Colorectal Case 23

Prof. Han-Mo Chiu
Clinical Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine,
National Taiwan University College of Medicine, Taiwan
Disclaimer:
NBI™, RDI™, and TXI™ technologies are not intended to replace histopathological sampling as a means of diagnosis.
NBI™, RDI™ and TXI™ Technologies are 510(k) cleared in the United State. This case study is being furnished to provide examples of these imaging technologies. The CF-HQ290ZI and PCF-H290TI used in this case is not available in the US market at this time, nor is there an established time for it’s release. The safety and effectiveness ofthis product and/or the use of these products has not yet been established in the United Statesmarket.
The positions and statements made herein by Prof. Han-Mo Chiu are based on Prof. Han-Mo Chiu’s experiences, thoughts and opinions. As with any product, results may vary, and the techniques, instruments, and settings can vary from facility to facility. The content hereof should not be considered as a substitute for carefully reading all applicable labeling, including the Instructions for Use. Please thoroughly review the relevant user manual(s) for instructions, risks, warnings, and cautions. Techniques, instruments, and setting can vary from facility to facility. It is the clinician’s decision and responsibility in each clinical situation to decide which products, modes, medications, applications, and settings to use.
The EVIS X1™ endoscopy system is not designed for cardiac applications. Other combinations of equipment may cause ventricular fibrillation or seriously affect the cardiac function of the patient. Improper