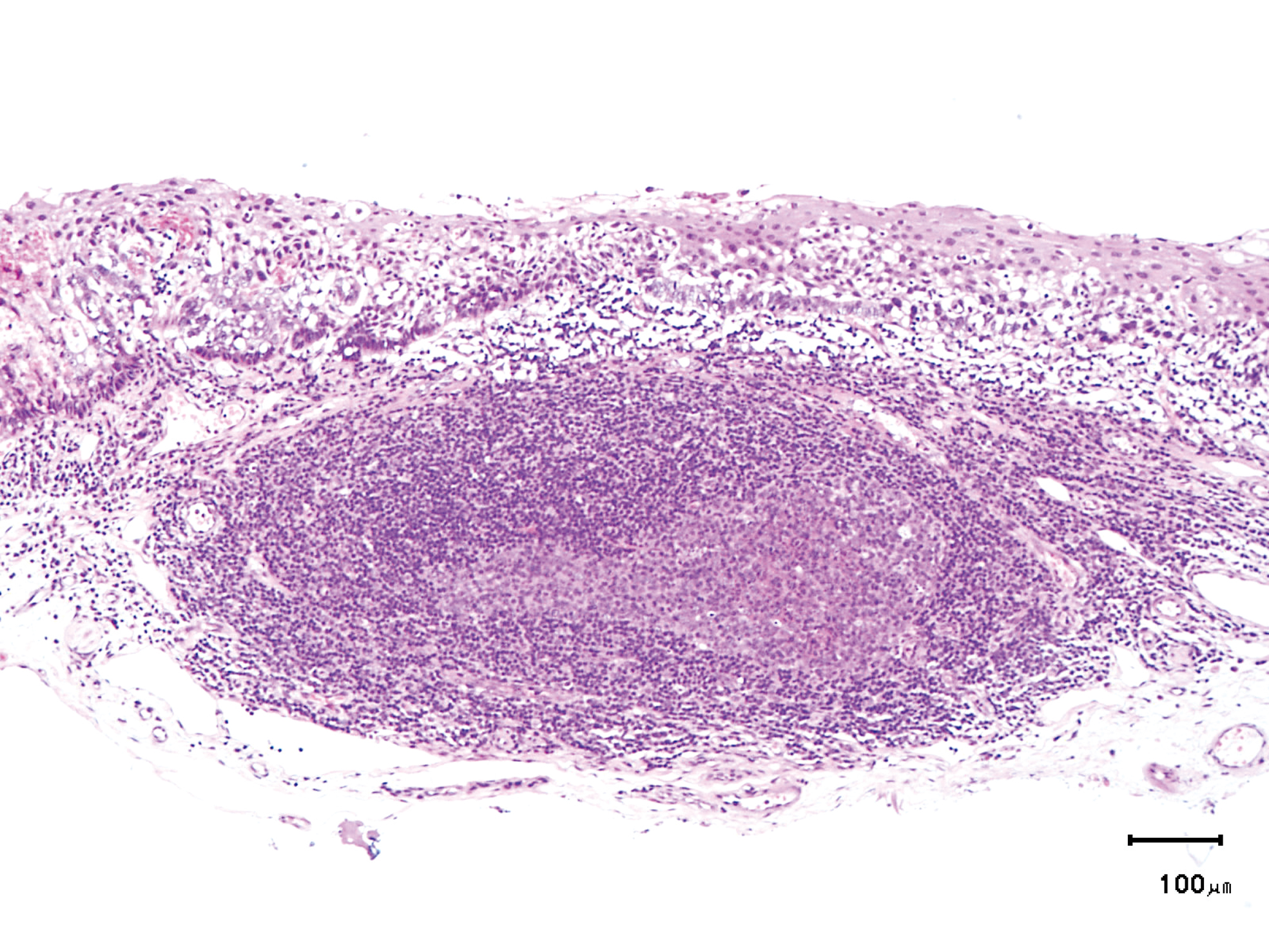
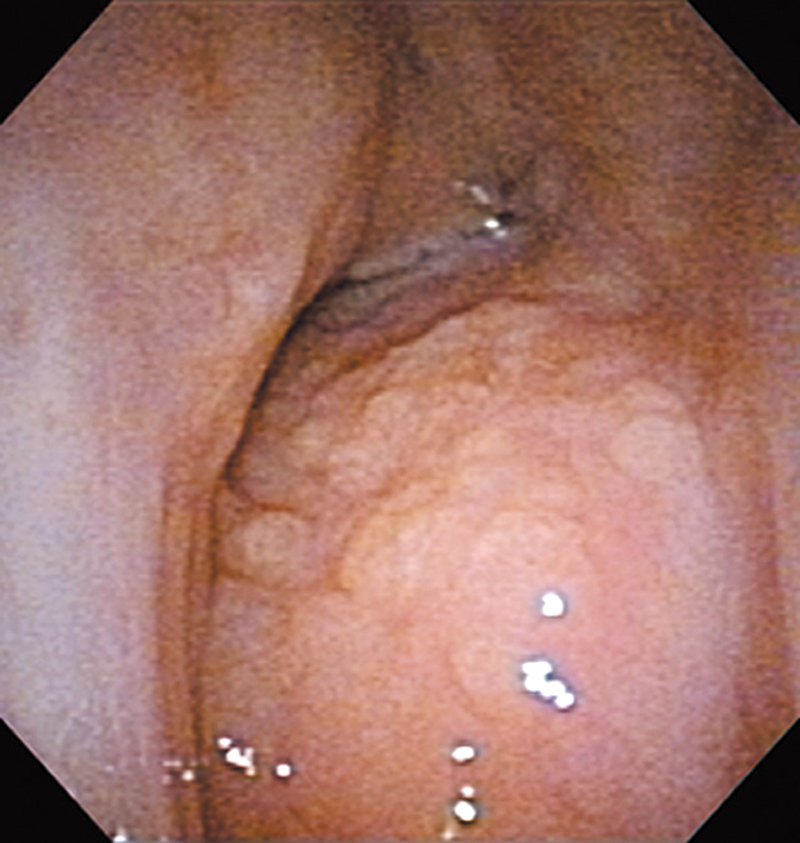
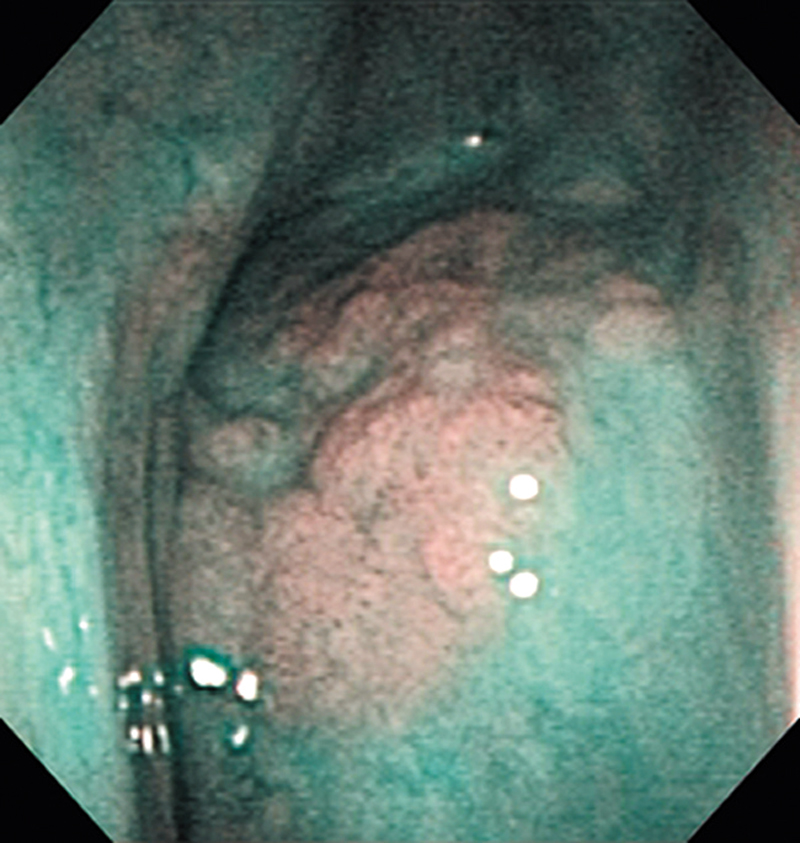
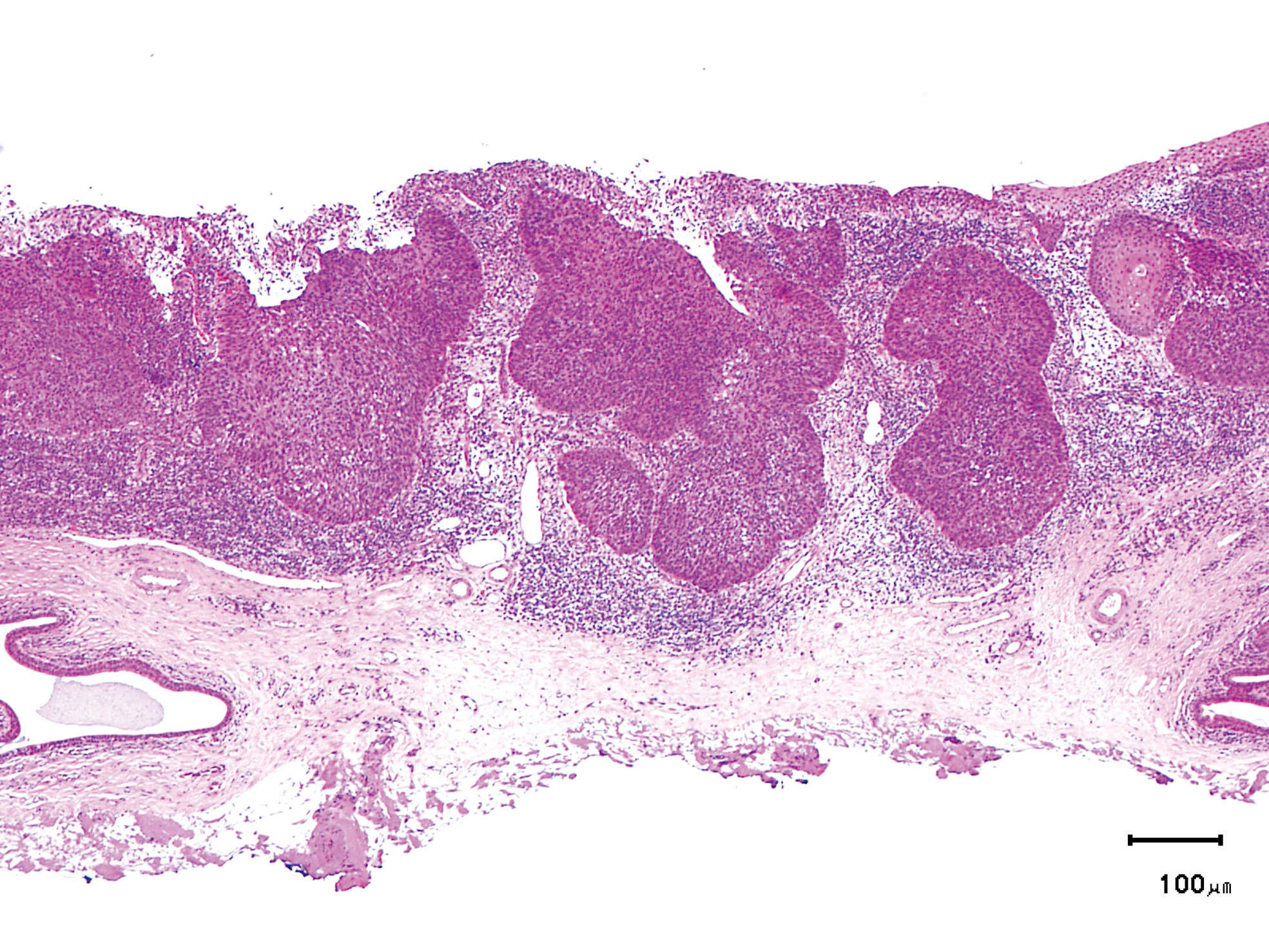
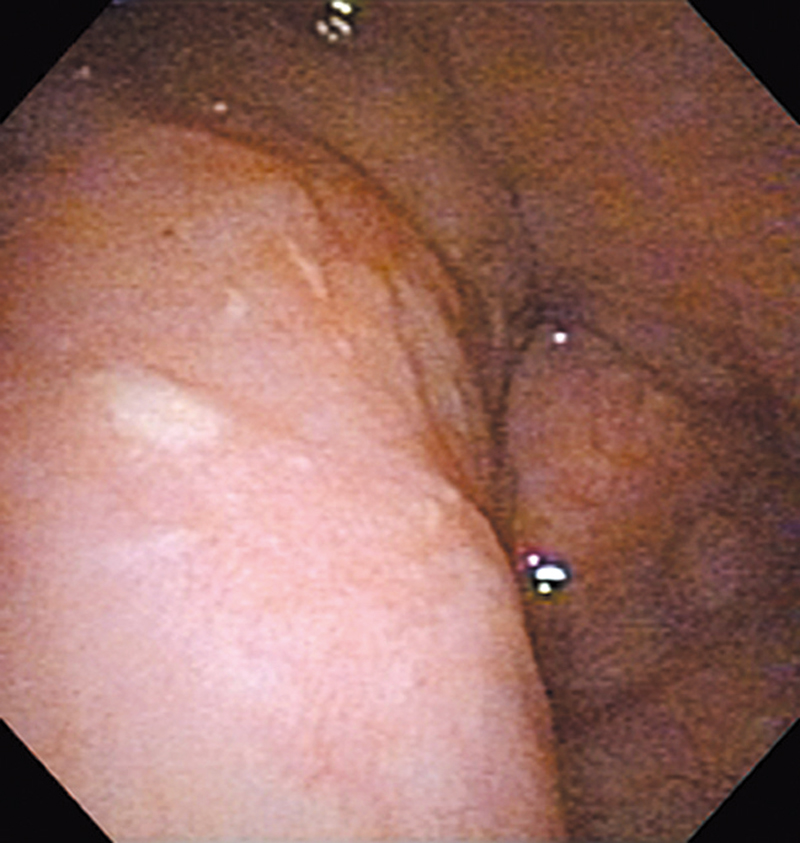
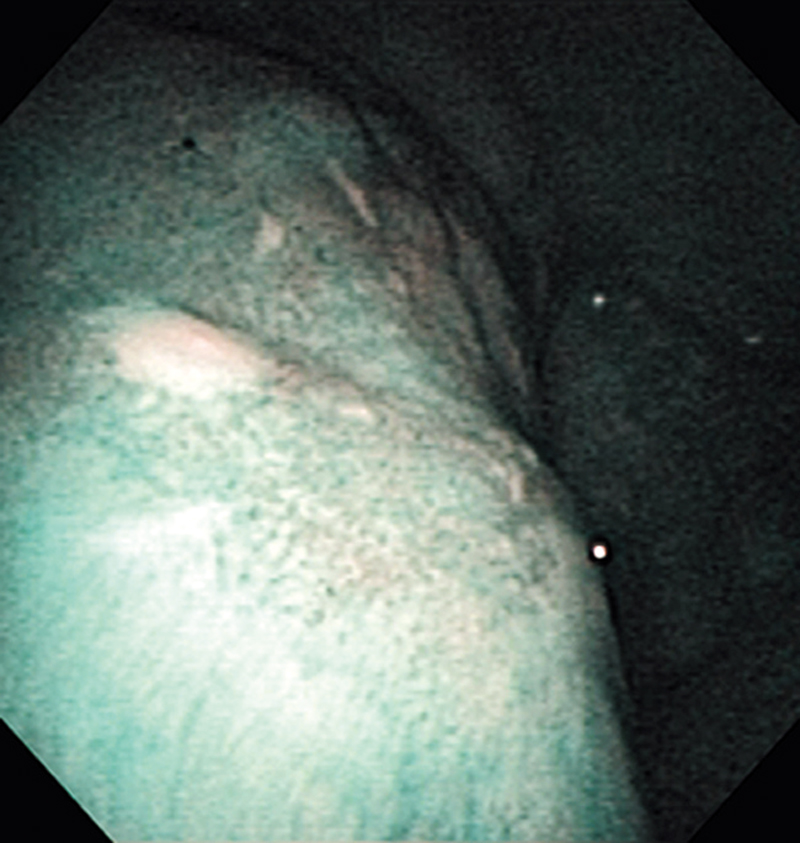
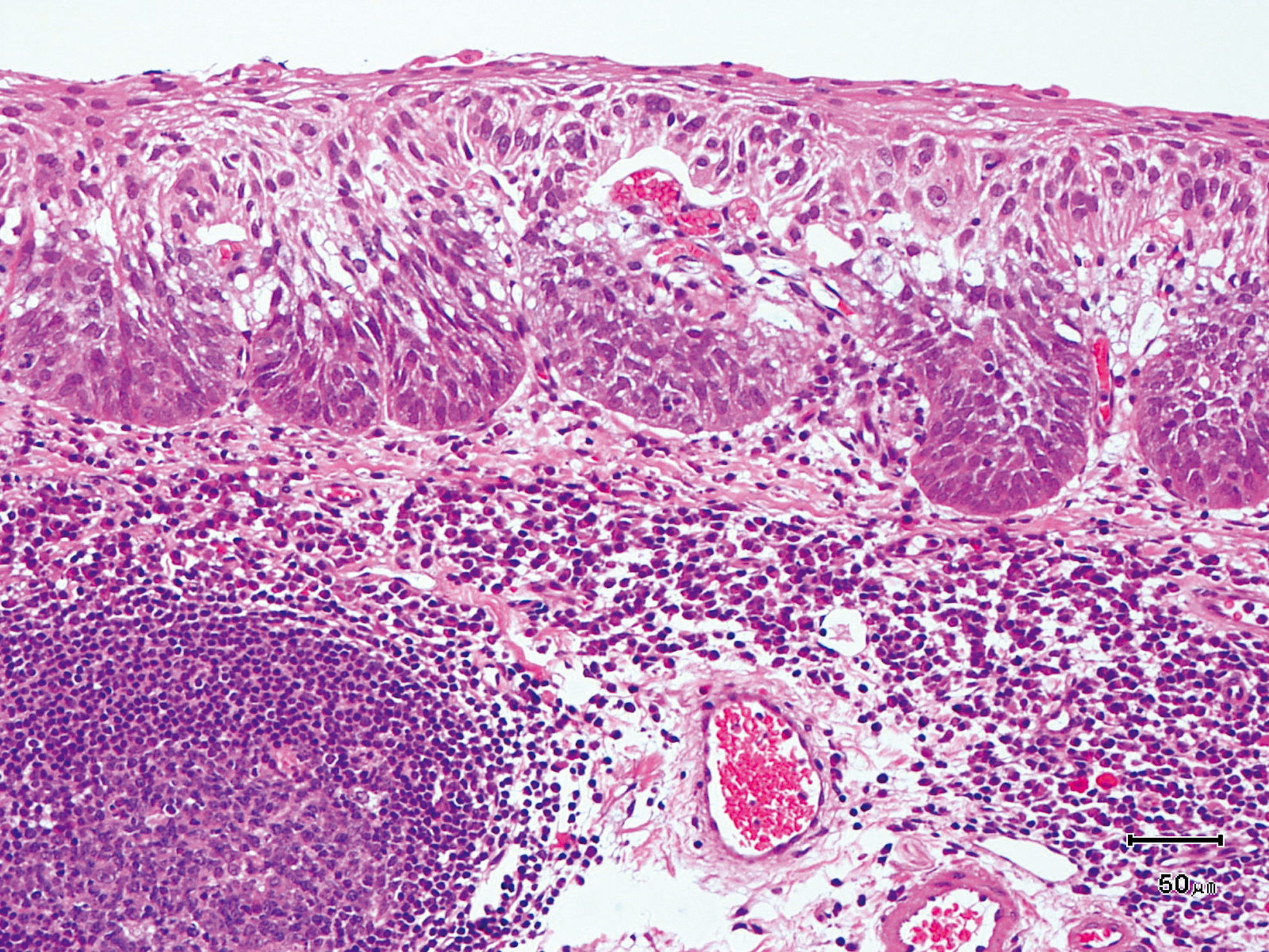
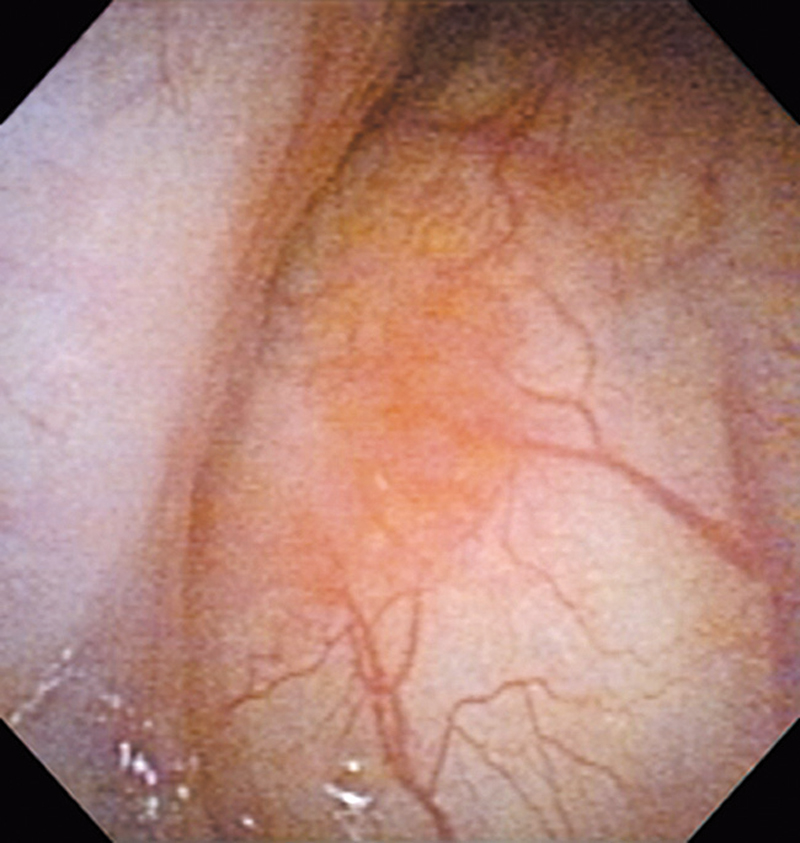
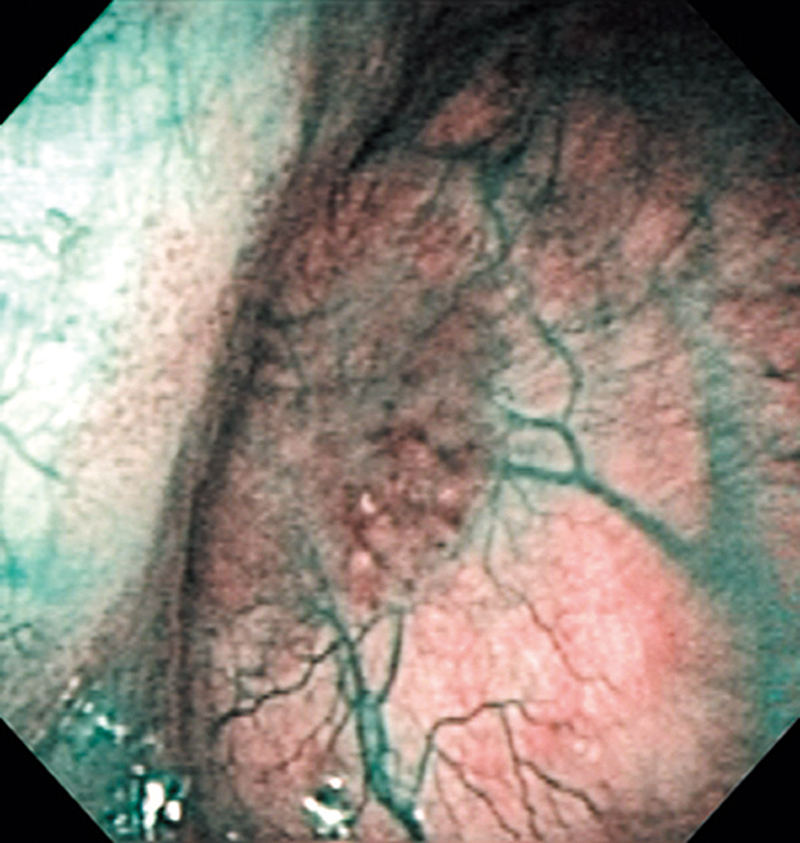
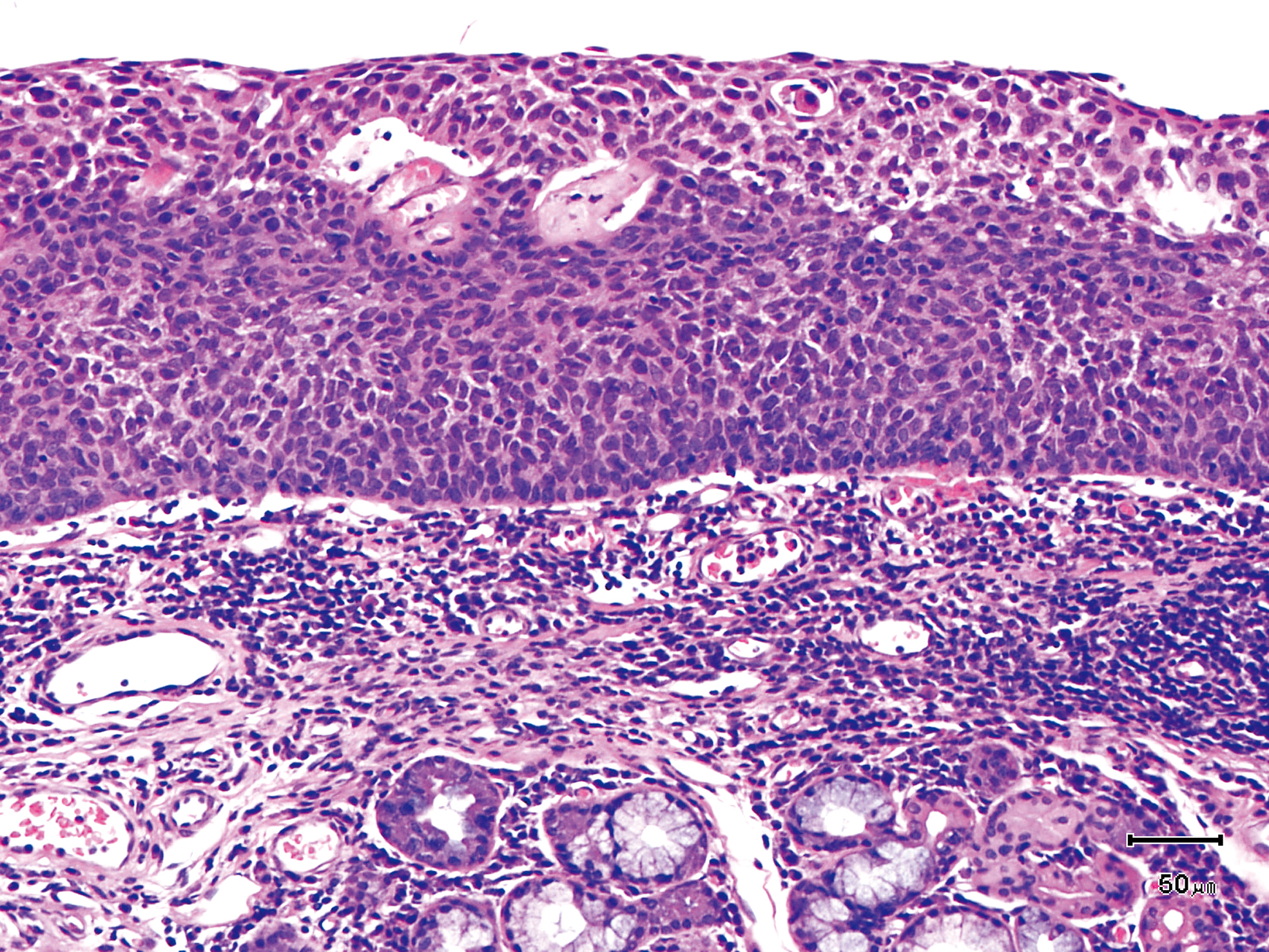
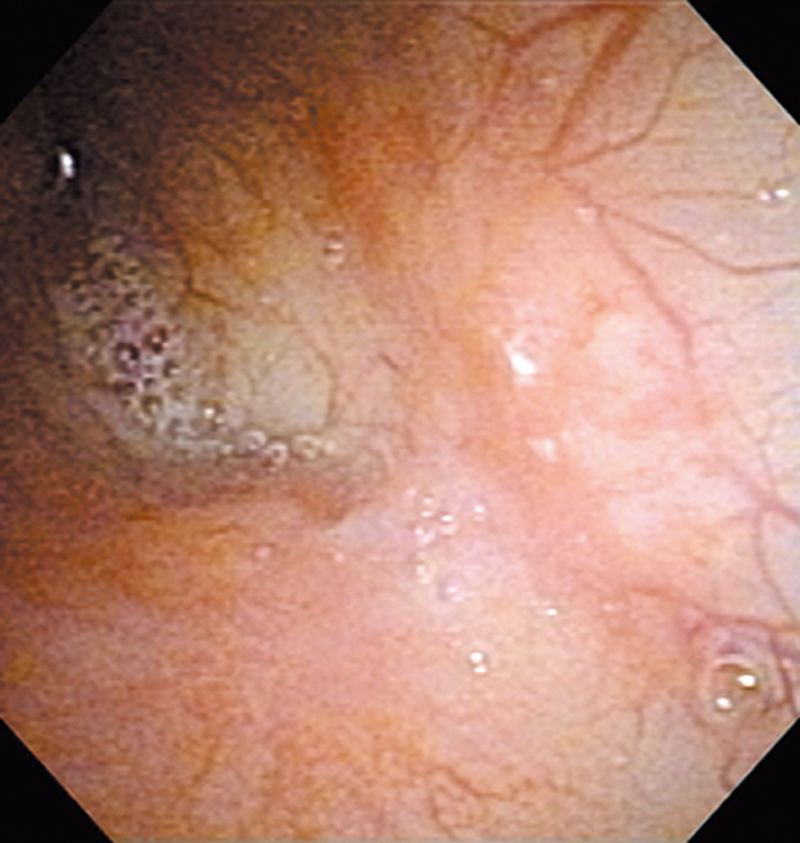
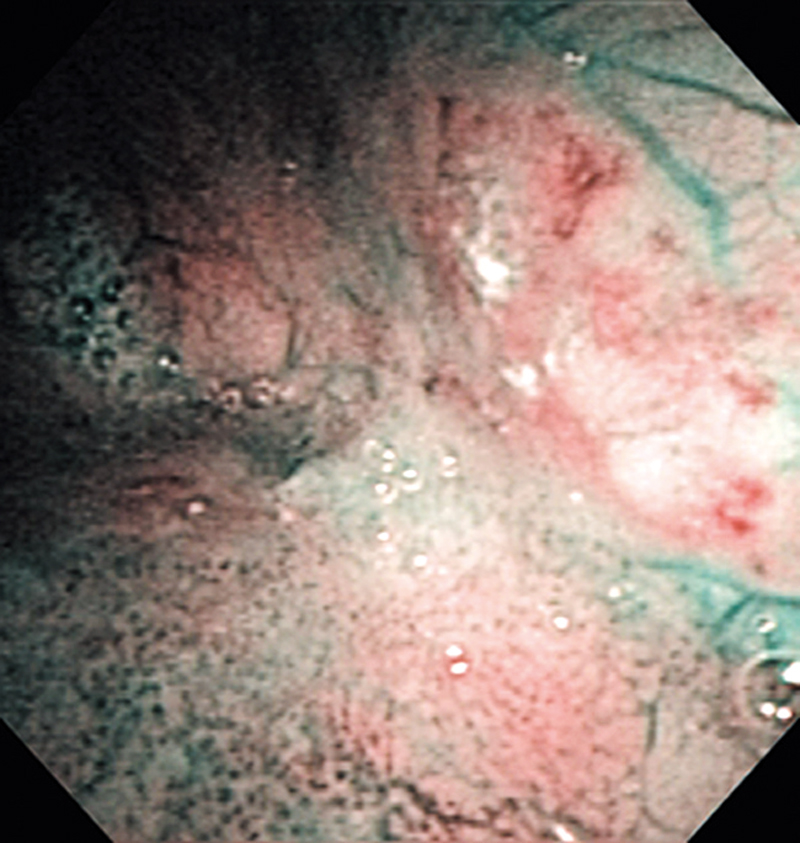
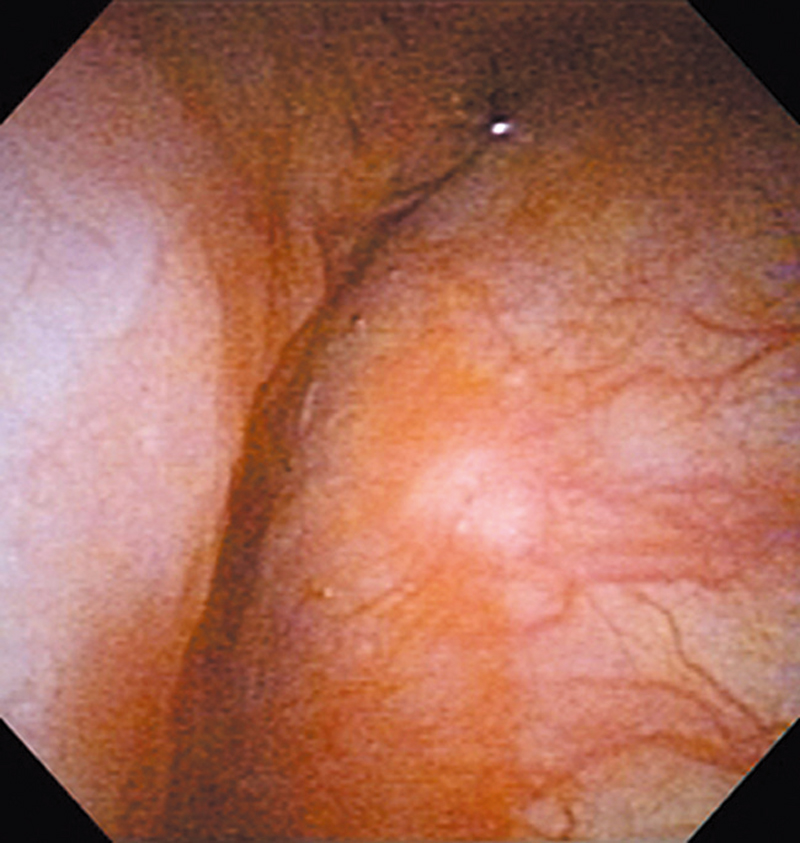
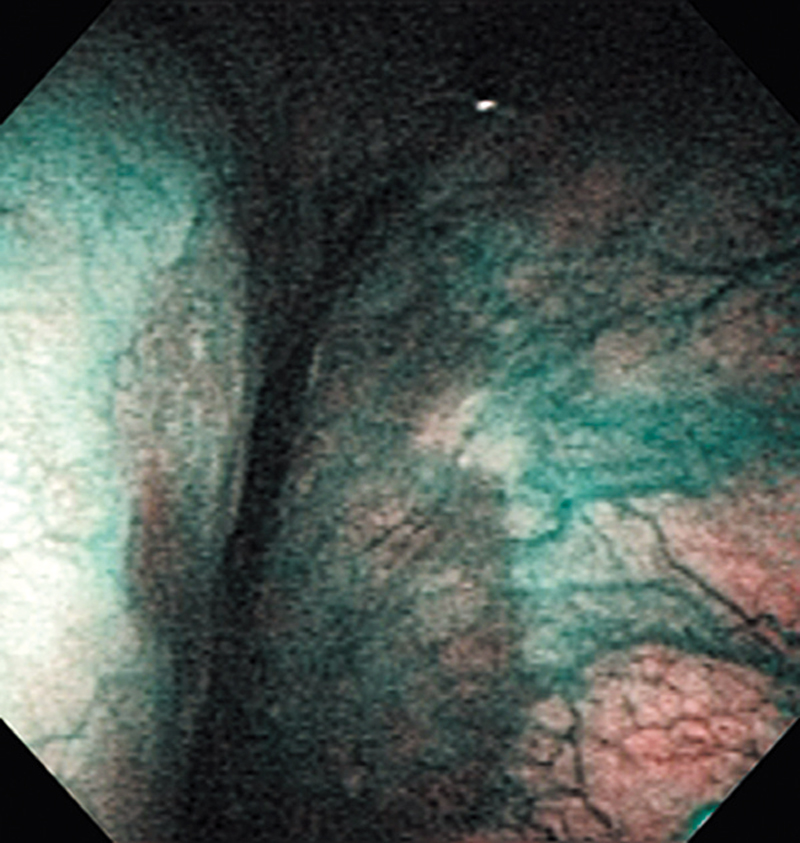
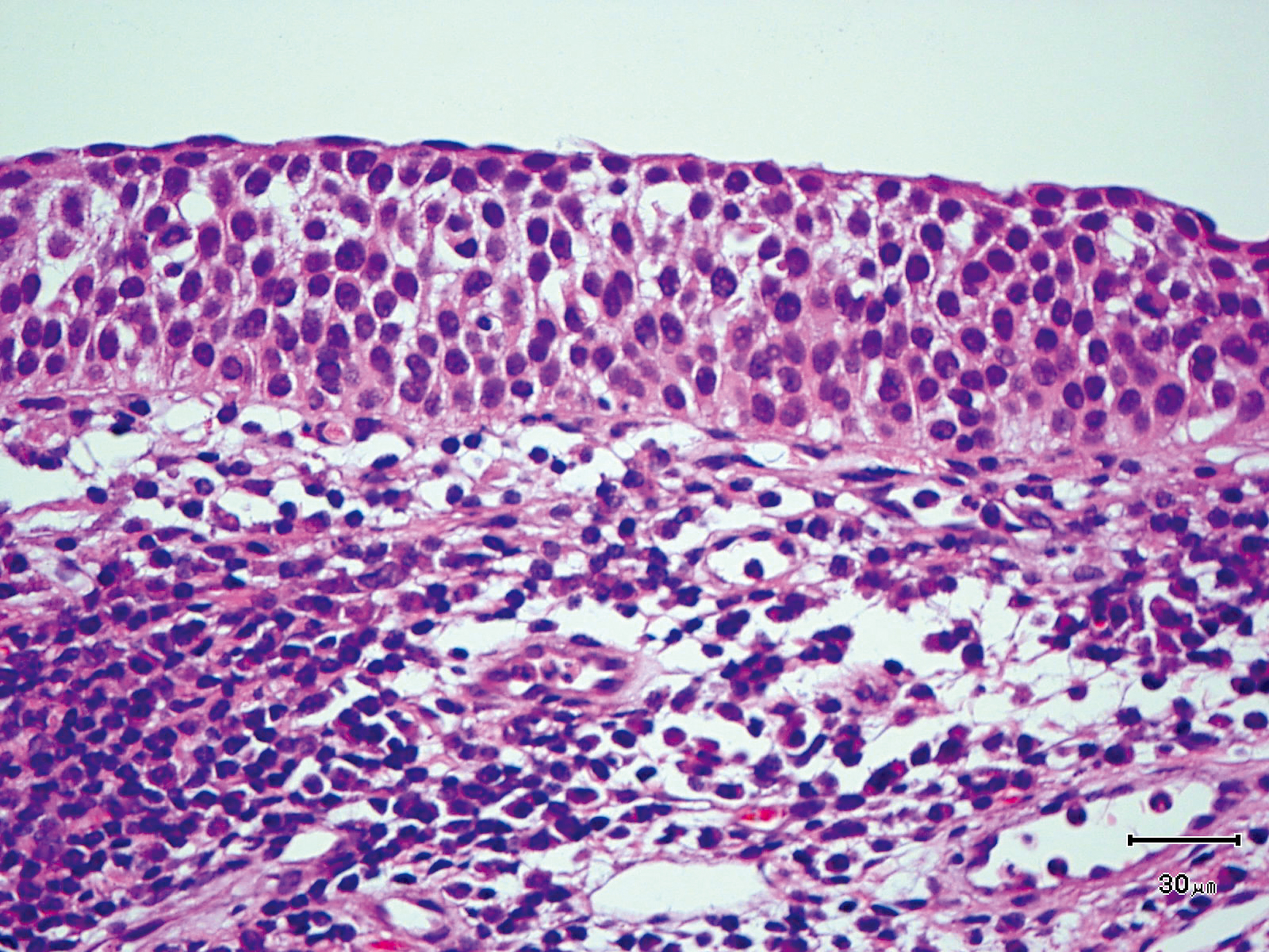
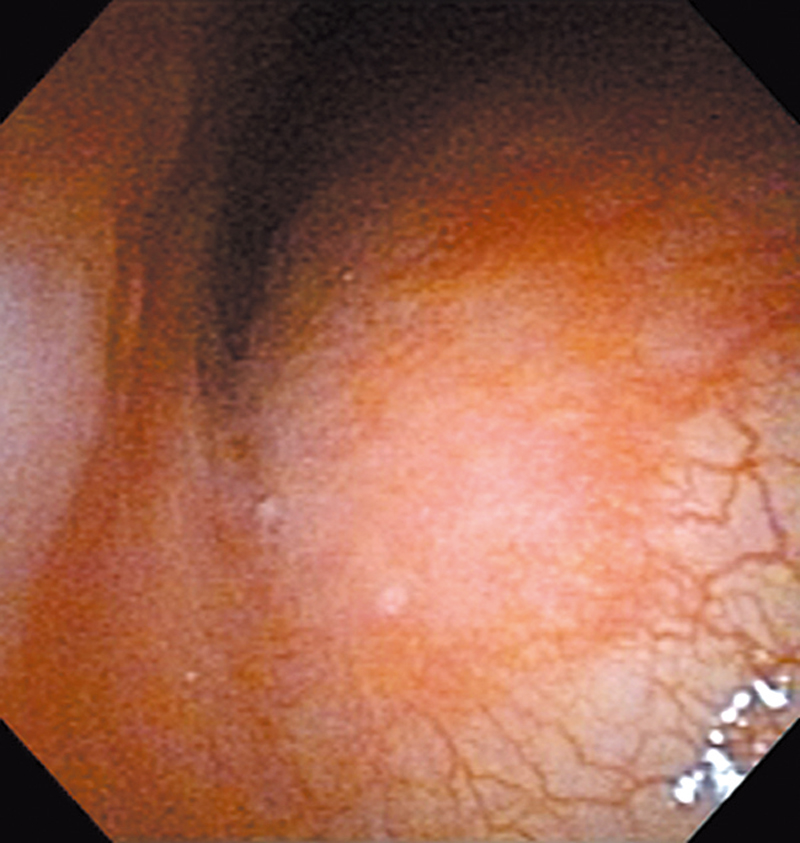
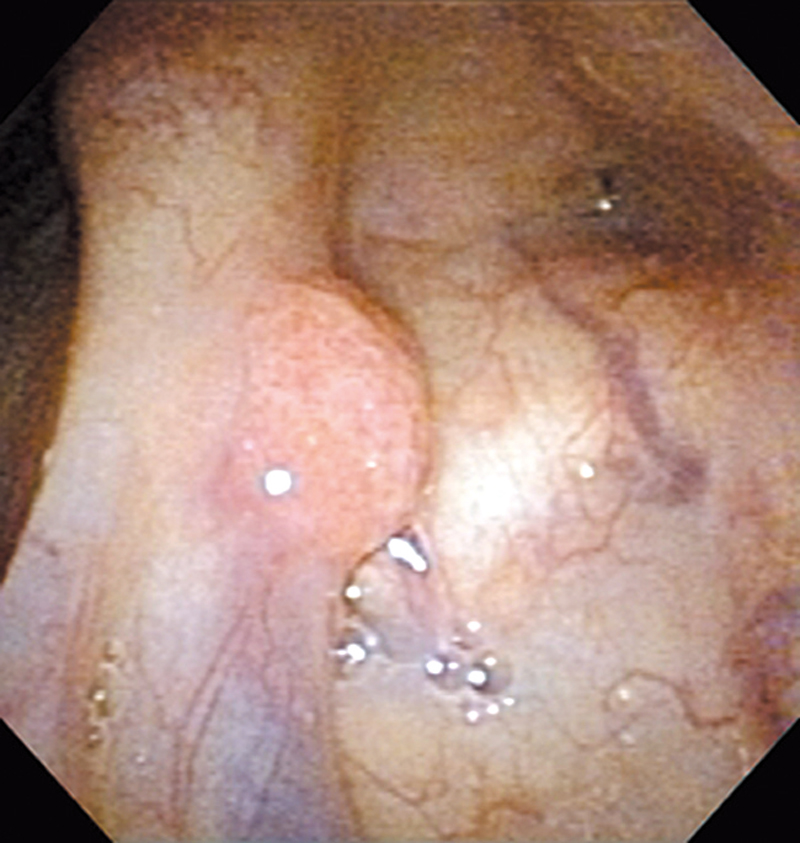
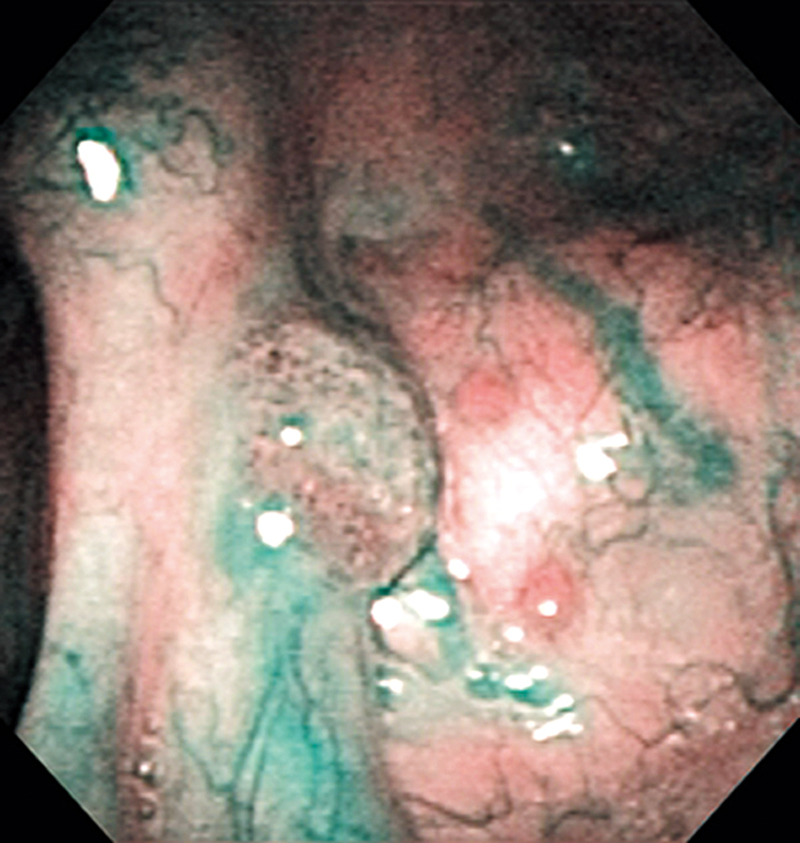
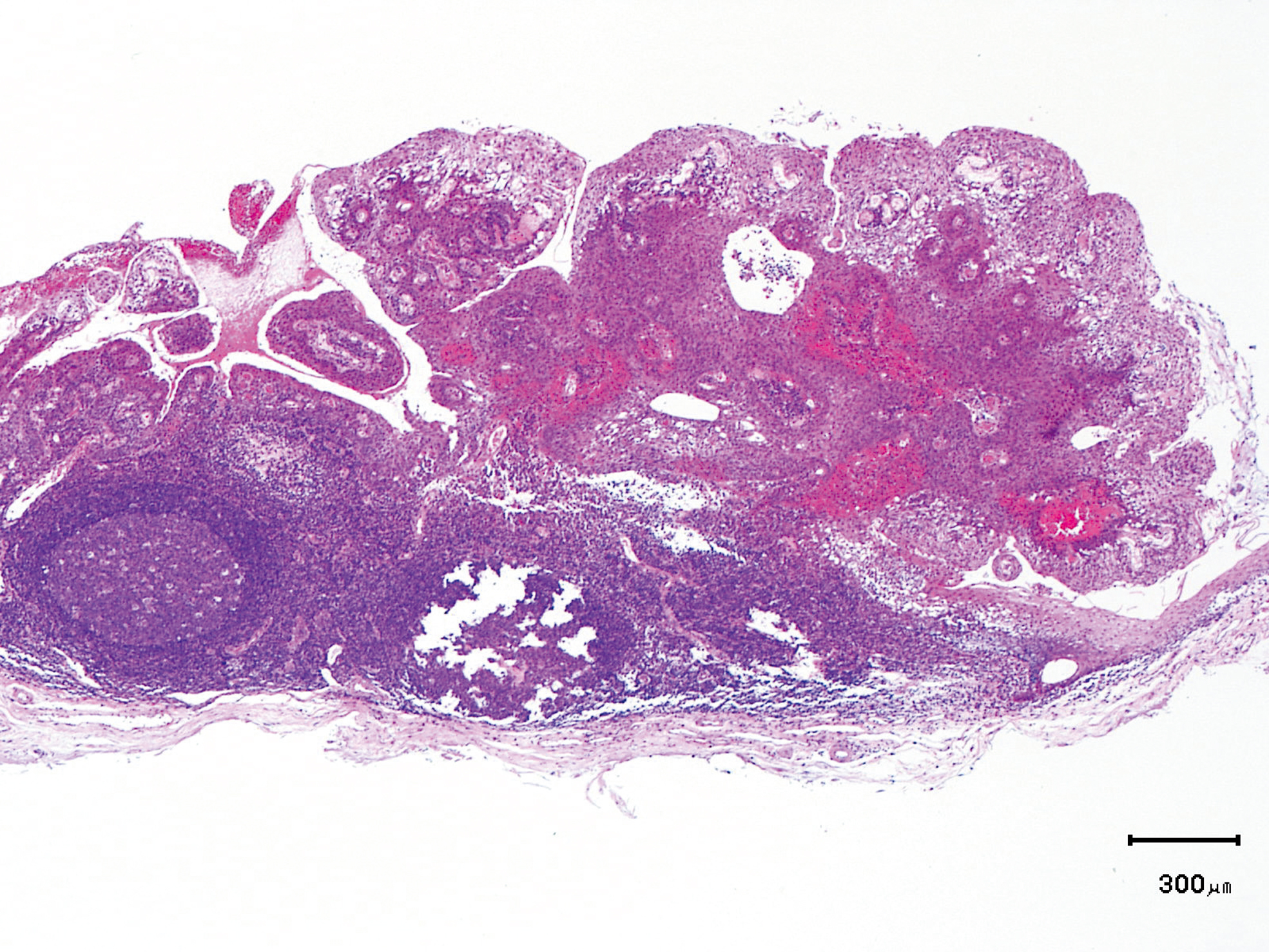
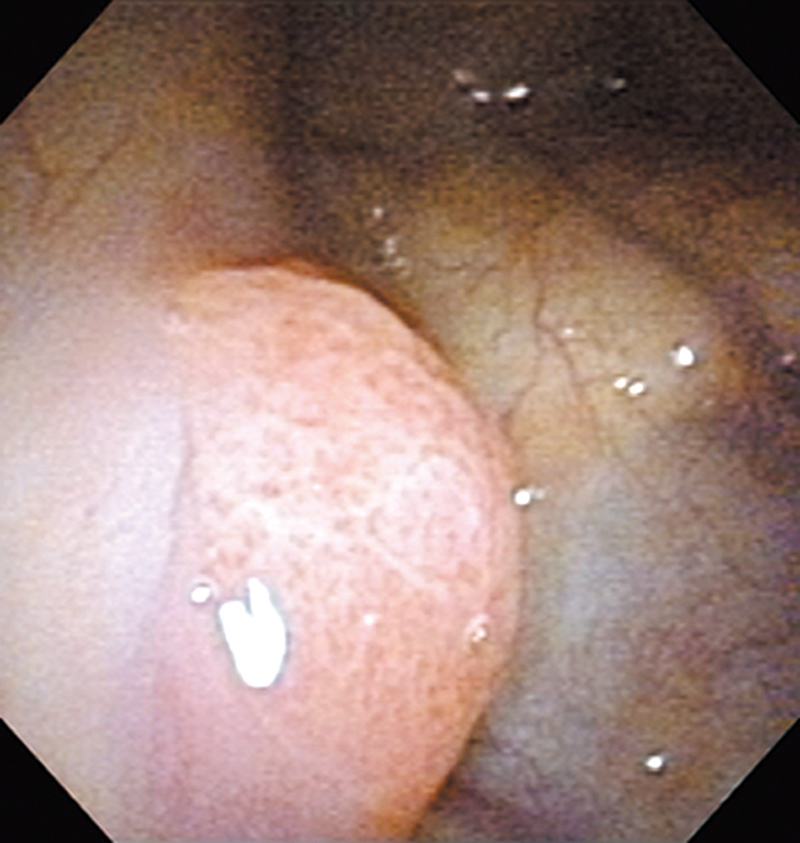
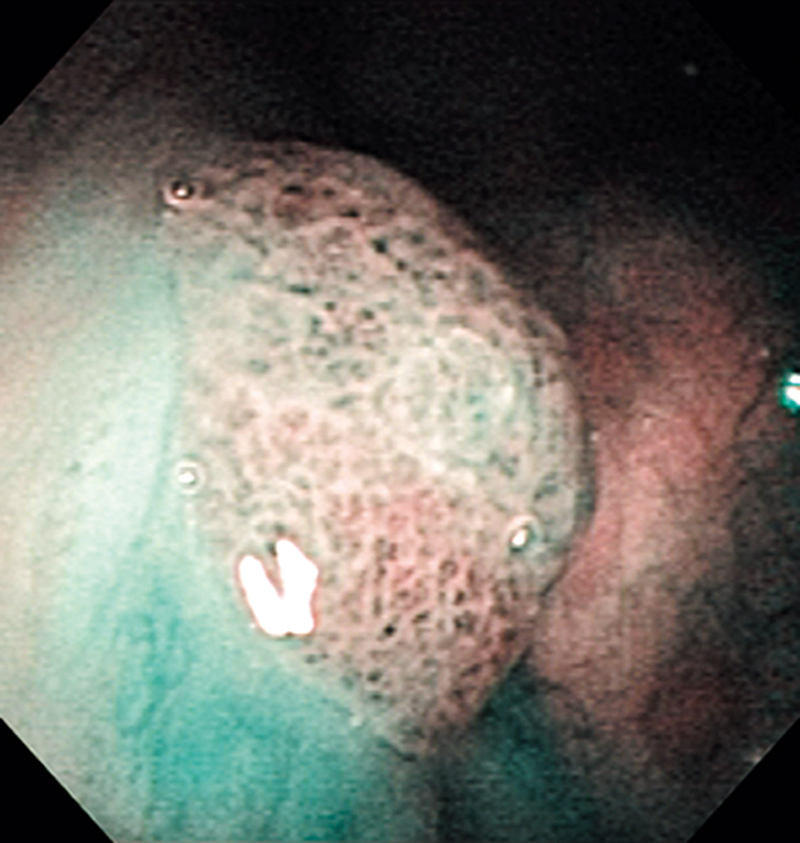
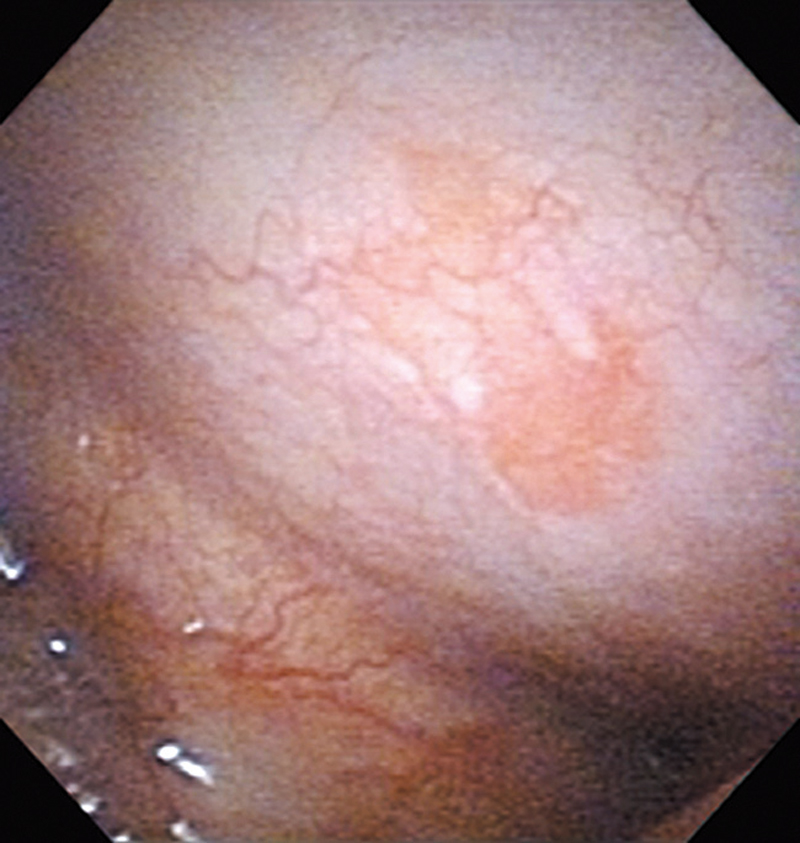
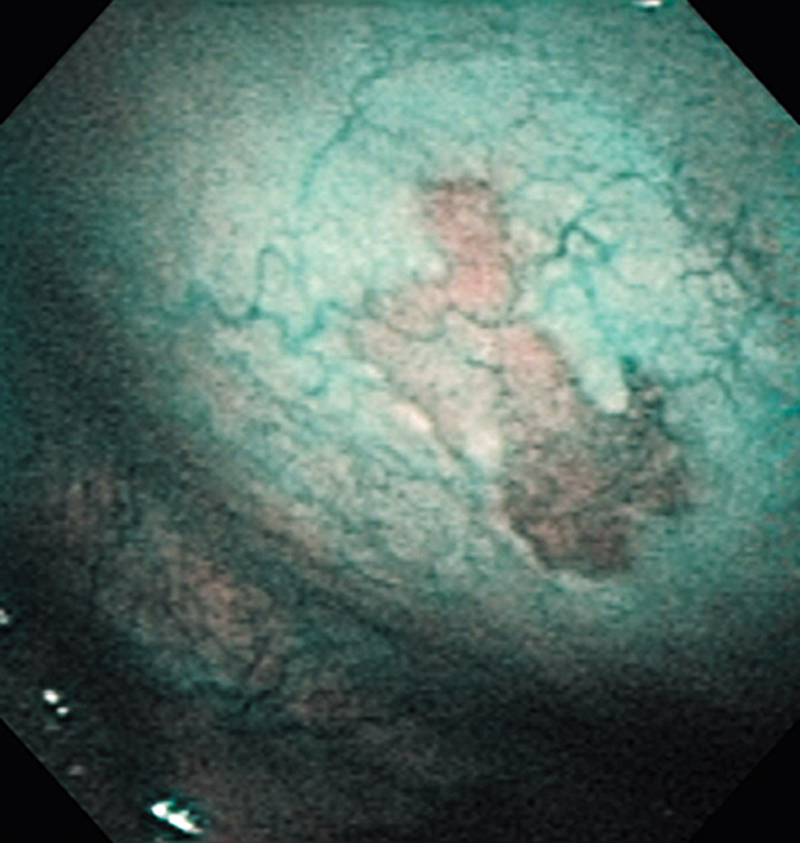
