Key to successful Cold Snare Polypectomy with New Technology: EDOF and RDI
Kanagawa Cancer Center, Yokohama, Japan
Introduction
In recent years, Cold Snare Polypectomy (CSP) has been widely adopted as a simple, minimally invasive, and safe procedure for removing small colorectal polyps. However, because the resection depth in CSP is shallower compared to methods like EMR, its indication is currently limited to adenomas. Therefore, accurate endoscopic diagnosis prior to CSP is crucial.
CSP Indications in Japanese Guidelines
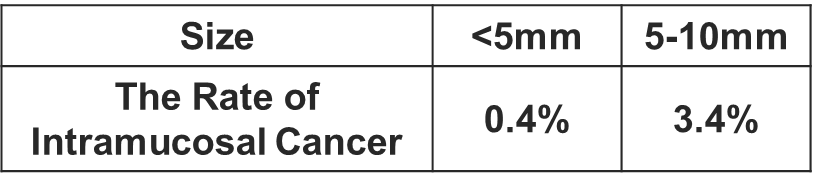
The Japanese guidelines for colorectal cold polypectomy recommend that “the indications should be limited to lesions smaller than 10 mm that are preoperatively diagnosed as adenoma and which can be resected completely en bloc1 “. Furthermore, the commentary states that “the use of image-enhanced endoscopy with magnification is recommended for a highly accurate preoperative diagnosis of colorectal lesion prior