Esophageal Case 7

Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan
Koc University Hospital
Istanbul, Turkey
Disclaimer:
- NBI™, RDI™ and TXI™ Technologies are not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis
- The positions and statements made herein by Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan are based on Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan’s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
- The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU)
- The GIF-XZ1200 used in this case is not available in the US market at this time nor is there an established time for its release. The safety and effectiveness of this product and or the use of these products has not yet been established in the United States market.
- Dr. Fatih Aslan, the authoring physician of this presentation, is a paid consultant(s) to the Olympus Corporation.
Scope: GIF-XZ1200, GIF-EZ1500
Case: Barrett Esophagus-Adenocarcinoma
Organ: Esophagus
Case video
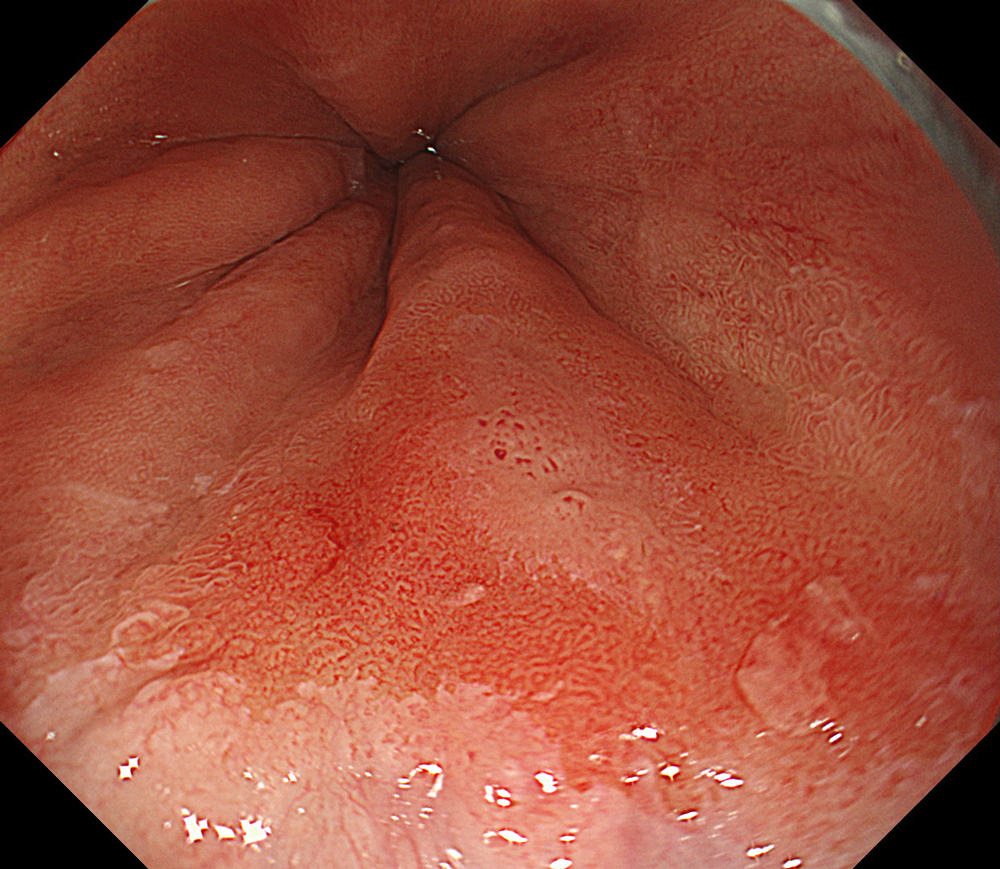