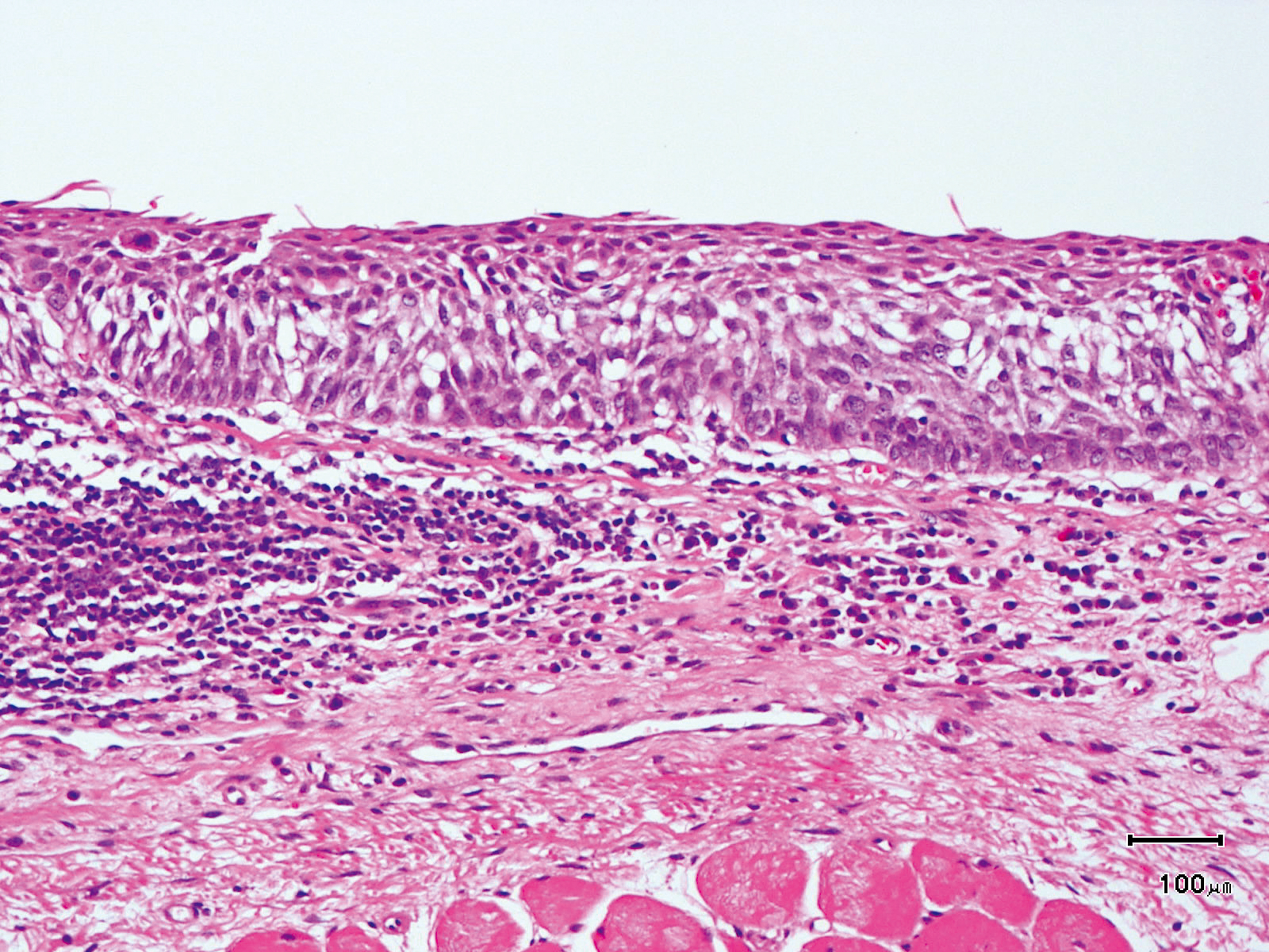
Hypopharynx Cancer (Right Pyriform Sinus) Aged 57, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected on the right pyriform sinus in a head/neck cancer screening with NBI laryngopharyngoscopy before an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed an irregular shaped brownish lesion. In the conventional white light image, a slight reddening was observed but the boundary was hard to identify.
The lesion was 9 x 6 mm, treated with endoscopic mucosal resection and diagnosed as a carcinoma in situ.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Right Pyriform Sinus) Aged 45, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected on the right pyriform sinus in a head/neck cancer screening with NBI laryngopharyngoscopy before an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed it as a well demarcated relatively depressed brownish lesion. In the conventional white light image, a slight reddening was observed in the same area.