to cold polypectomy 2.” This is because, even in lesions under 10 mm, the rate of intramucosal cancer is 0.4% in lesions less than 5 mm in diameter, and 3.4% in lesions between 5 mm and 10 mm, meaning that relying solely on size for CSP indications may lead to residual tumor risk3.
About the New EDOF Technology
The biggest drawback that often leads to magnified observation being avoided is the complexity of focusing. The newly installed Extended Depth of Field (EDOF) function on the CF-EZ1500D system overcomes this by simultaneously acquiring and synthesizing near-focus and far-focus images, resulting in a wider depth of field. This technology reduces the complexity of focusing associated with conventional magnified observation, facilitates high-magnification observation in near focus mode, and enables stable, easy magnified observation for any physicians. The conventional CF-HQ290 scope allowed for close observation up to 9 mm in normal focus mode, and magnified observation between 4 mm and 9 mm in near focus mode. The CF-EZ1500D scope allows for close observation up to 3 mm even in normal focus mode, and further utilizes the near focus mode to enable magnified observation between 1.5 mm and 5.5 mm.
Tips for Using EDOF in Pre-CSP Diagnosis
Tips for Performing CSP in the Colon
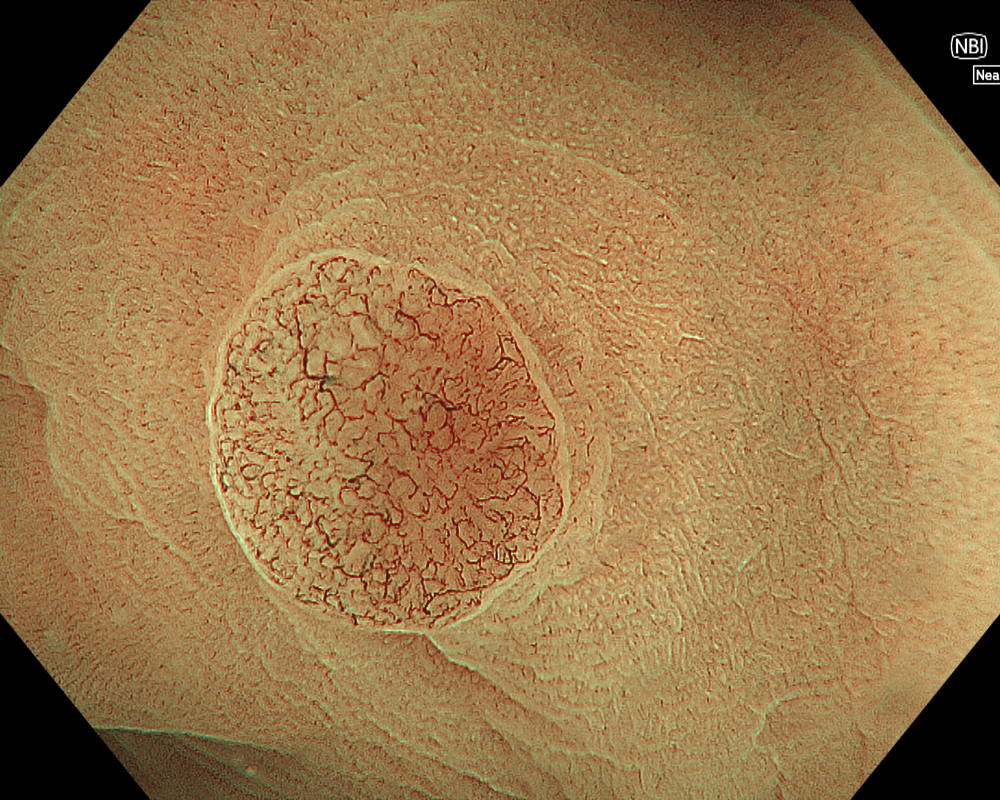
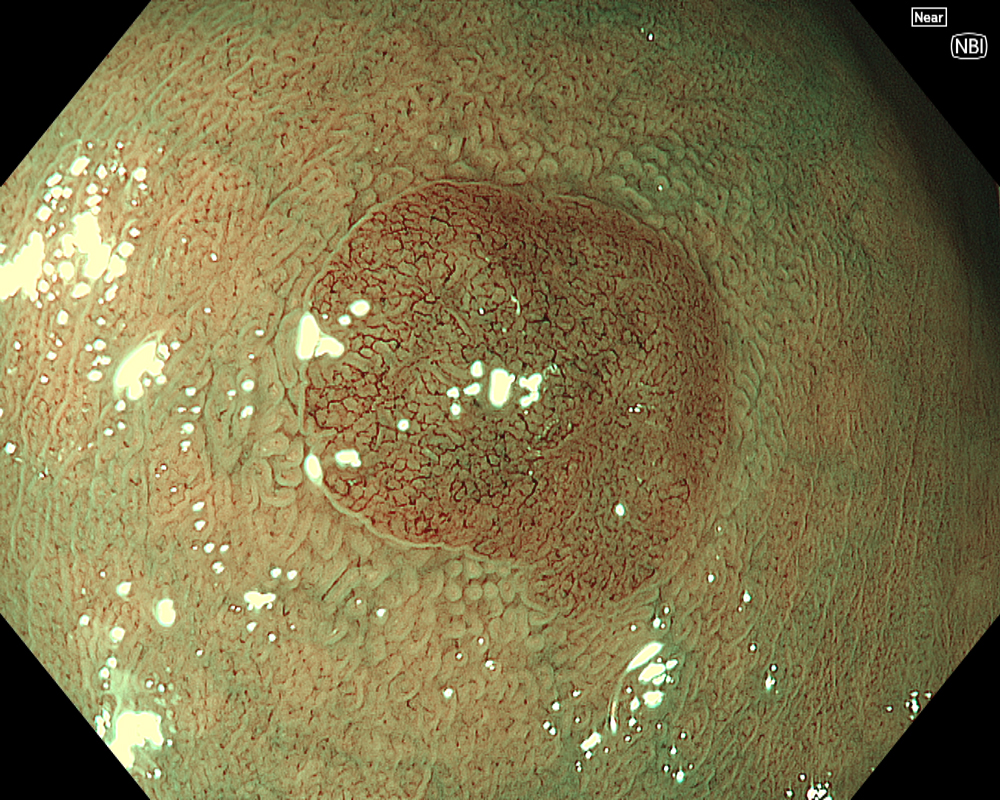
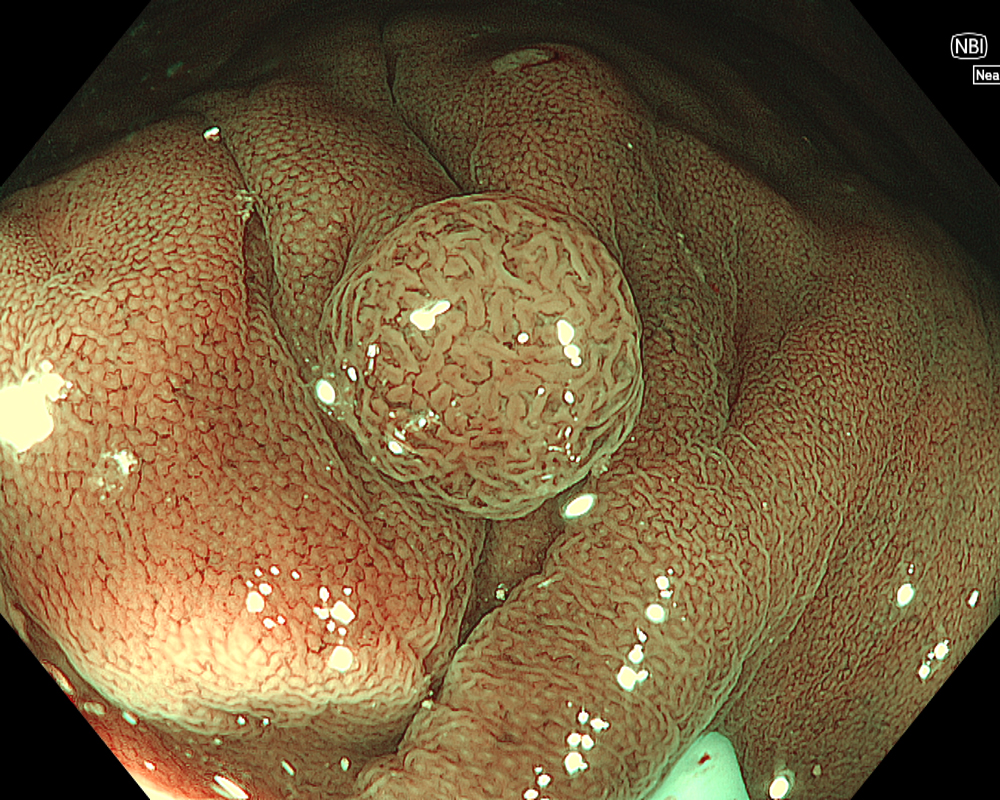
Figure 3: NBI image in near-focus mode under water immersion. Water immersion eliminates halation and provides clear images, while also enhancing magnification for more detailed observation.
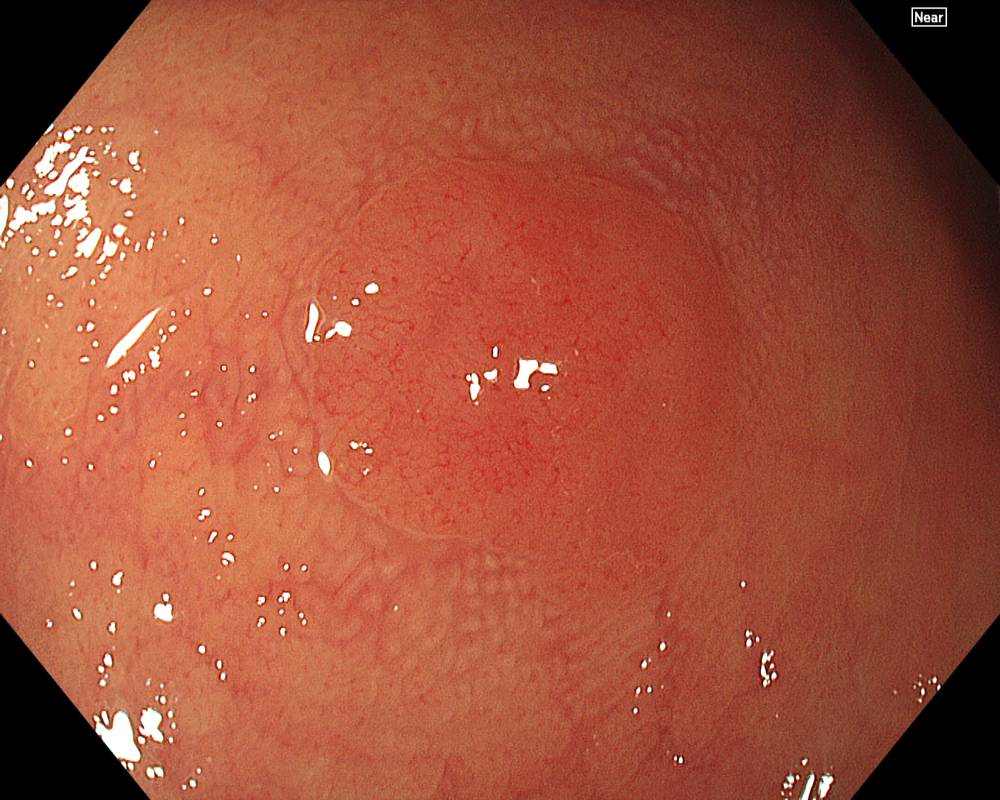
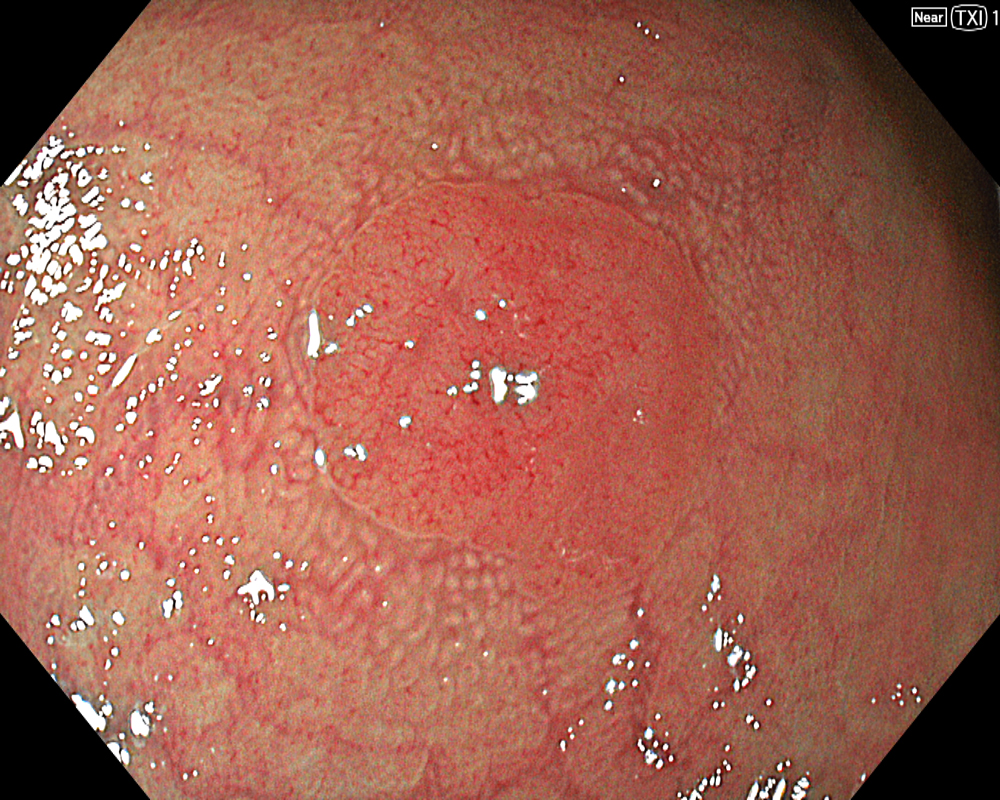
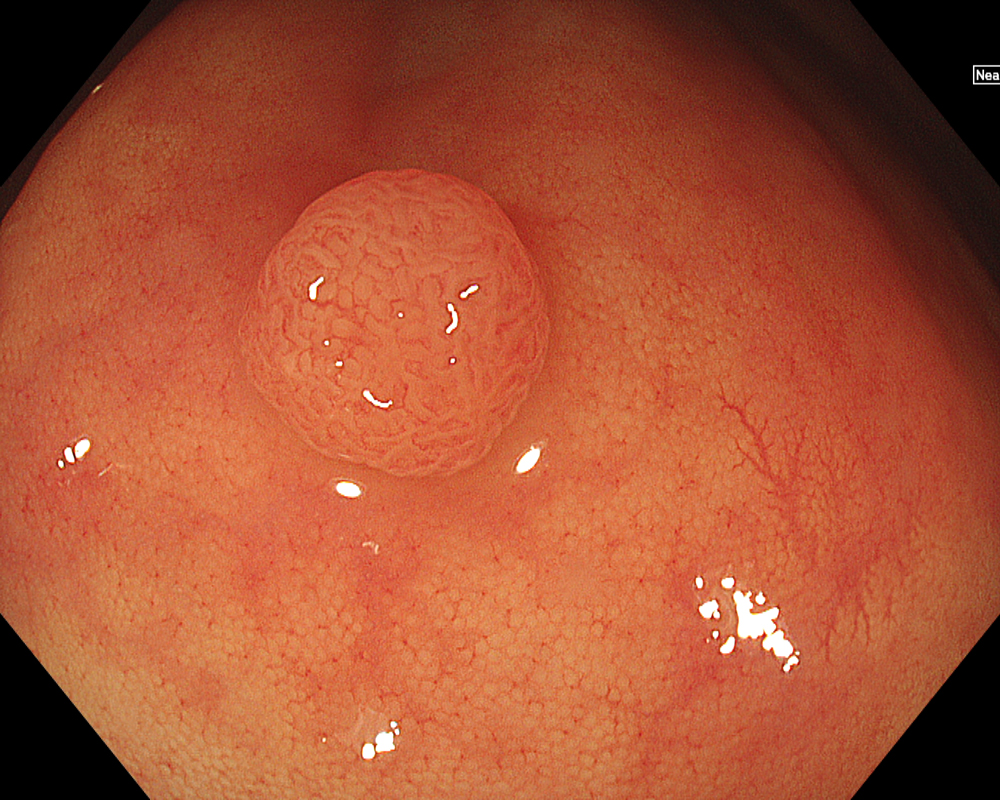
Once the lesion is detected using WLI or Image-Enhanced Endoscopy (IEE, such as TXI/NBI), the first step is to remove adherent debris from the lesion surface by washing. While a water jet may be used, caution is necessary, as