VOLUME REDUCTION OF THE TONGUE BASE
In the following chapter, it is demonstrated how to use bipolar radiofrequency-induced thermotherapy (RFITT) at the base of the tongue to treat snoring and mild obstructive sleep apnea. Before you use this method, make sure Uvula and webbing will shorten further during the healing that a proper diagnosis of the type and severity of the sleep-related breathing disorder has been made.
01 | Anesthesia and Medications
The tongue base can be treated with RFITT using local anesthesia.
It may be advisable to use general anesthesia for patients with a strong gag reflex, and for those requiring multilevel treatment, depending on your judgement.
Firstly, disinfect the tongue base, for example with hexetidine. It is also recommended to disinfect the oropharynx to avoid postoperative infections (abcess) at the tongue base.
Secondly, extend the tongue and apply a topical anesthetic like lidocaine gel to the rear of the tongue.
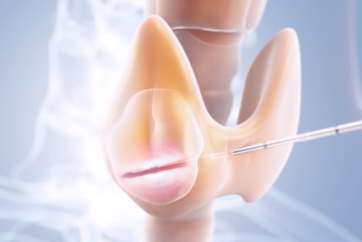
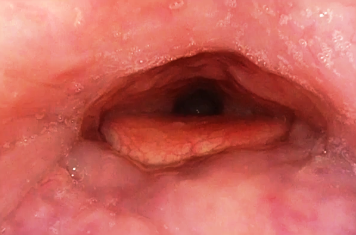
After that, it is suggested to use a long curved cannula to inject 6 to 9 ml of a two percent lidocaine solution in each of about three points in the circumvallate papillae area [Figure 01]. Make sure to stay in midline and wait for about five minutes before you start with the RFITT treatment.
02 | Treatment of the Tongue Base (with RFITT)
Power settings: A power setting of 7 watts (mode: PureRFITT) is recommended for treating the tongue. The power setting on the control unit determines the extent of coagulation induction. The lower the power setting, the longer the application time and the greater the extent of coagulation. The higher the power setting, the smaller the area of the coagulation.
Use the CelonProSleep plus applicator to treat the base of the tongue.
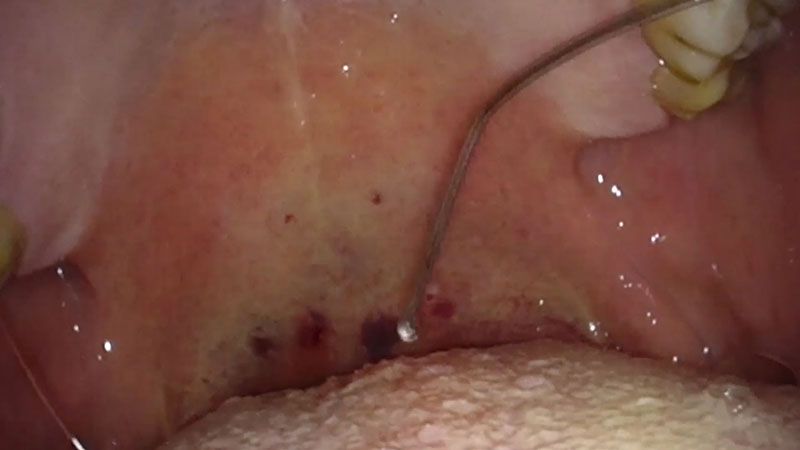
Insert the tip of the applicator into the tongue muscle until the insulation tube touches the tissue [Figure 02 a/b].
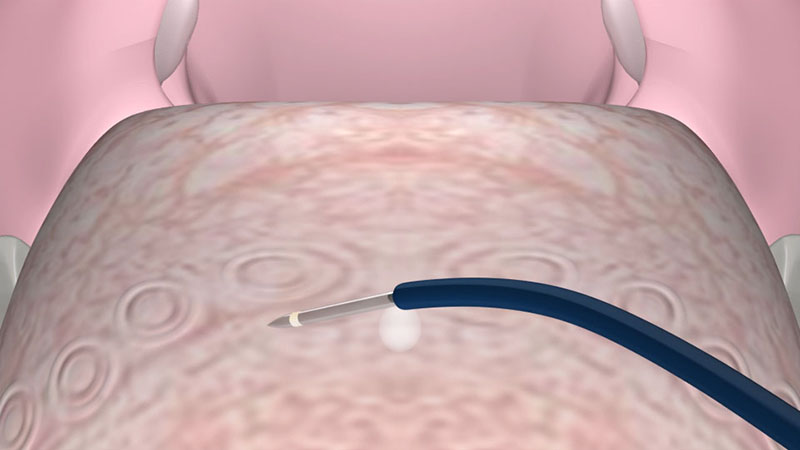
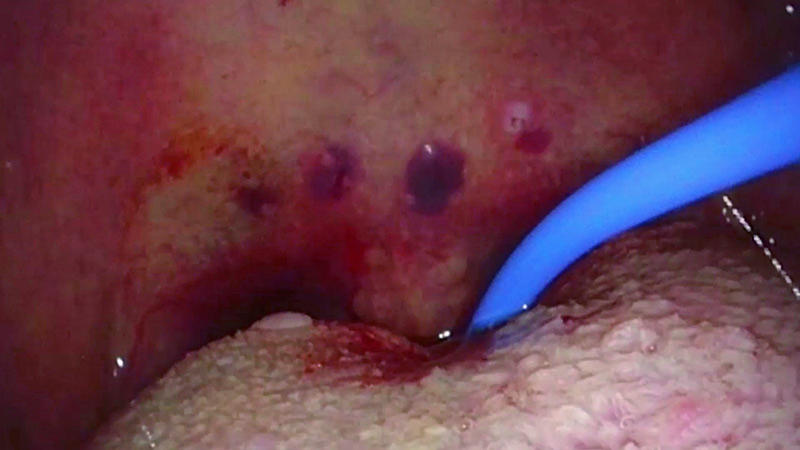
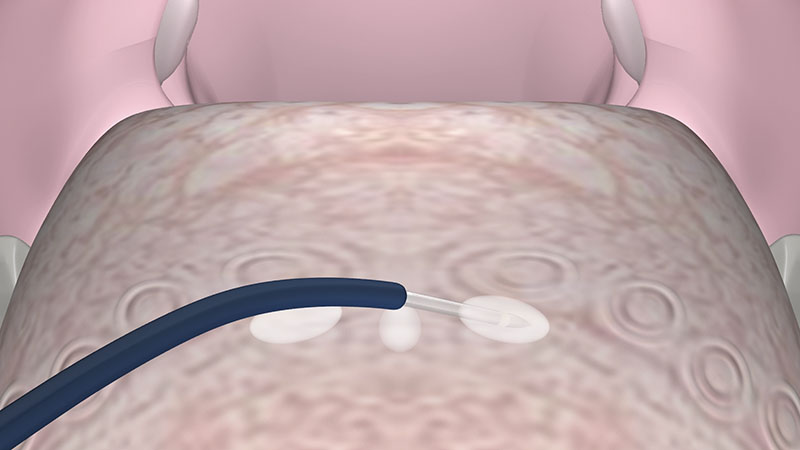
