Kei Morikawa1, Hirotaka Kida1, Hiroshi Handa1, Masamichi Mineshita1
ThoracCancer. 2025;16(7):e70065. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.70065
1.Department of Respiratory Diseases, St. Marianna University School of Medicine, Kawasaki, Japan.
Kei Morikawa received research funding from Olympus Corporation. The remaining authors report no conflicts of interest.
Study Design: Case-Based Technical Note
Objective
This case-based technical note aimed to compare the changes in lesion appearance across different imaging modes using case-basedimages, with white light observation serving as the standard.
Patient Characteristics
- The study is a technical note based on a series of five representative cases and does not involve a cohort of patients with defined characteristics.
Device
- CV-1500 (EVIS X1TM endoscopy system) with image enhancement endoscopy (IEE) including Brightness Adjustment Imaging with Maintenance Contrast (BAI-MACTM) technology, Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging (TXITM) technology, and Red Dichromatic Imaging (RDITM) technology
- BF-H1200 (diagnostic –Outer diameter 4.9 mm; 2.2 mm working channel)
- BF-1TH1200 (therapeutic –Outer diameter 5.8 mm; 3.0 mm working channel)
Assessment
- The appearance of lesions and image quality with different imaging modes (RDI, TXI, BAI-MAC).
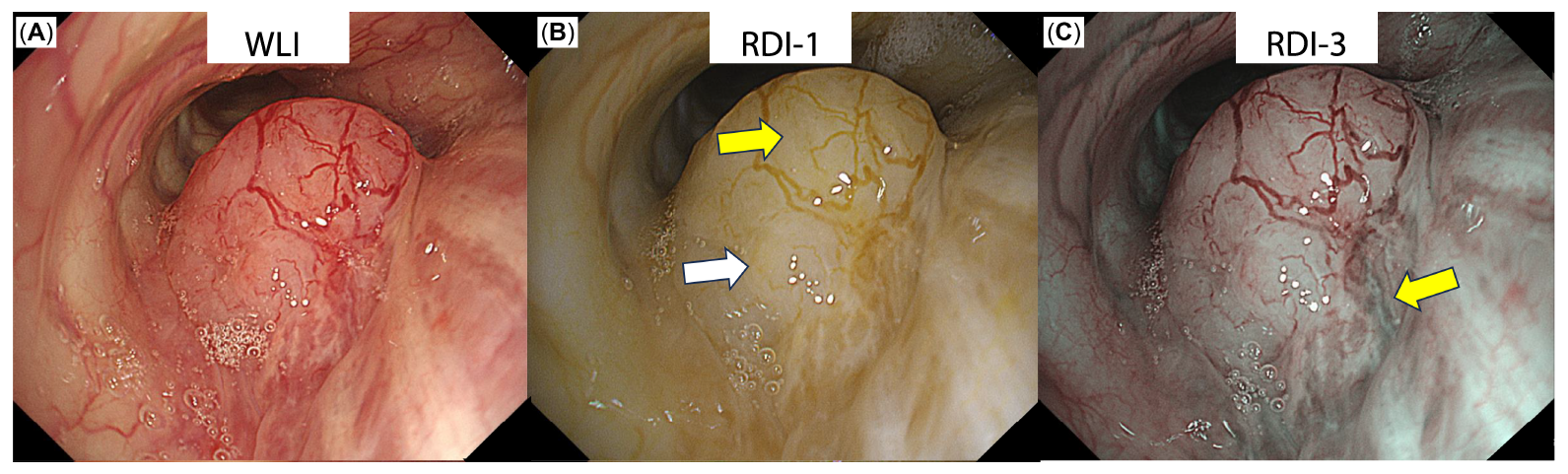
Main Outcome: Red Dichromatic Imaging for Optimal Site Selection
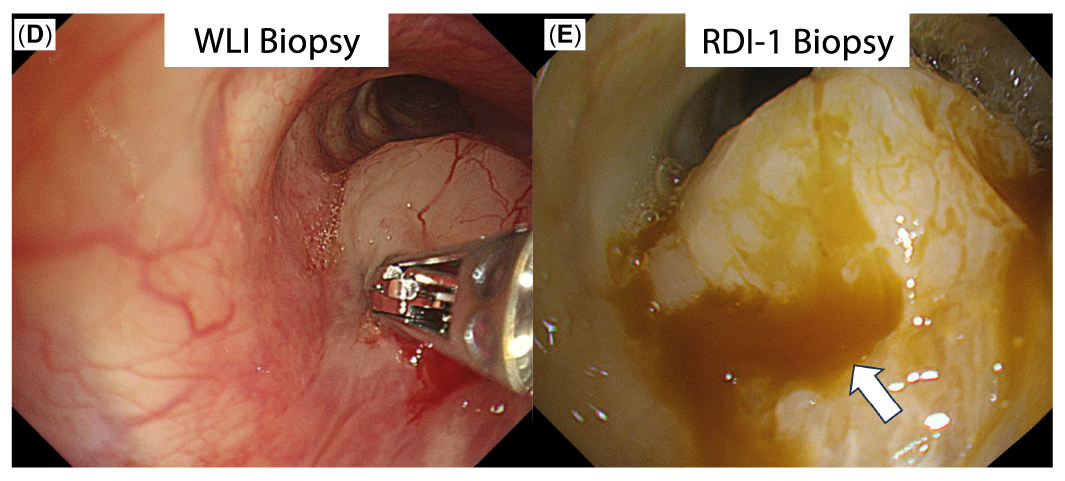
Red Dichromatic Imaging (RDITM ) technology aided the investigators in identifying local blood flow for optimal site selection, reducing bleeding risk.
- RDI-1 identified superficial blood vessels associated with the lesion (B; yellow arrow)
- RDI-3 detected a deep vessel (C)
- This information guided site selection to a low-perfusion area (B; white arrow), and RDI-1 was then used to detect bleeding points (E)
