Duodenum Case 5
Dr. Jae Young Jang
Associate professor in division of Gastroenterology,
Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital,
Seoul, Korea
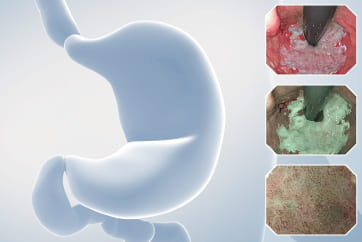
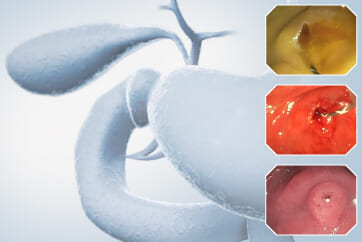
Scope: GIF-HQ290
Case: Low grade dysplasia
Organ: Duodenum, 2nd portion
Patient information: M, 60s
Medical history: Healthy person
Disclaimer:
- RDI™ & TXI™ Technologies are not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
- NBI™, RDI™, and TXI™ technologies are 510(k) cleared in the United States. This case study is being furnished to provide examples of NBI™, RDI™, and TXI™ technology use. The GIF-HQ290 used in this case is not available in the US market at this time, nor is there an established time for its release. The safety and effectiveness of this product and/or the use of these products has not yet been established in the United States market
- The positions and statements made herein by Dr. Jang are based on Dr. Jang’s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
- The EVIS X1™ Technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU)
Case Video
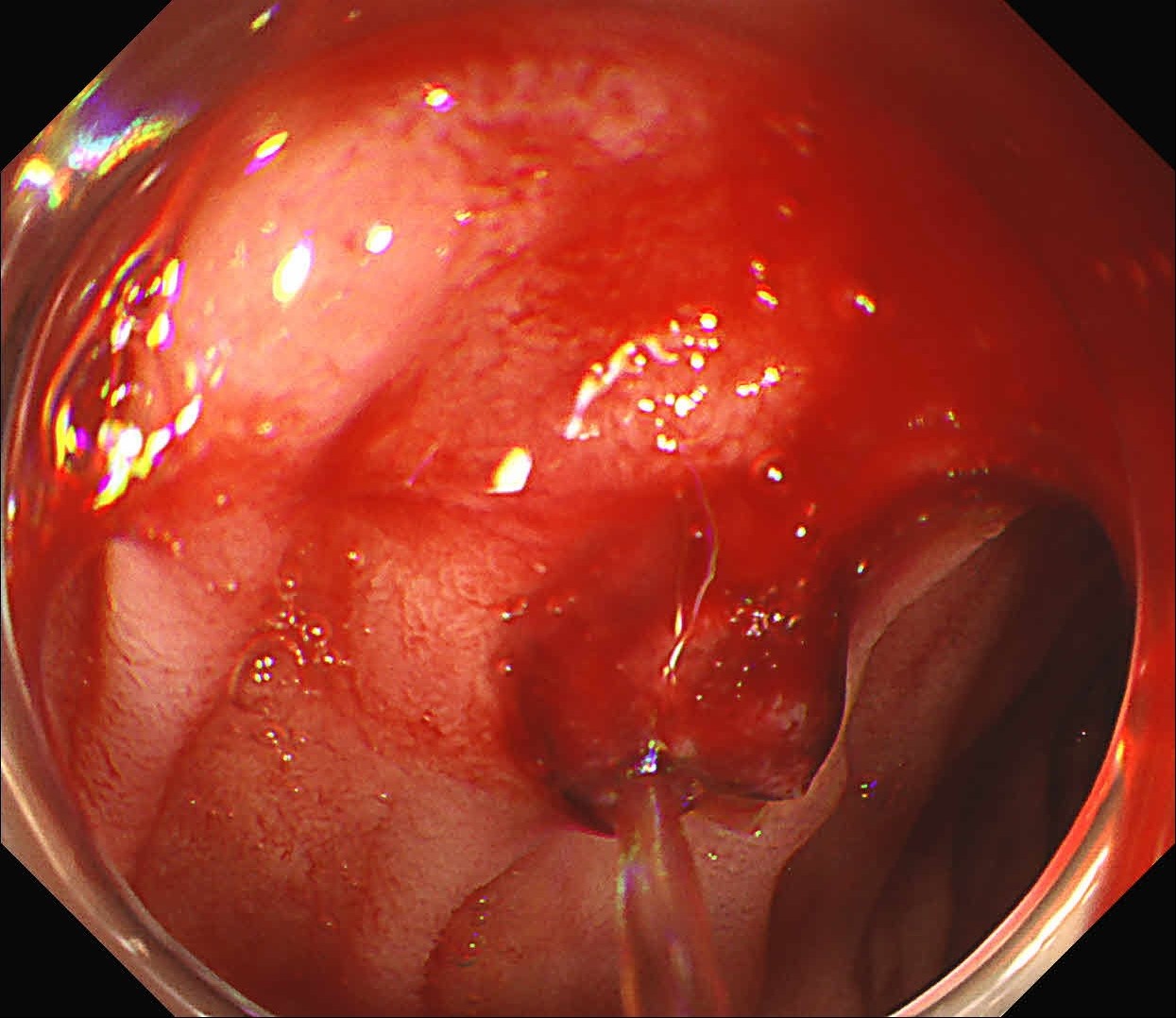
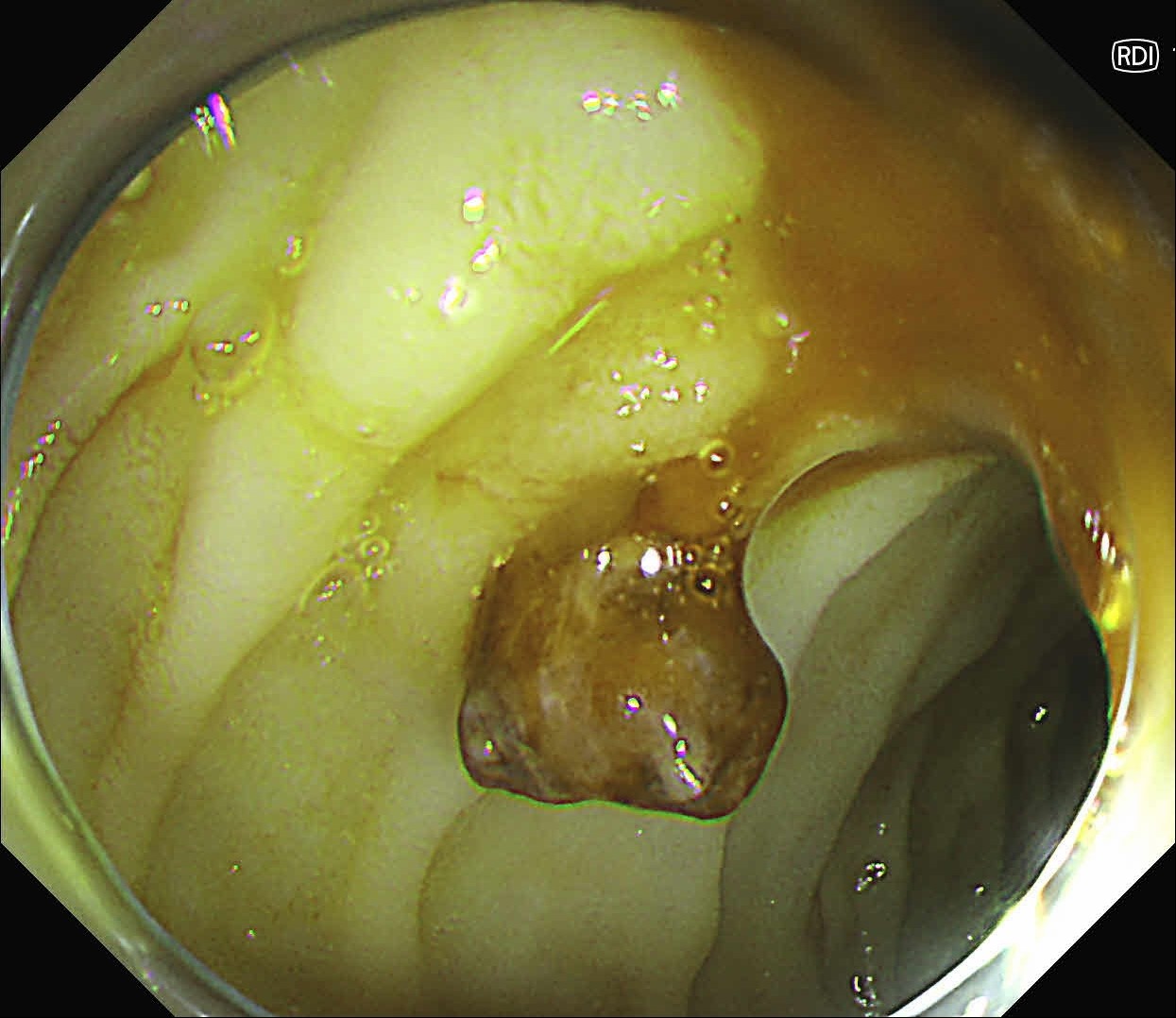
