Colorectal Case 27
.jpg)
Prof. Yoji Takeuchi
Gunma University Hospital, Japan
Disclaimer:
NBI™ technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis
The positions and statements made herein by Prof. Takeuchi are based on Prof. Takeuchi’s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU)
1) Data on file with Olympus as of 07/17/2020
2) Data on file with Olympus (DC00510434 )
3) Data on file with Olympus (DC00479164, DC00478777)
4) Data on file with Olympus (DC00510434, DC00567392)
Scope: CF-EZ1500DI
Organ: Sigmoid Colon
Patient information: F, 50s
Medical history: Colon Polypectomy (1 Year Prior)
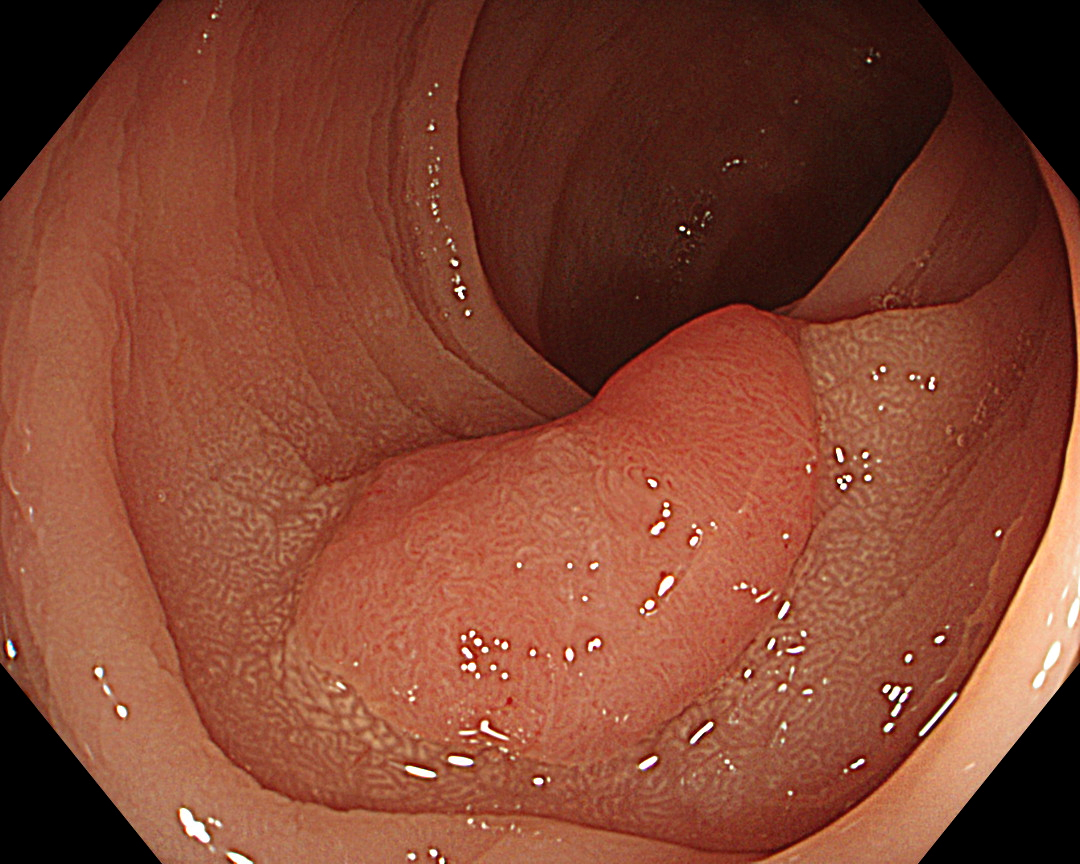
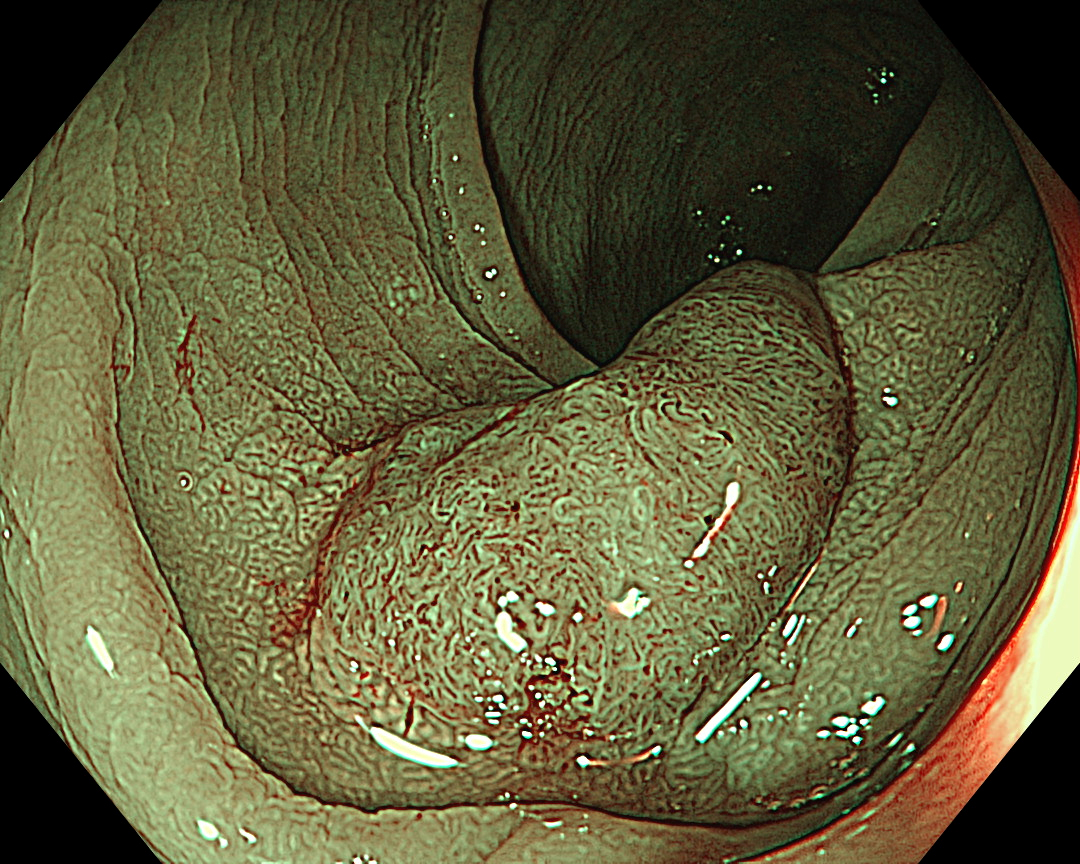
7. NBI™ Technology (Close Observation, without Near Focus)
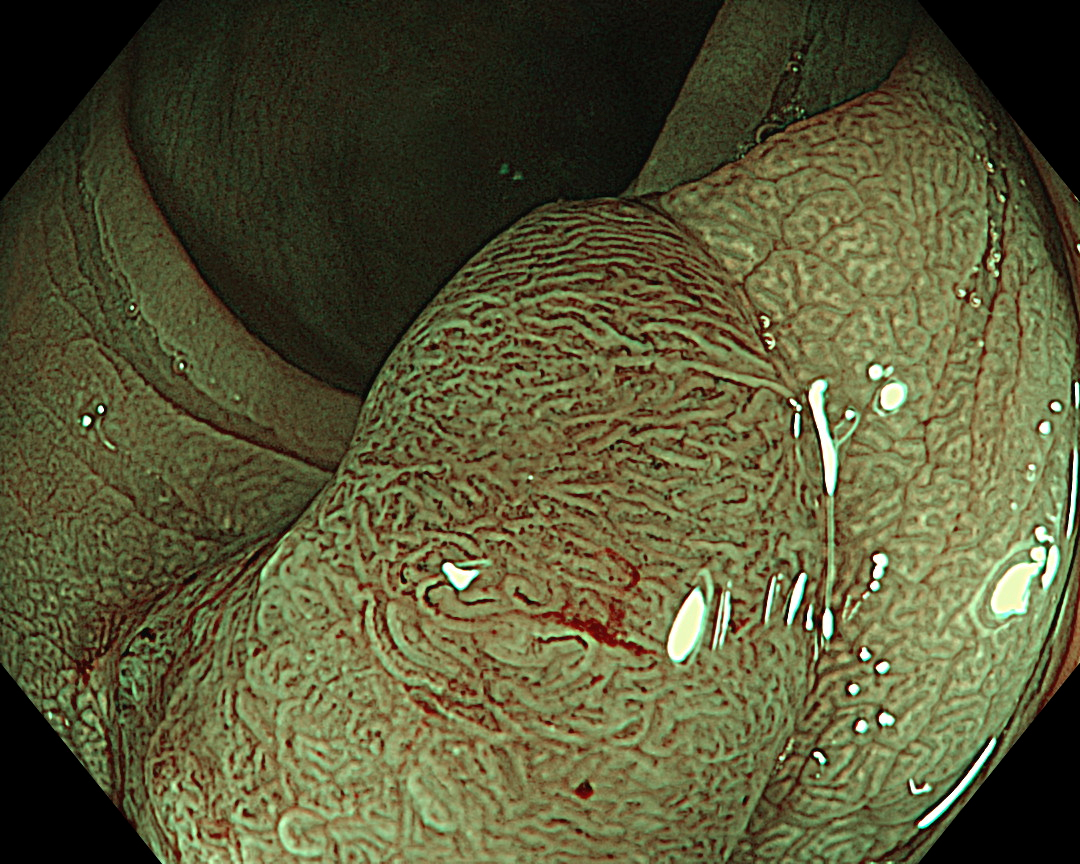
Enhancement: A8
NBI Mode: On
BAI-MAC: On
Near Focus: Off
8. NBI™ Technology (Close Observation, without Near Focus)
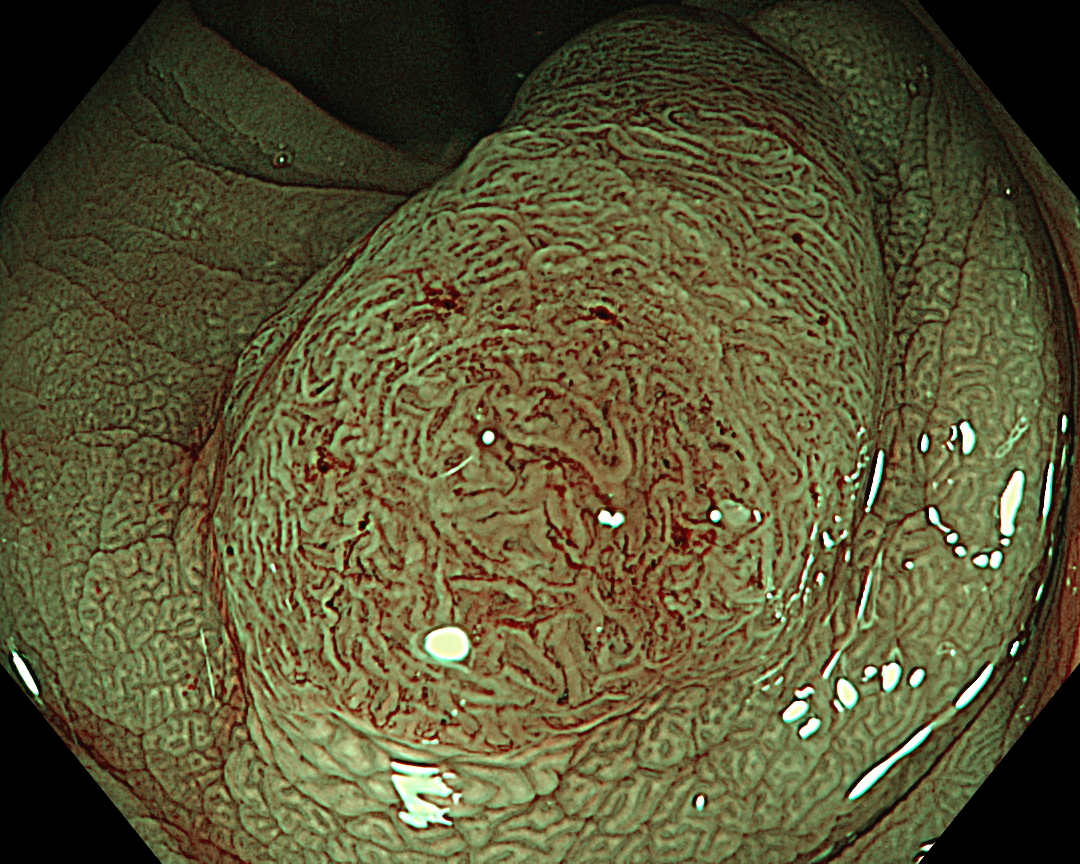
