Colorectal Case 33

Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan
Koc University Hospital
Istanbul, Turkey
Disclaimer:
NBI™ and TXI™ technologies are not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
The positions and statements made herein by Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan are based on Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan’s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU).
NBI™ and TXI™ technologies are 510(k) cleared in the United States. This case study is being furnished to provide examples of NBI™ and TXI™ technology use. The CF-XZ1200 used in this case is not available in the US market at this time, nor is there an established time for its release. The safety and effectiveness of this product and/or the use of these products has not yet been established in the United States market
Scope: CF-XZ1200
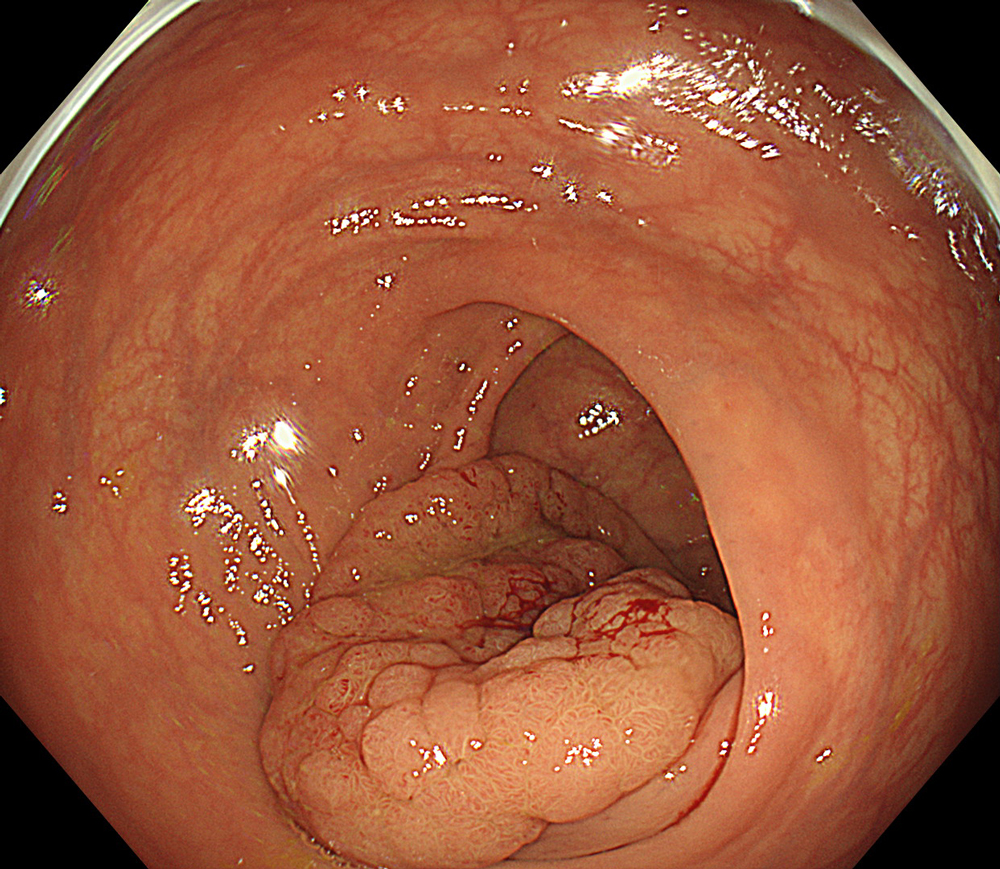