Disclaimer: RDI technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
Further Outcomes
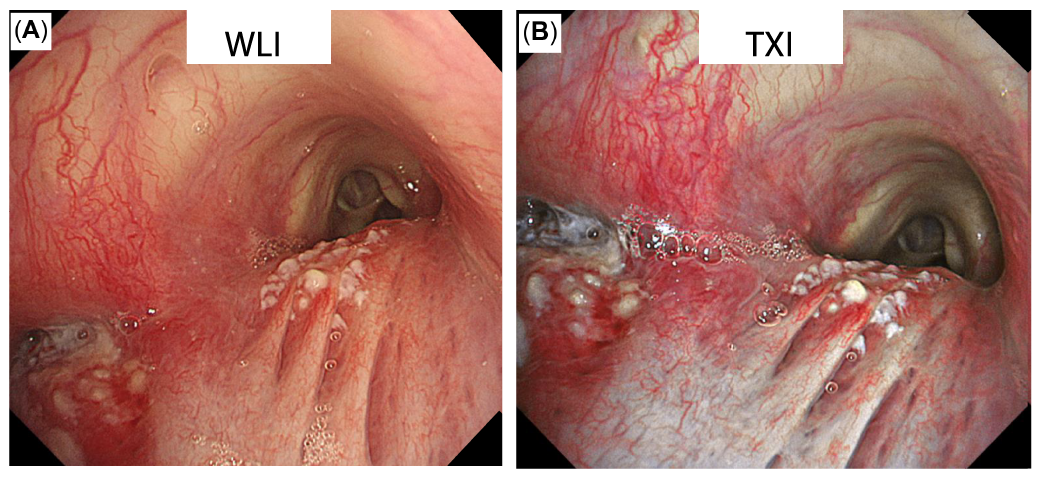
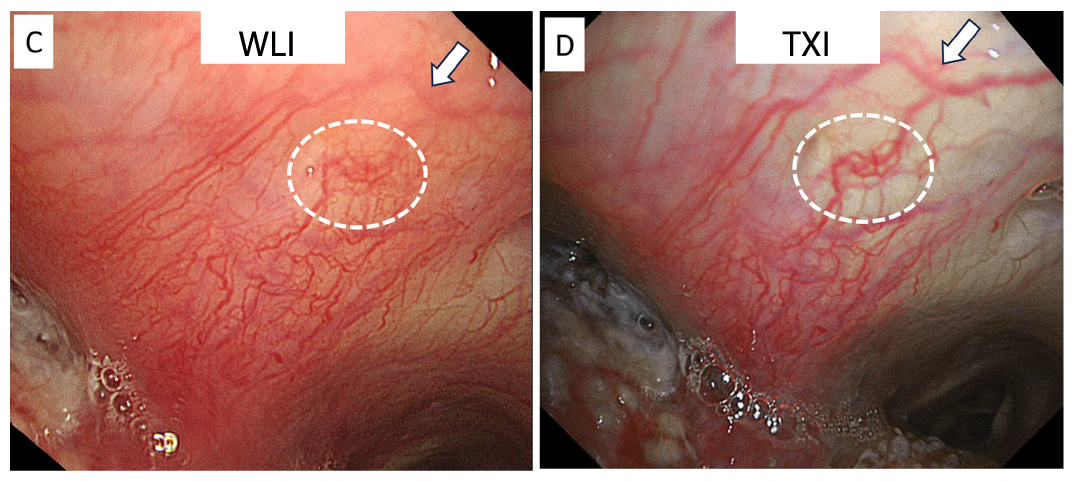
Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging (TXITM ) technology
Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging (TXI) provided stronger image contrast, enabling the distinction of epithelial redness, edema, and skip lesions with local necrosis.
- Improved the visibility of subepithelial blood vessels (A vs. B)
- Blood vessels were easily distinguishable and recognized more three-dimensionally (C vs. D)
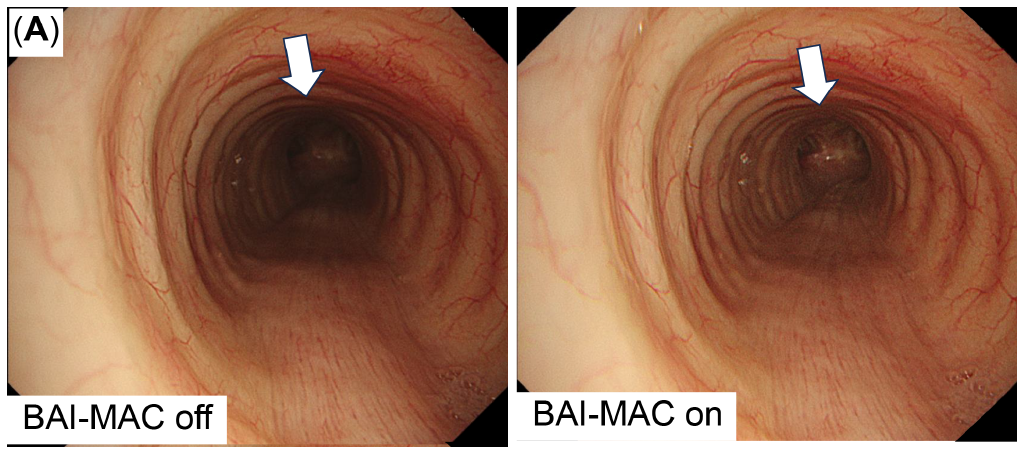
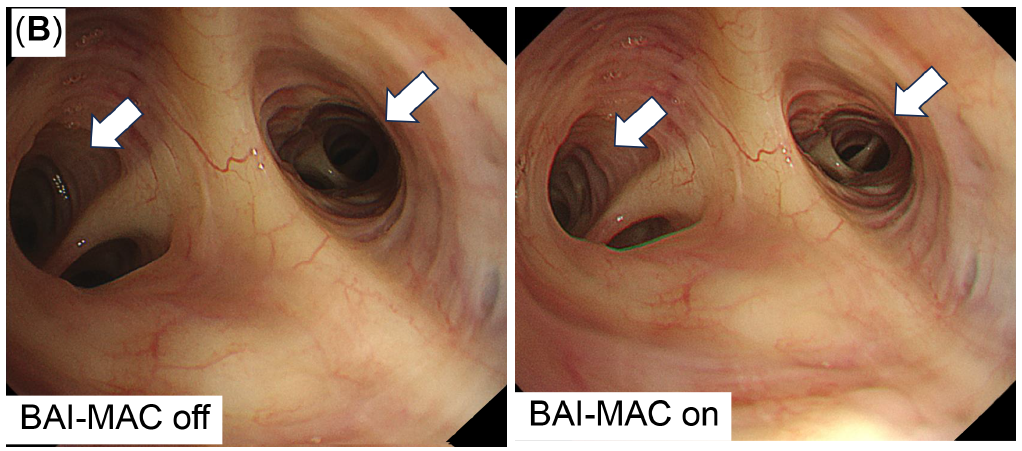
Brightness Adjustment Imaging With Maintenance of Contrast (BAI-MACTM ) technology
Brightness Adjustment Imaging With Maintenance of Contrast (BAI-MAC) enhanced distal brightness while preserving proximal brightness and thereby supports navigation throughout the lung.