Enhancement: A8
NBI Mode: On
BAI-MAC: On
Near Focus: Off
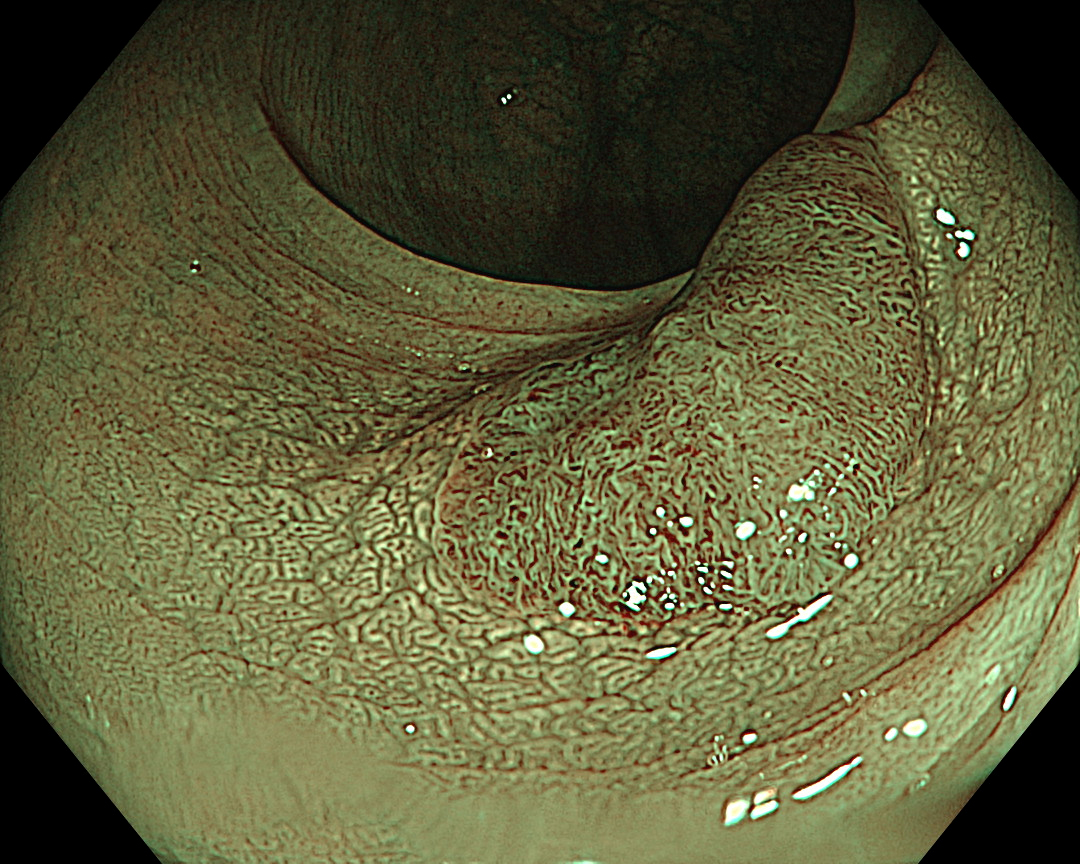
9. NBI™ Technology (Near Focus Mode)
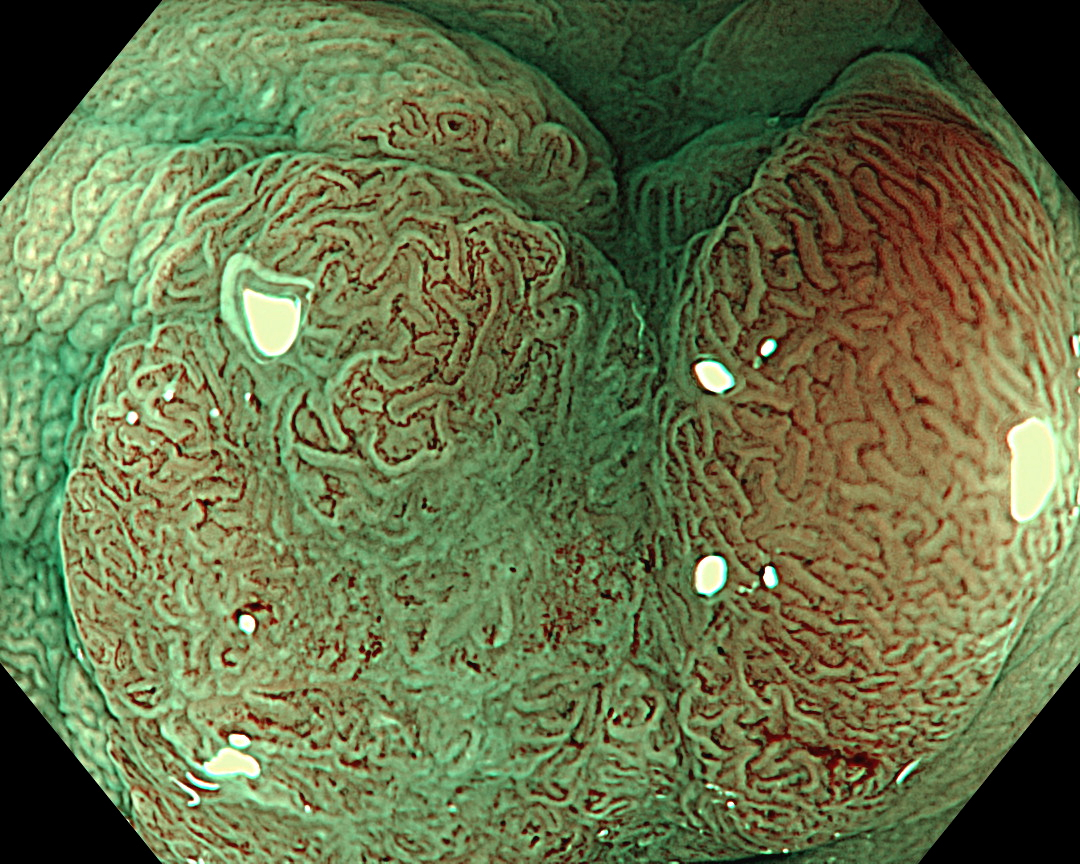
Enhancement: A8
NBI Mode: On
BAI-MAC: On
Near Focus: On
Overall Comment
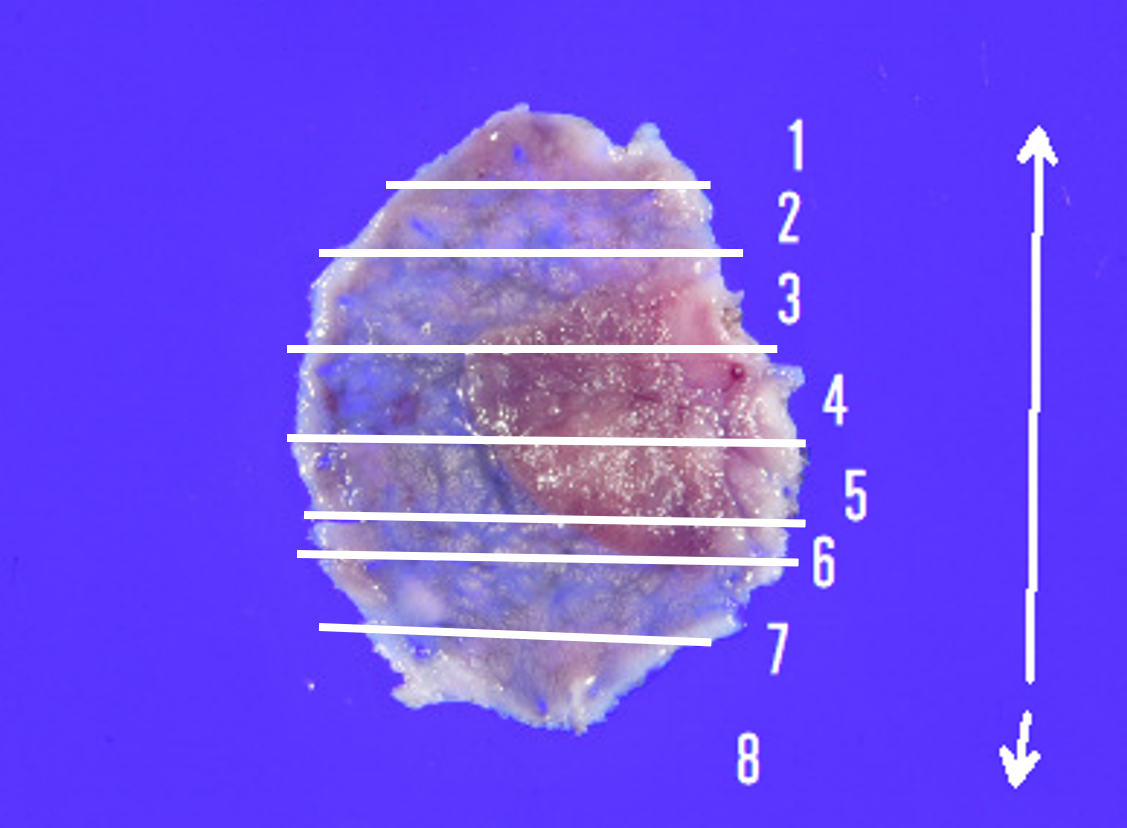
