Colorectal Case 31

Prof. Dr. Hu Xiao
Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, China
Disclaimer:
RDI™ technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis. RDI™ technology is cleared in the United States. This case study is being furnished to provide examples of RDI™ technology use. The CF-HQ290I used in this case is not cleared or available for use in the US market at this time nor is there an established time for its release. The safety and effectiveness of this product and/or the use of this product has not yet been established in the US market.
The positions and statements made herein by Prof. Hu Xiao are based on Prof. Hu Xiao ‘s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU)
Scope: CF-HQ290I
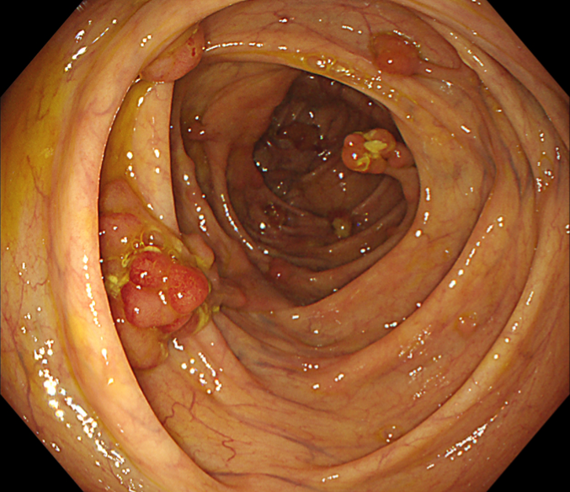
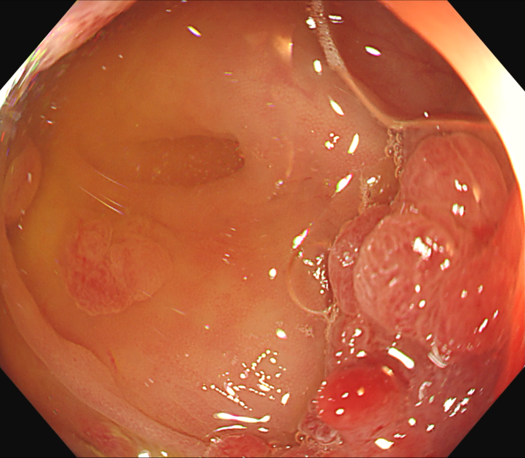
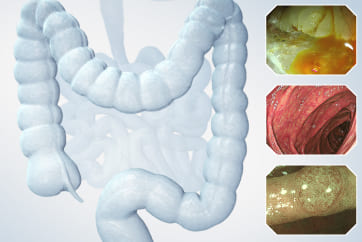
Case: Multiple lesions in ascending colon
Organ: Ascending colon
Patient Information: M, 40s
Medical History: Polyps were found in rectum 7 years ago, polypectomies were done multiple times
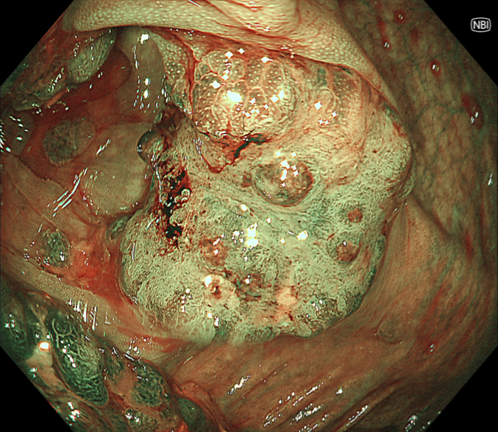
9. NBI™ technology
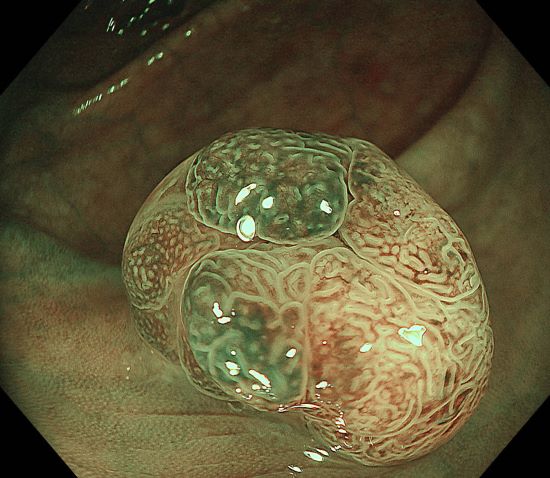
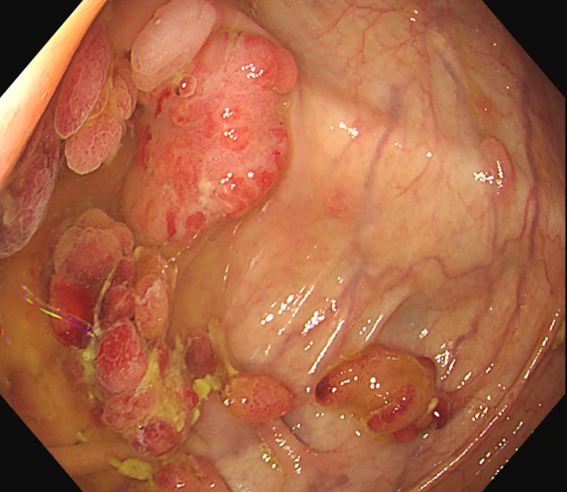
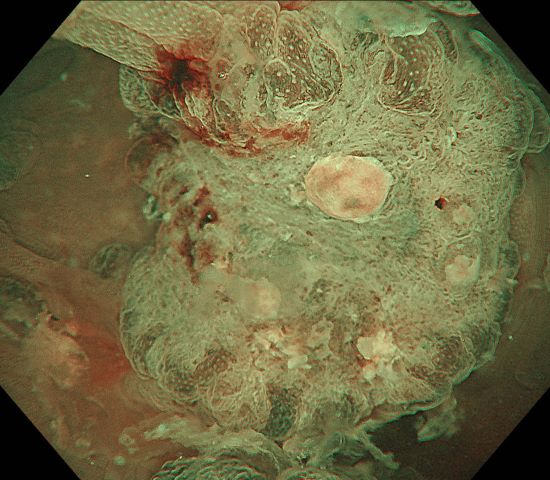
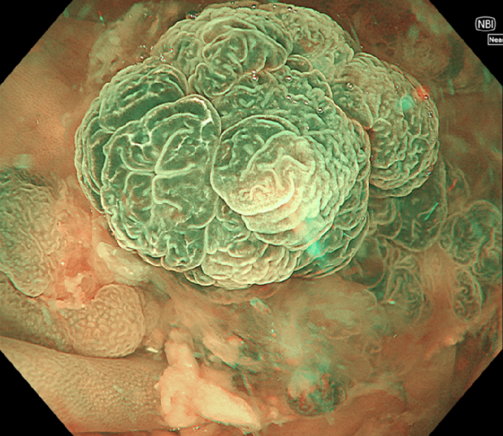
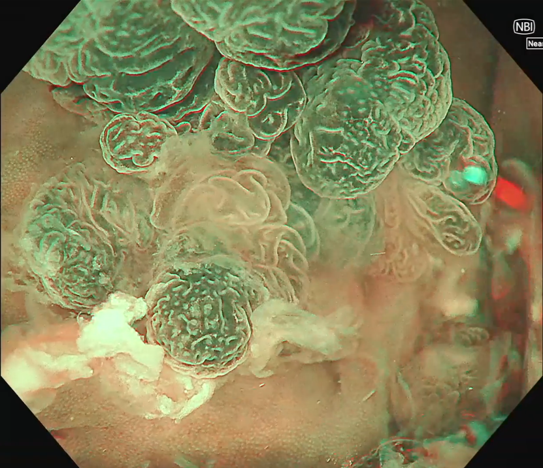
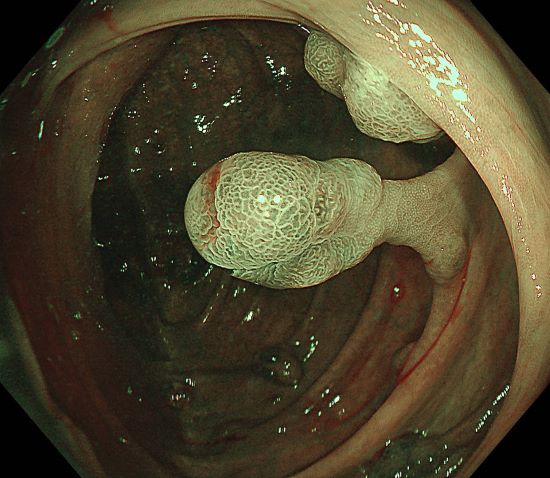
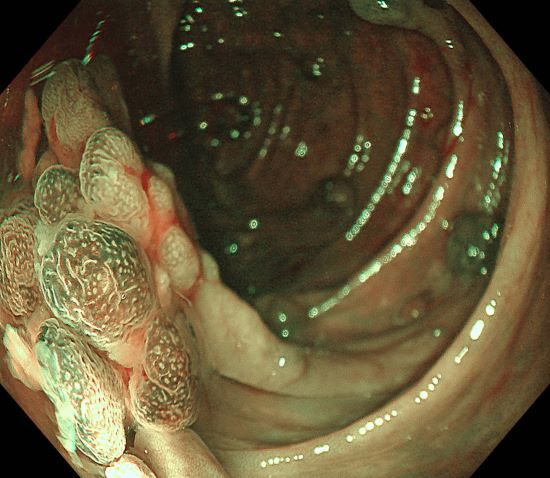