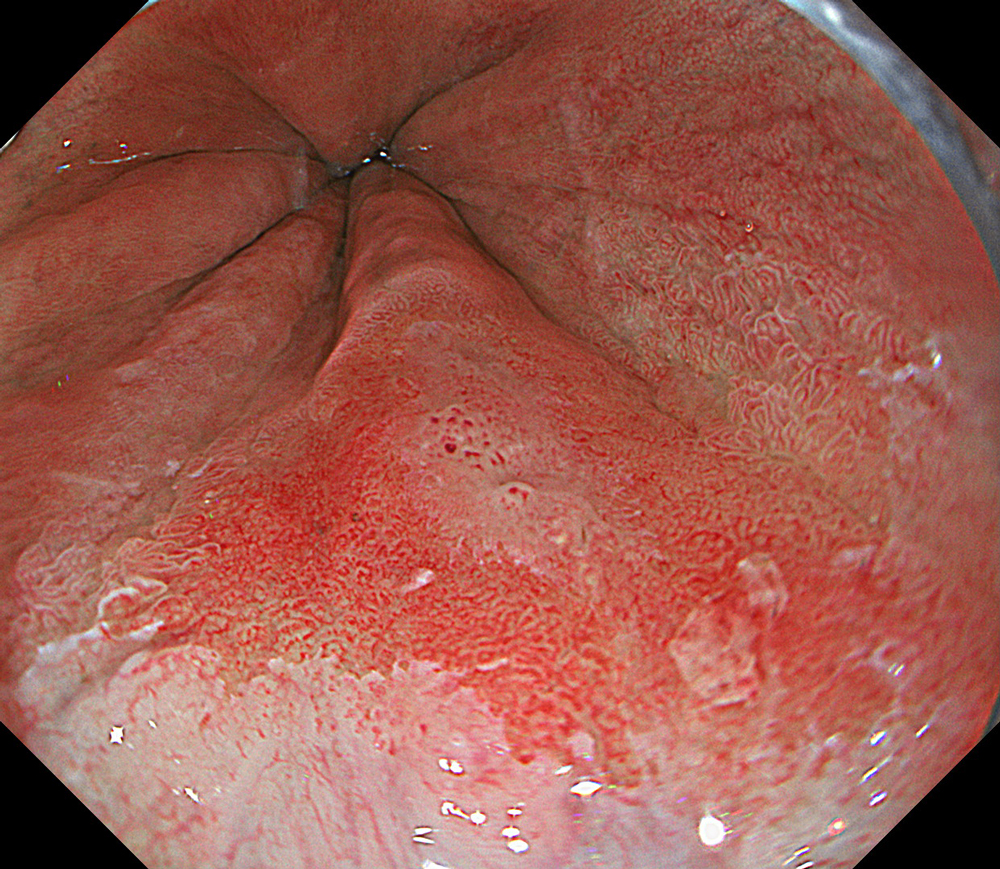
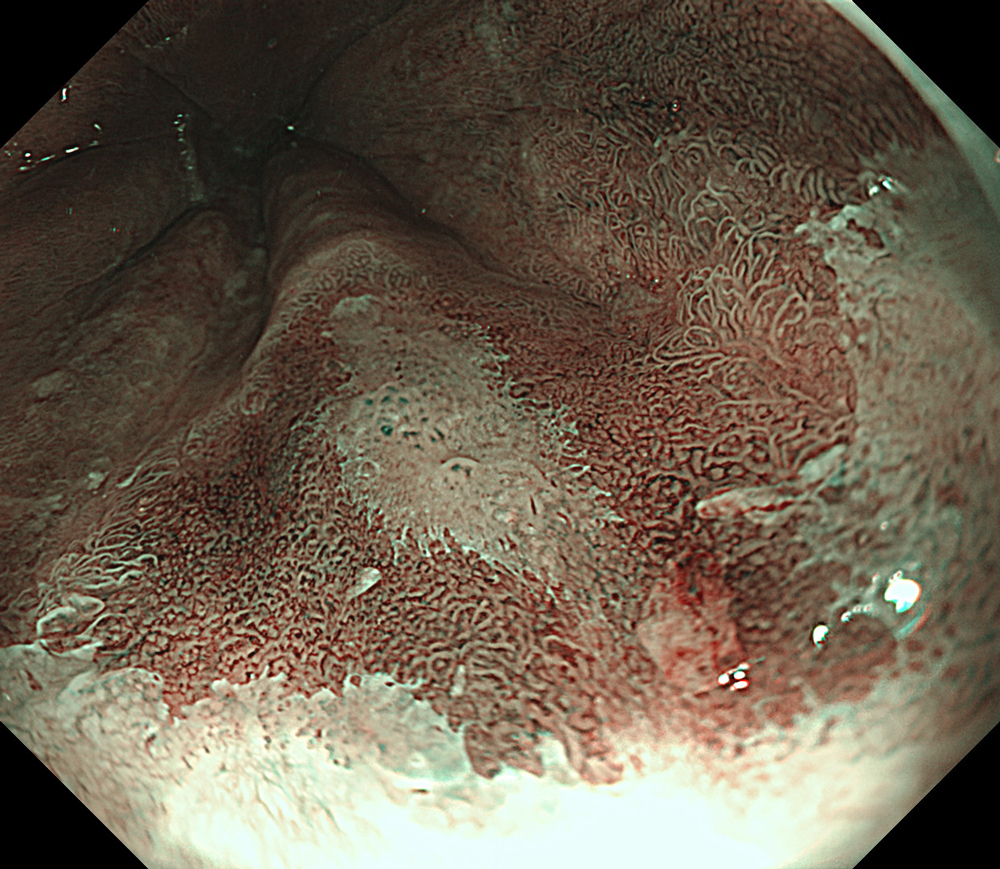
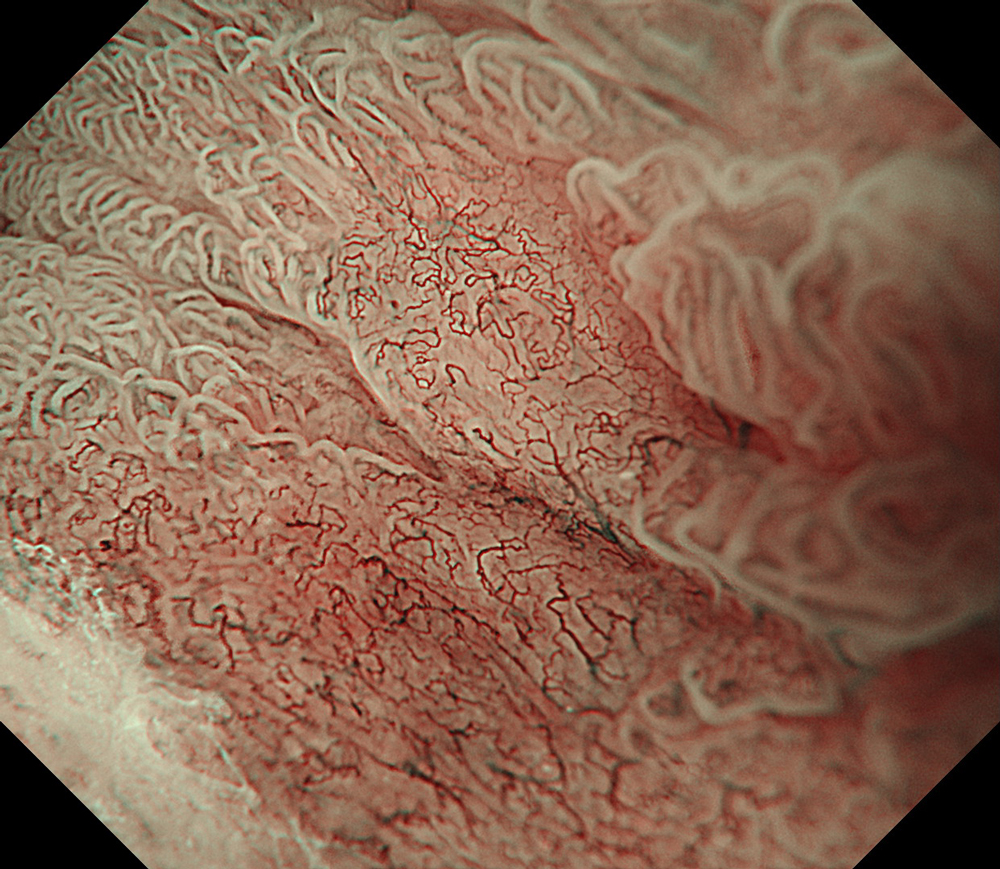
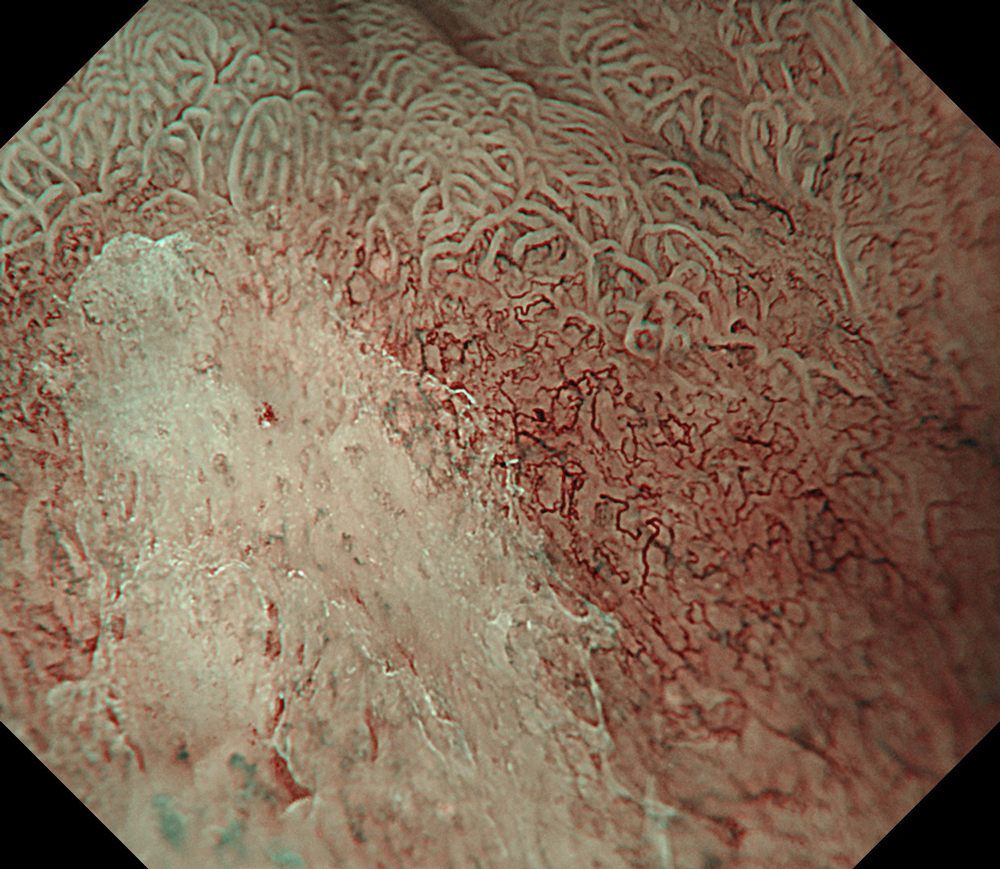
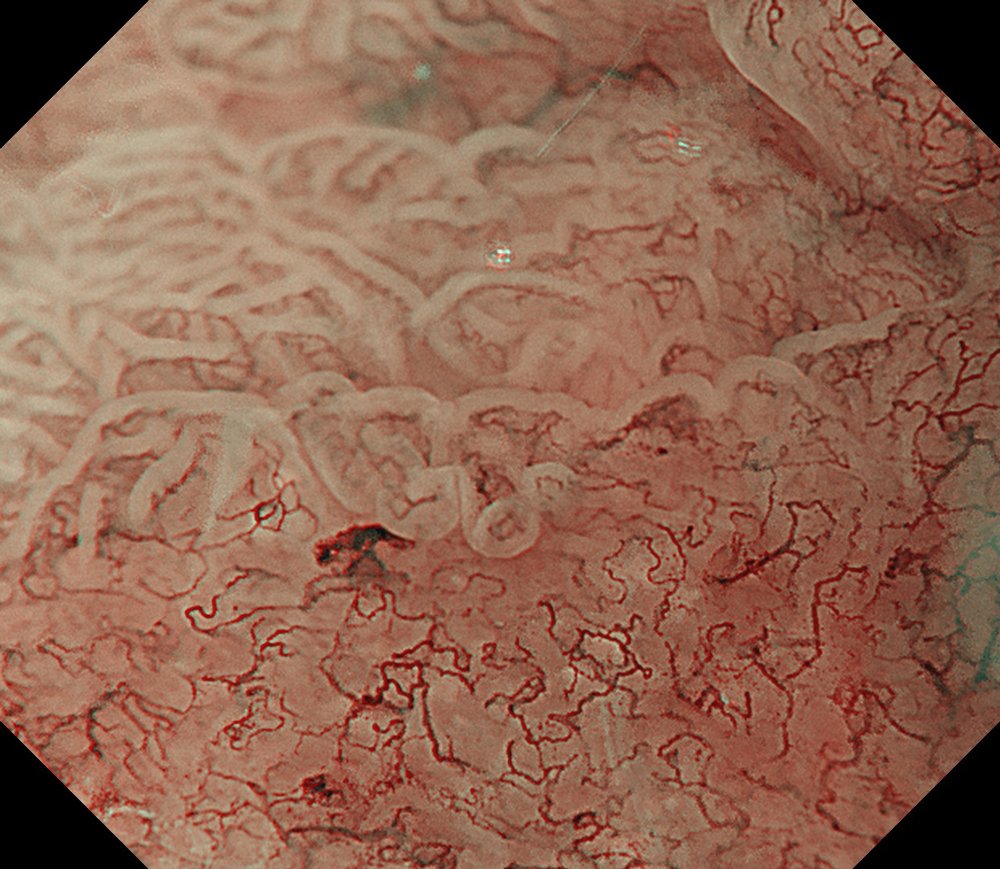
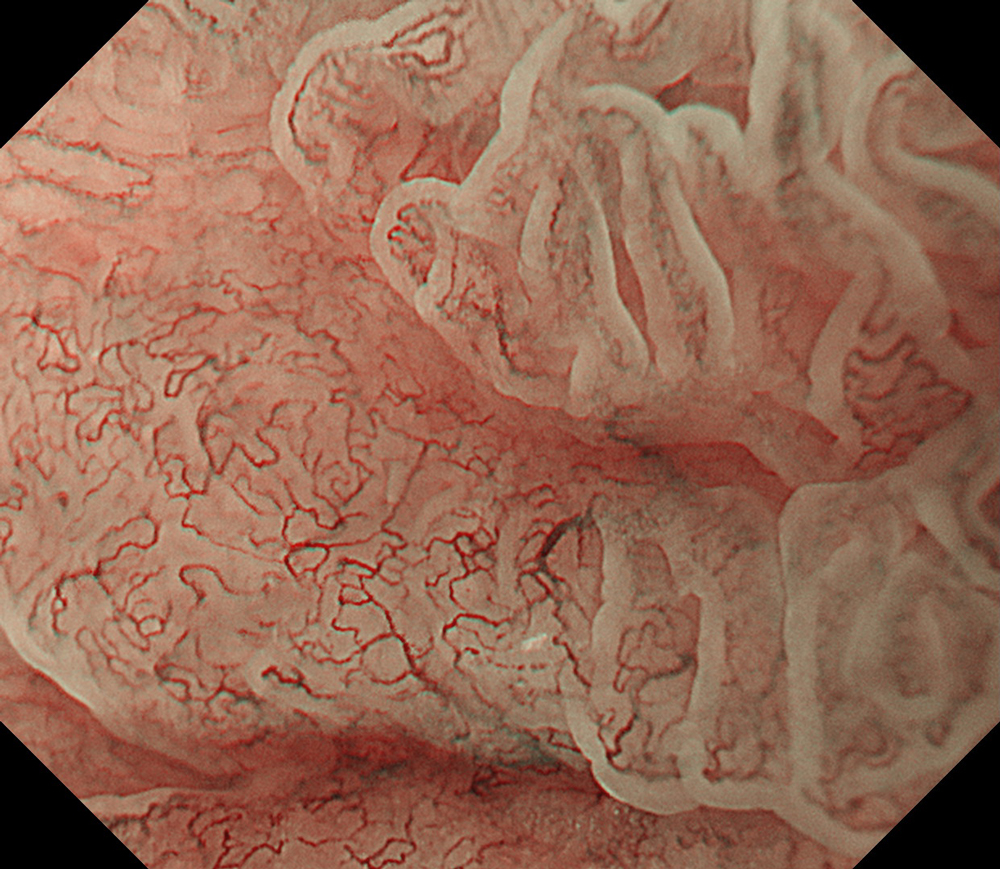
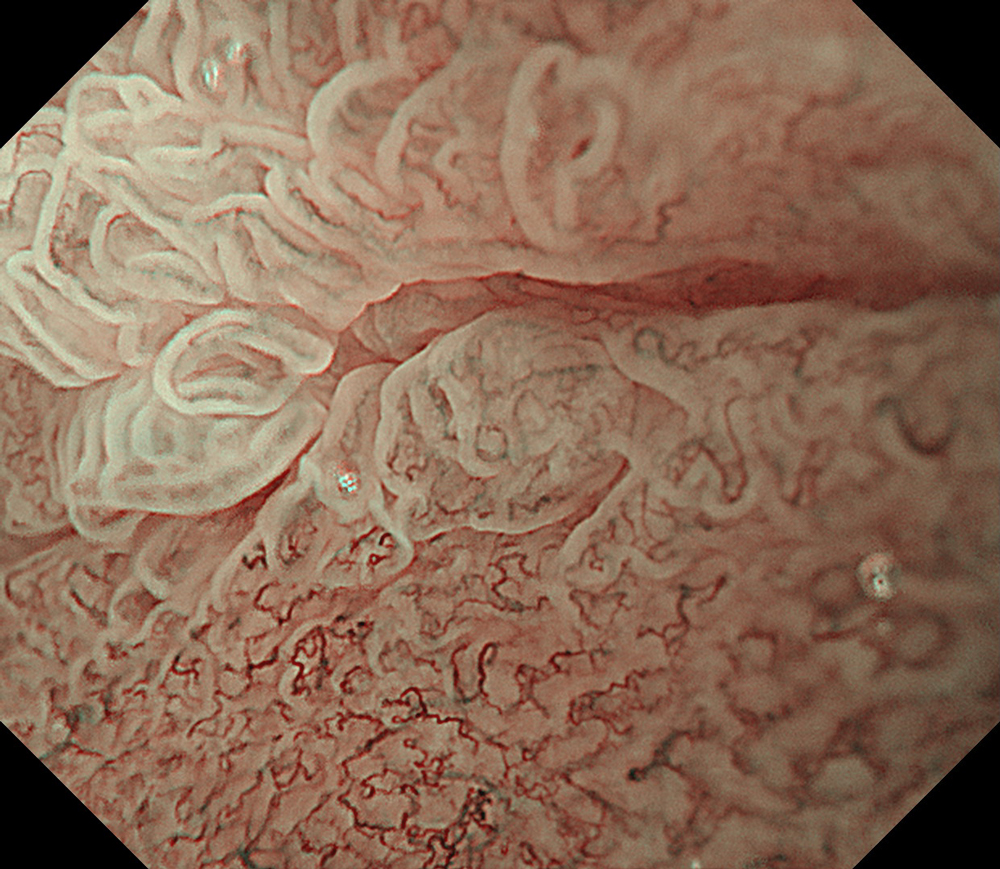
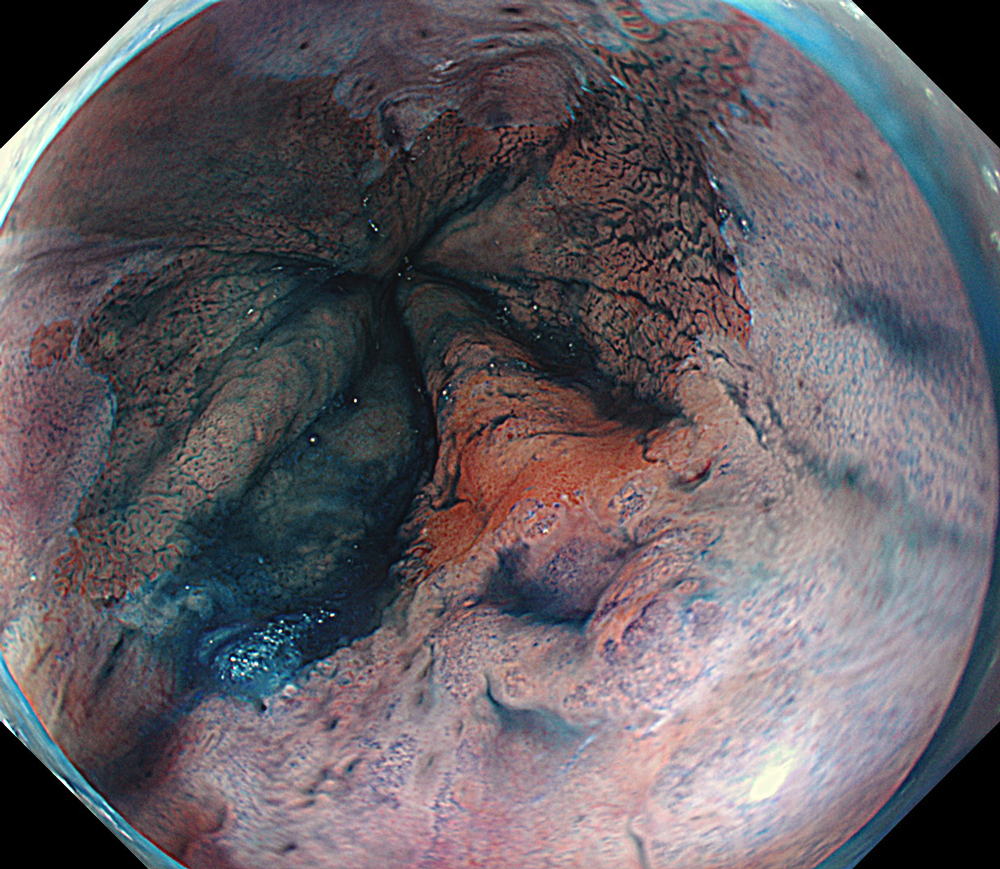
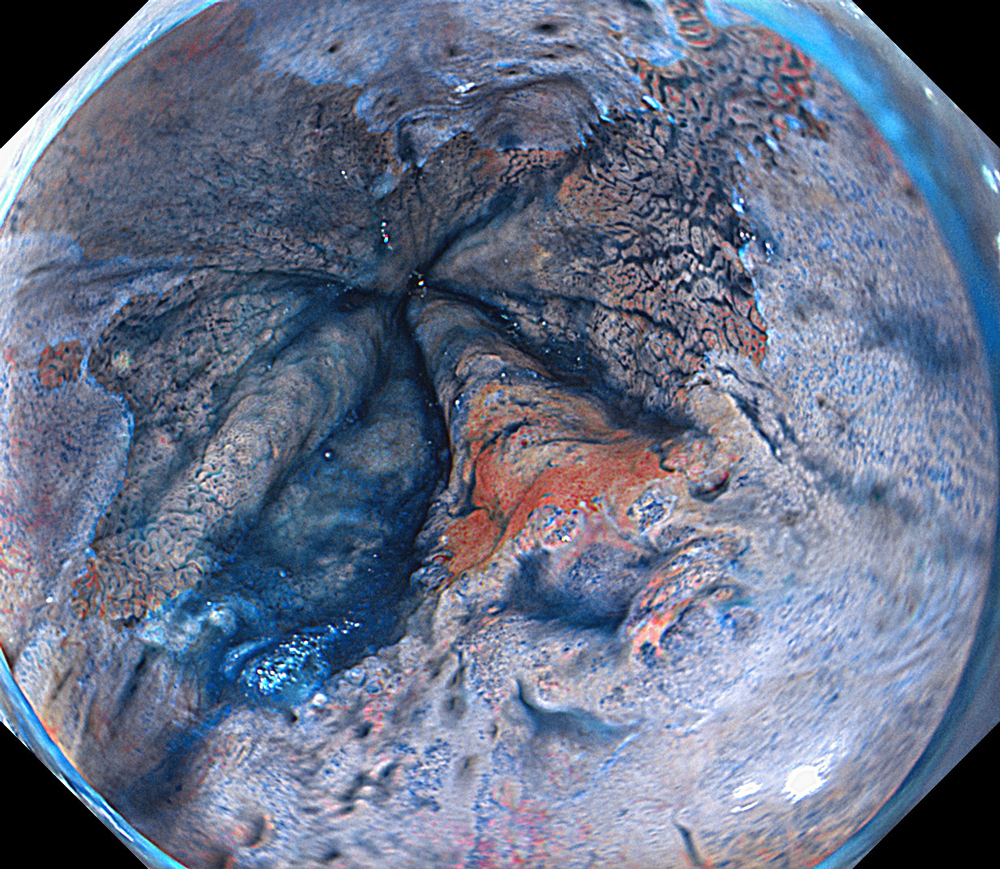
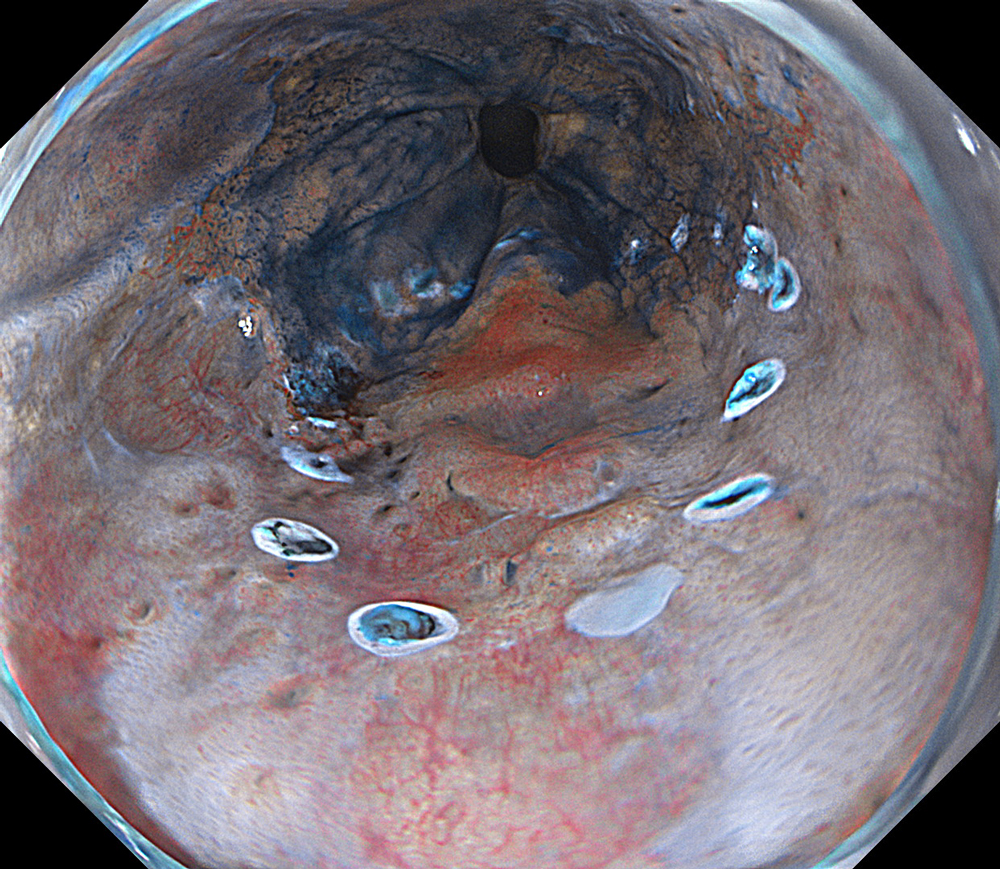
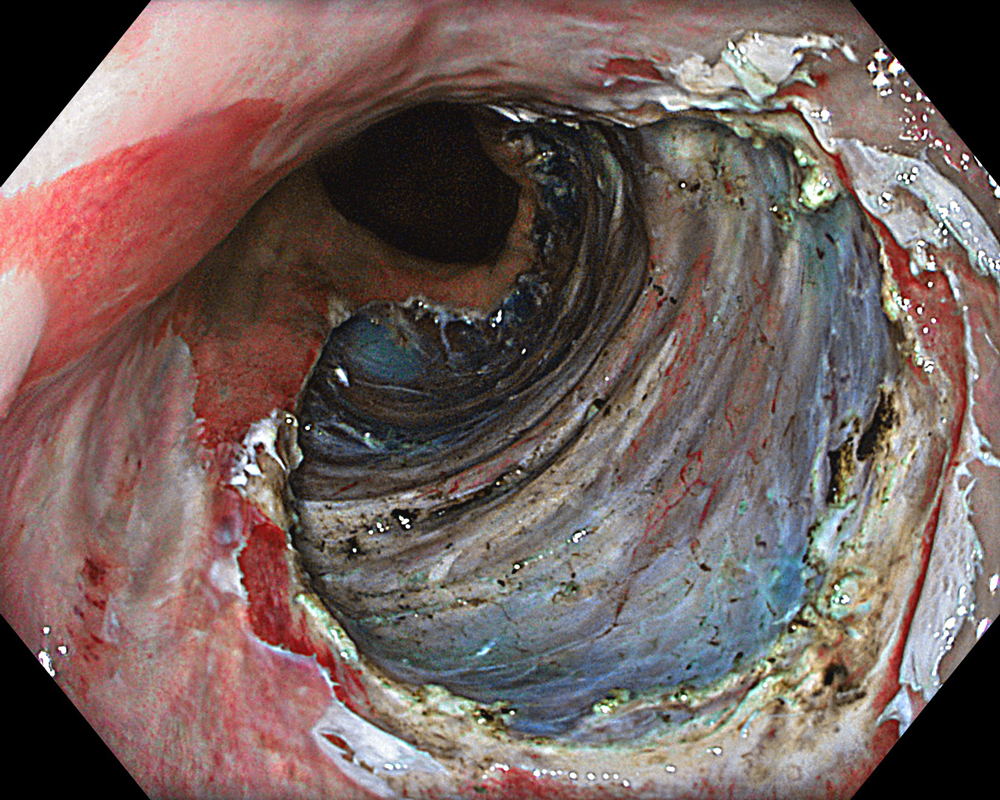
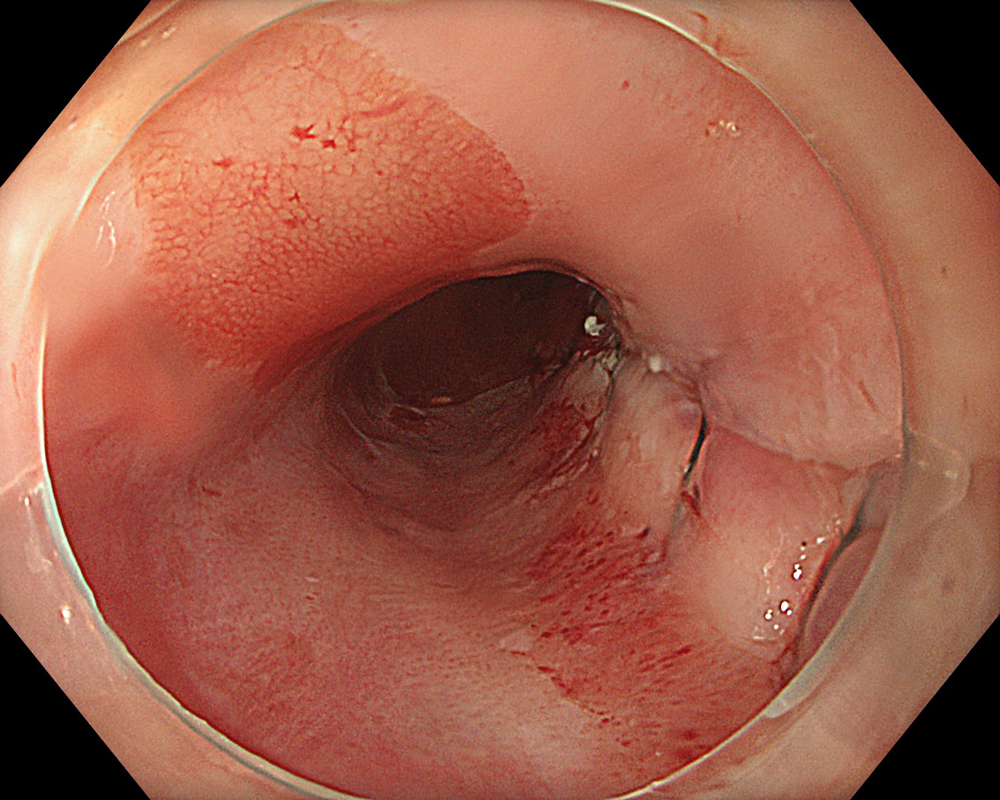
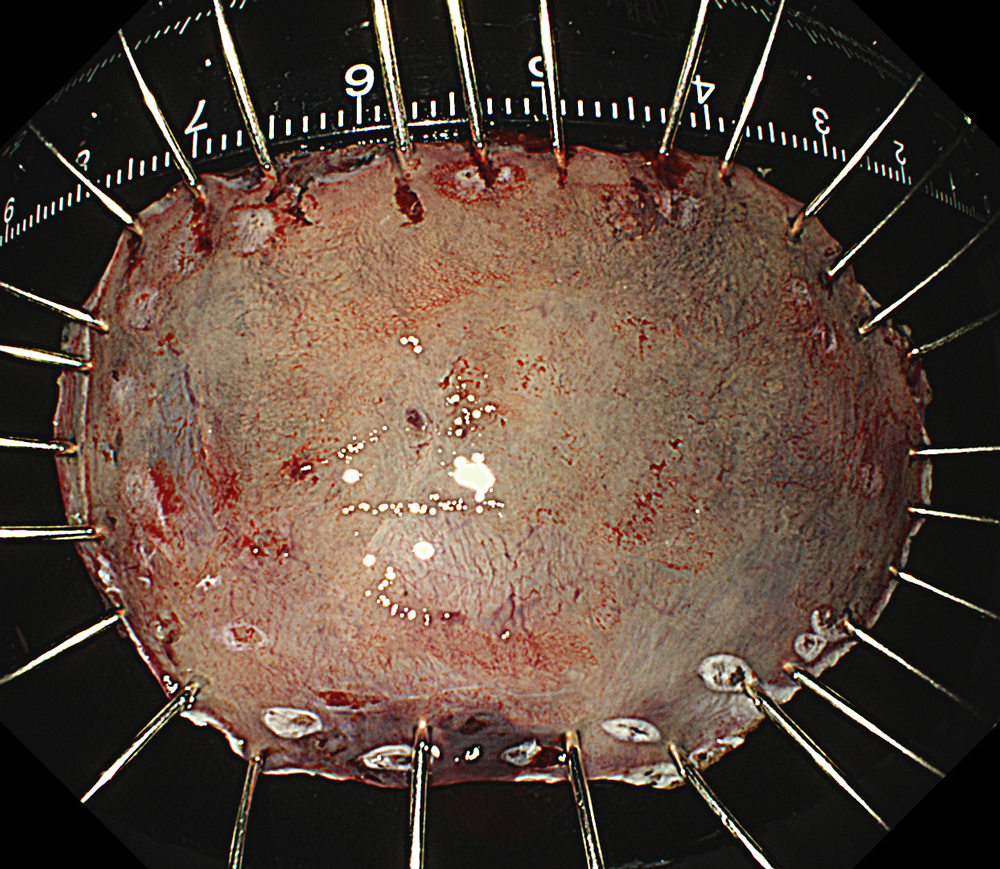
