Gastric Case 8

Prof. Dr. Liu Zhiguo
China
Scope: GIF-H290Z
Case: Early stomach cancer (M cancer)
Organ: Stomach
Patient Information: M, 50s
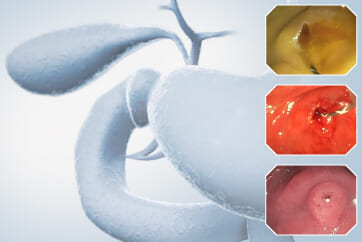
Medical History: Early esophageal cancer was resected by ESD 10 years ago, the patient was followed up since then. A 0-IIc lesion 10mm was found in lesser curvature below the cardia 1 year ago with biopsy confirming atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia, a biopsy was taken 1 month ago suggested epithelial low-grade neoplasia.
Case video
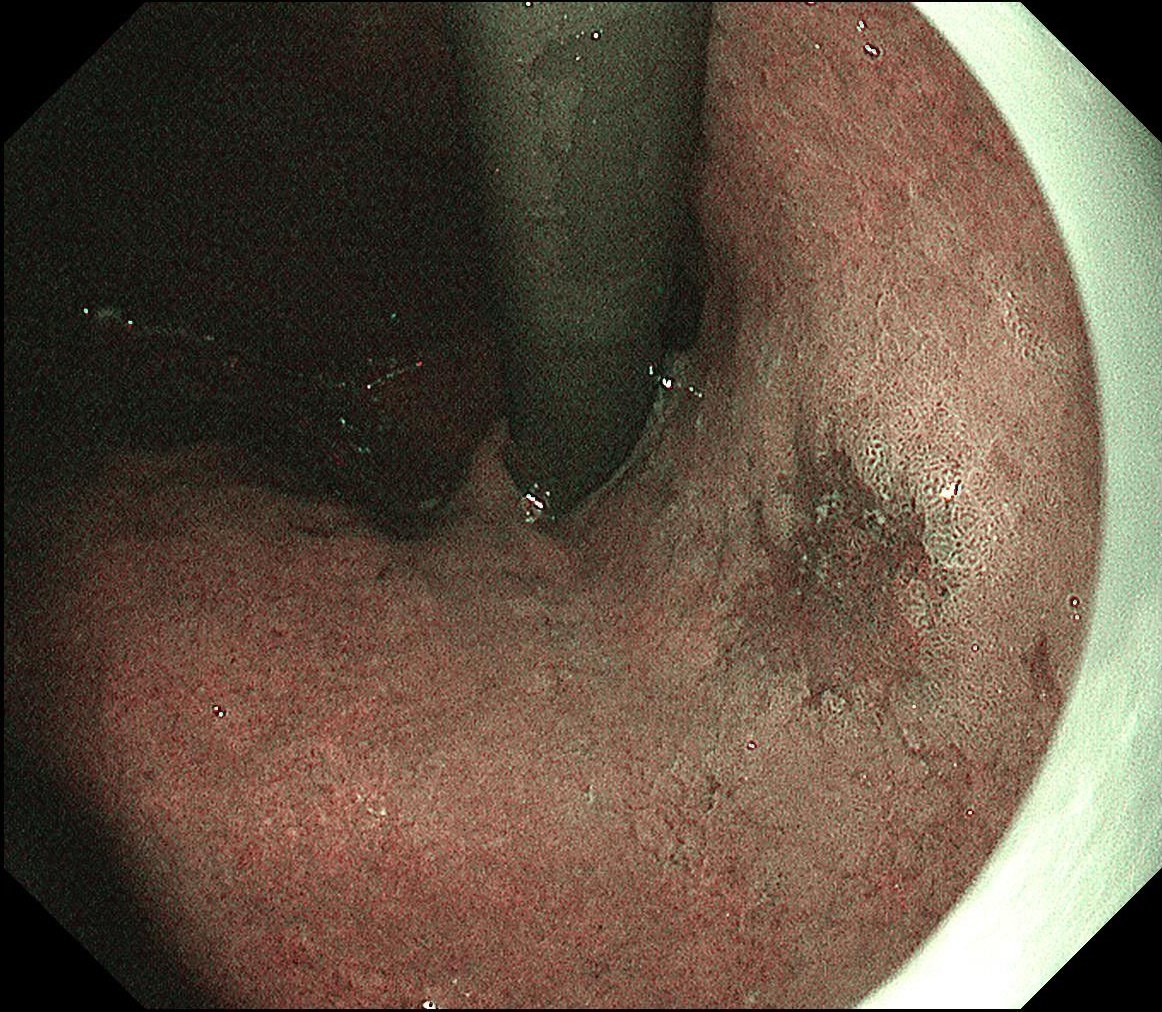
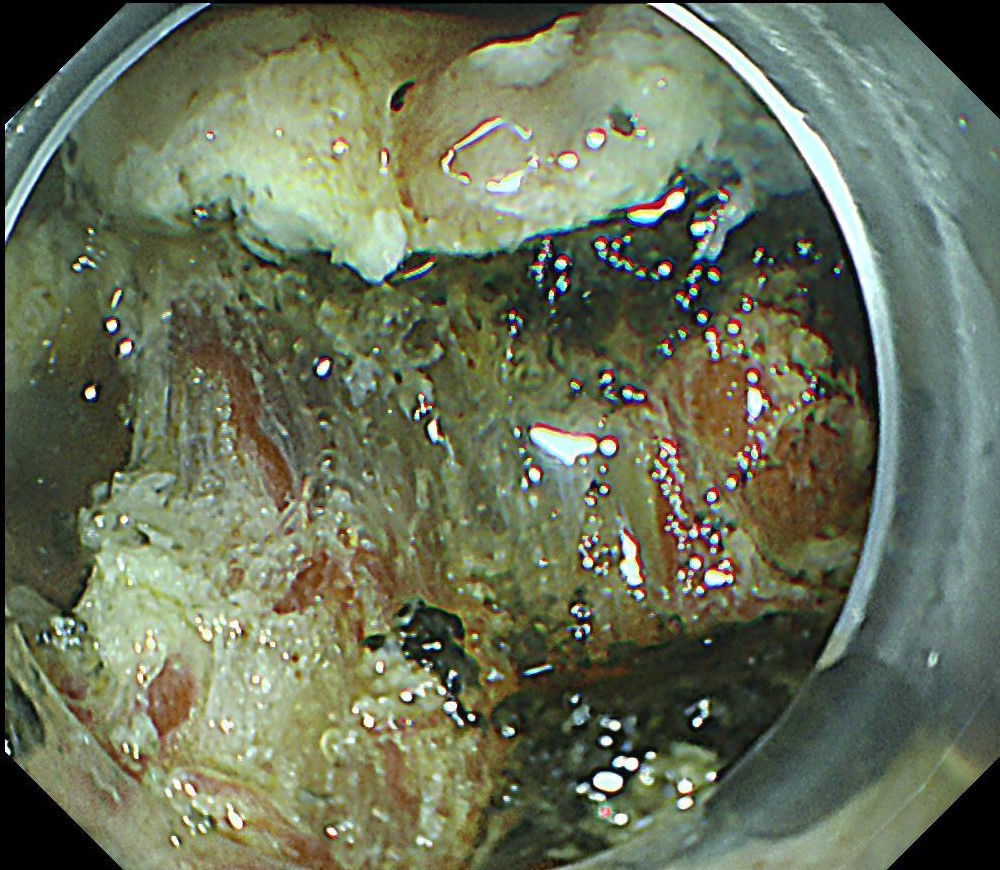
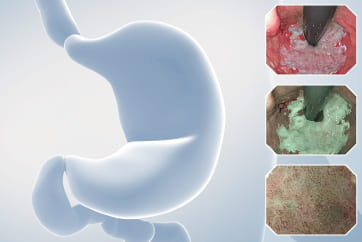
ESD under RDI showed a possibility to effectively improve the visibility of submucosal blood vessels.
Overall Comment
This is a case of gastric cancer after HP eradication found after 10-year follow-up after ESD resection for early esophageal cancer.