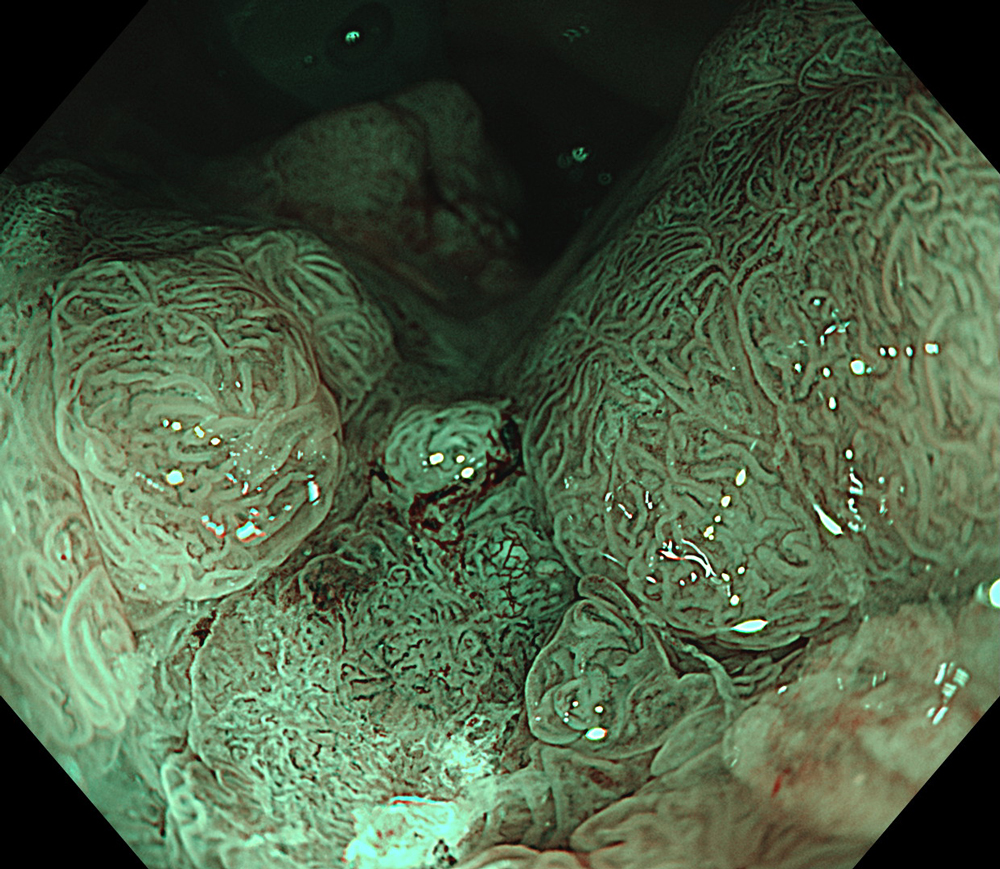
Case: LST-GM, invasive cancer
Organ: Rectum
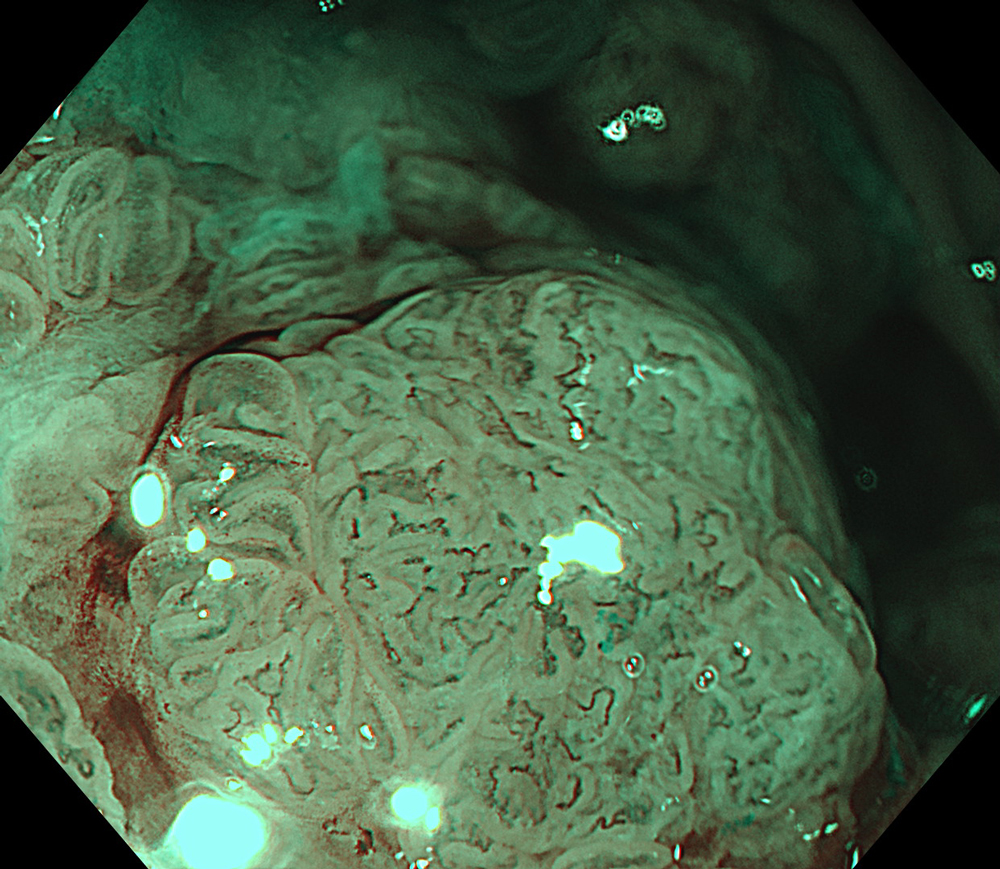
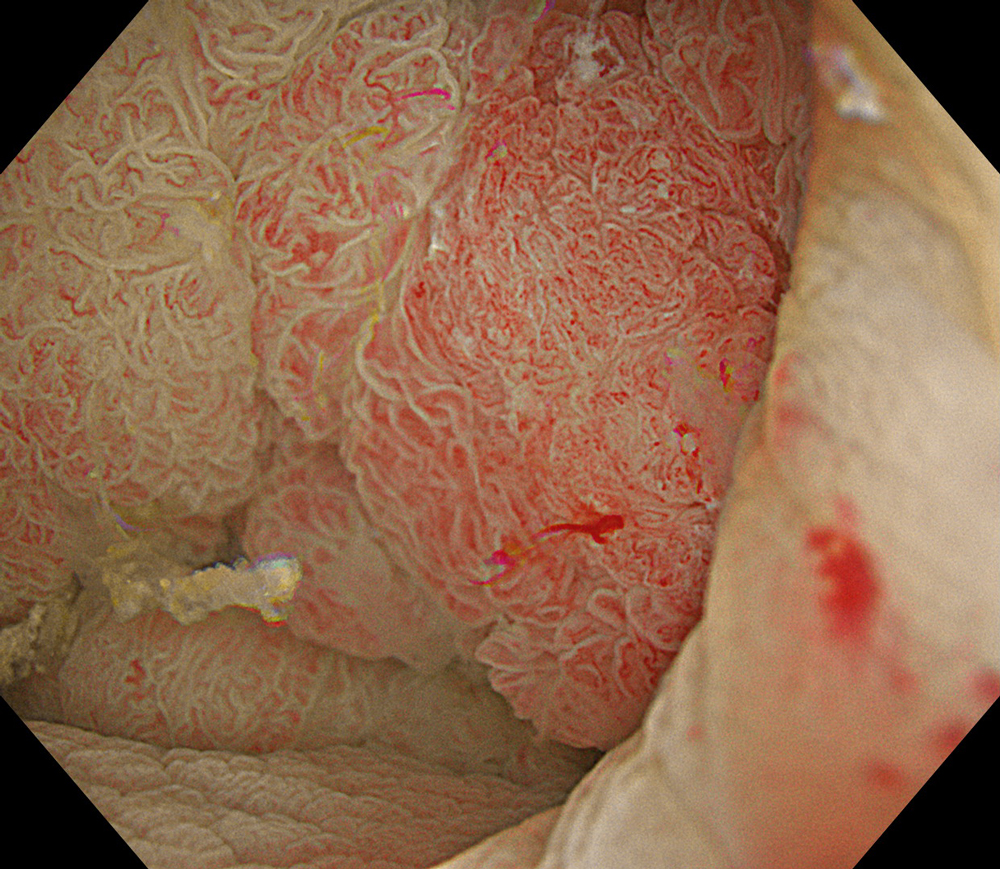
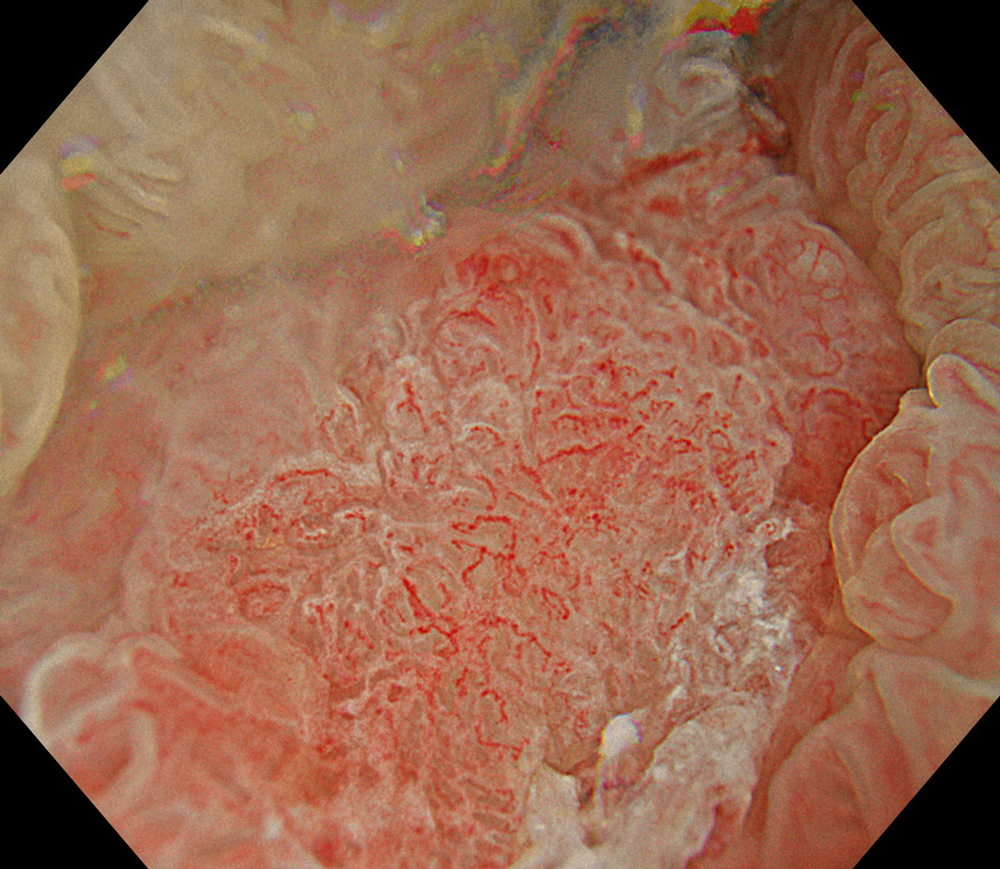
7. NBI™ Technology
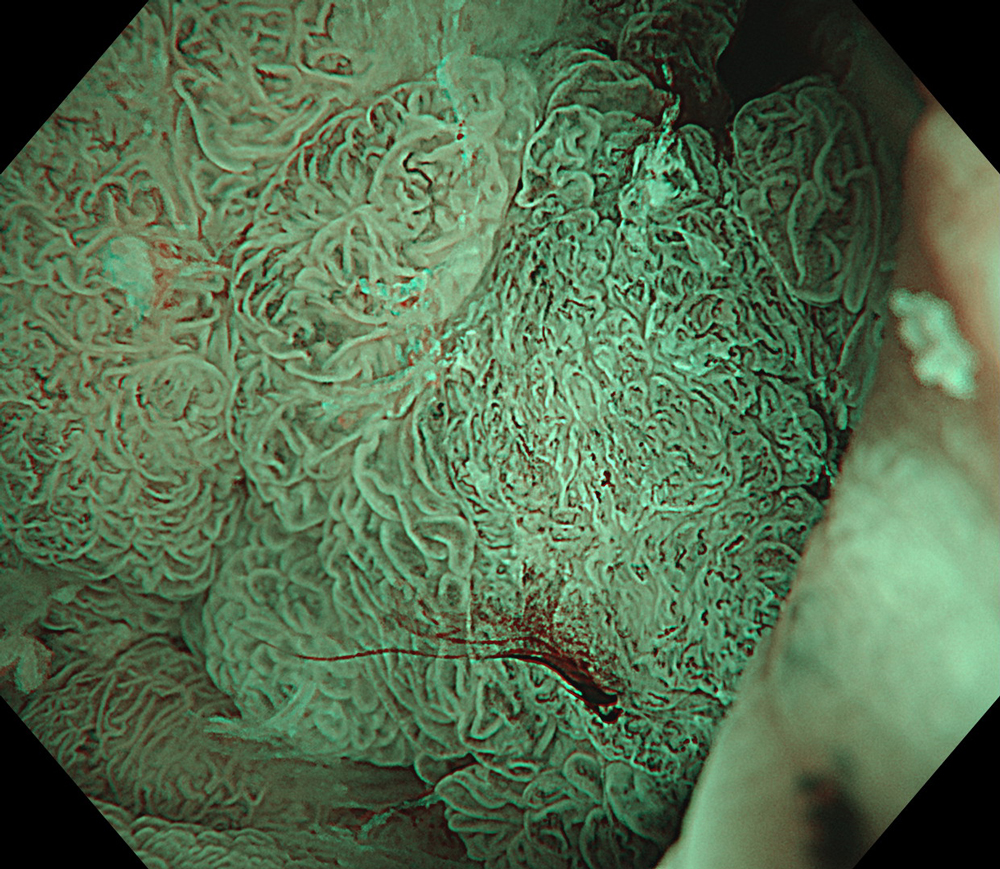
#NBI #A8 structure enhancement #optic magnification
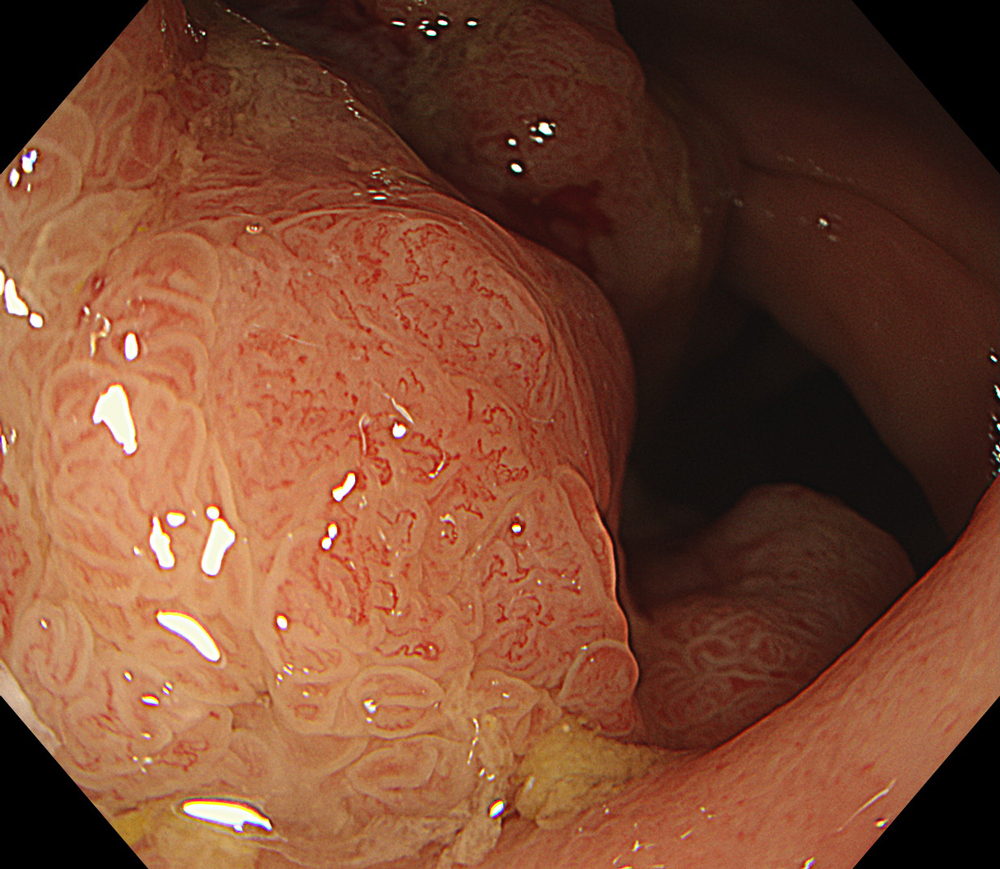
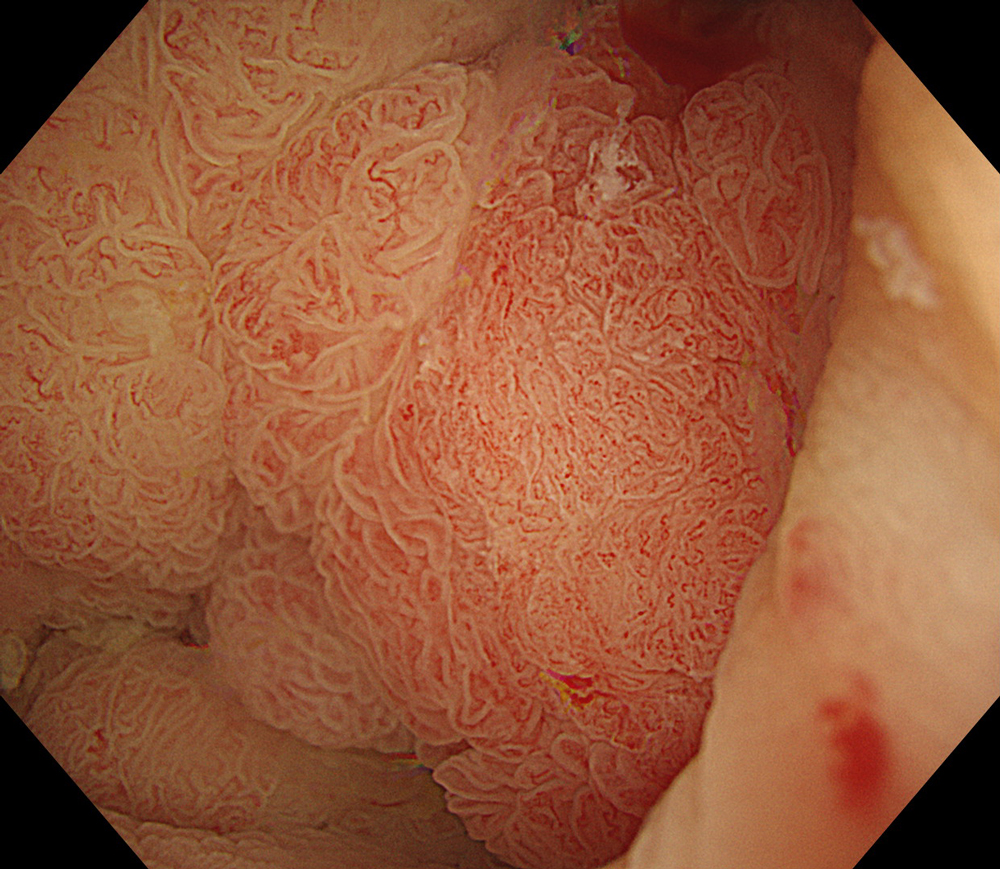
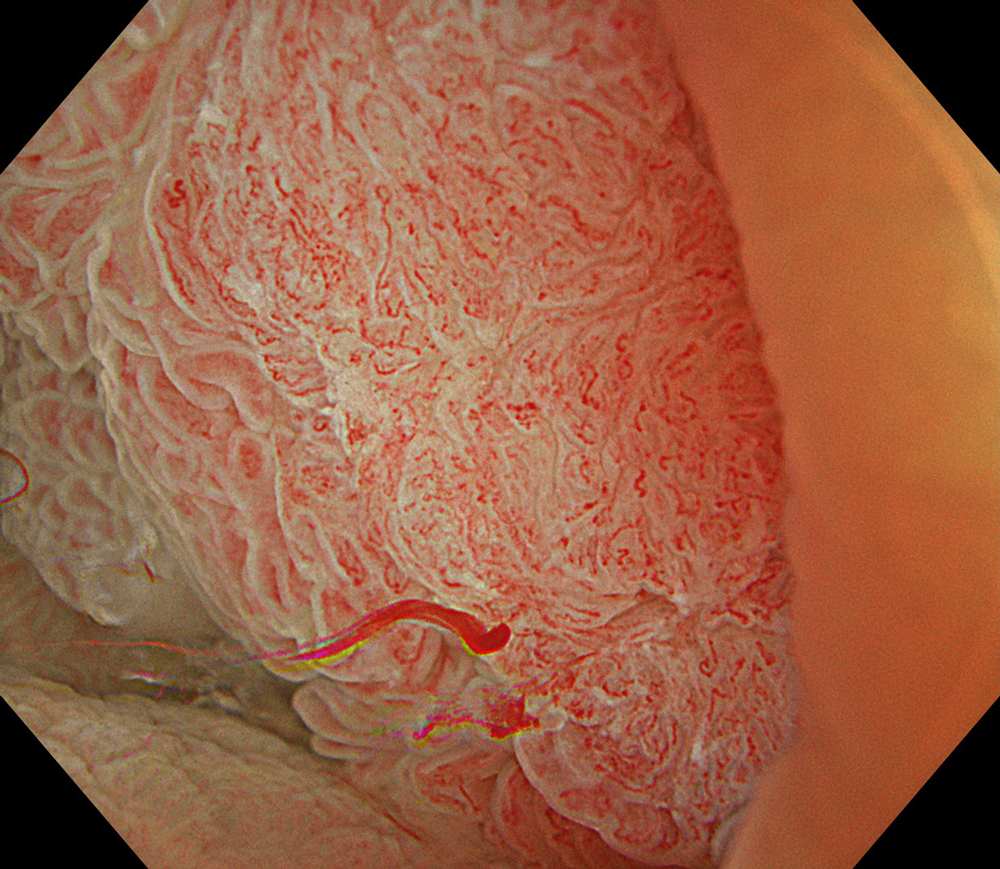