use of endoscopes may result in patient injury, infection, bleeding, and/or perforation. Complete indications, contraindications, warnings, and cautions are available in the Instructions for Use
Scope: Diagnosis: CF-HQ290ZI; ESD: PCF-H290TI
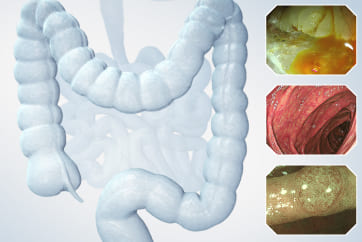
Organ: Colorectum
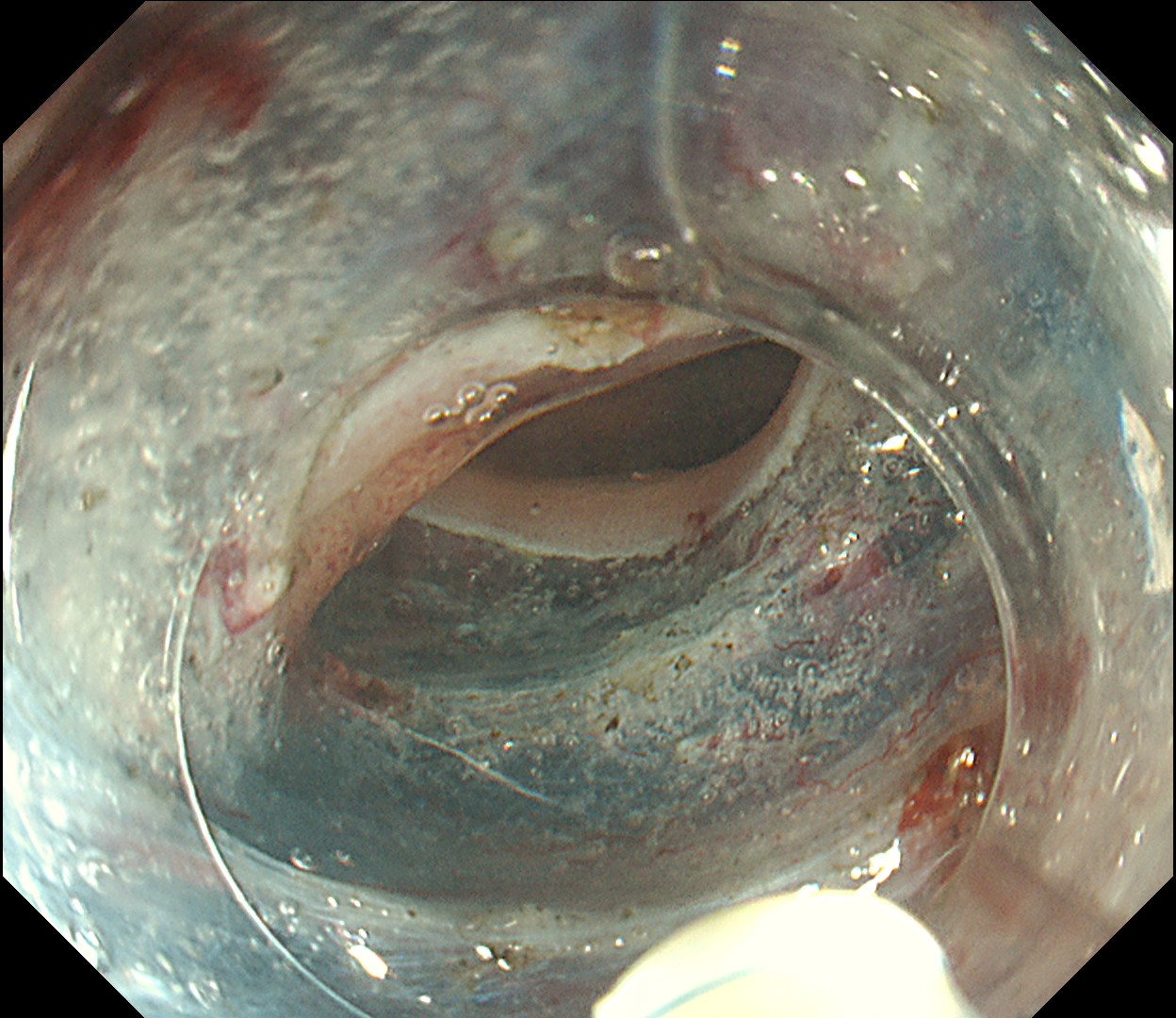
Patient information: M, 50s
Rectal tumor found at colonoscopy after a positive FIT (fecal immunochemical test)
Medical history: No systemic disease
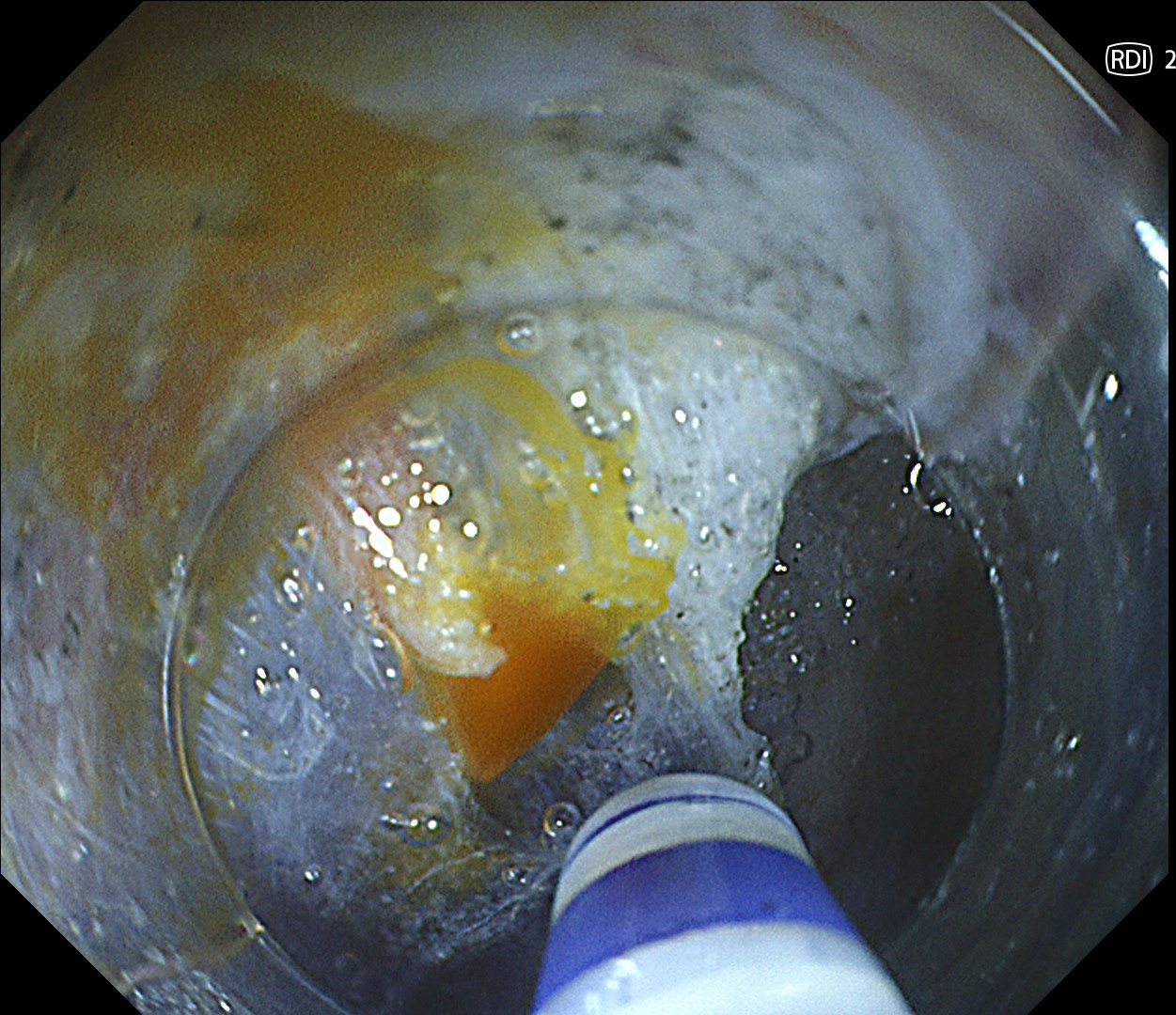
6. Chromoendoscopy

