Esophageal Case 11

Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan
Koc University Hospital
Istanbul, Turkey
Scope: GIF-XZ1200, GIF-EZ1500
Case: Barrett Esophagus-Adenocarcinoma
Organ: Esophagus
Case video
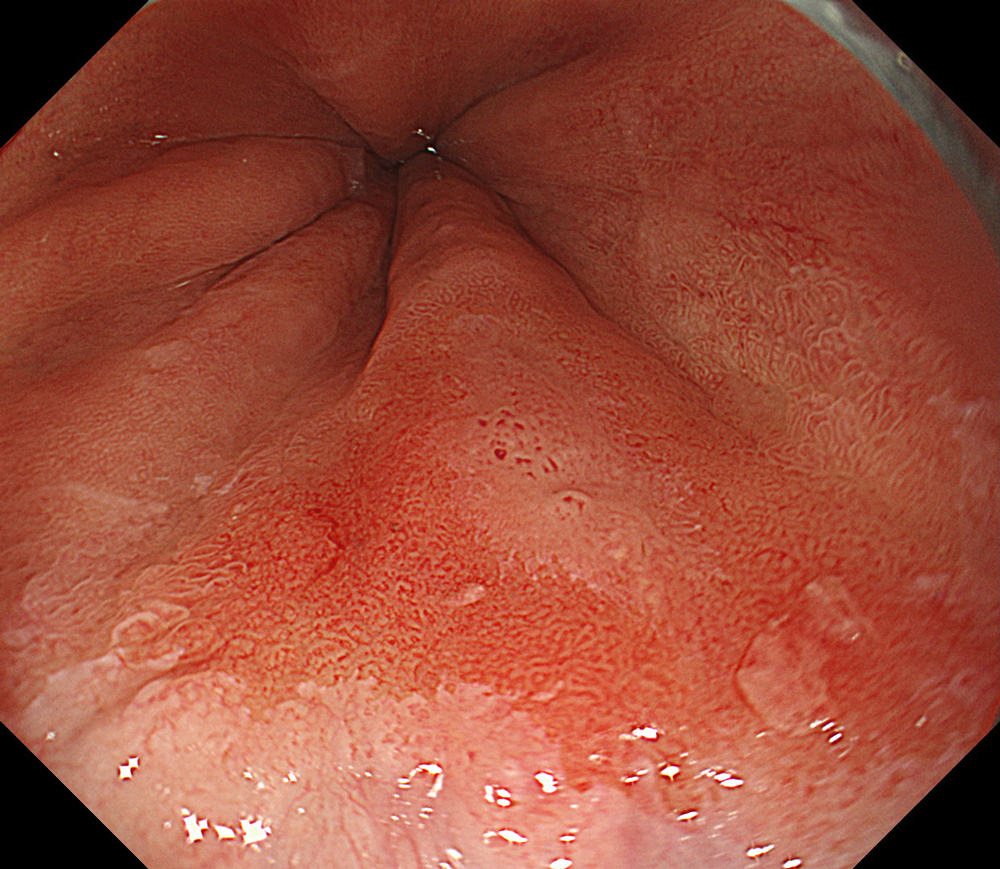
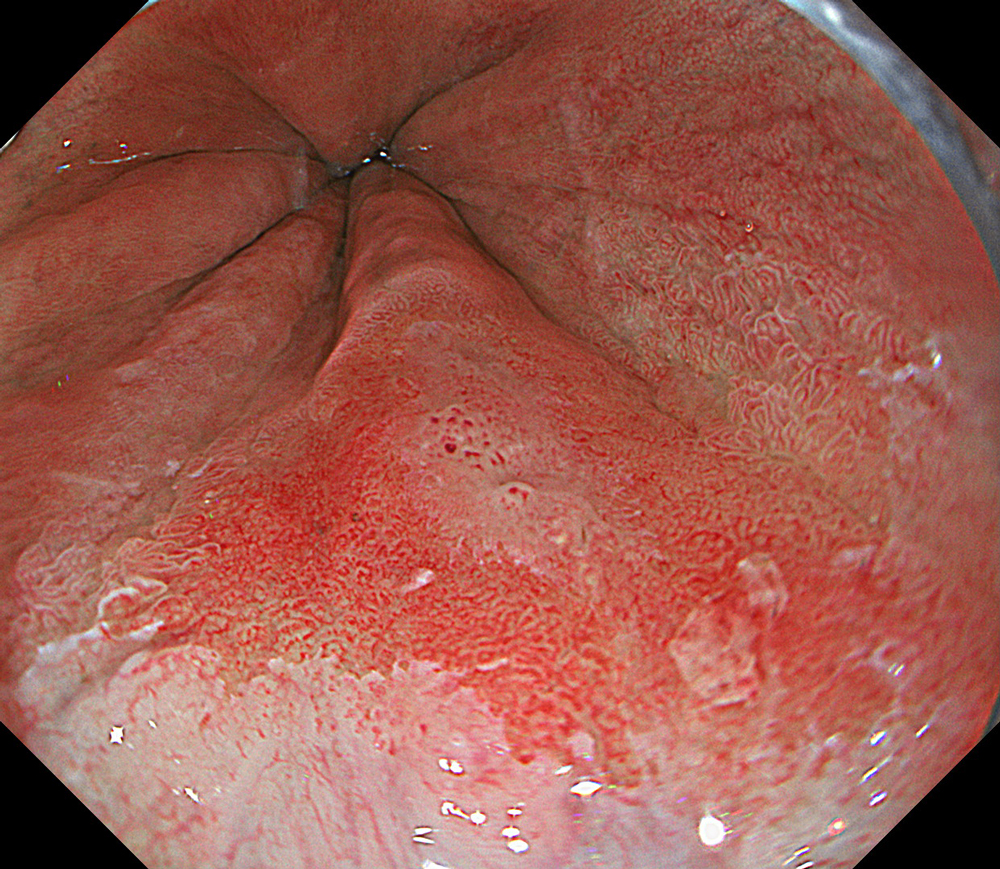
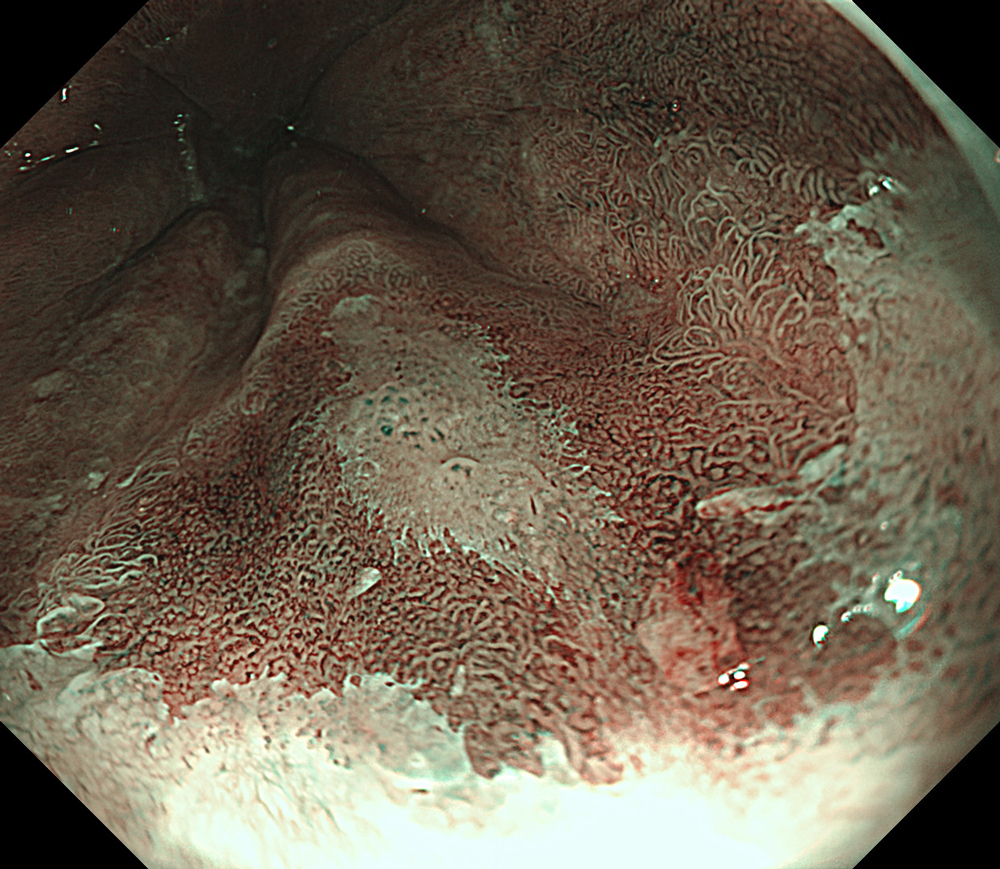
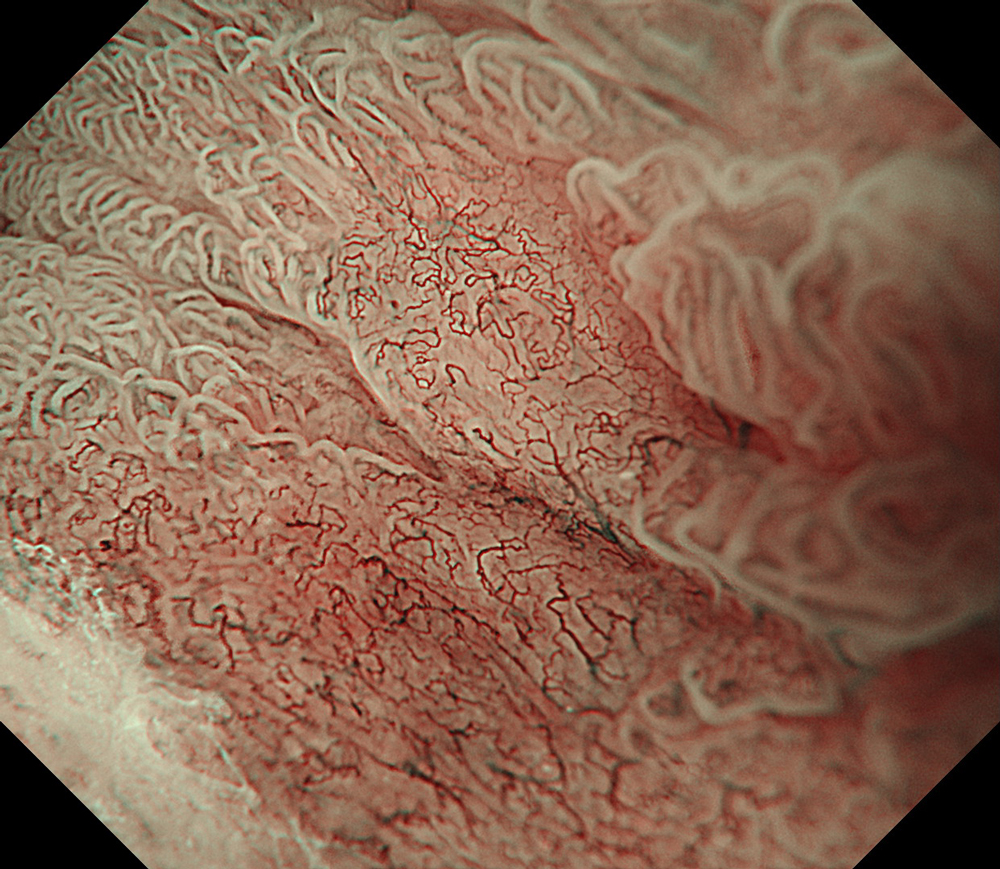
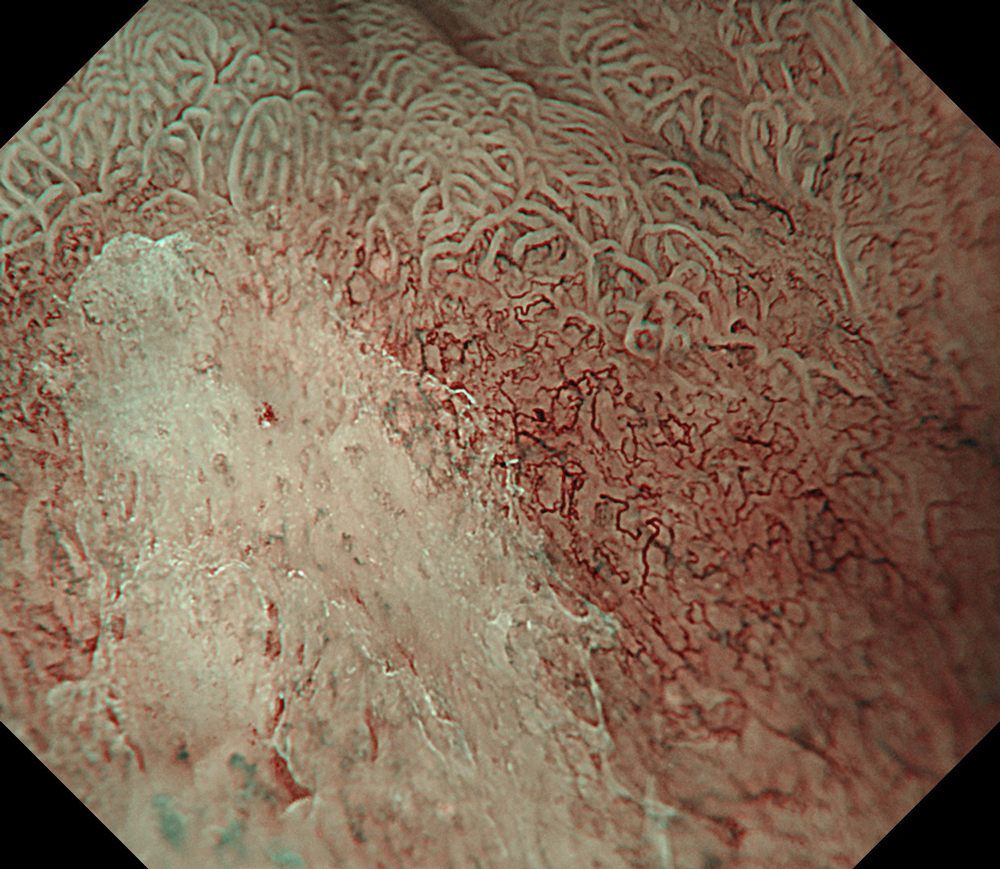
