Pancreatobiliary case 2

Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD, FASGE, FACG, FJGES
Professor of Medicine
Director, Digestive Disease Center
SoonChunHyang University School of Medicine,
Bucheon/Seoul, Korea

Il Sang Shin, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor
Digestive Disease Center
SoonChunHyang University School of Medicine,
Bucheon/Seoul, Korea
Disclaimer:
- NBI™ and TXI™ technologies are not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
- NBI™, RDI™, and TXI™ technologies are 510(k) cleared in the United States. This case study is being furnished to provide examples of NBI™, RDI™, and TXI™ technology use. The TJF-Q290V used in this case is not available in the US market at this time, nor is there an established time for its release. The safety and effectiveness of this product and/or the use of these products has not yet been established in the United States market.
- The positions and statements made herein by Dr. Moon are based on Dr. Moon’s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
- The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU)
1) Data on file with Olympus (DC00489968)
Scope: TJF-Q290V
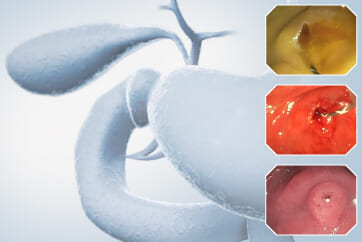
Organ: Ampulla of Vater
Patient information: 67-year-old, Female
Medical history: Medication for hyperlipidemia and hypothyroidism
Case Video
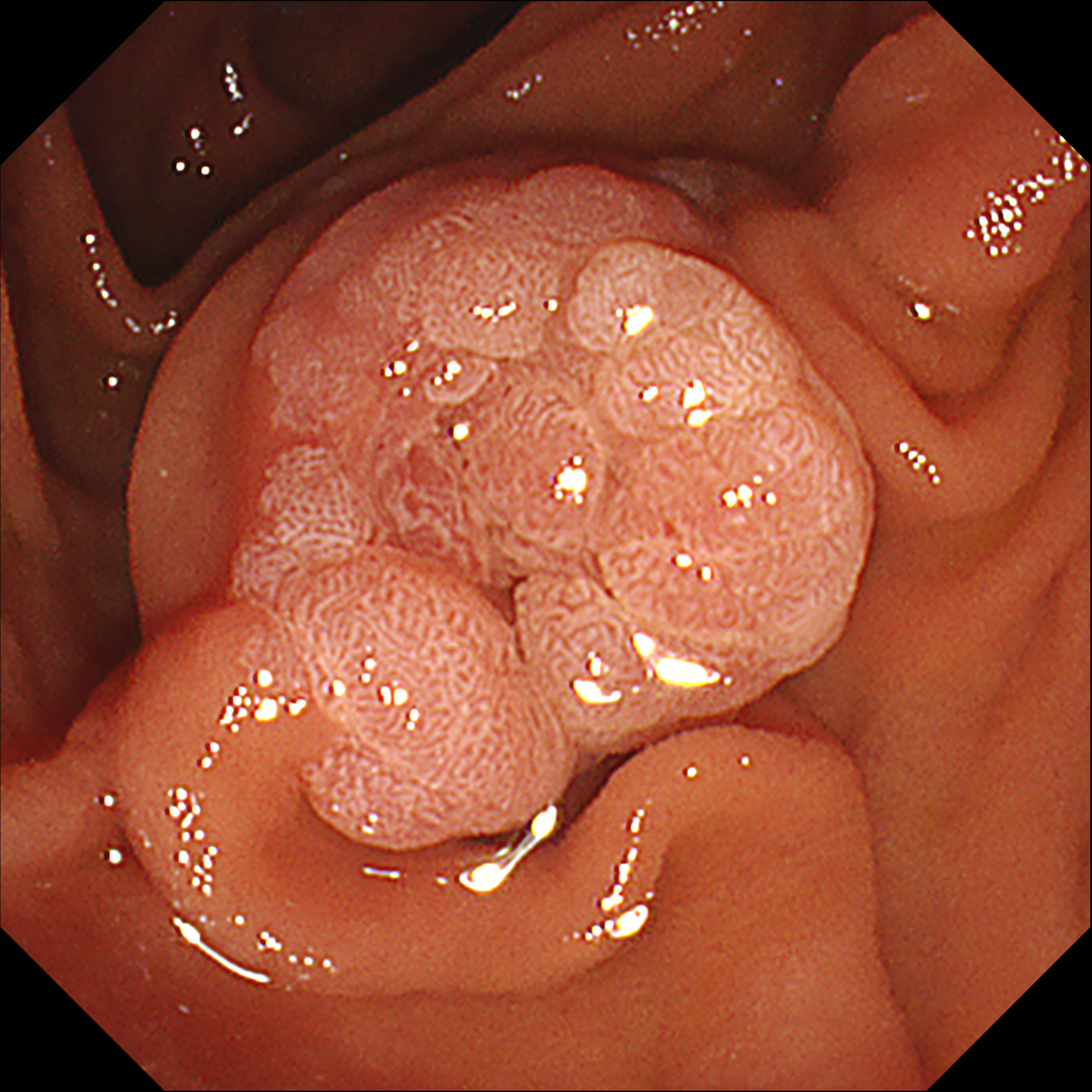
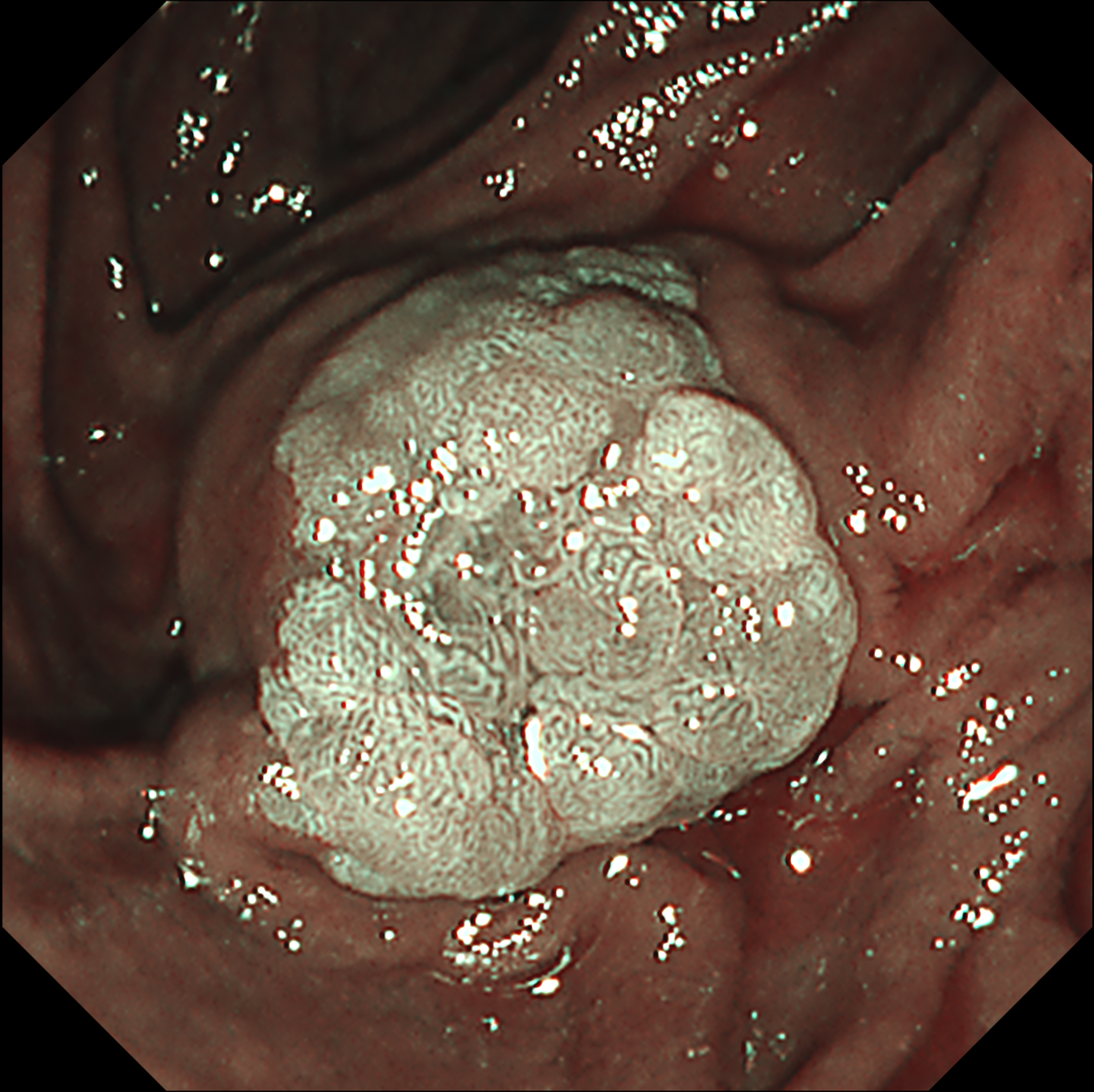
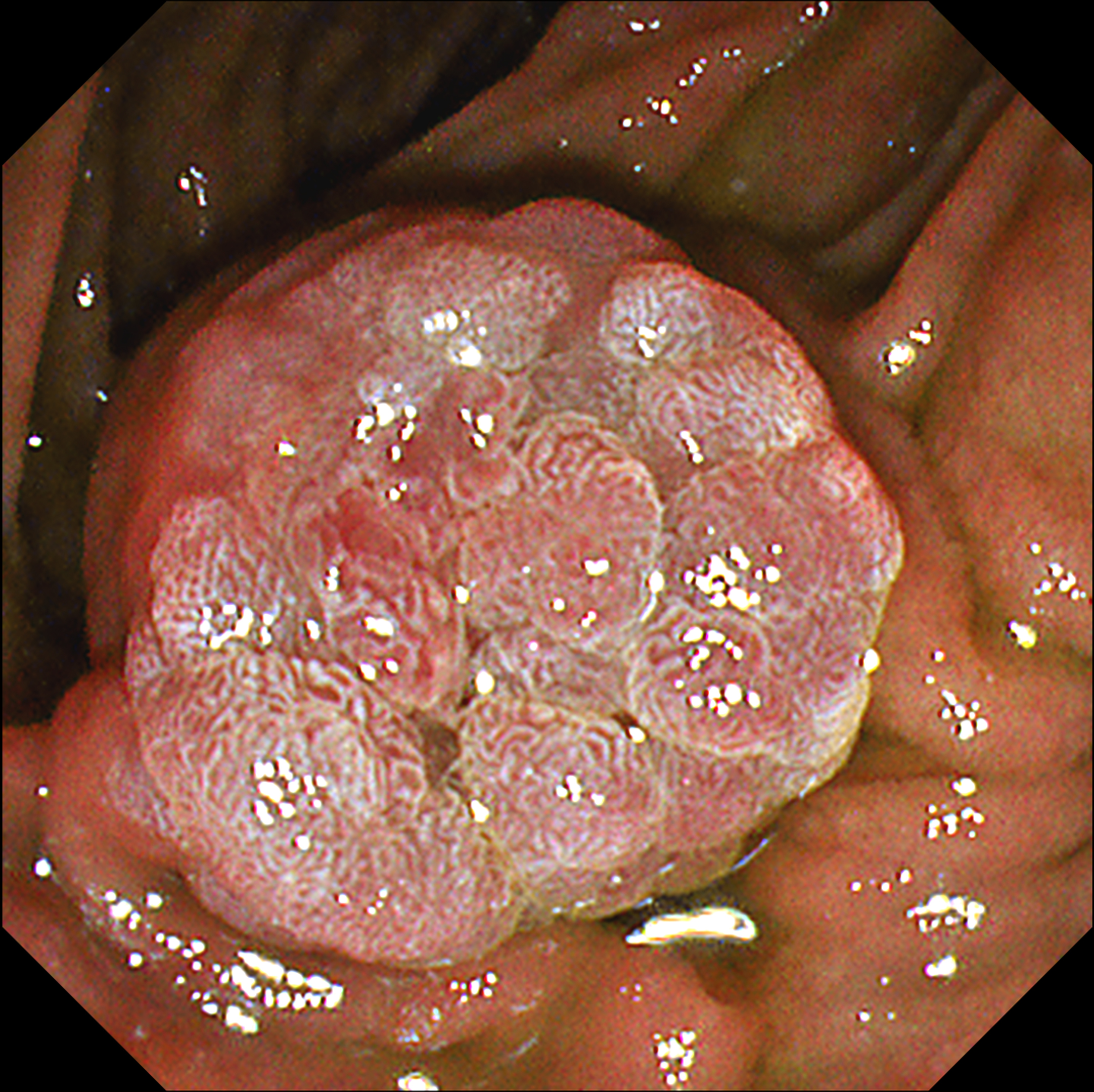
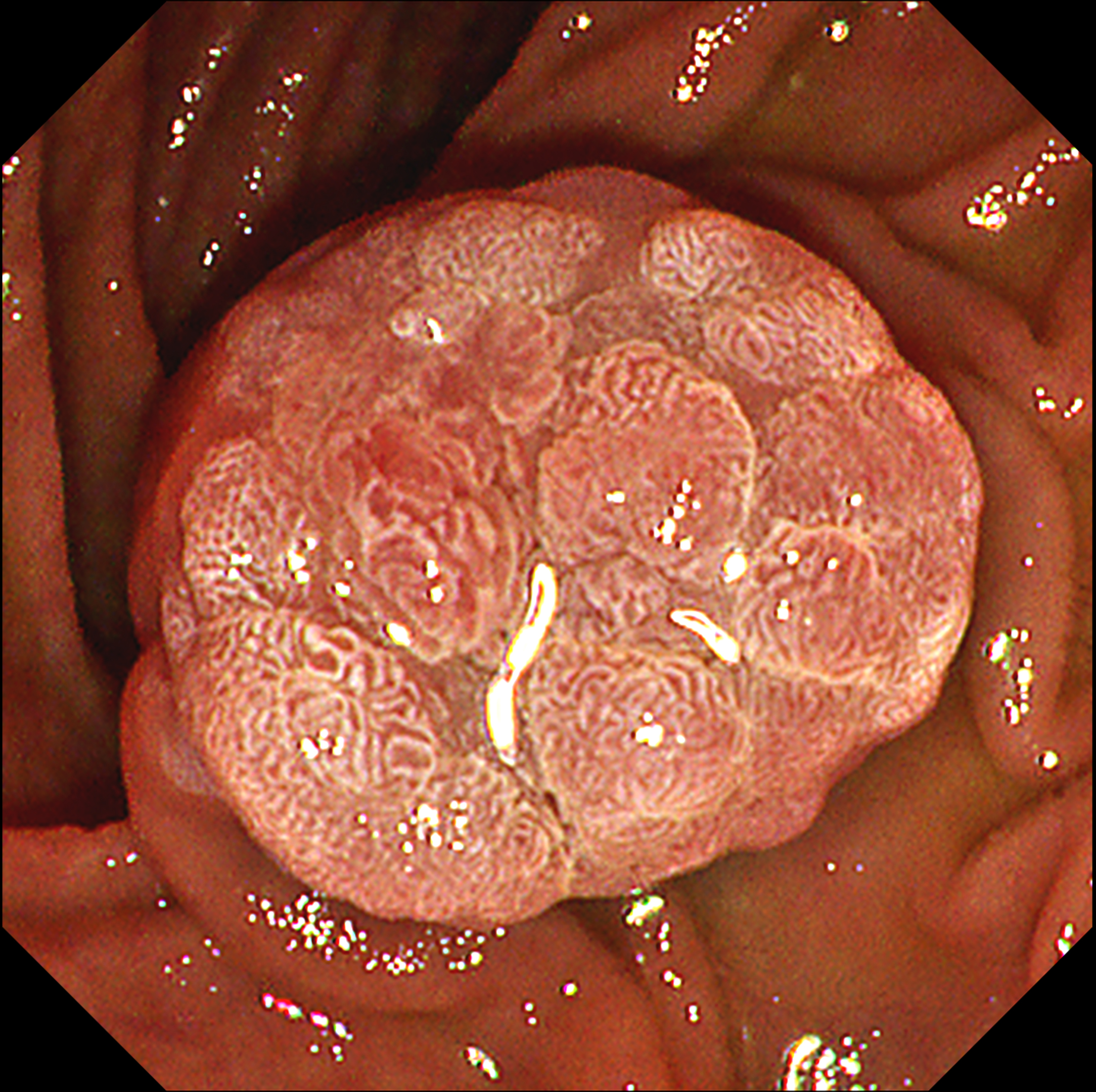