applying strong water pressure directly to the lesion can induce oozing, making subsequent NBI observation difficult. In such cases, aim the water jet at the adjacent mucosa instead of directly at the lesion to remove debris. Alternatively, use a syringe for gentle cleansing.
Next, initiate observation by approaching the lesion. As mentioned, the CF-EZ1500D scope allows proximity up to approximately 3 mm even in normal mode. Switching to Near focus mode with a single button press allows for observation up to 1.5 mm. EDOF facilitates easy focusing on both near and far distances, making it possible to continuously capture images that are sharply in focus across the entire screen, even for lesions with uneven surfaces or those with motion due to respiratory variation. Observation under water is useful if halation is a concern or if more detailed observation is desired.
In addition to eliminating halation, underwater observation has a magnification effect. When combined with the Near focus mode, it allows for even clearer magnified images. For determining the indication for CSP, the JNET (Japan NBI Expert Team) classification is used, which evaluates the surface Vessel pattern and Surface pattern using NBI + Near focus magnified observation. If the lesion is classified as Type 2A (characterized by a regular caliber and regular distribution (meshed/spiral pattern) in the Vessel pattern, and a regular pattern (tubular/branched/papillary) in the Surface pattern), it is highly likely to be a lowgrade intramucosal neoplasia, and CSP can be indicated if the size is less than 10 mm. If the lesion is classified as Type 2B (characterized by variable caliber and irregular distribution in the Vessel pattern, and an irregular or obscure pattern in the Surface pattern), there is a higher possibility of high-grade intramucosal neoplasia or deeper invasion. Indiscriminately performing CSP based solely on small size should be avoided in these cases.