Enhancement : A7
NBI Mode : NA
TXI Mode : NA
RDI Mode : NA
BAI-MAC : On
Case Video
IEE Diagnosis
ESD
RDI™ technology
Overall Comment
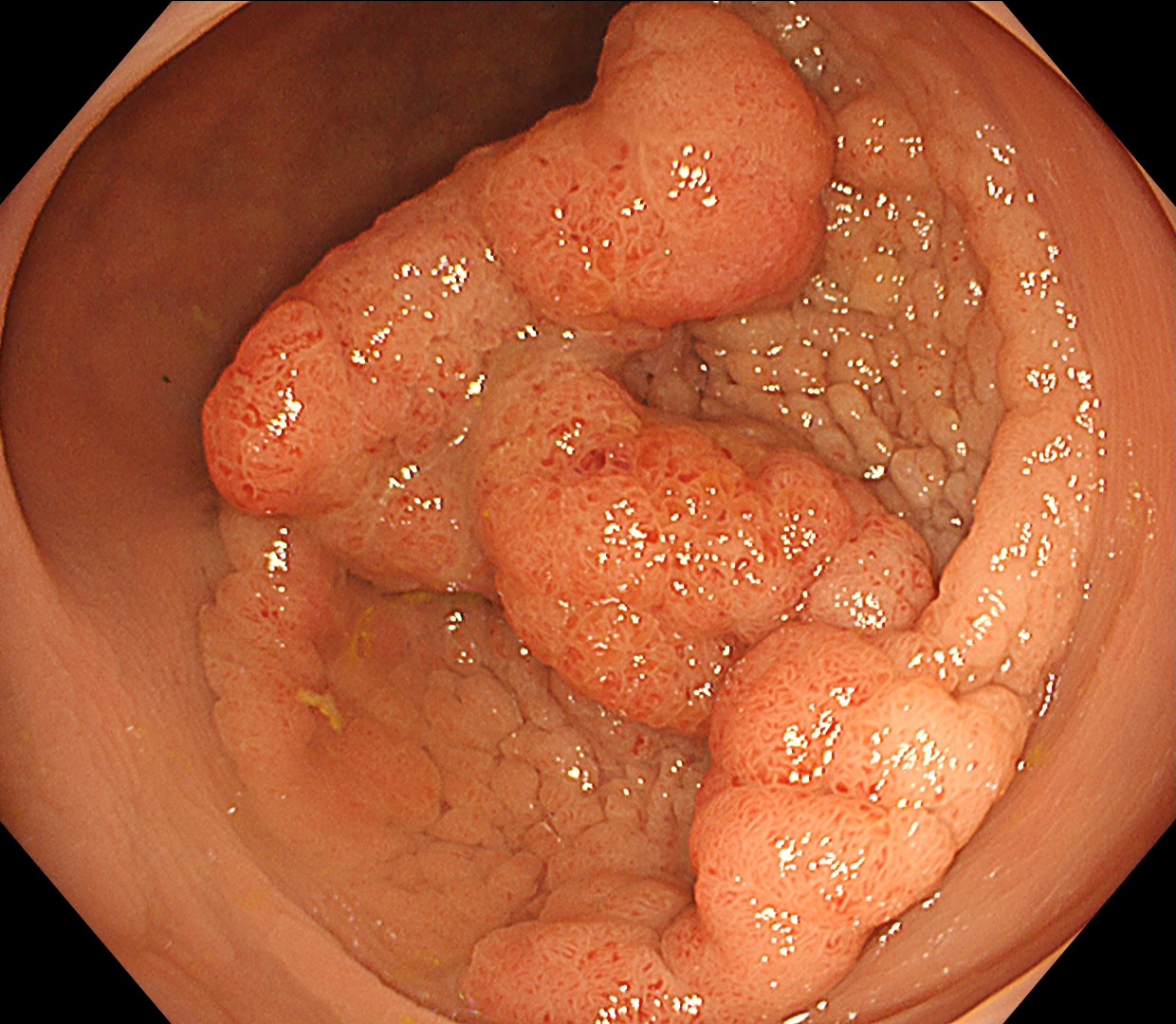
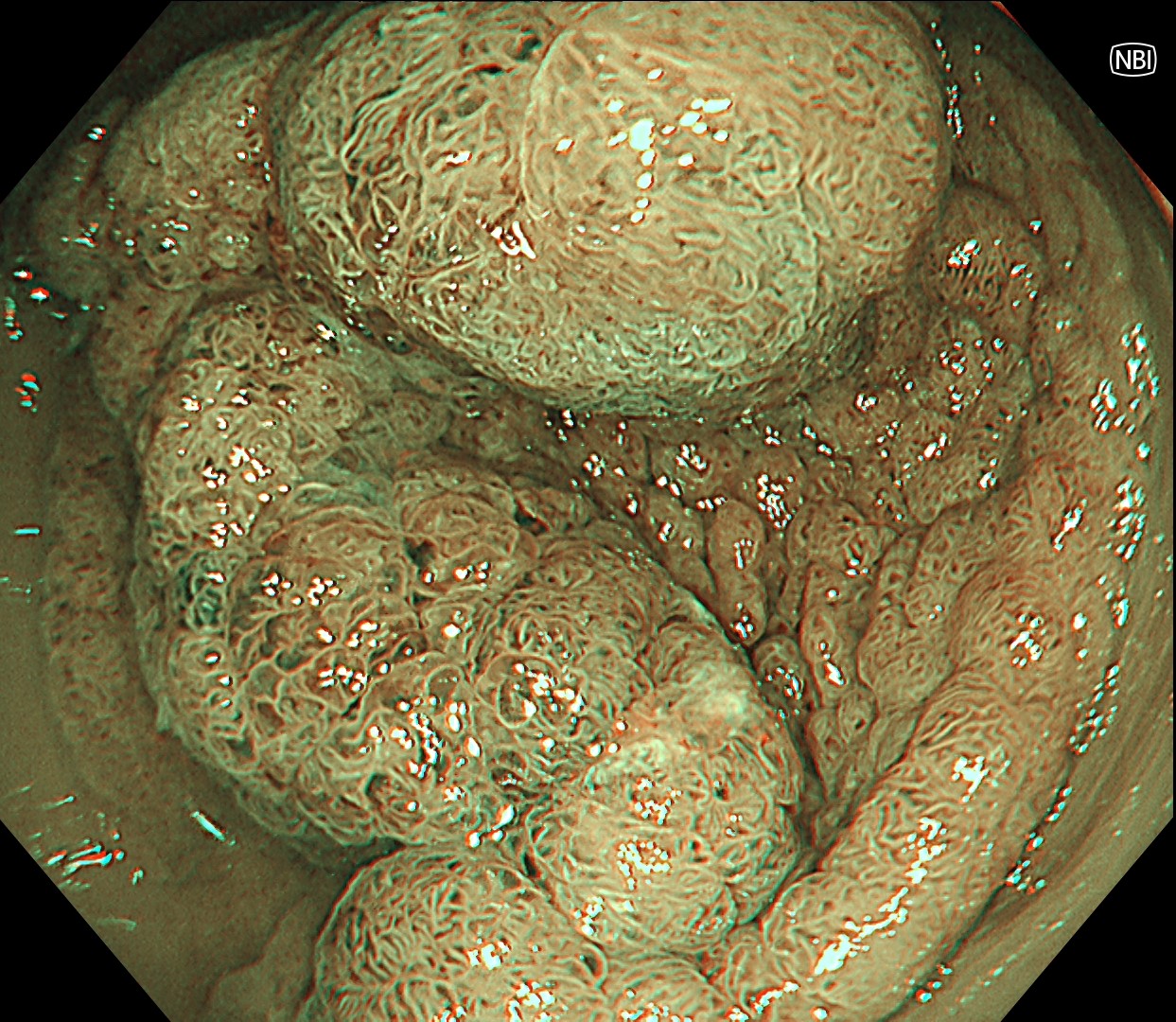
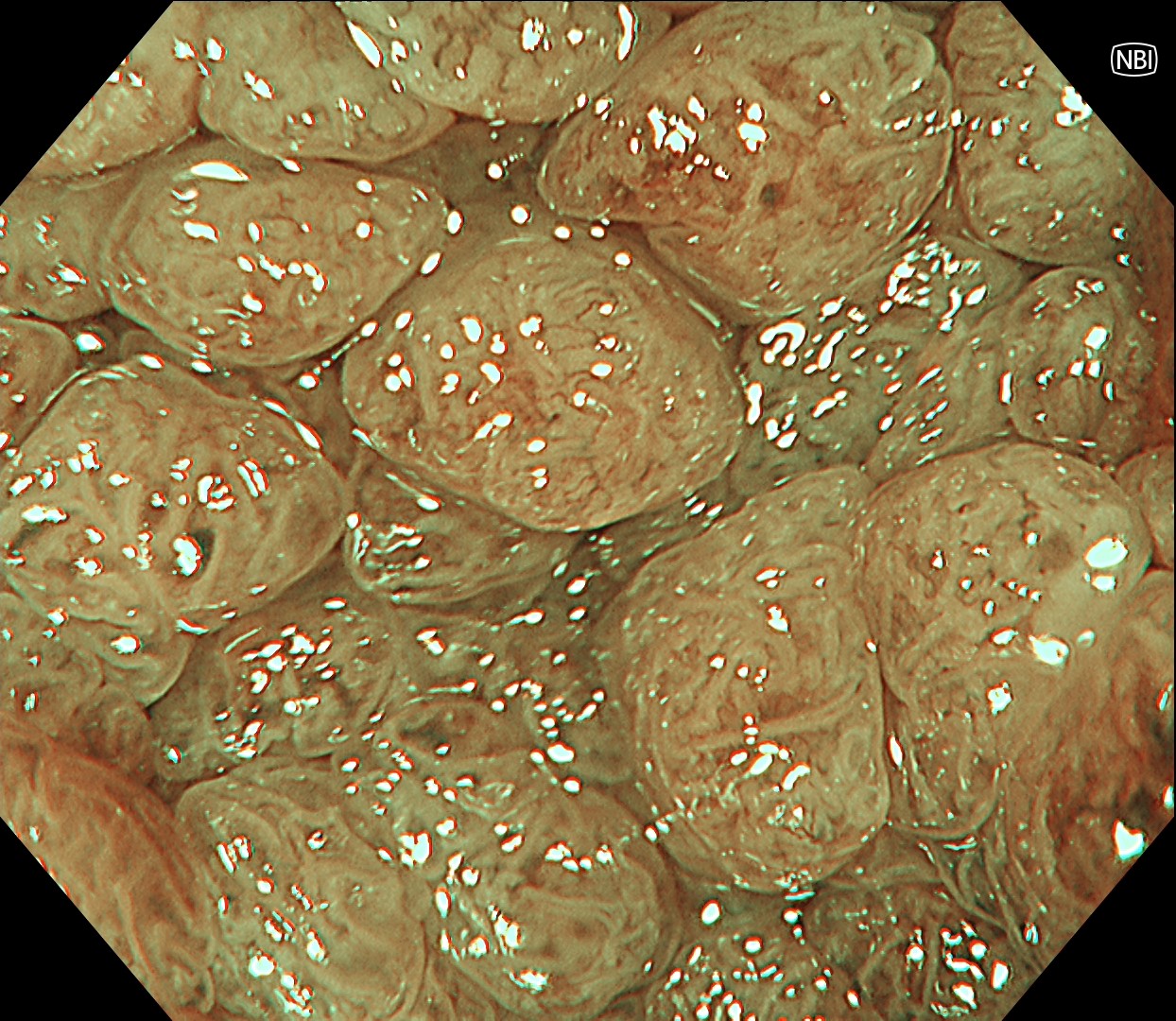
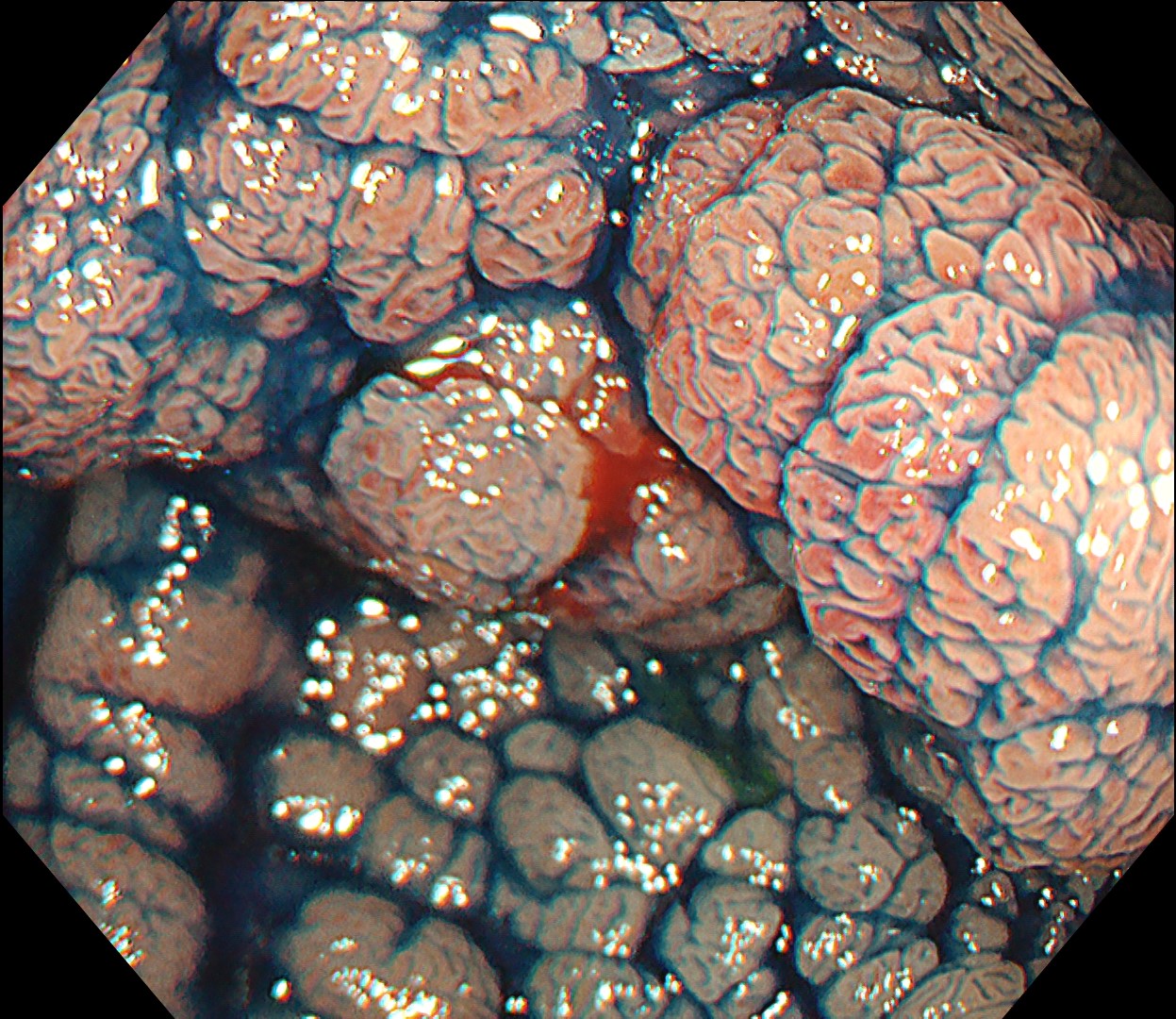
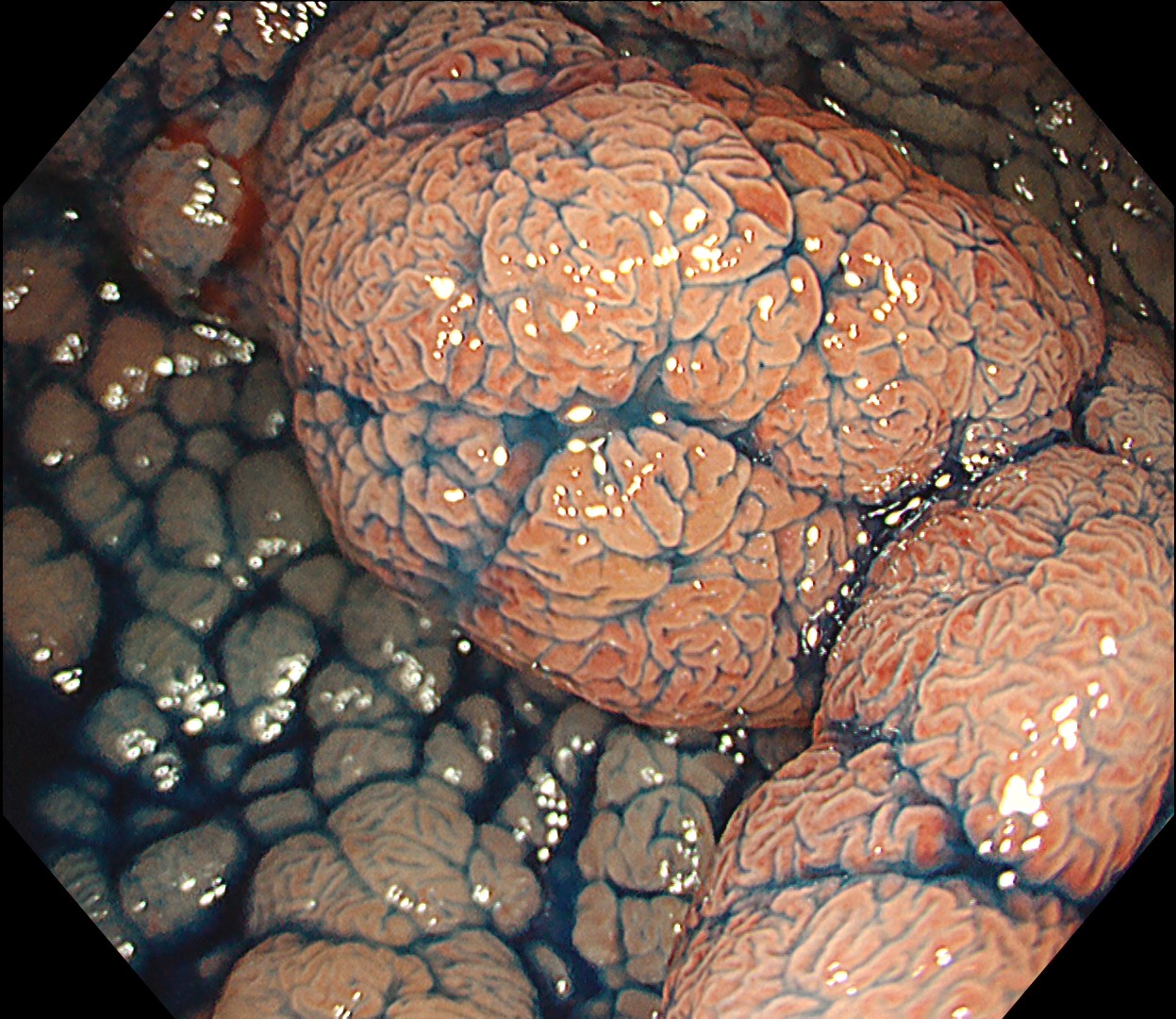
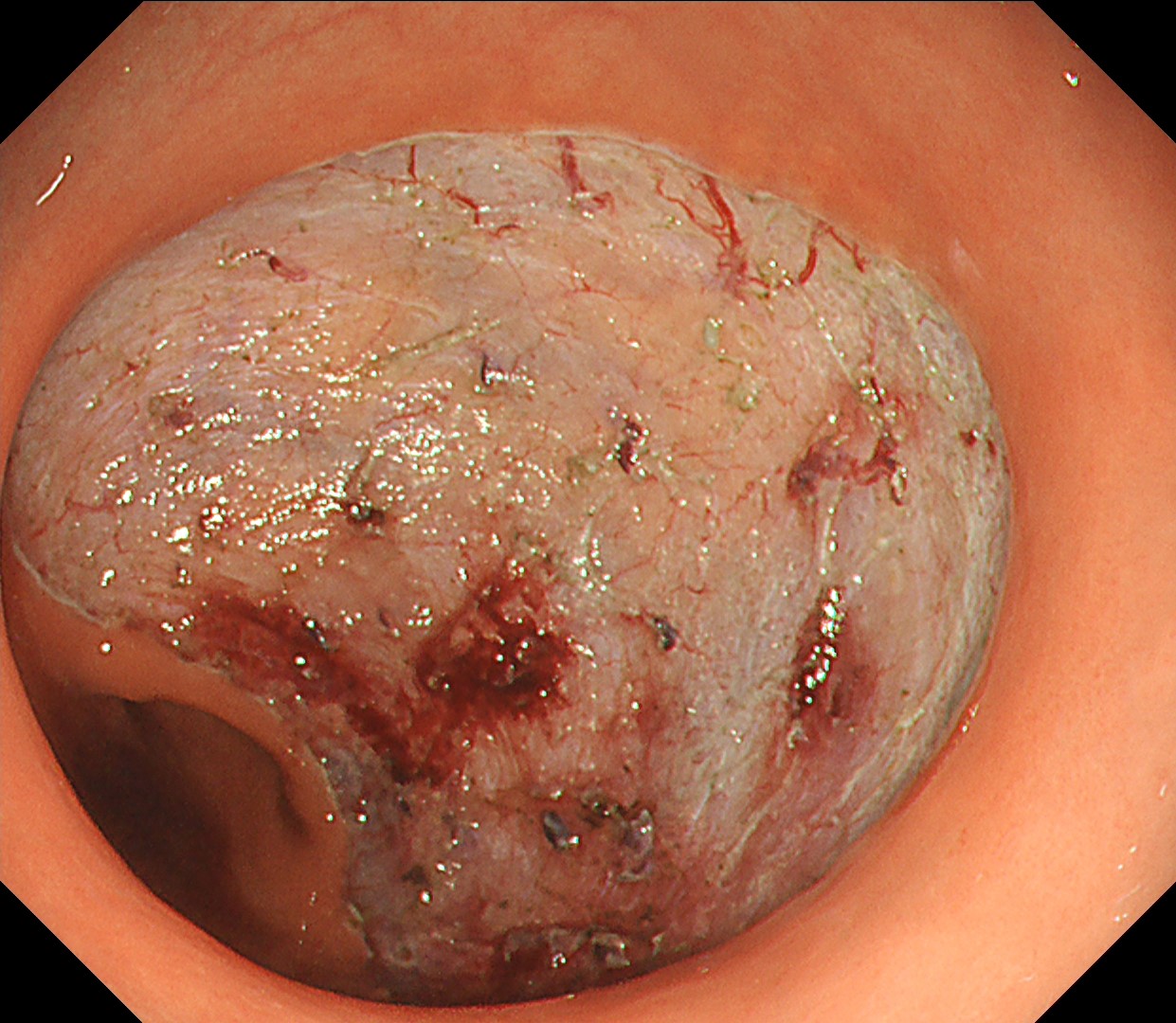
This is a large rectal tumor (7 cm in diameter) detected by FIT screening and subsequent colonoscopy. Initially, it was examined using a high-definition colonoscope with