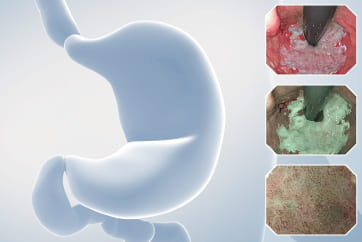
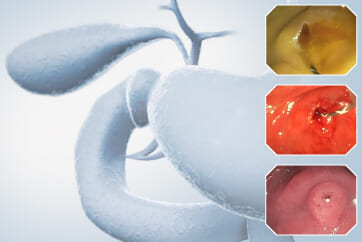
An 84-year-old male patient, dependent on proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and receiving antiplatelet therapy for coronary artery disease, with a known diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus, underwent endoscopic evaluation using an GIF-XZ1200 endoscope. In WLI mode, a reddish area was identified at the squamocolumnar junction. In TXI™ technology mode, the borders of this area were more clearly delineated. In NBI™ technology mode, the area appeared brownish and was further evaluated under water immersion with optical zoom. This assessment revealed malignant irregularities in the vascular pattern, as well as clearly defined lesion margins. Following conventional chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine, non-stained areas were more distinctly visualized in TXI mode, and marking was performed under this mode. For therapeutic purposes, ESD was performed using a GIF-EZ1500 endoscope. Before mucosal incision, submucosal injection was carried out under RDI™ technology mode to minimize the risk of accidental contact of the sclerotherapy needle with large vascular structures, thereby reducing the likelihood of submucosal hematoma formation prior to incision. Subsequently, stepwise submucosal dissection was performed using a DualKnife™ device. During dissection, the use of TXI™ technology mode was found to be helpful in differentiating the submucosal layer. The procedure was completed successfully, and the ESD specimen was retrieved. To minimize the risk of delayed adverse events, the resection site was closed using barbed sutures.
Overall comment
This case highlights the value of advanced imaging modalities-particularly TXI™ and NBI™ technology in enhancing lesion characterization at the squamocolumnar junction. The combination of underwater evaluation and optical zoom enabled precise delineation of malignant features and accurate lesion mapping. TXI™ technology mode proved especially useful in defining unstained areas after chromoendoscopy, facilitating targeted marking. The integration of RDI™ technology mode for submucosal injection minimized vascular injury risk, while meticulous ESD followed by barbed suture closure ensured both therapeutic efficacy and procedural safety. This approach underscores how next-generation endoscopic platforms can optimize diagnosis, staging, and treatment outcomes in Barrett’s-associated neoplasia.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
- Keyword
- Content Type