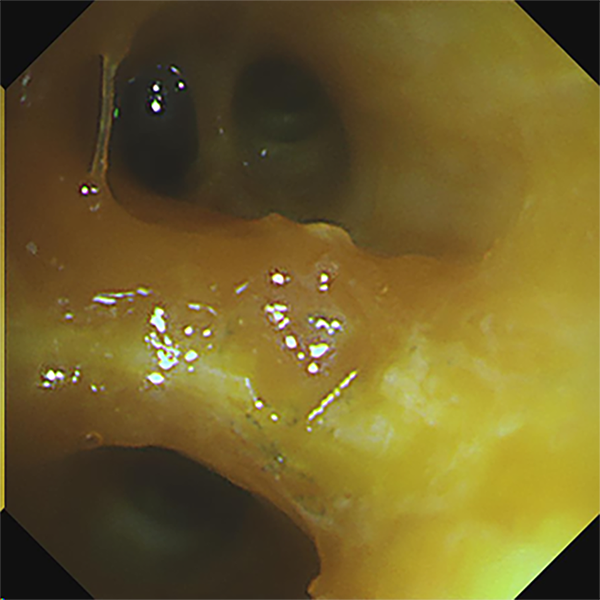
Case : Snare resection of tumor in the proper segment of the left upper lobe

Li Shiyue Professor Guidance Expert
The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University

Tang Chunli Professor Operation Expert
The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University
Disclaimer:
- TXI™ and RDI™ Technologies are not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis
- The positions and statements made herein by Dr. Shiyue and Dr. Chunli, are based on Dr. Shiyue’s and Dr. Chunli’s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
- The BF-Q290 used in this case is not available in the US market at this time nor is there an established time for its release. The safety and effectiveness of this product and or the use of these products has not yet been established in the United States market.
- The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use (IFU)
- Dr. Shiyue and Dr. Chunli, the authoring physicians of this presentation, are paid consultant to Olympus Corporation
Scope: BF-Q290
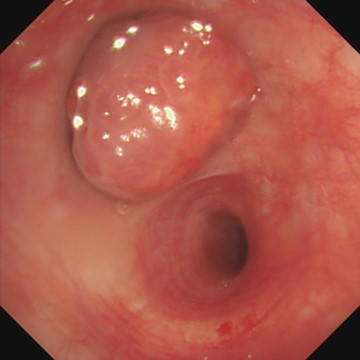
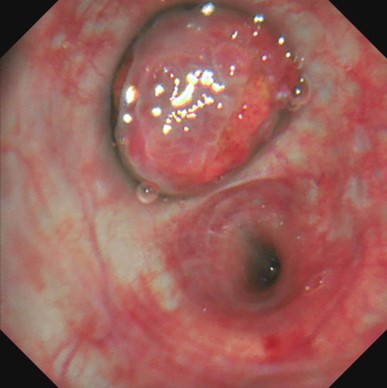
Location: Left upper lobe
Patient information: Male, 18 years old
Medical history: Intermittent coughing for two years, hemoptysis for one week, no fever, chest pain, or dyspnea. Chest CT indicates a neoplasm in the left upper lobe.
Case Video
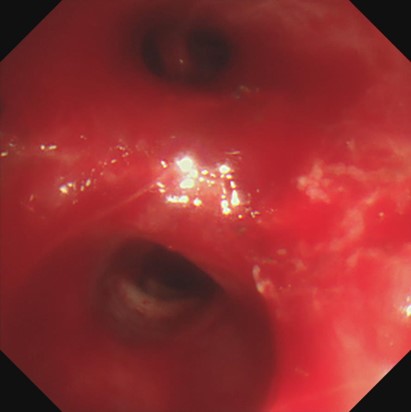
The bleeding site can be clearly displayed in RDI mode
Hemostasis of active bleeding
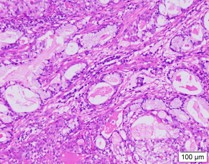
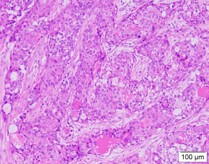
Pathological diagnosis
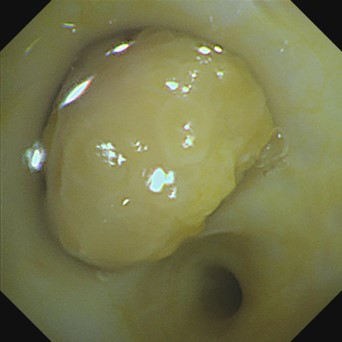
- Two pieces of gray-white tissues (1.2cm×0.8cm×0.5cm and 1.5cm×1.0cm×0.5cm in size) in the proper segment of the upper lobe of left lung was seen with the naked eye (full covered)
- Endoscopic findings: The tumor cells in the tissues (of the proper segment of the upper lobe of left lung) examined were composed of nonkeratinized squamous cells with the shape of sheet and polygon, intermediate cells, and mucus-secreting columnar cells. Most of the intermediate cells had round or oval nuclei with nucleoli, and a small number were columnar cells that secrete mucus, forming small glands, tubules or cysts. Nuclear division was not obvious and no necrosis was observed.
- Molecular pathology results: MAML2(+)
- Immunohistochemistry results: TTF1(-), NapsinA(-), P40(partially+), SMARCA4(+), ALK-P(D5F3)(-), ALK-P(Neg)(-), Ki67(hot-spot 15%+),PD-L1(E1L3N)(-),PD-L1(Neg)(-),CK5/6(+),CK7(+)
- Special staining results: Mucicarmine (+)
- Pathological diagnosis: Tissue (of the proper segment of the upper lobe of left lung) changes in line with bronchial low-grade mucinous epidermoid carcinoma
Overall Comment
Compared with the WLI mode of the bronchoscope, the TXI™ technology mode can display deeper vascular structures, which help determine the treatment of lesions. If bleeding occurs during treatment or biopsy, the RDI™ technology mode can help avoid the impact of blood on the bronchoscope camera. Especially for beginners, it can reduce the effect of blood contamination on the camera’s field of view and help them easily see the bleeding site and accurately implement local hemostasis at the same time.
- Content Type