Be aware that the surface is difficult to penetrate. Therefore, it is suggested that, after each puncture, you try to make more than one coagulation by partially removing and repositioning the applicator [Figure 03a].
After positioning the applicator, activate the power supply by pressing the foot switch. You can monitor the status of coagulation via the acoustic signal. The power supply is reduced automatically to prevent overdose effects.
The application takes less than ten seconds for each lesion.
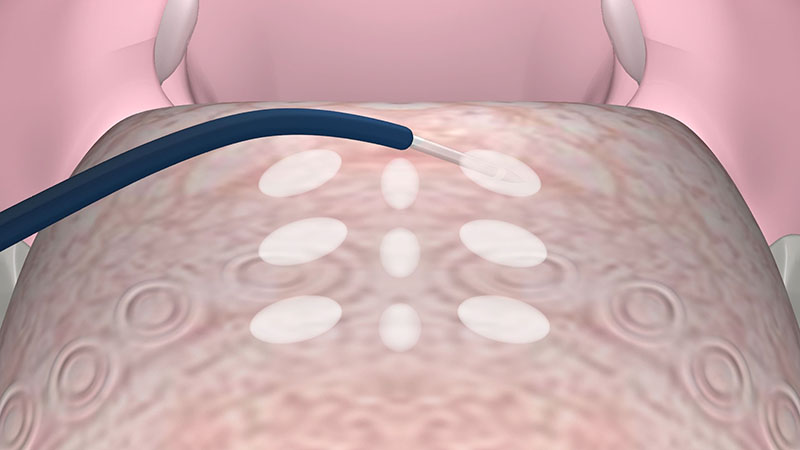
It is recommended that the individual coagulation zones are along the midline and approximately 1 cm apart to maintain a seam of untreated tissue between them.
Depending on the size of the tongue base, approximately nine coagulations in the circumvallate papillae area are recommended [Figure 03b].
Note:
To avoid damage to the hypoglossal nerve, do not coagulate too laterally.
03 | Therapeutic Effect
The coagulation results in a local denaturation of the treated tissue area. You can expect a visible reduction in volume accompanied by a tightening of the tissue within the next four to six weeks as a result of scarring and the body’s resorption process [Figure 04].
04 | Postoperative Care
Because swelling at the tongue base may occur, it is recommended to observe your patient for a couple of hours following the treatment.
A follow-up visit is usually not necessary, only in very rare cases of complications.
To prevent postoperative pain and swelling treatment, if necessary, ibuprofen or diclofenac is generally suitable.
Postoperative antibiotic prophylaxis is highly recommended using cephalosporin or clindamycin orally, for example to avoid abscess formation.
Note:
- Clinical experience indicates that an additional coagulation treatment of the base of tongue is usually necessary to achieve optimal results. When conducting additional treatments, the CELON applicator should be placed between the scarred areas of the tissue.
- It is recommended to wait at least four weeks before conducting a follow-up intervention.
- Content Type