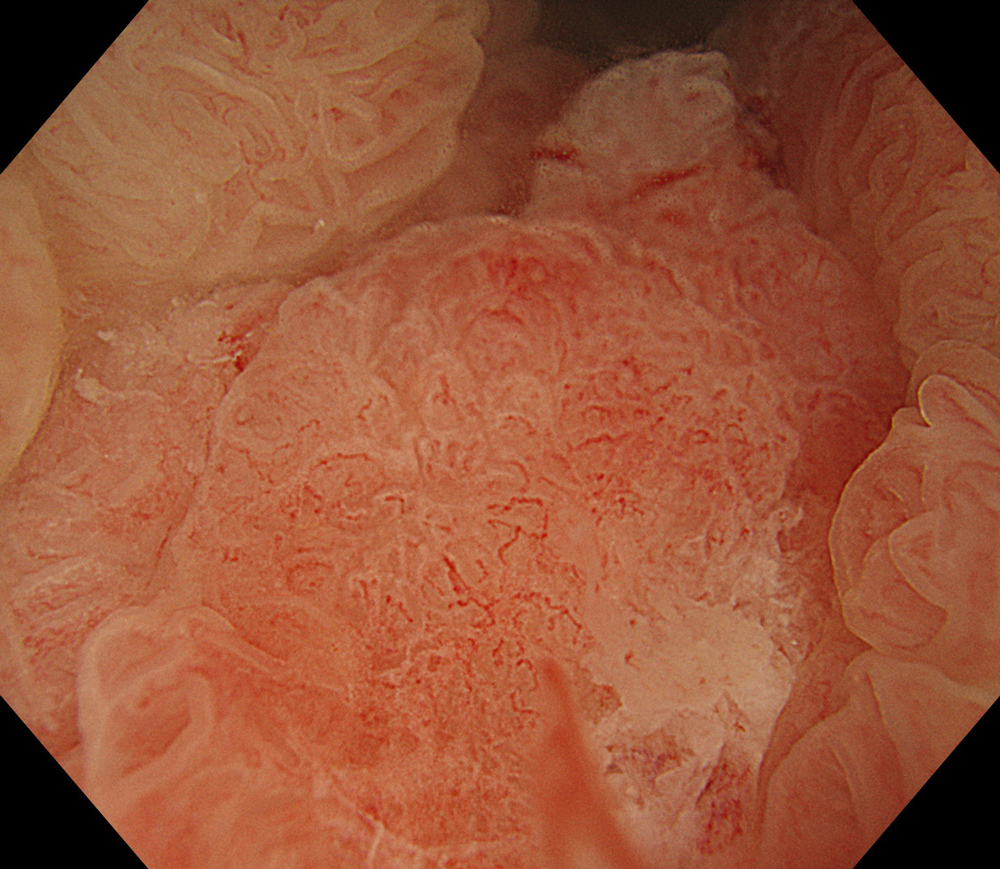
8. TXI™ Technology
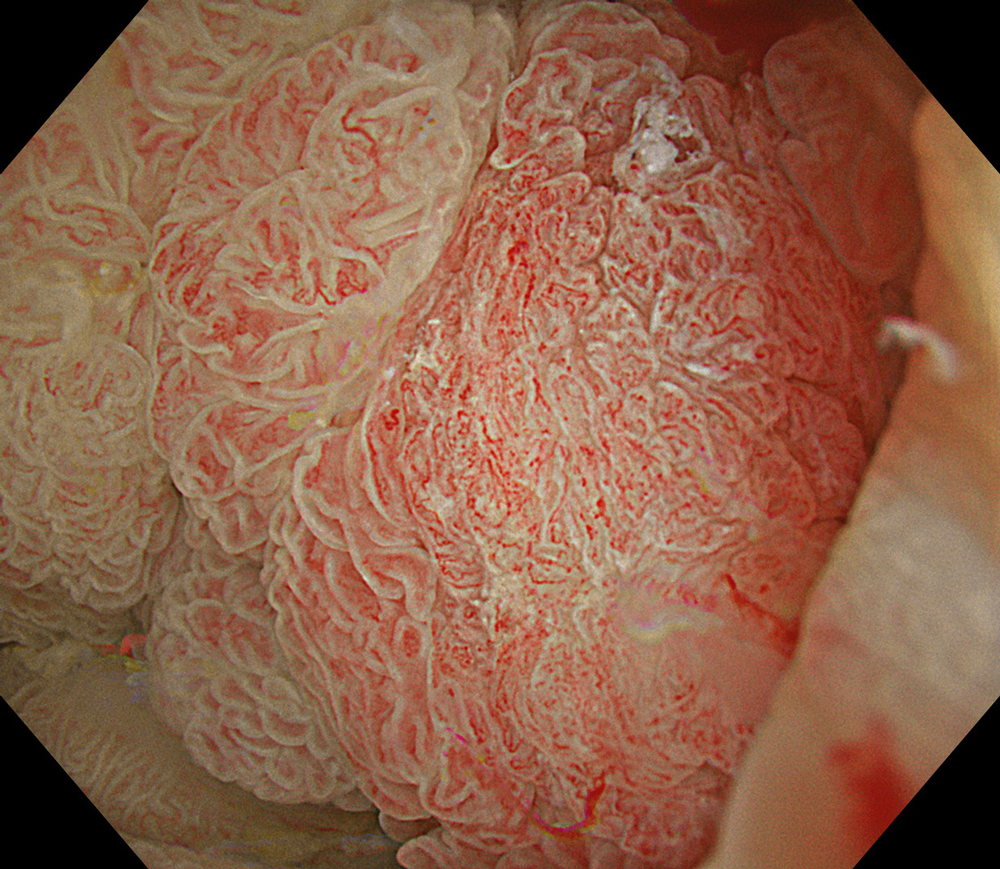
#TXI #A8 structure enhancement #optic magnification
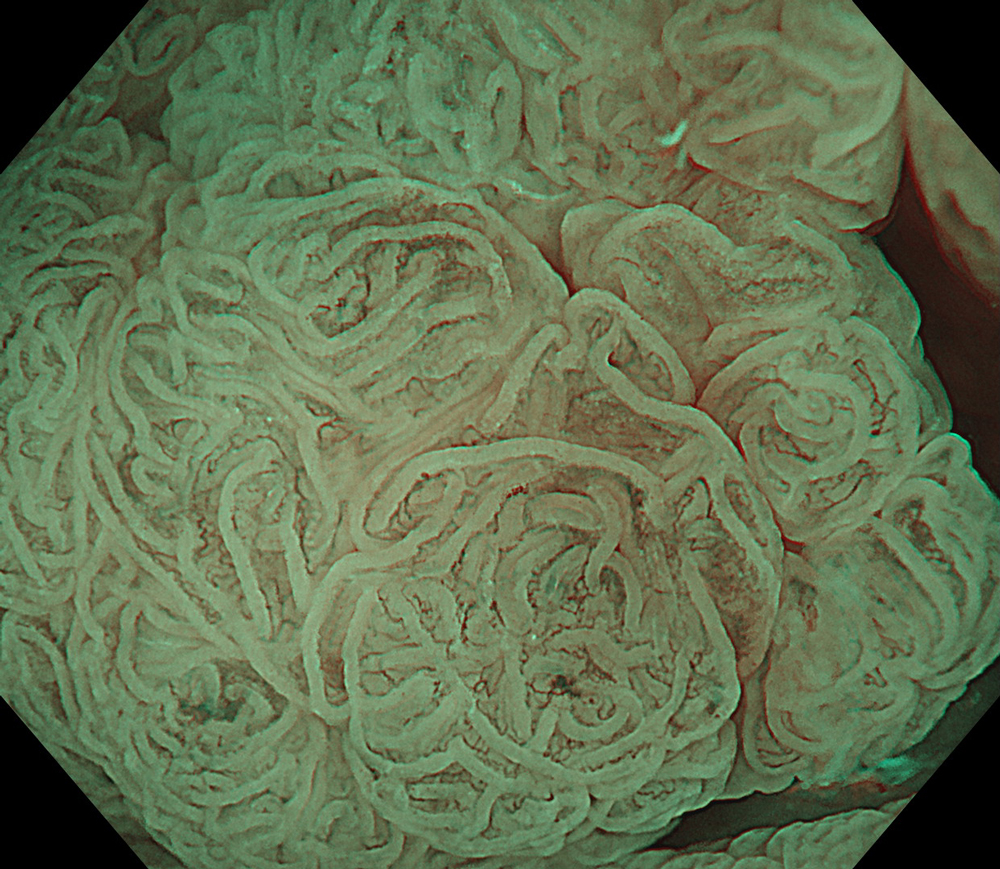
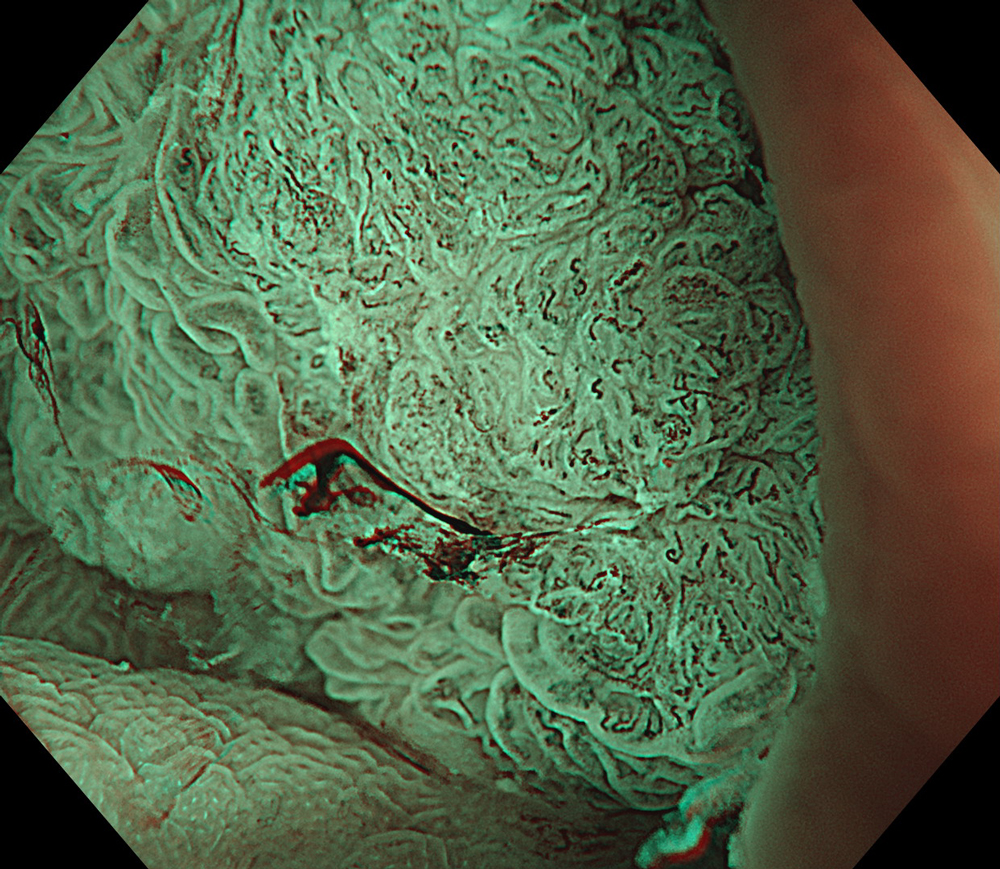
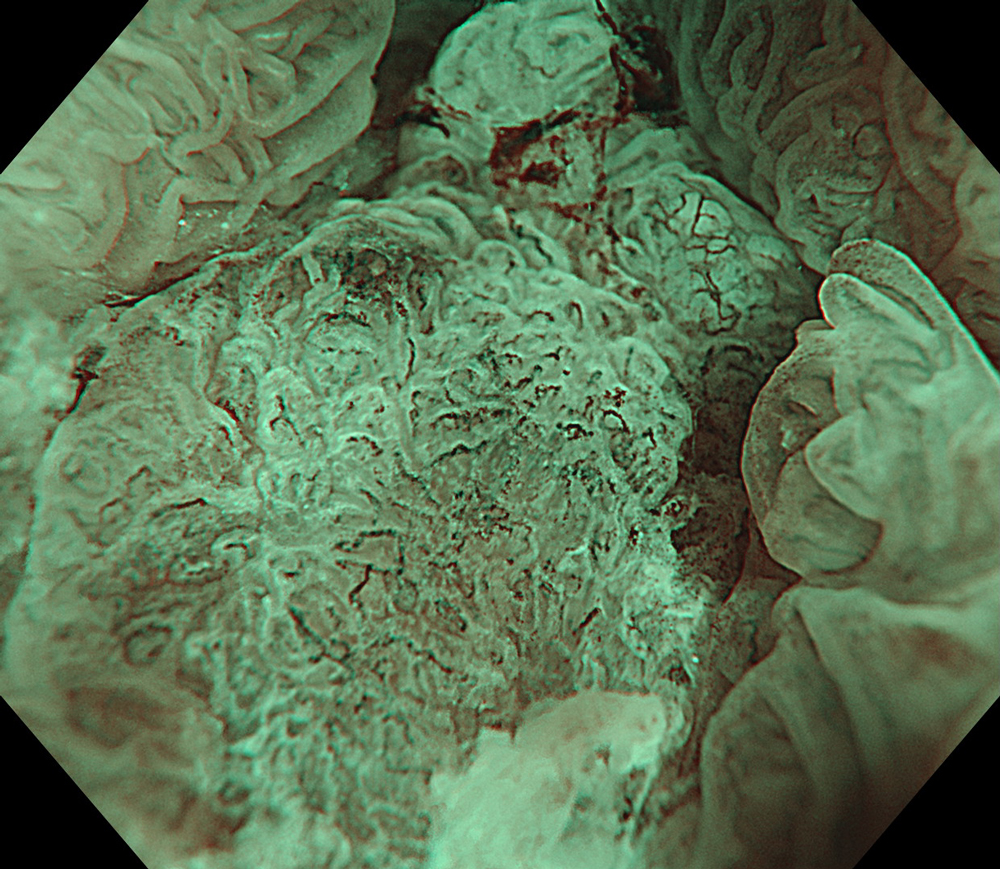
9. NBI™ Technology
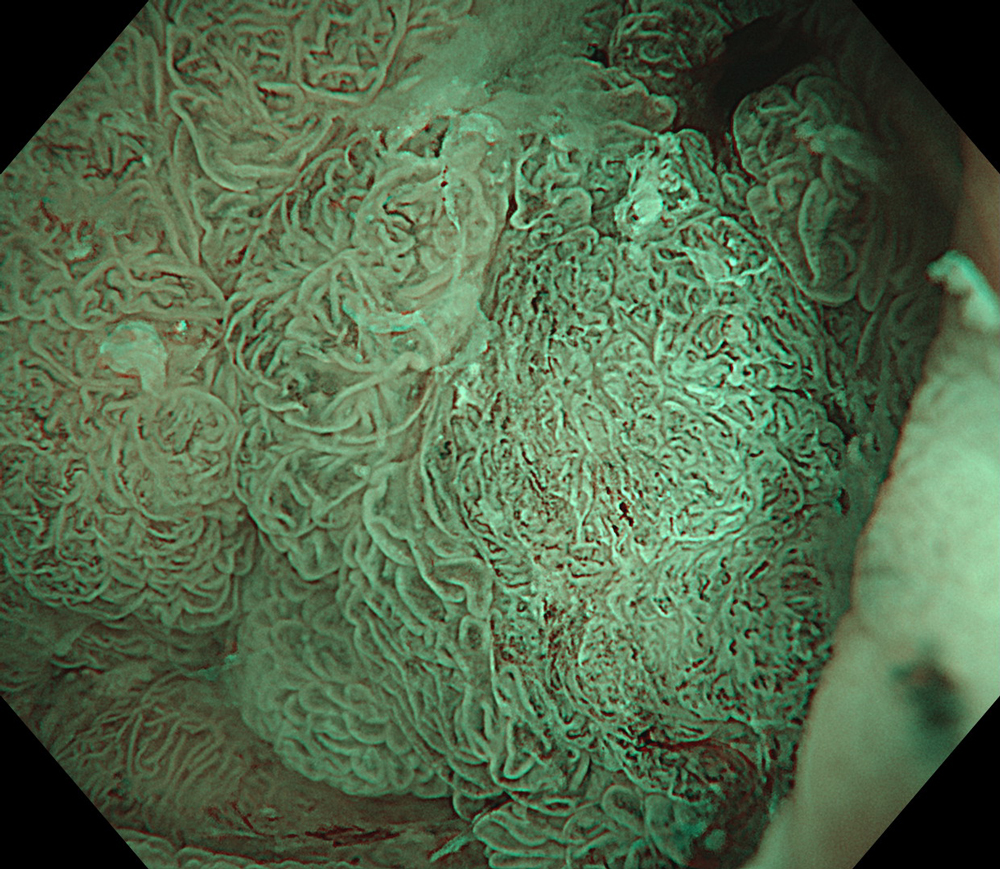
#NBI #A8 structure enhancement #optic magnification
Case Video