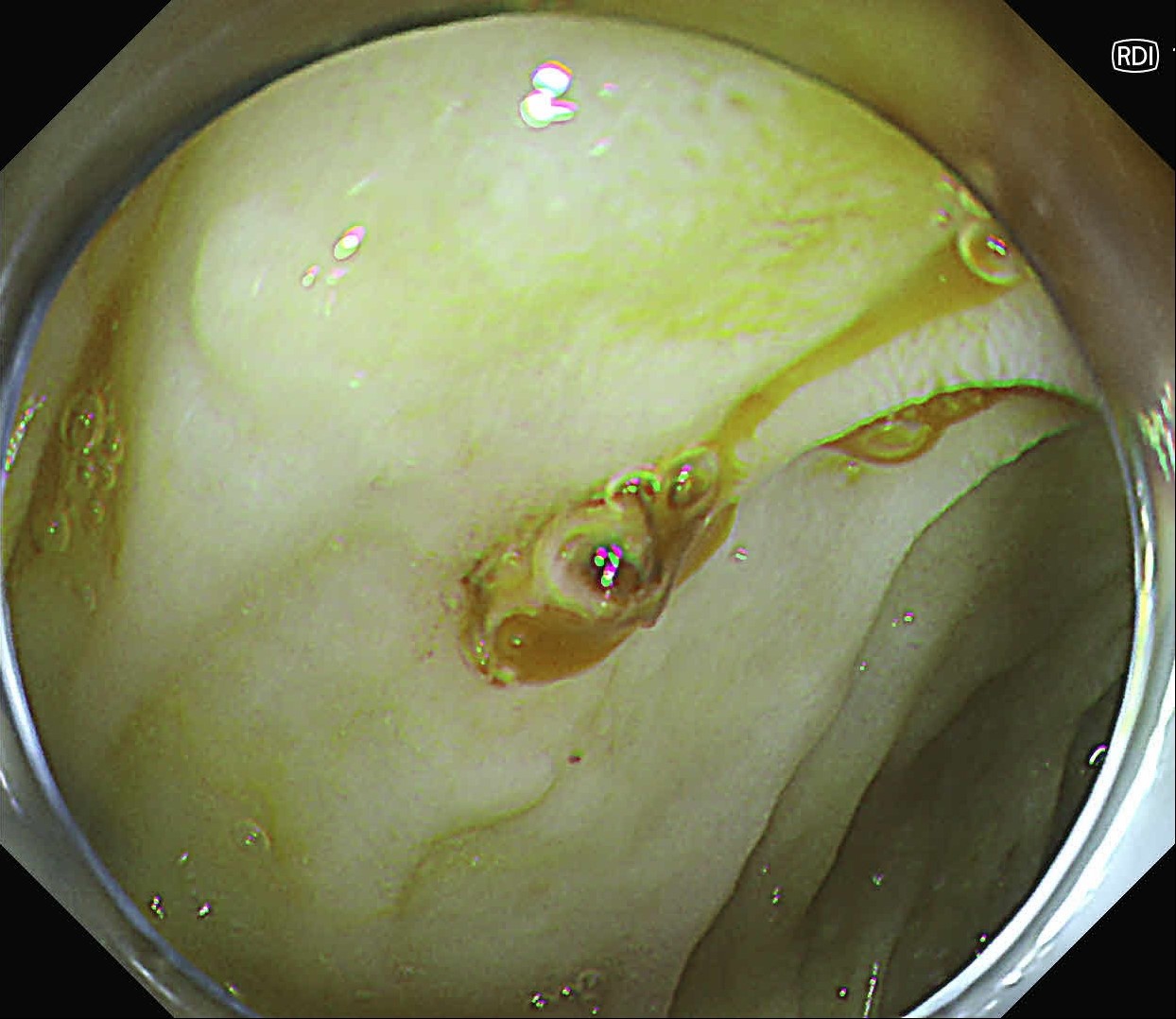
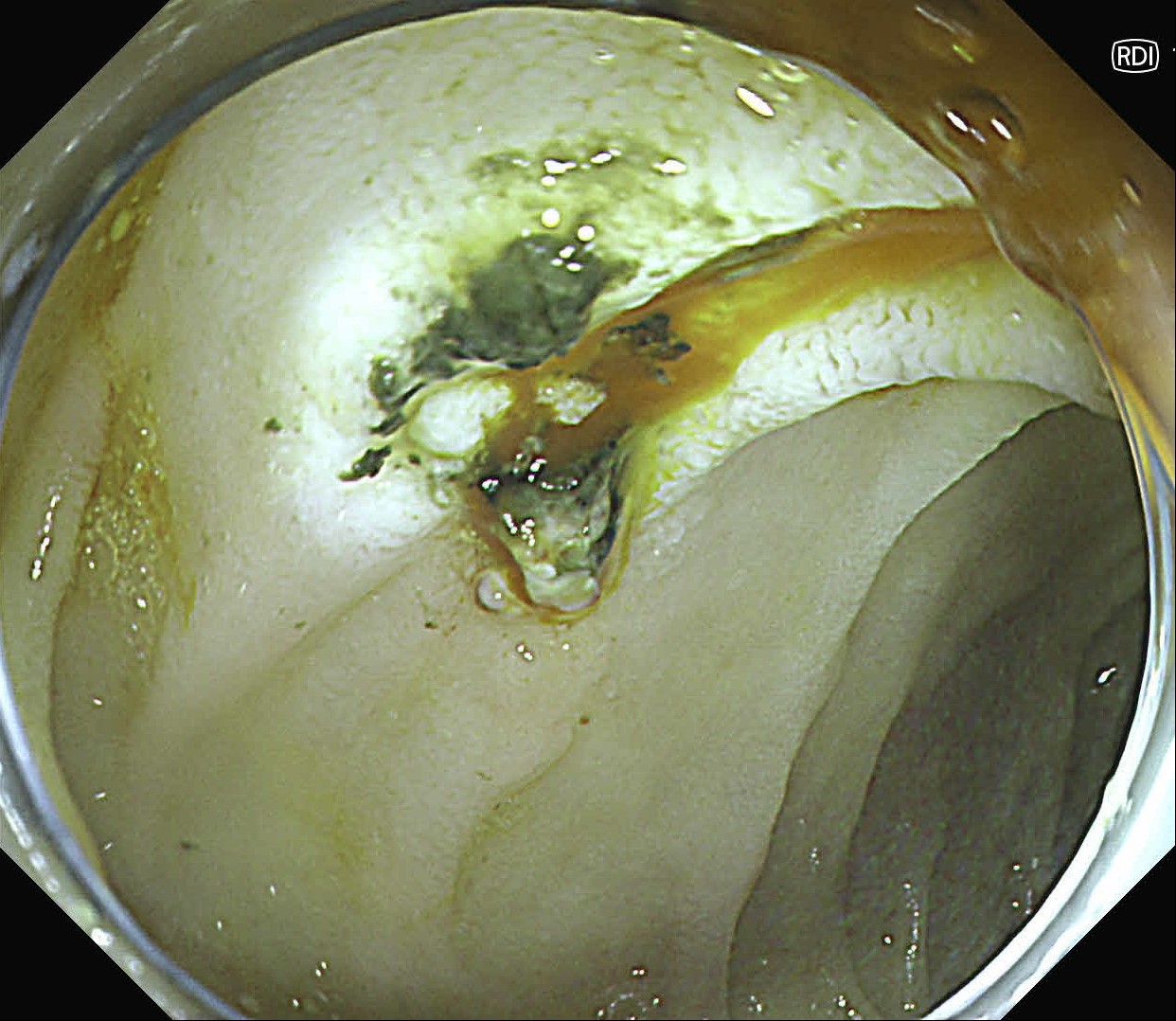
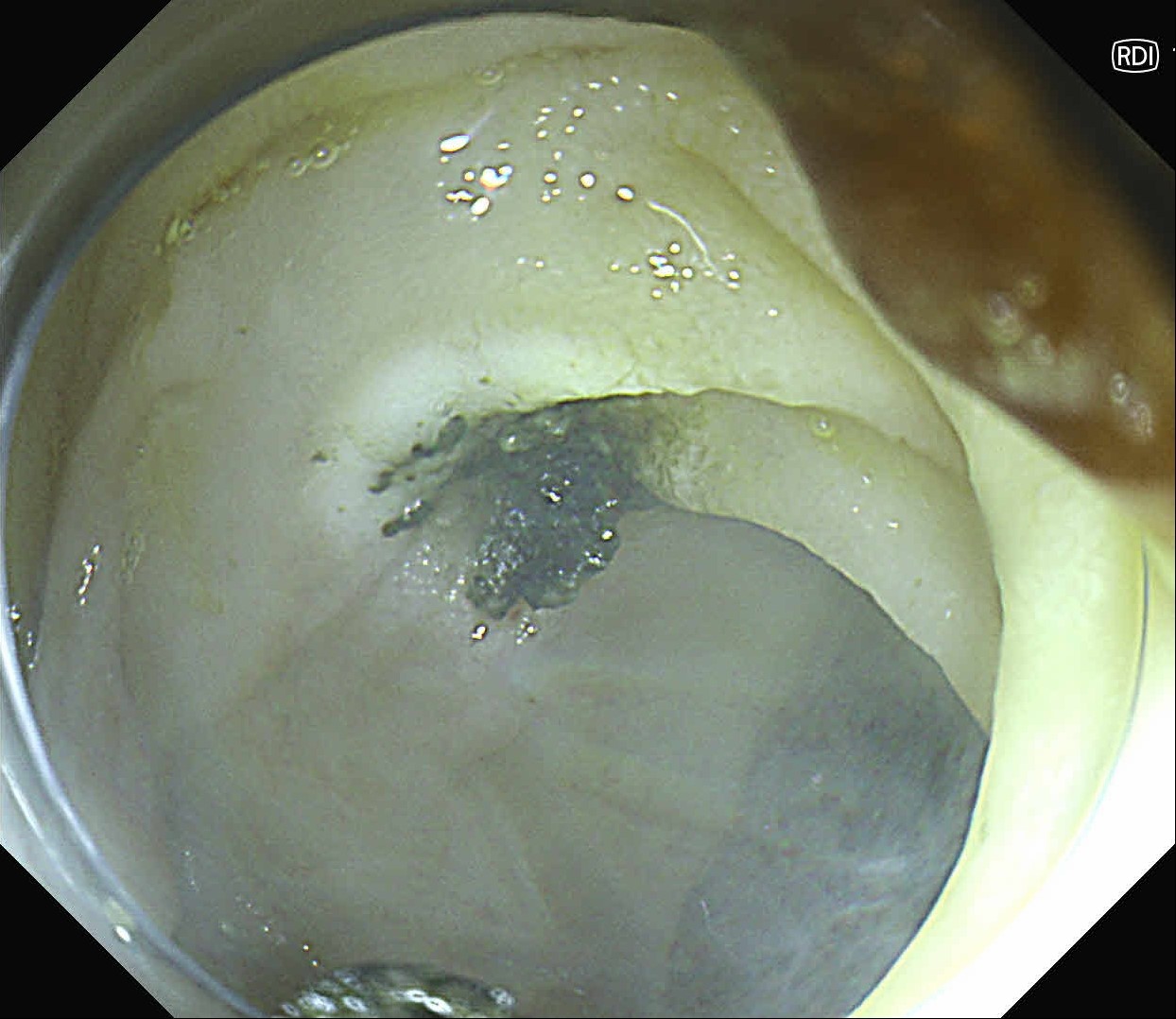
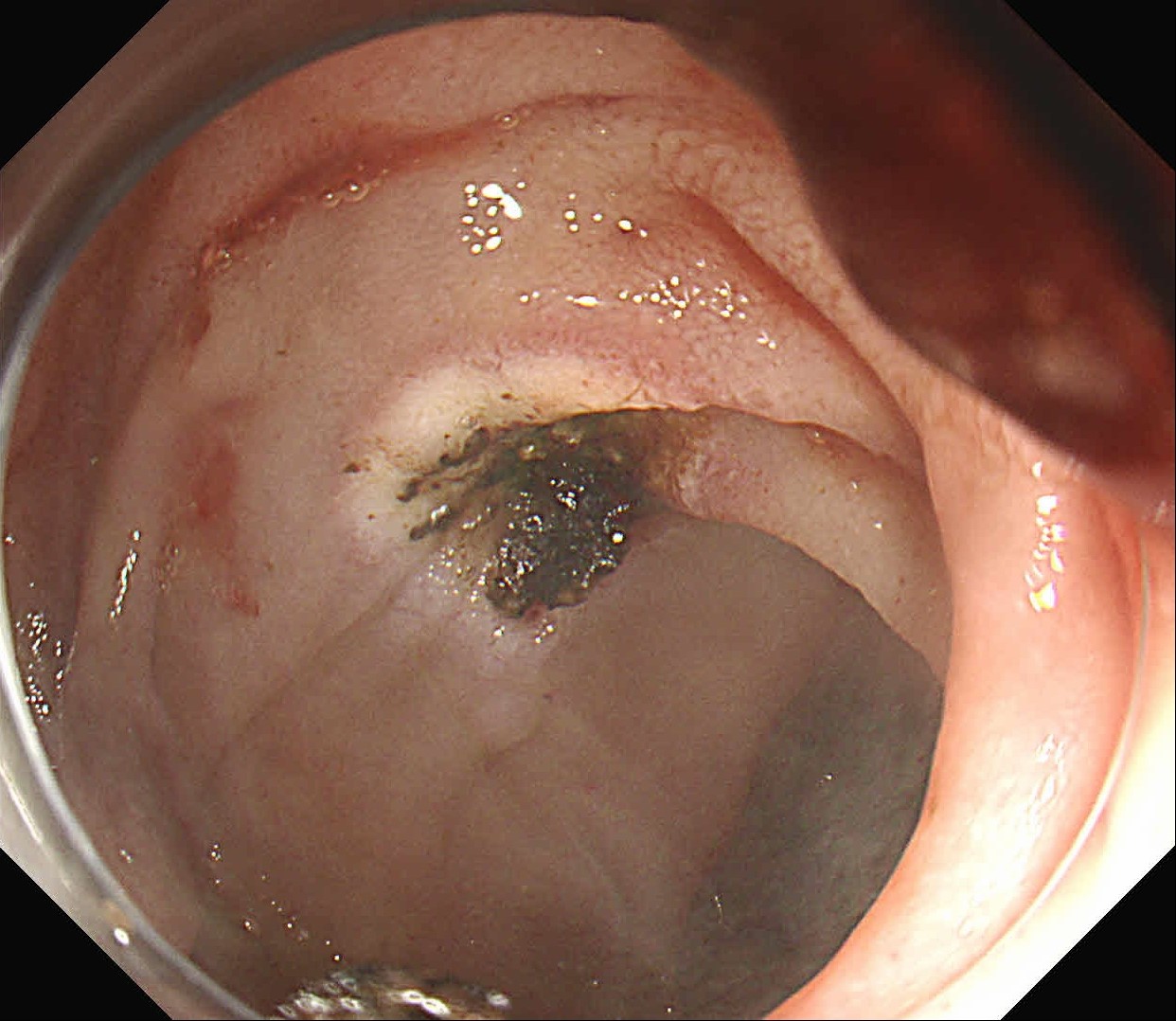
At first, it was difficult to identify the bleeding point due to continuous bleeding after the procedure. However, after turning on the RDI™ technology function, the bleeding site could be clearly identified. By distinguishing between the bleeding source and its surroundings and by quickly stopping bleeding, additional time and effort could be saved.
Overall Comment
It was difficult to find the bleeding point particularly in heavy bleeding. However, when observed with RDI™ technology, the color of blood was observed as light reddish brown, making it easier to find the bleeding point than it was before. With this point of view, RDI™ technology enhances the efficiency of the procedure and patient safety at the same time it increases the rate of hemostasis of possible bleeding during and after resection.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer.
Dr. D Nageshwar Reddy
Dr. Hardik Rughwani Case 9: Duodenal second part tubular adenoma with high grade dysplasia
Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan
- Content Type