NBI: The Power of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate optical diagnosis is important when assessing lesions to determine potential histology, confirm the lateral extent, and thereby guide therapy decisions and suitable patient surveillance intervals.
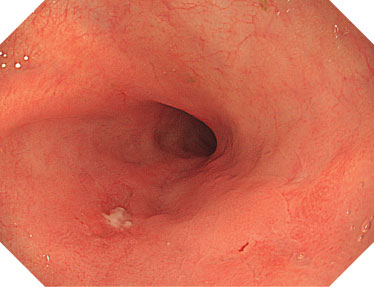
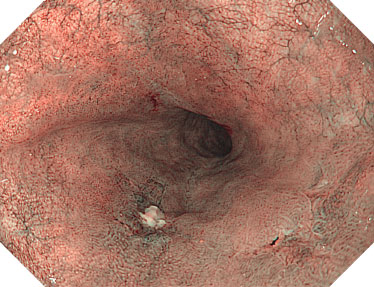
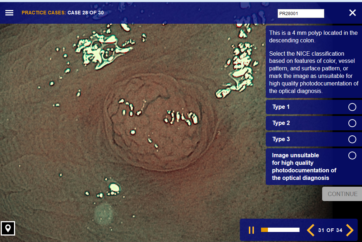
NBI is a powerful and proven optical technology that allows for a reliable optical diagnosis of all major indications in the gastrointestinal tract.1-8
NBI
Narrow Band Imaging
Utilizing specific blue and green wavelengths absorbed by hemoglobin, NBI creates a strong contrast between vessels and surrounding mucosa.9 This facilitates the visibility of highly vascularized areas, blood vessel patterns and surface structures that are predictive for distinct histopathologies.10-13
Efficient lesion management strategies that are empowered by NBI include:
- Targeted biopsies in the upper gastrointestinal tract.2,5
- Easier decision-making for suitable endoscopic resection techniques.4,5
- Potentially avoiding histological assessment of low-risk lesions6-8
(e.g. diminutive rectosigmoid polyps under the resect and discard paradigm).
- Sharma et al. Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar; 150(3): 591-8.
- Thosani et al. Gastrointest Endosc 2016 Apr; 83(4): 684-698.e7.
- Kaise et al. Endoscopy 2009 Apr; 41(4): 310-5.
- Yao et al. New Challenges in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 2008, pp 169-176.
- Pimentel-Nunes et al. Endoscopy 2019; 51: 365-388.
- Dayyeh et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Mar; 81(3): 502.e1-502.e16.
- Kaminski et al. Endoscopy. 2014 May; 46(5): 435-49.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). 2017; Diagnostics guidance [DG28]; available at https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/dg28.
- Gono et al. J Biomed Opt. 2004 May-Jun; 9(3): 568-77.
- Inoue et al. Annals of Gastroenterology 2015; 28, 41-48 (Esophagus – SCC).
- Sharma et al. Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar; 150(3): 591-8.
- Yao. Ann Gastroenterol. 2013; 26(1): 11-22.
- Hewett et al. Gastroenterology 2012; 143, 599-607.
- Content Type