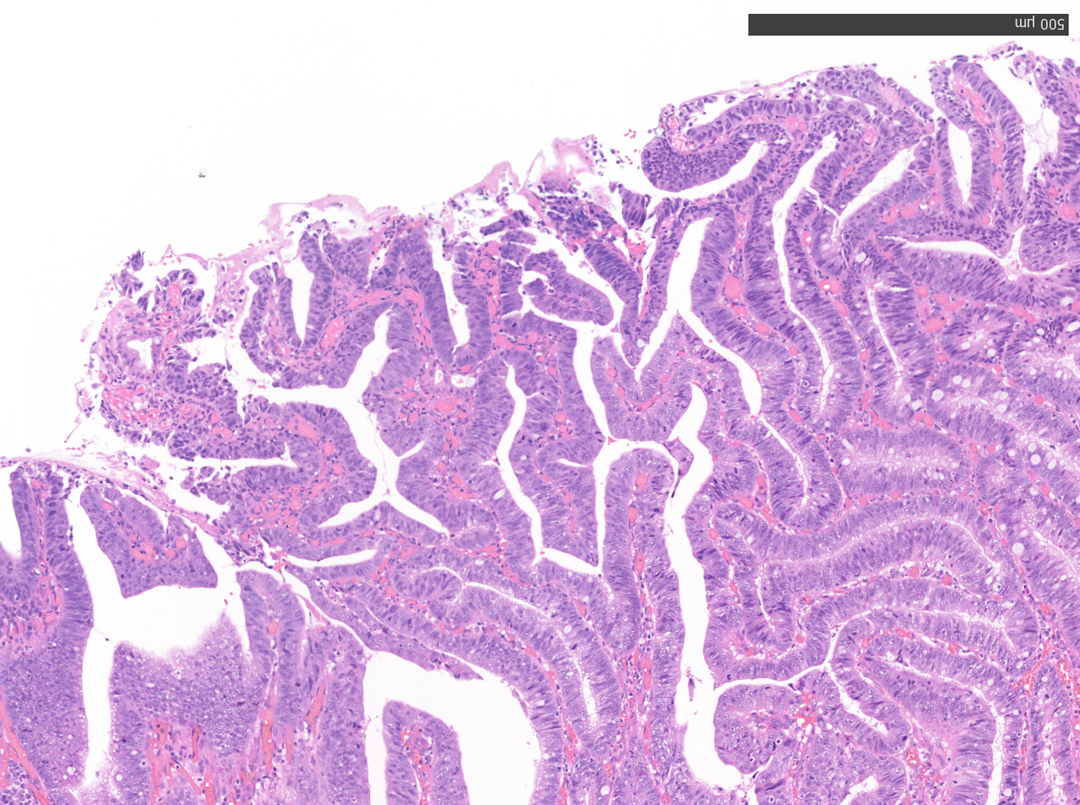
This case presented a 12 mm-sized intra-adenoma carcinoma in the sigmoid colon. It was located near a previous polypectomy scar and was considered to be a residual recurrent lesion. Although en bloc resection would have been preferable, there was a risk that the lesion could not be resected en bloc by conventional EMR due to the presence of a scar, and ESD was chosen despite the small size of the lesion. Inadequate observation could have led to an easy choice of EMR, and we believe that the near focus observation with the CF-EZ1500 colonoscope allowed us to select an appropriate treatment option.