Utility of EDOF and RDI Immediately After CSP
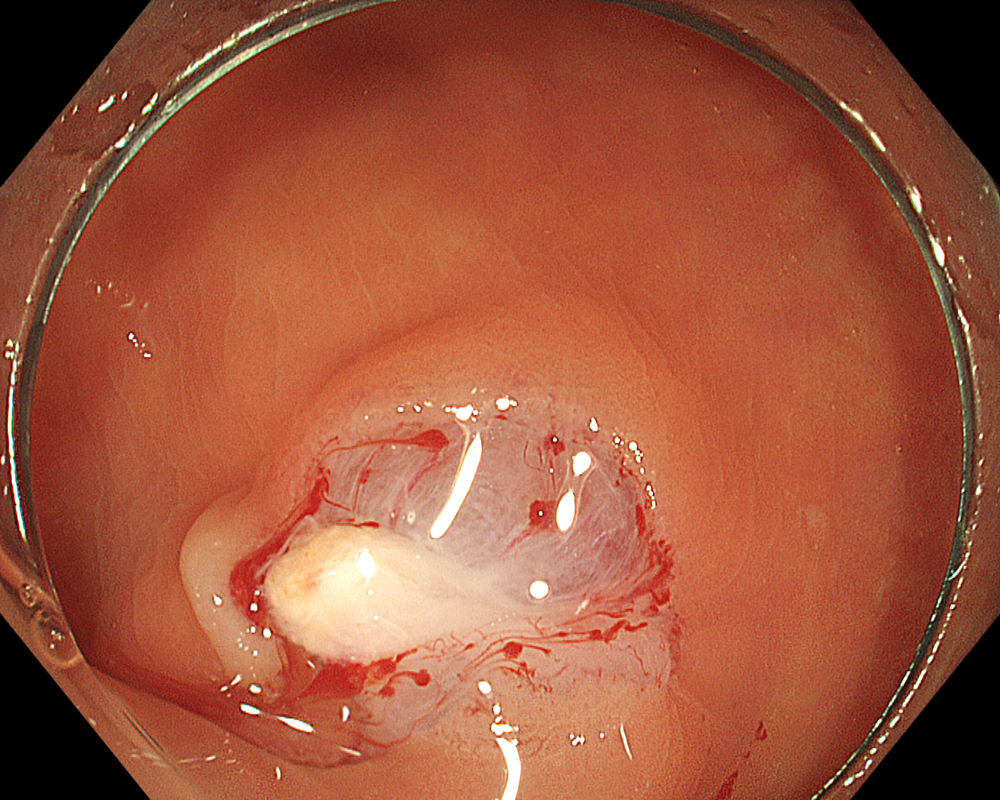
The points to note immediately after CSP are bleeding and residual tissue. Since CSP does not involve electrocautery, there is no so-called “burning effect.” Therefore, when capturing the lesion with the snare, it is important to include a margin of surrounding non-neoplastic mucosa. After CSP, re- examine the mucosal defect margin using NBI + Near focus to check for any residual tissue. Again, the EDOF function makes focusing and magnified observation significantly easier here.