High-definition imaging with the Olympus CF-XZ1200 endoscope and its optical zoom feature allowed for meticulous inspection of the lesion. The integration of TXI™ and NBI™ technology modes, in conjunction with underwater magnified observation, proved particularly valuable in delineating suspicious zones and assessing potential submucosal invasion, as clearly seen in the video documentation.
Overall Comment
A 66-year-old female patient presented with rectal bleeding. Colonoscopic examination revealed a granular mixed-type laterally spreading tumor-mixed type measuring approximately 8 cm in diameter. Random biopsies were reported as tubular adenoma with low-grade dysplasia. The patient was referred to our center for endoscopic resection.
The lesion was evaluated using an Olympus CF-XZ1200 endoscope equipped with optical magnification. With the use of TXI™ and NBI™ technology modes, the entire lesion surface was examined in detail. As demonstrated in the accompanying images and video, these imaging modes—combined with underwater observation and optical magnification—enabled me to complete a thorough assessment of suspicious areas, particularly with respect to potential submucosal invasion.
In this case, targeted biopsies taken from areas suspicious for malignancy were reported as invasive carcinoma. Radiological evaluation revealed malignant lymph nodes in the mesorectum, and the lesion was observed to have invaded the muscularis propria in certain regions.
Next-generation magnifying endoscopes, together with advanced imaging technologies such as TXI™ and NBI™ technology, enhance my ability to perform targeted biopsies and improve diagnostic accuracy. Moreover, accurate diagnosis and staging through these modalities facilitated my selection of the most appropriate therapeutic approach.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer.
- Content Type