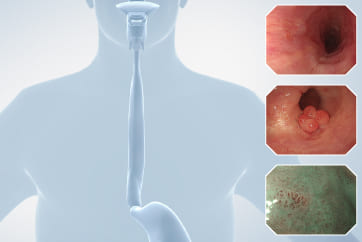
Esophageal Case 7

Haruhiro Inoue, MD, PhD
Digestive Disease Center
Showa University Koto Toyosu Hospital
Scope : GIF-XZ1200
Case : Superficial esophageal cancer
Organ : Upper thoracic esophagus
Patient Information : M, 60s
Medical History : Nothing relevant
Non-magnifying NBI

In non-magnifying Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) observation, the lesion can be recognized as a clear brownish area. This observation mode ensures a high level of brightness not only throughout the lesion, but also in the deep areas of the esophagus, facilitating detection of a suspected lesion. Because there is no need to increase the light intensity in NBI observation, the problem of halation is prevented.
TXI

When observed in the Texture and Color Enhancement (TXI) mode, images can be obtained that feature optimized texture enhancement, color enhancement, and brightness correction. Here we see an extremely red, slightly elevated lesion. Unevenness can also be seen within the lesion.
High-magnification NBI (1)

Assessment of IPCLs is possible with high-quality images in NBI observation at high magnification. Images with very little blur can be obtained, which makes possible IPCL observation with high accuracy. The “tetrad criteria” of IPCLs, namely, dilation, tortuosity change in caliber, and various shapes, can be confirmed.
High-magnification NBI (2)

Assessment of IPCLs is possible with high-quality images in NBI observation at high magnification. Images with very little blur can be obtained, which makes possible IPCL observation with high accuracy. Here, abnormal vessels that do not show a loop-like formation can be clearly recognized. High-magnification NBI is considered optimal for invasion depth analysis.
Overall comment
The use of the new EVIS X1 endoscopy system and its new GIF-XZ1200 scope has enabled us to detect lesions and improve qualitative diagnosis. Detecting esophageal lesions using Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) observation has become commonplace, but distant points in the esophagus remain hidden in darkness due to its anatomical narrowness. The EVIS X1, however, can illuminate even the deepest parts of the esophagus, making it possible to recognize a lesion as a clear brownish area and thus facilitating easier detection of lesions. Also in white light observation, uniform light intensity is available throughout the lumen, which has allowed us to observe the site with clear colors and contrasts with respect to the surrounding normal mucosa, as well as to confirm the absence of visible vessels in the lesion.
Using the new color enhancement technology called Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging (TXI) enables you to obtain optimized images featuring texture enhancement, color enhancement, and brightness correction. In the case discussed above, the lesion exhibited strong redness and slight elevation under white light, and we were able to clearly view the unevenness within the lesion.
Moreover, thanks to the increased magnification power (125x max.) and decreased color shift achieved by optimal image processing using a high-speed field sequential method, we were able to perform reliable evaluation of intrapapillary capillary loops (IPCLs) using this new system’s NBI magnifying observation. The four morphological changes (IPCL Type V-1, JES Classification B1), namely, dilation, tortuosity, change in caliber, and various shapes (i.e., the “tetrad criteria”), could all be confirmed. Abnormal vessels lacking a loop-like formation could also be observed in detail (IPCL Type V-2, JES Classification B2).
In general, we think that the combination of the EVIS X1 system and GIF-XZ1200 scope will significantly increase the quality of endoscopic diagnosis of esophageal cancer.
Co-editor:
Dr. Yuto Shimamura
Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Koto Toyosu Hospital
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
- Content Type

観察.jpg)