This video demonstrates the usefulness of an image-enhanced endoscopy system in a patient with suspected ampullary adenoma. Using white-light imaging (WLI), a lobular mass-like lesion without ulceration or bleeding was observed. On narrow-band imaging™ technology (NBI™ technology) observation, the lesion boundaries were clearly observed with strong contrast. Texture and color enhancement imaging (TXI™ technology) observation mode 1 helped to observe the surface meandering microvessels well while further emphasizing the surface cone-like lobularity. TXI™ mode 2 highlighted the surface irregular nodularity and pit pattern while maintaining visual naturalness1. In patients with suspected ampullary mass, applying TXI™ observation mode can help to identify the characteristics of mass-like lesion of ampulla of Vater and make treatment decisions.
Overall Comment
This case shows that the observation of the mass-like lesion in ampulla of Vater using TXI™ technology observation mode strongly emphasized the surface lobularity and the irregular meandering surface microvessels. TXI™ technology highlights the difference in color tone of the surface mucosa1, so the pine-cone like surface lobularity and surface microvessels of suspicious ampullary adenoma could be usefully identified using TXI™ technology mode.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD, FASGE, FACG, FJGES
Il Sang Shin, MD, PhD Case 3: Regular follow-up exam for discrimination of ampullary adenoma
Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD, FASGE, FACG, FJGES
Il Sang Shin, MD, PhD
- Keyword
- Content Type