The lesion was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection and diagnosed as a carcinoma in situ.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Right Pyriform Sinus) Aged 58, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected in the right pyriform sinus in a periodic laryngopharyngoscopic NBI examination after an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed scattered brown dots. In the conventional white light image, reddening was observed in the same area but scattered dots were hard to identify.
The lesion was 7 x 5 mm, treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a carcinoma in situ.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Left Pyriform Sinus) Aged 60, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected in a periodic laryngopharyngoscopic NBI examination after an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed scattered brown dots within the brownish lesion. In the conventional white light image, slight reddening was observed in the same area.
The lesion was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a moderately-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma mostly remaining in the epithelium.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Left Pyriform Sinus) Aged 62, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected in the left pyriform sinus in a head/neck cancer screening with NBI laryngopharyngoscopy before an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed a demarcated brownish lesion that was accompanied with scattered brown dots. With the conventional white light image, a slight reddening lesion was observed in the same area.
The lesion was as small as 3 mm in diameter, and was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a carcinoma in situ.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Left Pyriform Sinus) Aged 64, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected in the left pyriform sinus in a head/neck cancer screening with NBI laryngoscopy before an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed a well demarcated slightly-elevated brownish lesion. In the conventional white light image, a lesion with uneven surface was observed but the boundary was hard to identify.
The lesion was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a moderately to poorly-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Left Pyriform Sinus) Aged 64, male
Comment:
The patient visited us with a chief complaint of abnormal sensation in the pharynx and the lesion was detected in the left hypopharynx in a laryngopharyngoscopic NBI examination.
The NBI image showed a well demarcated brownish lesion on the left pyriform sinus with scattered brown dots. In the conventional white light image, the same area was observed as a slight reddening.