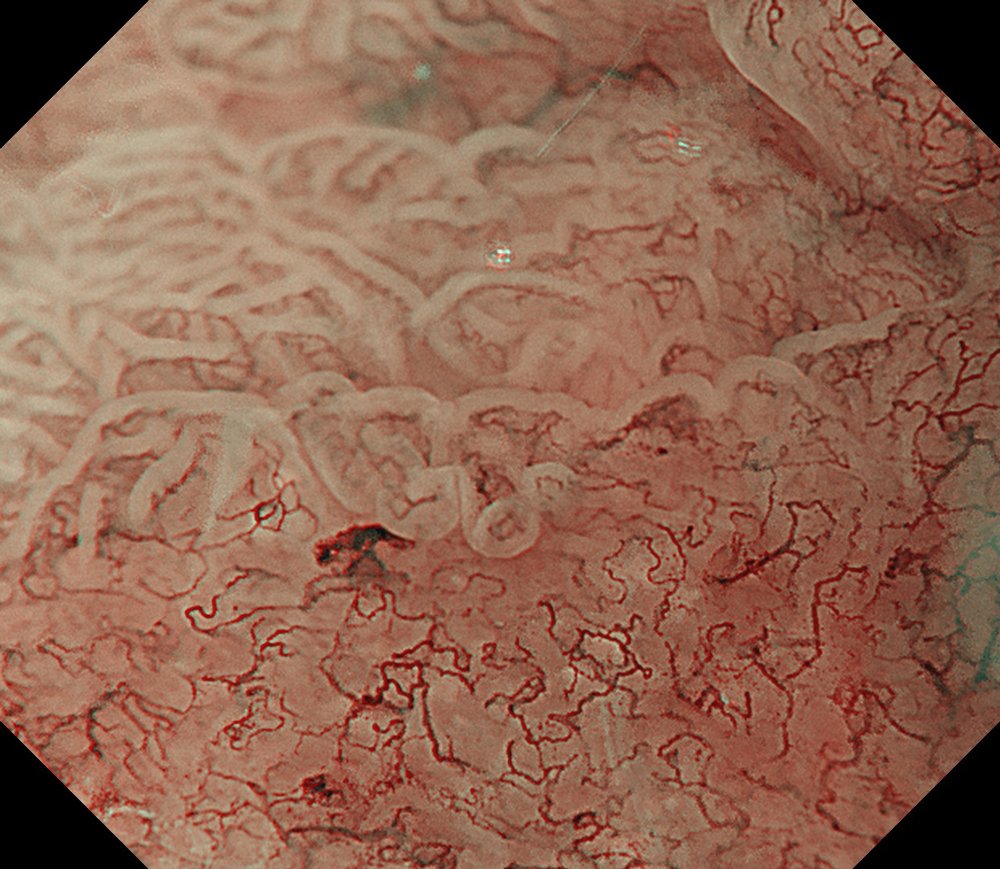
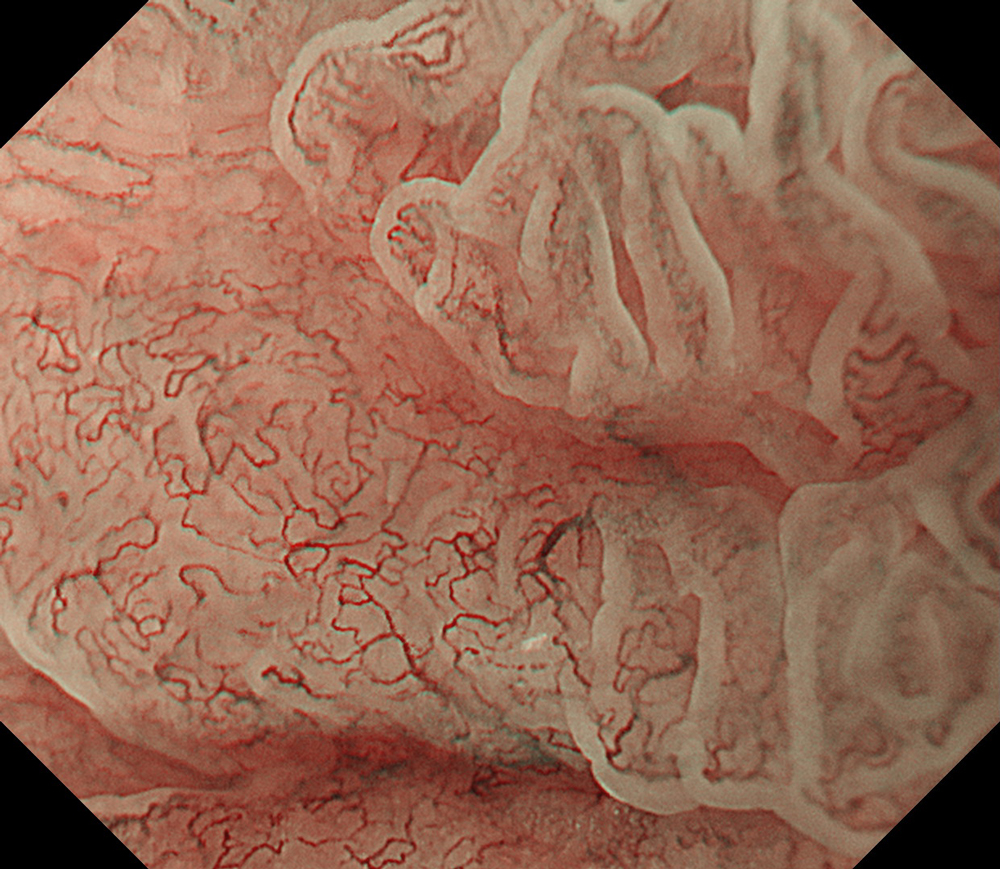
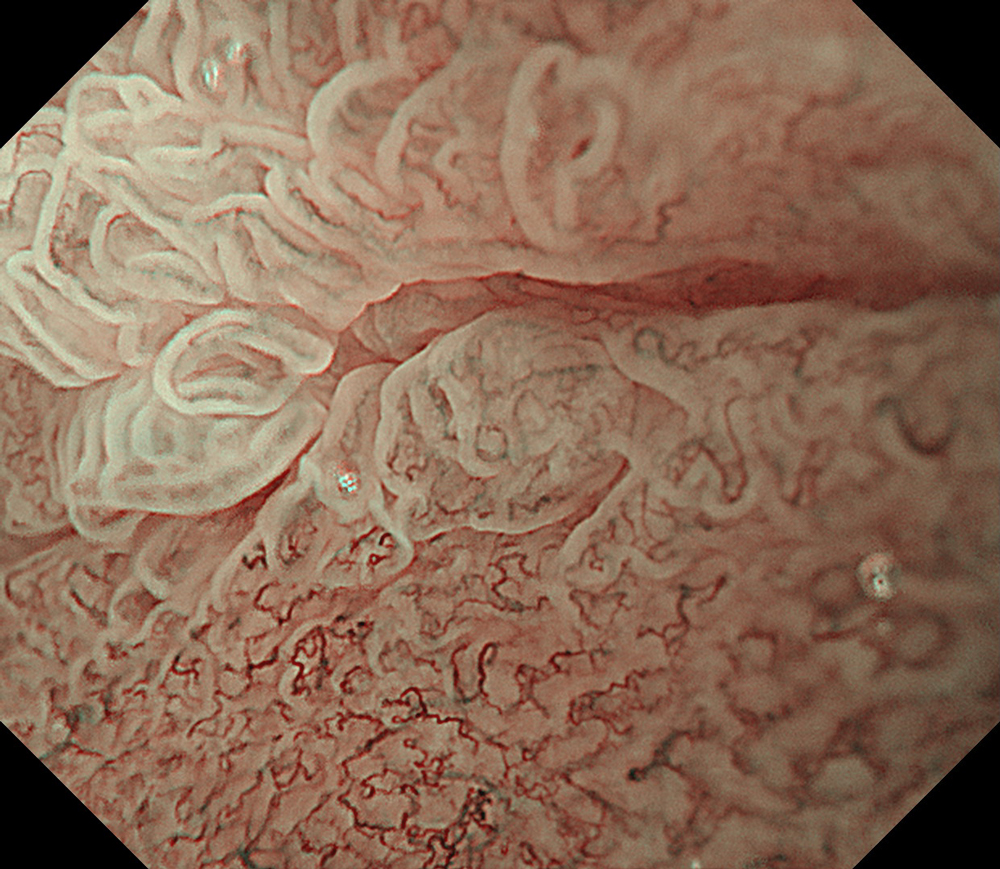
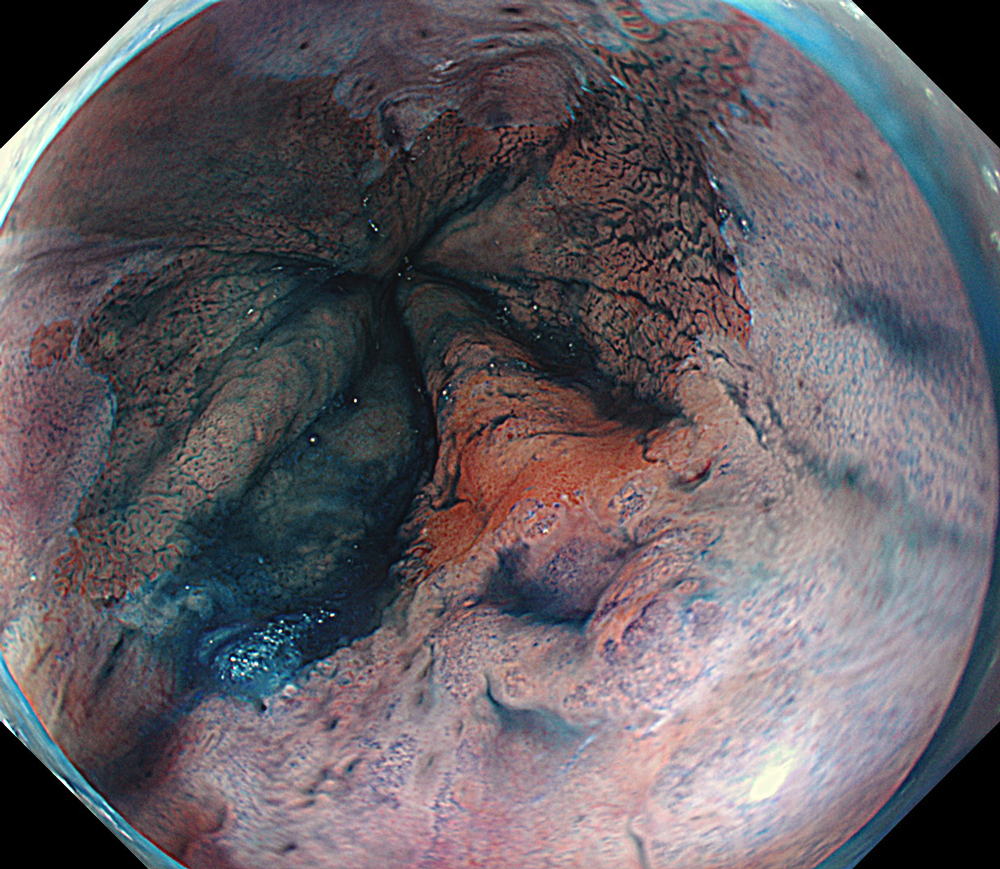
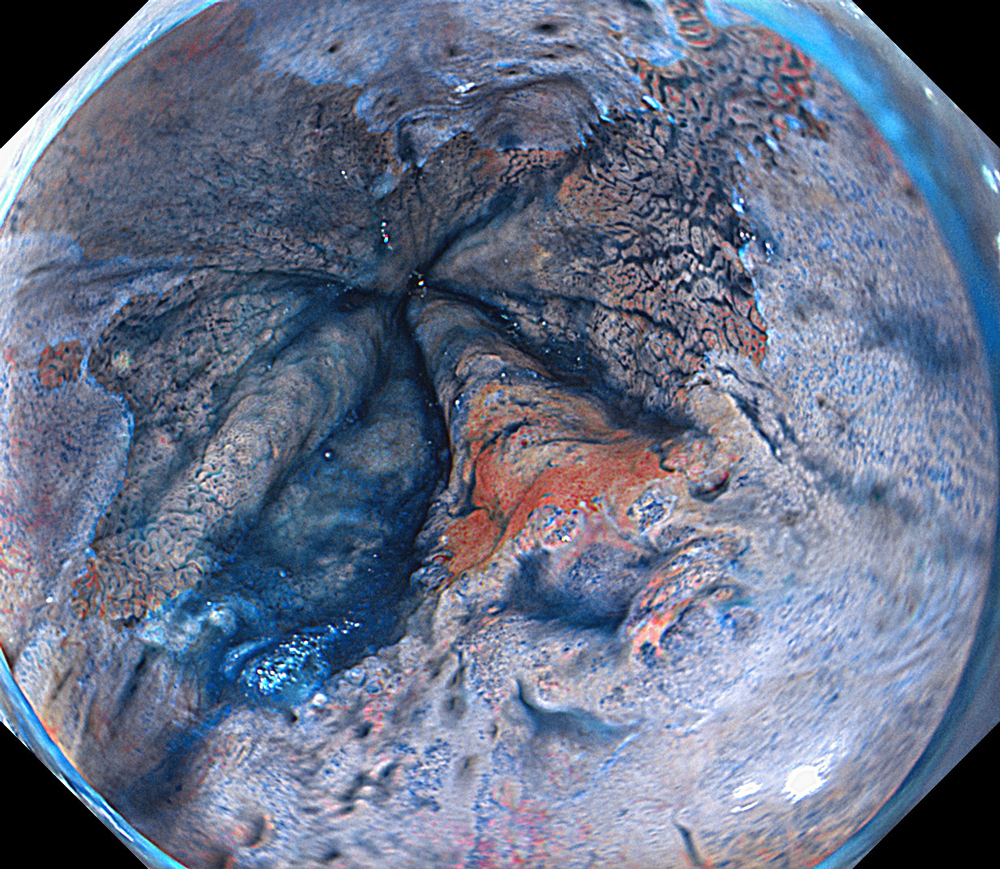
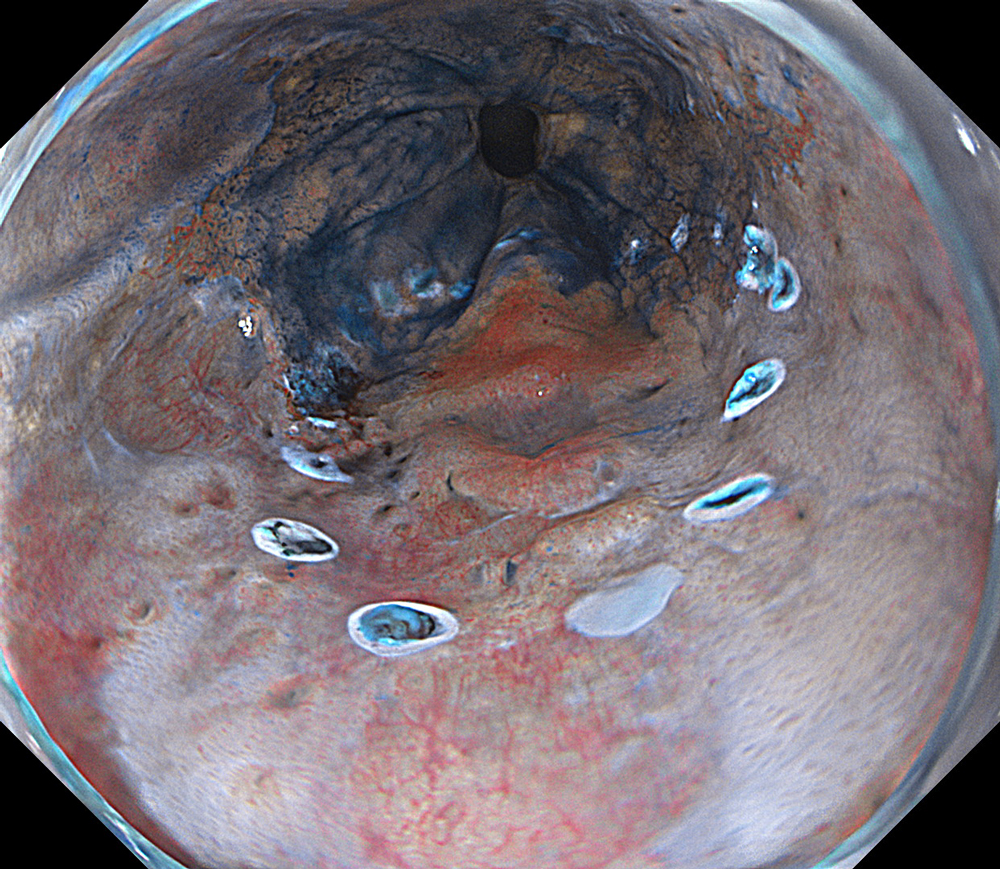
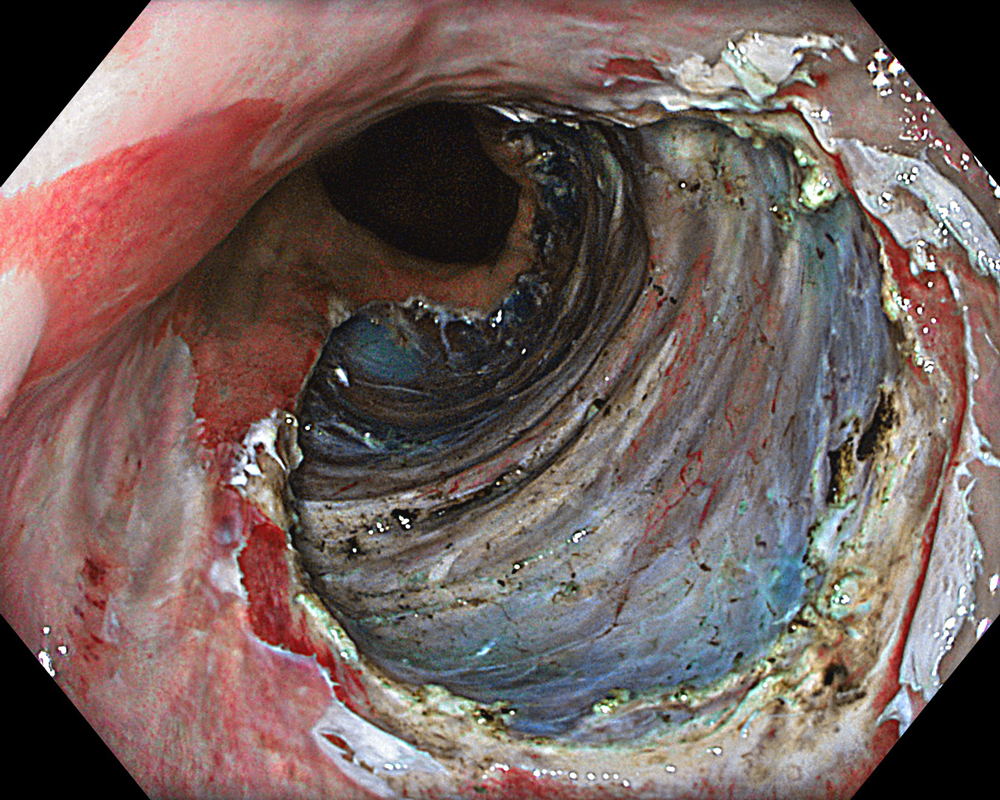
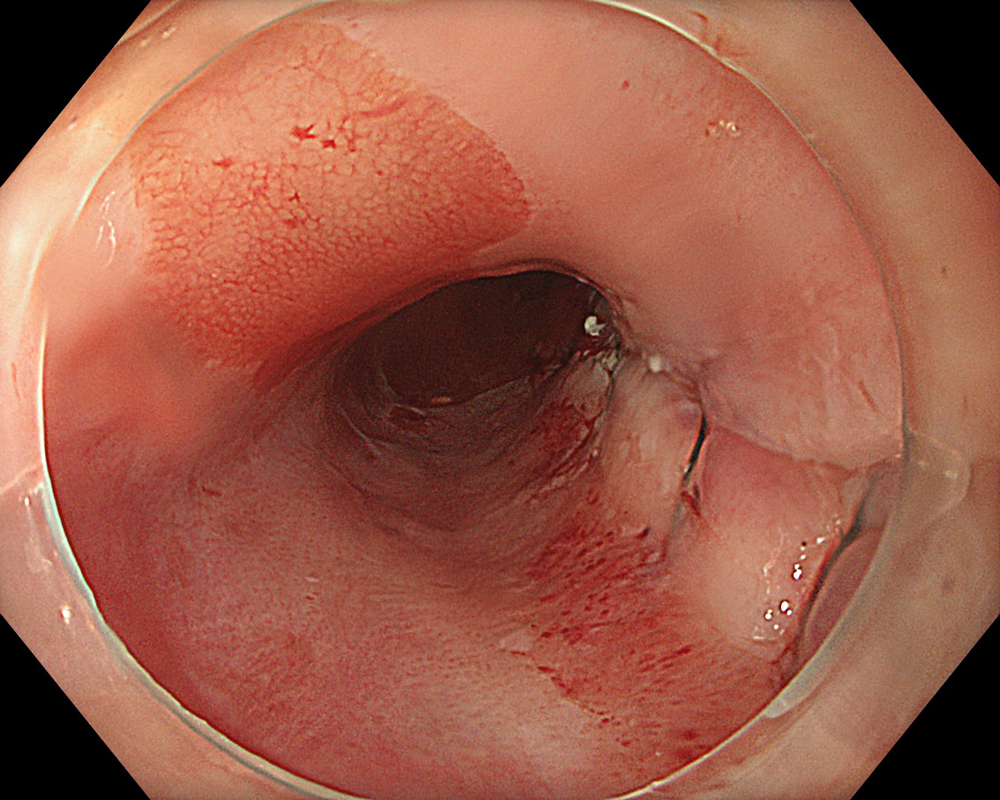
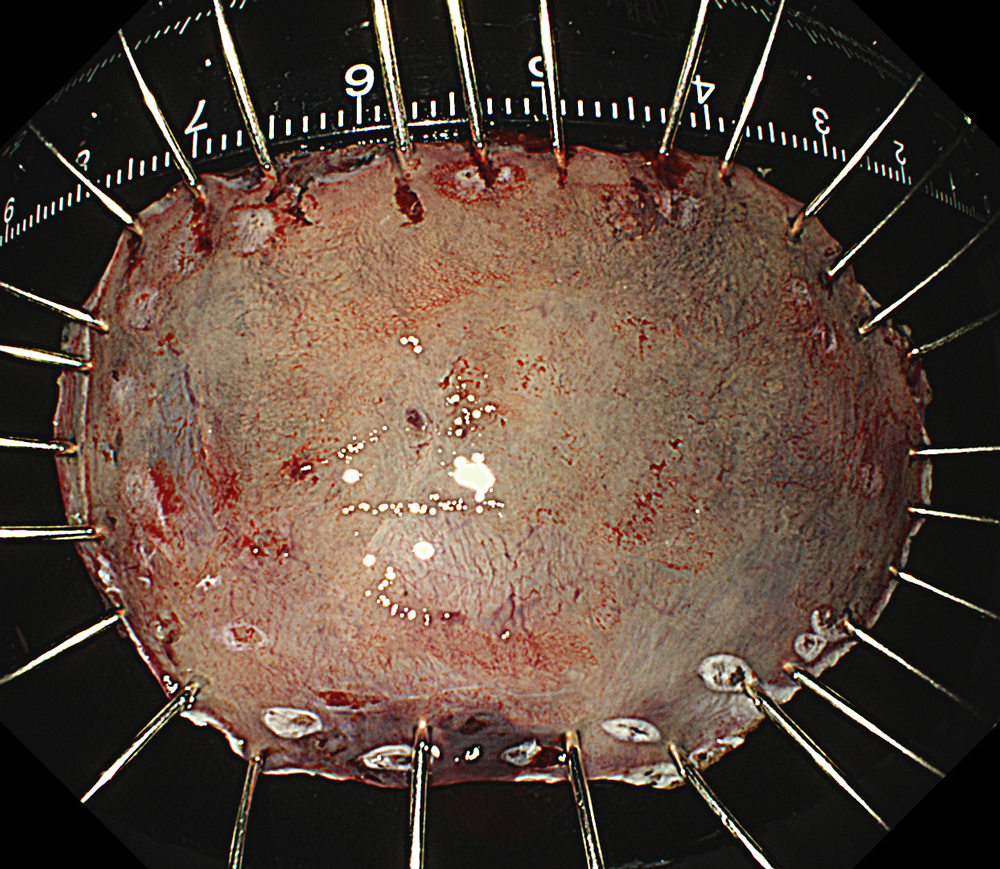
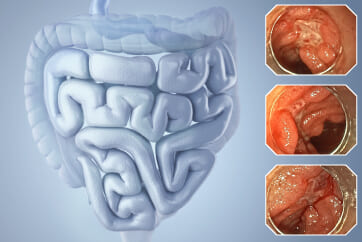
