Colorectal Case 21

Prof. Yasushi Sano
Kansai Medical University, Osaka, Japan
Sano Hospital, Kobe, JapanDisclaimer:
NBI™ and TXI™ technologies is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis
The positions and statements made herein by Prof. Yasushi Sano are based on Prof. Yasushi Sano experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU)
1) Data on file with Olympus (DC00489968)
2) Data on file with Olympus as of 07/17/2020
3) Matsuda T, Fujii T, Sano Y, et al. Randomised comparison of post-polypectomy surveillance intervals following a two-round baseline colonoscopy: the Japan Polyp Study Workgroup. Gut. 2020 Nov 2;70(8):1469–78.
4) Sano Y, Hotta K, Matsuda T, et al. Japan Polyp Study Workgroup. Endoscopic Removal of Premalignant Lesions Reduces Long-Term Colorectal Cancer Risk: Results From the Japan Polyp Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug 6:S1542-3565(23)00588-8.
Scope: CF-EZ1500DI
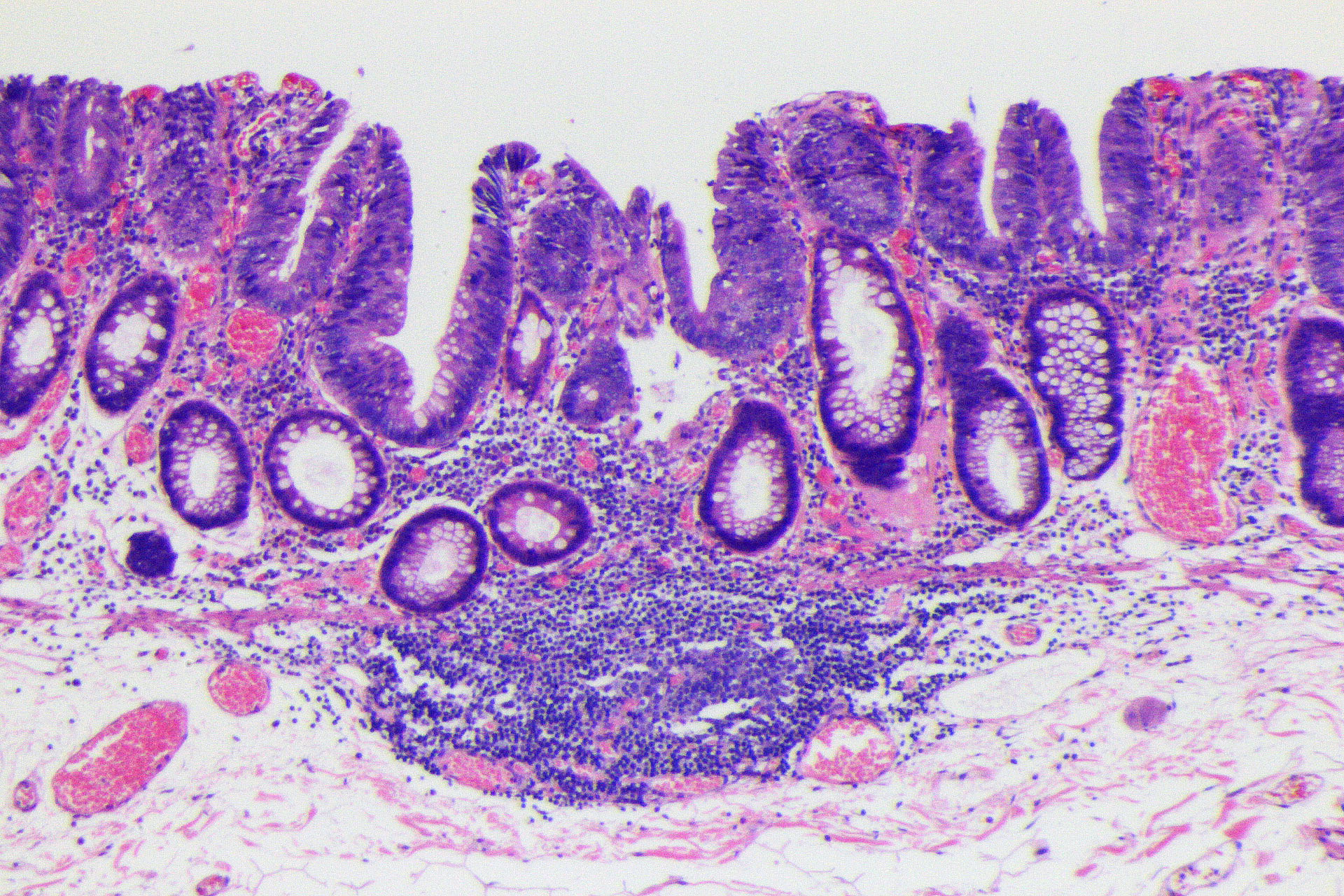
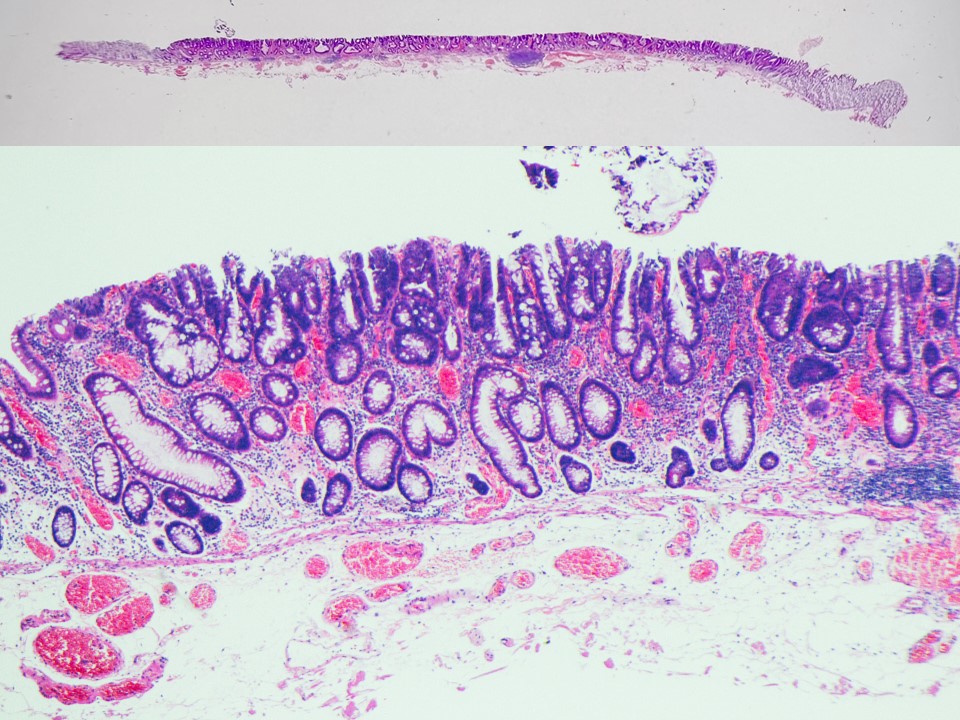
Histology: Tubulovillous adenoma, low-grade dysplasia, including small foci of high-grade dysplasia with lymphoid follicular formation.
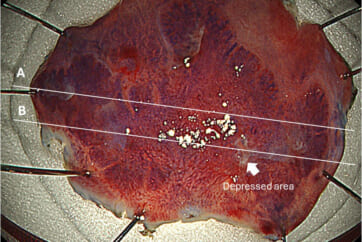
Organ: Transverse colon
Patient information: M, 60s
Medical history: Postoperative for pharyngeal cancer, Screening colonoscopy
11. Histology (low power)
Case Video
Video 1: Observation by WL, TXI™, & NBI™ technologies
Video 2: Observation by chromoendoscopy with Indigo carmine
Overall Comment
LST-NG lesions are considered precursor lesions of PCCRC 3,4) and should not be missed on colonoscopy. In this LST-NG case, the lesion was detected by pale redness. NBI™ technology observation was very useful in visualizing the extent of the lesion. In general, LST-NG lesions show a depressed area, and detailed endoscopic observation of this area is important for endoscopic histology predictions. In this case, a JNET 2B region was observed in the depressed area. The pathological diagnosis of the depressed area was adenoma with high-grade dysplasia. In Japan, it is recommended that dye endoscopy be added to the endoscopy to improve sensitivity when a lesion showing JNET 2B characteristics is observed.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
Prof. Yasushi Sano Case 22: 0-Is (submucosal invasive carcinoma), 11mm, JNET 2B
Prof. Yasushi Sano
- Keyword
- Content Type