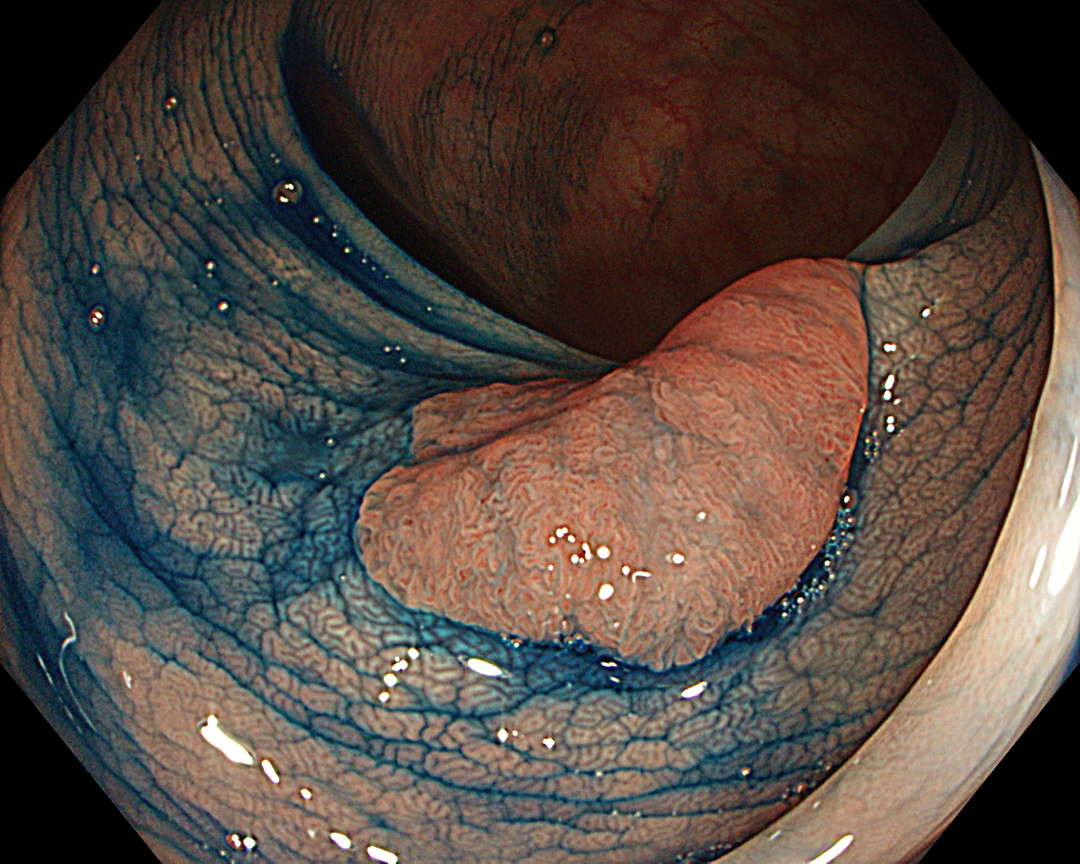
White-light observation showed a reddish, flat elevated lesion with a notch near the center, which appeared to be slightly thicker. At this point, the lesion should not be considered a simple low-grade adenoma, but a more dysplastic lesion that requires close examination, including near mode observation.