The lesion was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection and diagnosed as a squamous cell carcinoma.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Left Pyriform Sinus) Aged 61, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected in the left pyriform sinus in a head/neck cancer screening with NBI laryngoscopy before an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
It was recognized under NBI image as a lesion with a brownish area, and the close-up view showed scattered brown dots within the lesion as well. Under the conventional white light, the same area was recognized as a reddening lesion,
but the demarcation was less defined compared to the NBI image, and the scattered dots were hard to identify even with the close-up view.
The lesion was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a carcinoma in situ.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Left Pyriform Sinus) Aged 58, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected in the left pyriform sinus in a periodic laryngopharyngoscopical examination after an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed a well demarcated brownish lesion in the left pyriform sinus. In the conventional white light image, a reddening lesion was observed in the same area but demarcation was less defined compared to the NBI image.
The lesion was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a moderately-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Left Pyriform Sinus: Elevated Type) Aged 80, male
Comment:
The patient visited us with a chief complaint of abnormal sensation in the pharynx and the elevated lesion was
detected on the left pyriform sinus in a laryngopharyngoscopic NBI examination.
The NBI image showed a brownish elevated lesion with scattered brown dots. In the conventional white light image, it was recognizable as a reddish elevated lesion.
The lesion was treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a squamous cell carcinoma in situ.
Hypopharynx Cancer (Posterior Wall) Aged 62, male
Comment:
The lesion was detected in the right side of the posterior wall of the hypopharynx in a head/neck cancer screening with NBI laryngopharyngoscopy before an esophageal carcinoma surgery.
The NBI image showed a well demarcated brownish lesion with irregularly shaped border. As subepithelial blood vessels were visible in the lesion, it was expected that the lesion remained within the epithelium or that the subepithelial infiltration was minimal. With the conventional white light image, the area was recognized as a slight reddening lesion.
The lesion was 7 x 4 mm, treated with endoscopic mucosal resection, and diagnosed as a carcinoma in situ.
- Content Type