- With the use of the BAI-MAC function, the tracheal carina is clearly visible from above the trachea (A).
- In peripheral bronchial branches, BAI-MAC aids in correctly accessing the next bronchus (B).
Disclaimer: BAI-MAC technology is not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
Safety Outcomes
Safety of the CV-1500 and scopes was not assessed within the case series.
Study Conclusions
High-definition bronchoscopes with advanced image processing allow for a more thorough and objective image evaluation that can enhance diagnostic accuracy, prevent complications, and reduce examination times.
The integration of high-definition bronchoscopy with advanced image processing (RDITM, TXITM and BAI-MACTM technologies) shows potential for enhancing clinical knowledge and refining diagnostic strategies.
- The challenge of bronchoscopy for diagnosing malignant tumors is to sample viable cancer cells and avoid bleeding, a common sideeffect of bronchoscopy.
- RDI technology can assist in selecting optimal biopsy sites by identifying necrotic areas and regions with a high risk of bleeding, thus balancing the need to avoid bleeding while obtaining viable cancer cells.
- TXI technology provides a precise contrast on superficial blood vessels, even allowing the estimation of the depth of blood vessels.
Strengths & Limitations as discussed by the authors
Strengths
- Have not been discussed by the authors
Limitations
- Limited Case Studies: The study is limited to five representative cases demonstrating the usefulness of high-definitionimage quality at a single institution.
- Limited Number of Lesions: The number of lesions observed under direct vision was limited, and imaging with various modes was not possible in all cases undergoing bronchoscopy due to bleeding and sedation effects.
- Conflict of Interest: There is potential bias from the endoscopic device development company, although they were not involved in the study design and interpretation.
Definitions & Abbreviations
| RDITMtechnology | Red Dichromatic Imaging |
| TXITM technology | Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging |
| BAI-MACTM technology | Brightness Adjustment Imaging With Maintenance of Contrast |
| IEE | Image Enhancement Endoscopy |
This Study Overview is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It provides an objective summary of data from a single publication. It does not constitute a comprehensive literature review and should not be interpreted as a substitute for evaluating the full body of evidence on the topic. For complete methodology, results, and context, please refer to the original publication.
Contact Olympus Scientific Affairs at SciA@olympus.com with any questions on this information.
Any content or information (“Content”) presented herein is illustrative in nature and does not guarantee or represent specific information, outcomes, or results. Olympus Medical Systems Corp. and its parents, subsidiaries, affiliates, directors, officers, employees, agents, and representatives (collectively “Olympus”) does not represent to or warrant the accuracy or applicability of the Content. Under no circumstances shall Olympus be liable for any costs, expenses, losses, claims, liabilities, or other damages (whether direct,indirect, special, incidental, consequential, or otherwise) that may arise from, or be incurred in connection with, the Content or any use thereof.
As medical knowledge is constantly growing, technical modifications or changes of the product design, product specifications,accessories, and service offerings may be required. Medical devices listed may not be available for sale in all countries.
- Content Type