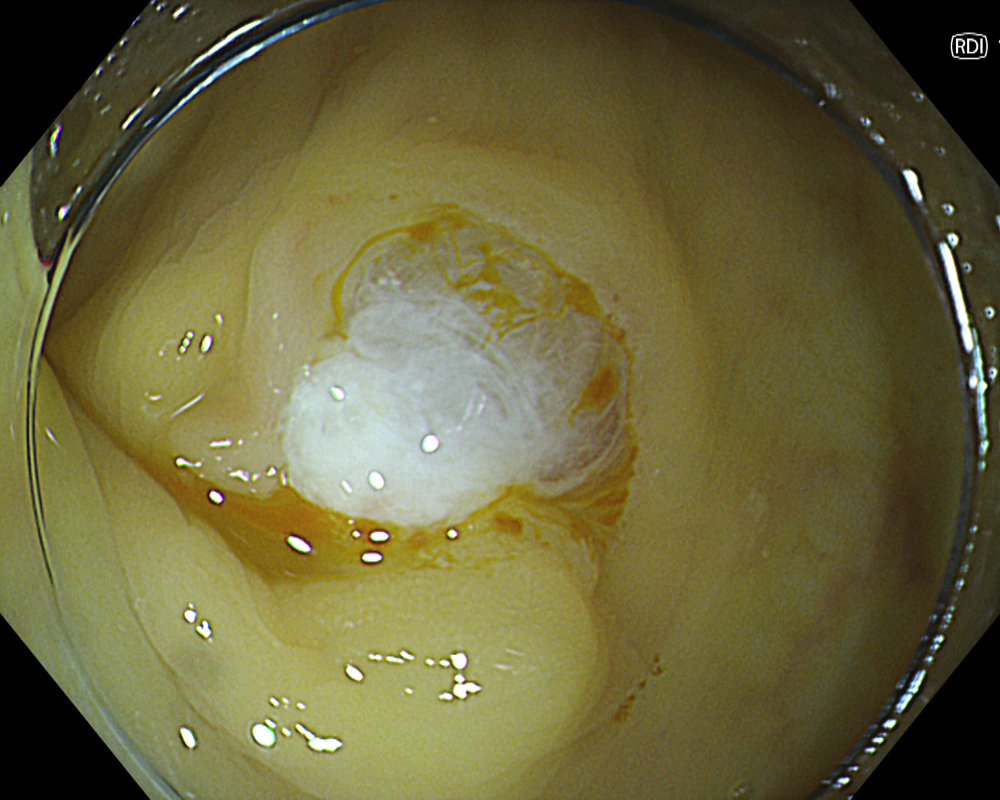
While pulsatile or arterial bleeding is rare after CSP, minor oozing is almost always present. Applying the water jet to the post-CSP mucosal defect helps achieve a tamponade state for pressure-based hemostasis. Red Dichromatic Imaging (RDI) is a wavelength selection technology that enhances the visibility of deep vessels and bleeding points, making it useful for identifying bleeding sites and evaluating hemostasis. Even when a bleeding point is difficult to confirm, switching to RDI facilitates its identification, making hemostatic procedures and confirmation of successful hemostasis much easier and highly useful.
Conclusion
The newly installed EDOF function on the CF-EZ1500D scope dramatically simplifies conventional magnified observation and enables the acquisition of very clear magnified images that are in focus over a wide range. This function allows for accurate determination of the indication during the pre-CSP diagnostic phase and is also highly effective in checking for residual tissue after resection. Furthermore, the combination with RDI facilitates the identification of bleeding points and confirmation of hemostasis after CSP, which we believe will significantly contribute to the treatment of colorectal polyps, including CSP.
1,2 Uraoka T, Takizawa K, Tanaka S, et al. Guidelines for Colorectal Cold Polypectomy (supplement to “Guidelines for Colorectal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection/Endoscopic Mucosal Resection”). Digestive Endoscopy 2022;34:668–75.
3 Yamano H, Kuroda K, Yoshikawa K, et al. Endoscopic management of early colorectal cancer: endoscopic diagnosis and EMR by magnifying endoscope. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2007; 42:1053-1059
CSP Procedures
Touch Panel / Scope Switch Setting
Recommended Settings
- Structure enhancement (WLI/NBI): A5-7/A8
- Color enhancement (NBI): Color 3
- BAI-MAC: ON
- Distal Hood: MAJ-2187
- CO2 Insufflation: UCR
- Keyword
- Content Type