magnification function. The lesion size exceeded half of the rectal circumference, and its macroscopic morphology was interpreted as 0-Is+IIa (LST-G-NM). According to a previous meta-analysis, lesions with such morphology carry a higher risk of submucosal invasion, estimated at around 10% (Bogie R et al. Endoscopy. 2018;50:263-282). While invasive cancer was reported to mainly occur in the large nodular part, a later study on a large ESD cohort revealed that invasive cancer may also be present in a multi-focal fashion and even in the non-nodular portion, justifying en bloc resection for such lesions (Yamada M et al. Endoscopy. 2016;48:456-64).
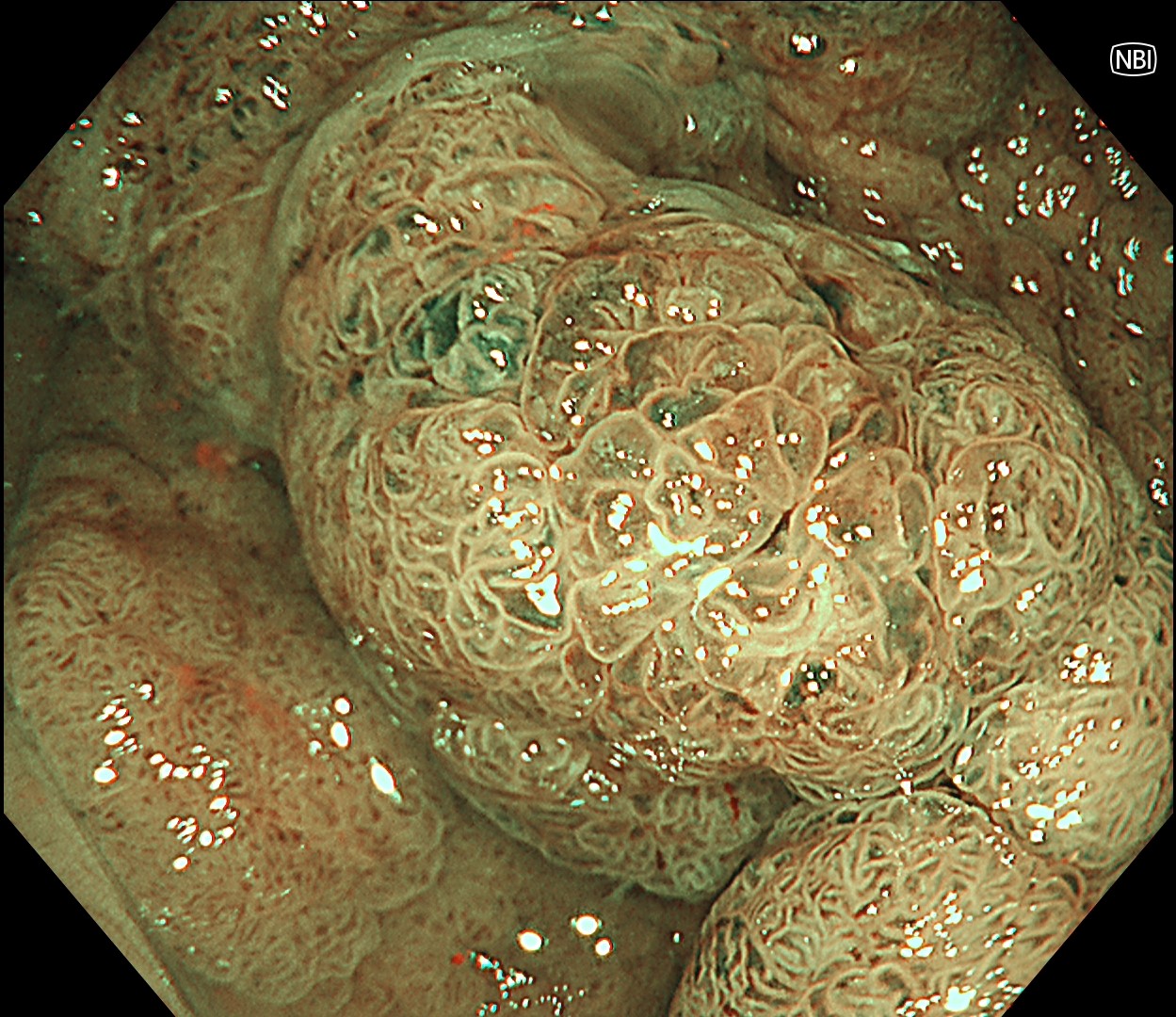
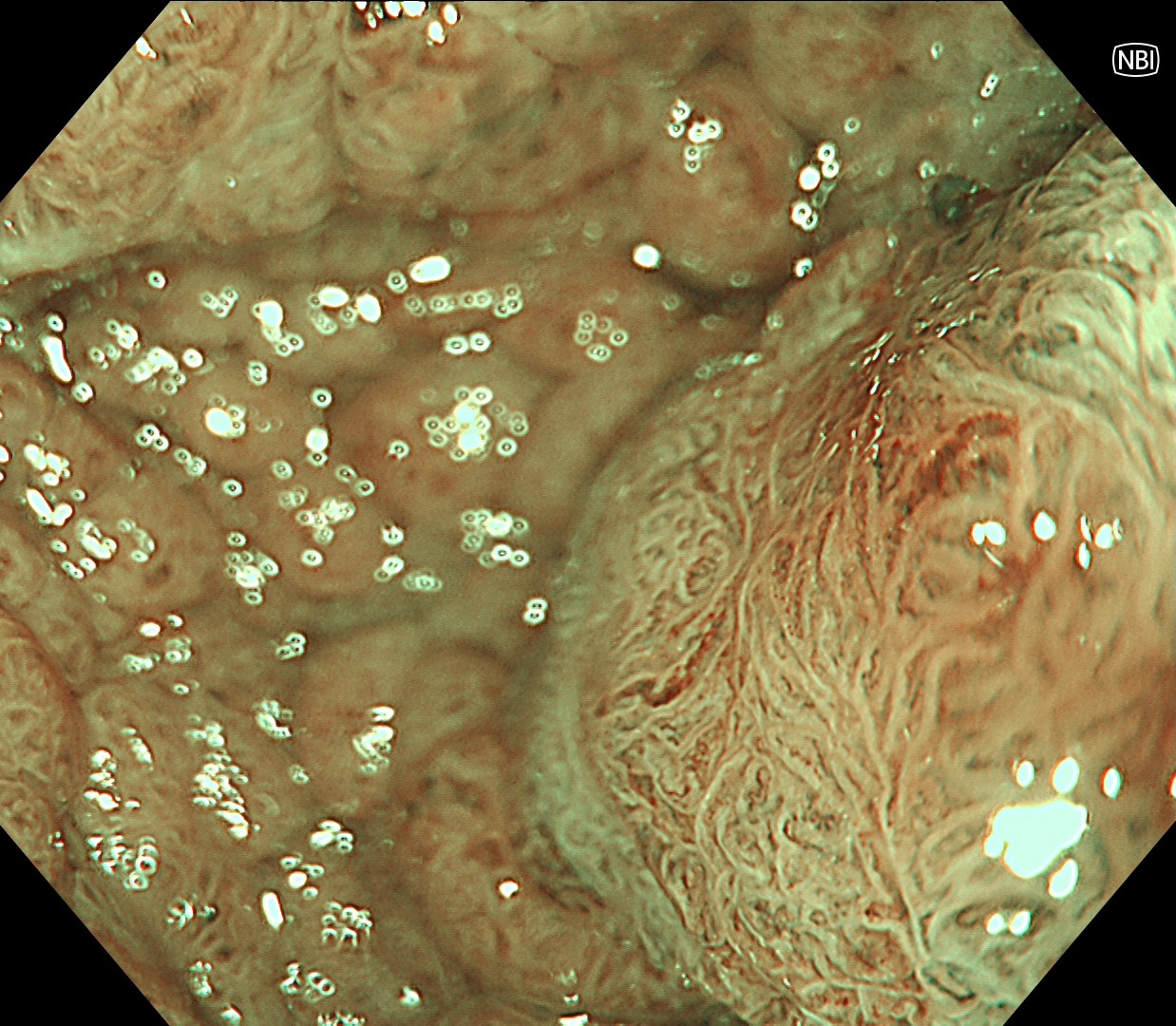
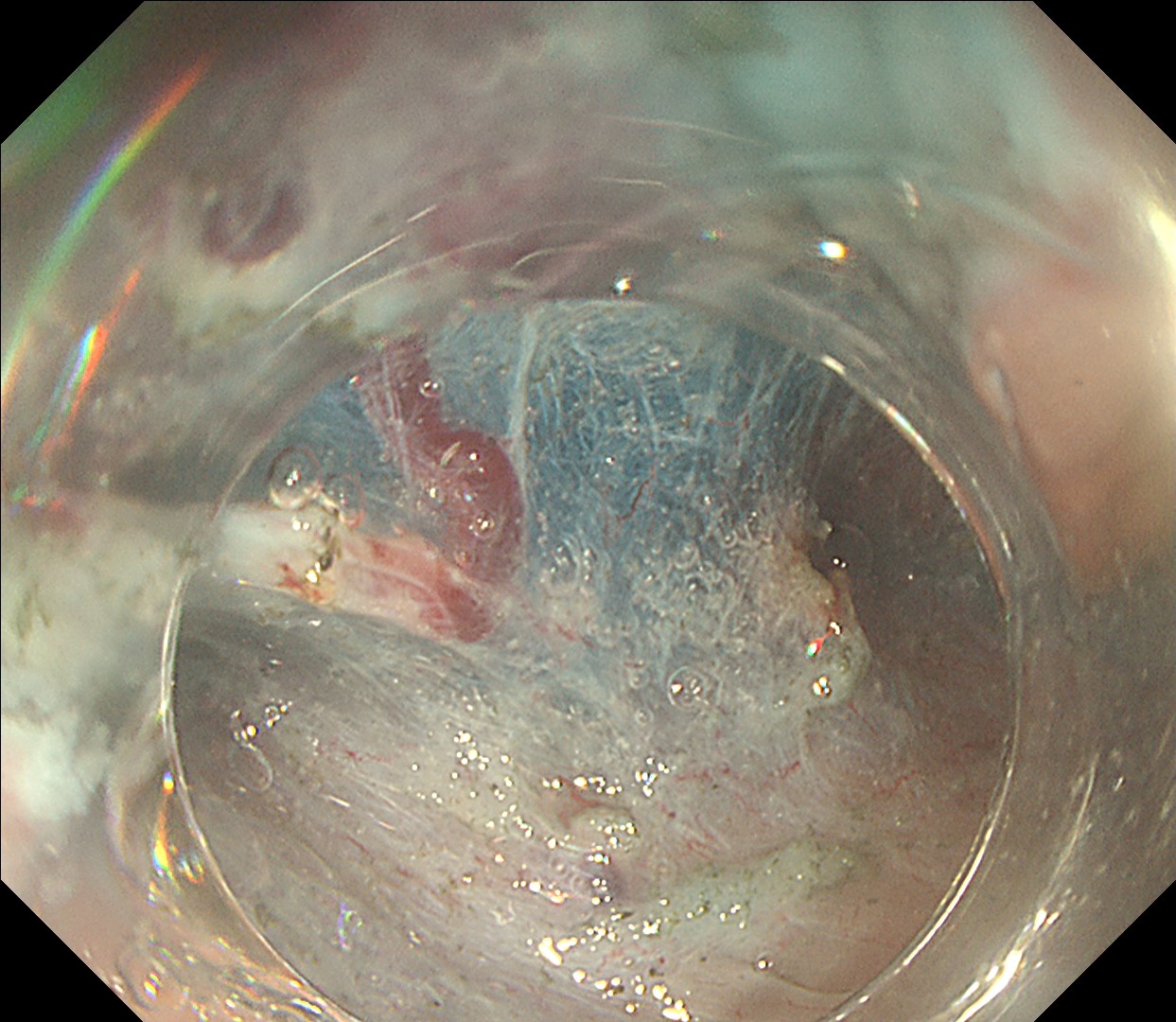
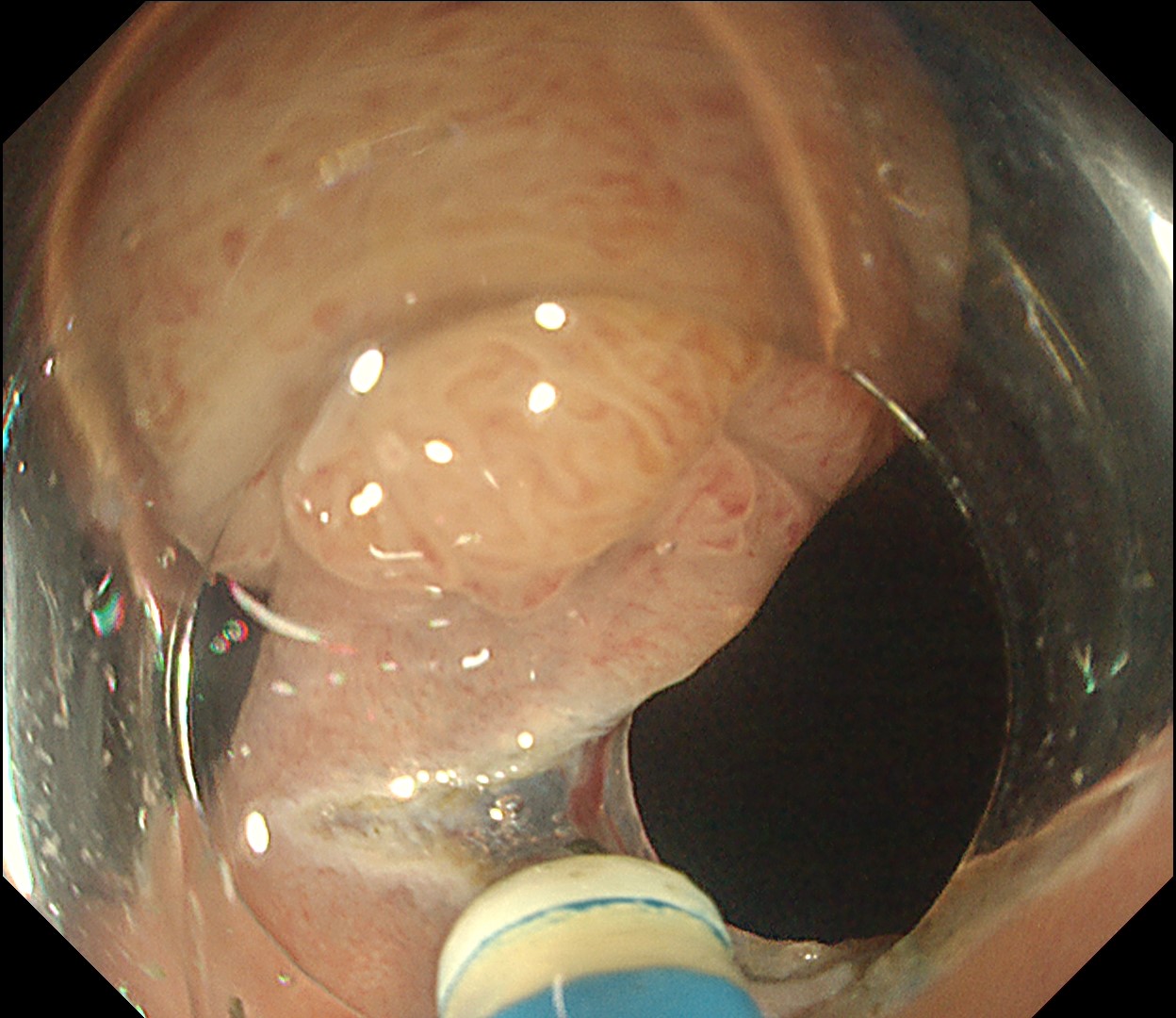
In this case, a focal JNET-2B capillary pattern was observed, indicative of advanced histology including high-grade dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, or even superficial invasive cancer. However, chromoendoscopy revealed a focal Kudo type Vi pit pattern without a demarcation line, indicating a non-invasive lesion and justifying endoluminal therapy.
ESD was performed using the Olympus DualKnife ™ J device (KD-655U) with a therapeutic colonoscope (PCF-H290TI), featuring an up angulation of 210° and a short bending section, facilitating the ESD procedure.
Histologically, this lesion was diagnosed as a tubulovillous adenoma with high-grade dysplasia, which was consistent with the area where the JNET 2B capillary pattern and Kudo type Vi pit pattern were observed.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer