Scope: BF-H1100
Patient information: Male, 73 years old
Medical history: Past history head and neck cancer. Presentend with rapid deterioration with mediastinal adenopathy
2. TXI
(trachea and pars membranacea)
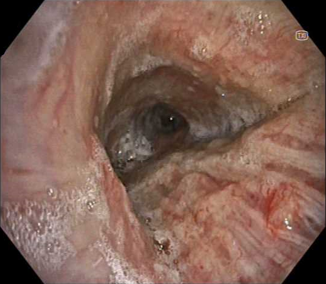
5. TXI
(left main bronchus)
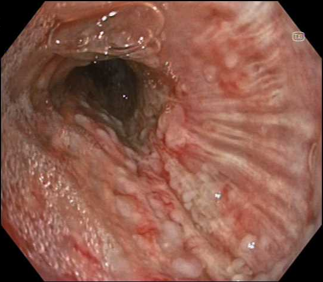
Case video
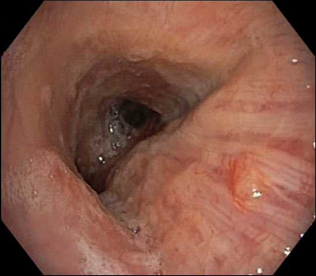
In white light view there is a suspicion of mucosal abnormality, but often in this location there are mucus secretions, which could be bypasssed by the bronchoscopist.
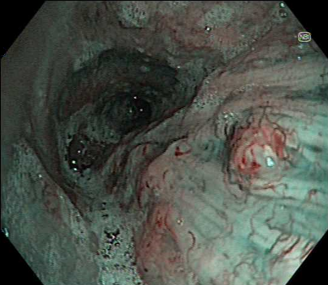
However changing to TXI gives a view of the index mucosal nodular lesion being a distinct pathologic process, seen in the foreground.
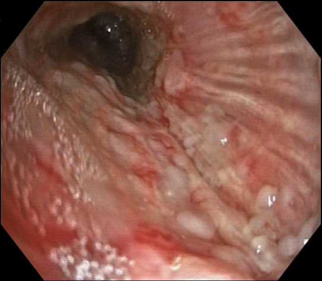
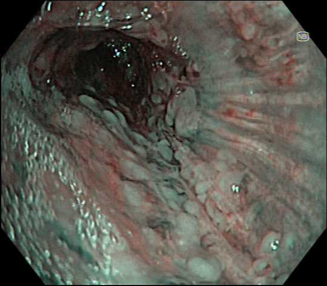
It does this in a way which is relatively close to white light in terms of general appearance with there being no need to adjust to a different way of viewing. Additionally with TXI it is quickly apparent that there are multiple other nodules on the far wall. NBI also shows the vascular changes of these nodules and also shows the multiple nature of the nodules.
Overall Comment
Even though there was other evidence of metastatic disease ( mediastinal adenopathy) defining the extent of the endobronchial mucosal involvement with malignant nodularity gave a clear emphasis on the rapidly progressing nature of this metastatic involvement. TXI helped the clinician to rapidly observe the true extent of the nodules, which in this location could have been easily overlooked as just non-specific secretions. NBI helped to then confirm the suspicion of malignancy.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
- Keyword
- Content Type