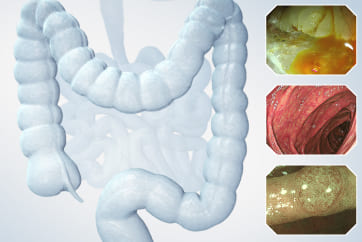
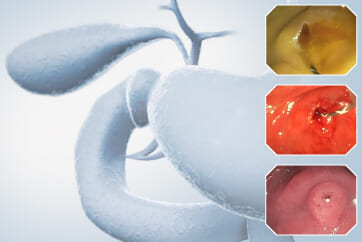
An 84-year-old male patient, dependent on proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and receiving antiplatelet therapy for coronary artery disease, with a known diagnosis of Barrett’s esophagus, underwent endoscopic evaluation using an GIF-XZ1200 endoscope. In WLI mode, a reddish area was identified at the squamocolumnar junction. In TXI mode, the borders of this area were more clearly delineated. In NBI mode, the area appeared brownish and was further evaluated under water immersion with optical magnification. This assessment revealed malignant irregularities in the vascular pattern, as well as clearly defined lesion margins. Following conventional chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine, non-stained areas were more distinctly visualized in TXI mode, and marking was performed under this mode. For therapeutic purposes, ESD was performed using an GIF-EZ1500 endoscope. Before mucosal incision, submucosal injection was carried out under RDI mode to minimize the risk of accidental contact of the sclerotherapy needle with large vascular structures, thereby reducing the likelihood of submucosal hematoma formation prior to incision. Subsequently, stepwise submucosal dissection was performed using a Dual Knife. During dissection, the use of TXI mode was found to be helpful in differentiating the submucosal layer. The procedure was completed successfully, and the ESD specimen was retrieved. To minimize the risk of delayed adverse events, the resection site was closed using barbed sutures.
Overall comment
This case highlights the value of advanced imaging modalities-particularly TXI and NBI-in enhancing lesion characterization at the squamocolumnar junction. The combination of underwater evaluation and optical magnification enabled precise delineation of malignant features and accurate lesion mapping. TXI mode proved especially useful in defining unstained areas after chromoendoscopy, facilitating targeted marking. The integration of RDI mode for submucosal injection minimized vascular injury risk, while meticulous ESD followed by barbed suture closure ensured both therapeutic efficacy and procedural safety. This approach underscores how next-generation endoscopic platforms can optimize diagnosis, staging, and treatment outcomes in Barrett’s-associated neoplasia.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
- Keyword
- Content Type