0-Is lesion in ascending colon, lobulated, anal side of the lesion showed type IV , Kudo Pitt Pattern, the central part of the lesion was blue colored, the IP was significantly widened, the , Kudo Pitt Pattern was short rod-shaped, strip-shaped, the opening of the glandular ducts on the oral side of the lesion was more dense, Kudo Pitt Pattern showed type III~IV
Case video
Overall Comment
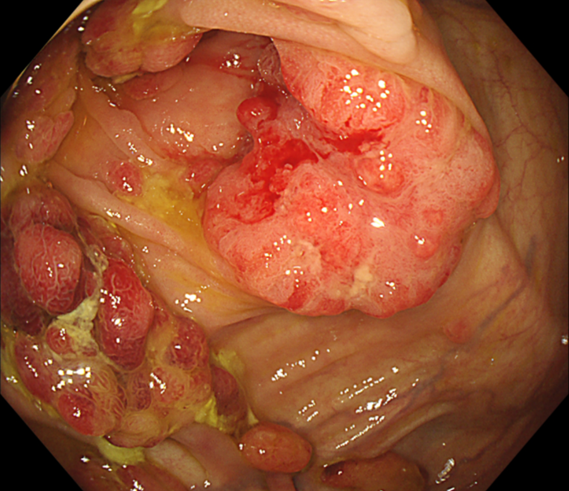
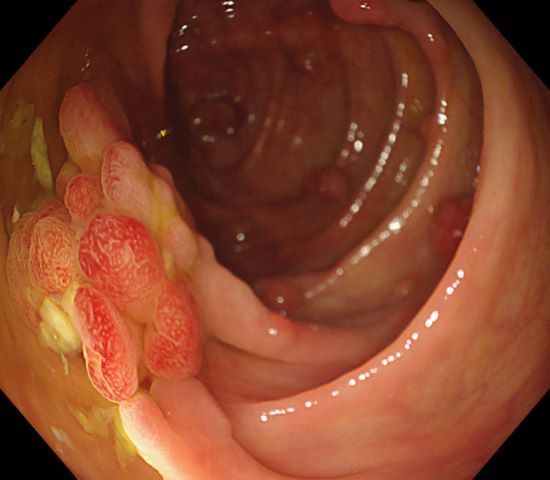
49 years old male patient with multiple polyps found in the rectum 7 years ago. His mother has a history of rectal cancer (alive), his uncle had a history of ascending colon cancer (passed away), and no abnormality was found during gastroscopy. Polypectomy had been performed three times in 2017, 2018, and 2023, polyps were found in ascending colon, ileocecal region, and the sigmoid colon 18cm away from anus and its downstream rectum. There were more than a dozen of 5-15mm 0-Is and 0-Ip-type polyps seen, in the form of clusters and lobes. After resection, the pathology showed “rectal” serrated adenoma with mild heterogeneous hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium and “rectal polyp” tubular adenoma with low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia of the glandular epithelium and high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia of the glandular epithelium in a focal area (Moderate Dysplasia). The polyps were all located in the ascending colon, the lesions in ileocecal region were suspected to be carcinomatous with deep infiltration, no polyps were found on the anal side of the ascending colon, and the rectum showed scarring from previous polypectomy.
Multiple lesions seen in the ascending colon were multicolored and polyphyletic, with the general morphology of type 0-IIa, type 0-Is, type 0-Ip, partly lobulated or clustered, and mucus cap was seen on the surface of some lesions, and type 0-I lesions were predominantly Kudo Pitt Pattern type III-IV,some glandular ducts showed serrated margins, partly granular and chorionic, and partly Kudo Pitt Pattern type II. The center of the suspected invasive carcinoma in the ileocecal region was predominantly JNET type 3, with a predominantly Kudo Pitt Pattern type I opening at the margin, but with a partly villous structure on the oral side near cecum, JNET type 2A. The final pathology report suggested adenomatous changes in the vast majority of the lesions, and the infiltrating carcinoma in the ileocecal region was moderately differentiated, with muscularis propria involvement and vascular invasion, but there were variations between different pathologists as to the cancerous pathway of the lesions.
Final genetic testing suggested a mutation in the BMPR1A gene, which manifested as hereditary polyposis syndrome type 2 (HMPS2), characterized by mixed hyperplastic, adenomatous, and occasional youthful-type colon polyps, with polyposis eventually progressing to colorectal cancer.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
Mr. Peter Borch-Johnsen Case 33: LST-GM, invasive cancer
Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan
- Content Type