NBI™ technology provides more information than white-light observation because micro-vessels and surface structures can be enhanced at the switch’s flick1. Normal focus NBI™ technology shows a uniform brown lesion, which can be classified as Type 2 in the NICE classification. However, the microvascular and surface structures are opaque and complex, especially near the center of the lesion, suggesting that further detailed observation should be performed. As optical zoom magnifying endoscopes are not commonly used in Europe and the USA, no further information used to be obtained.
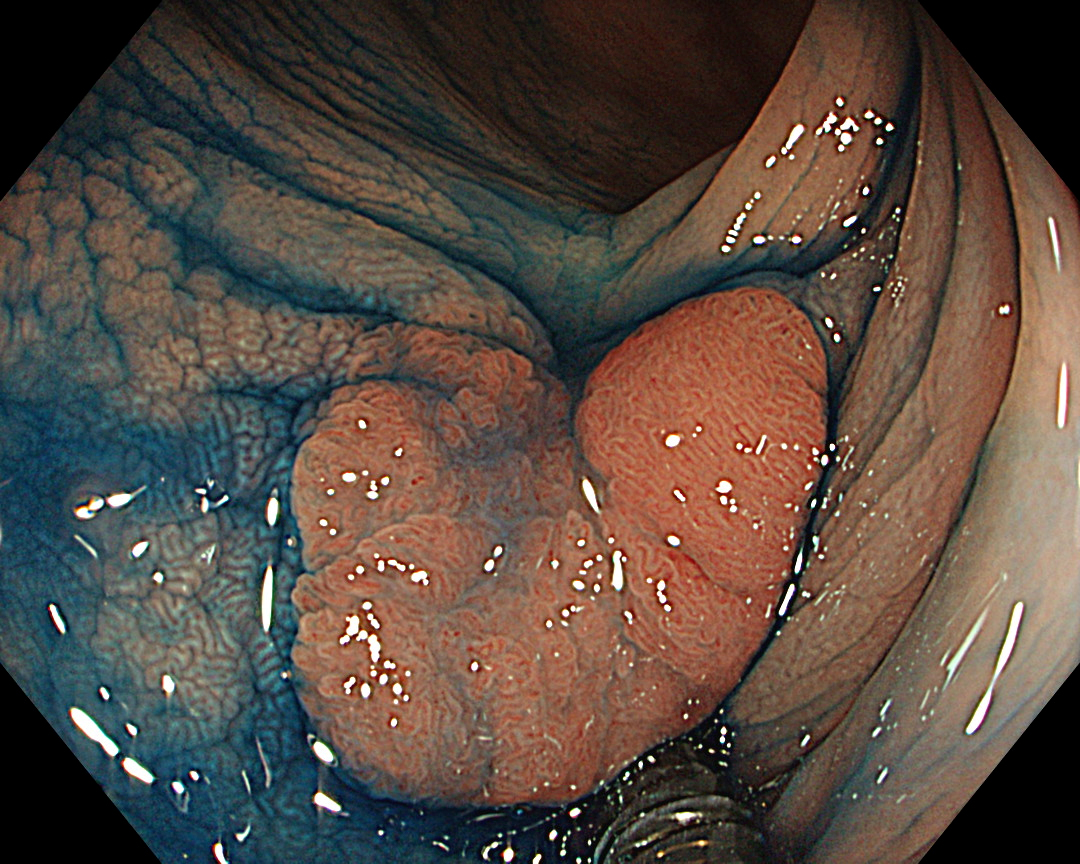
The CF-EZ1500DI’s short focal length enables clear images to be obtained even when the lesion is as close as 3 mm2, and microvascular and surface structures can be assessed without magnification. As the EZ1500DI does not require the difficult lever operations like conventional optical zoom magnification, a certain degree of magnification can be obtained simply by approaching the lesion, and it is possible to determine whether observation in Near Focus mode is required by pressing a button3.
The Near Focus mode enables detailed observation with magnification and the EDOF function widens the focal distance and facilitates focusing, making it easy to obtain sharp images even when the area of interest is slightly concave, as in this case.4
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
Dr. Shiaw-Hooi Ho Case 28: Pedunculated polyp
Mr. Peter Borch-Johnsen
- Keyword
- Content Type