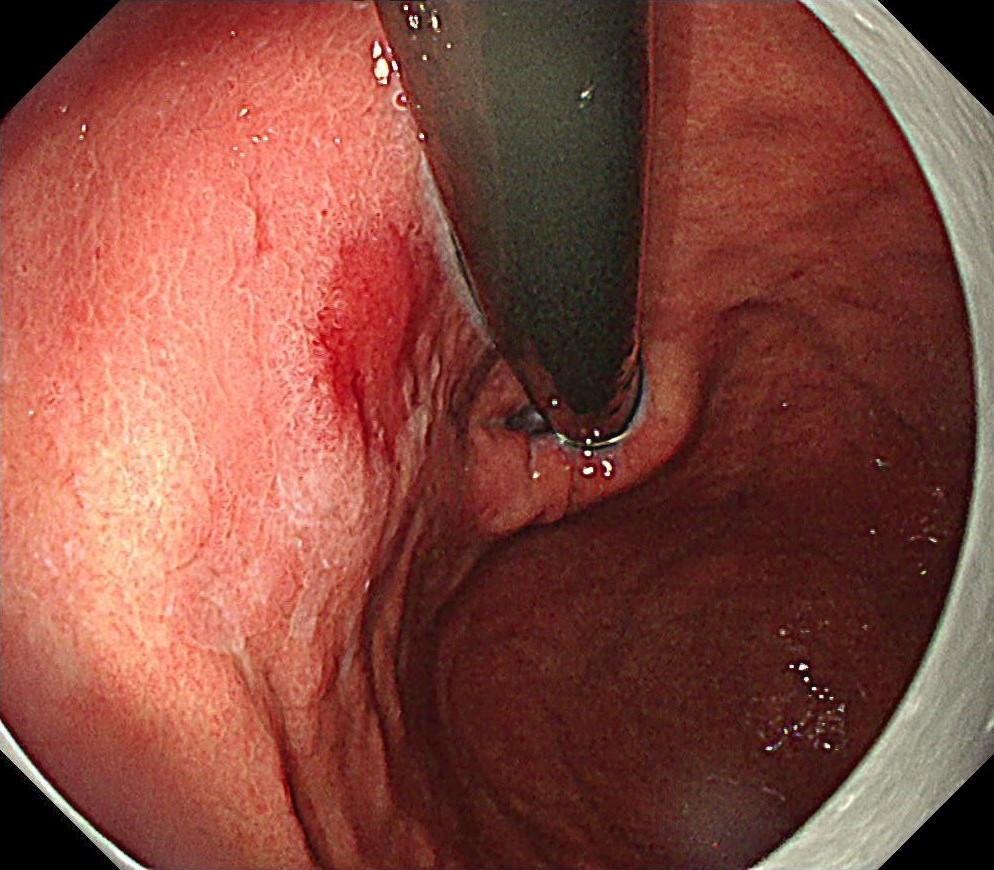
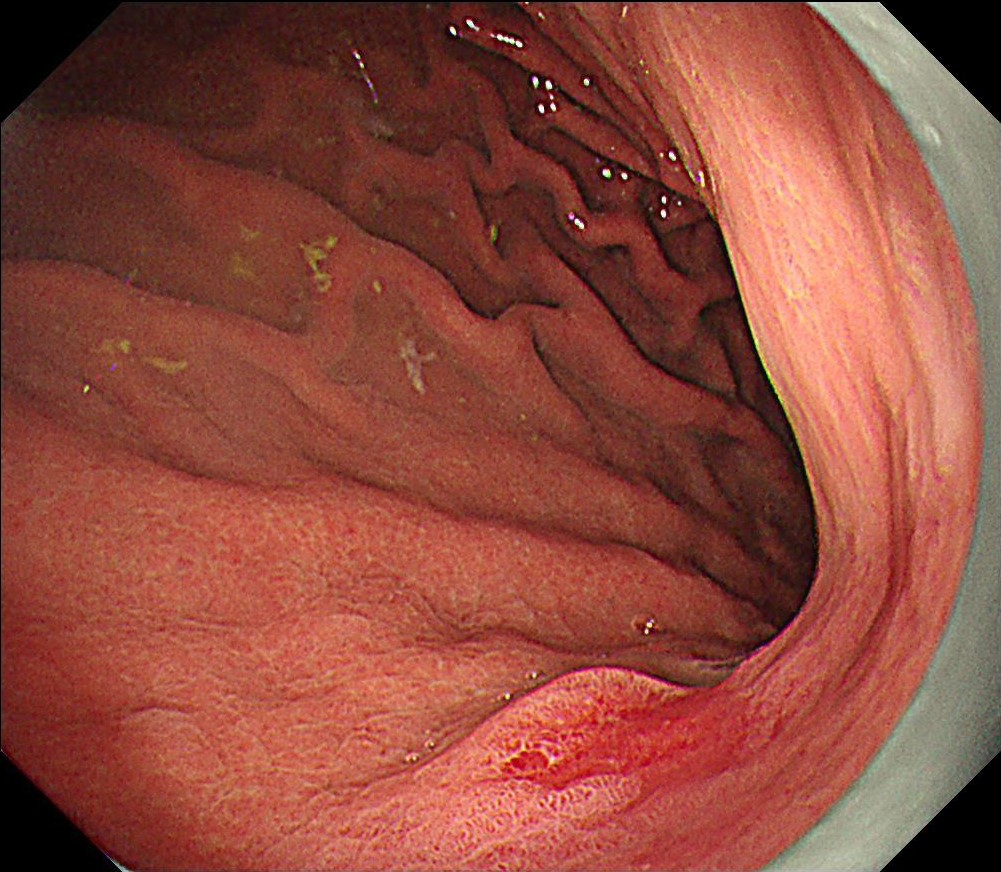
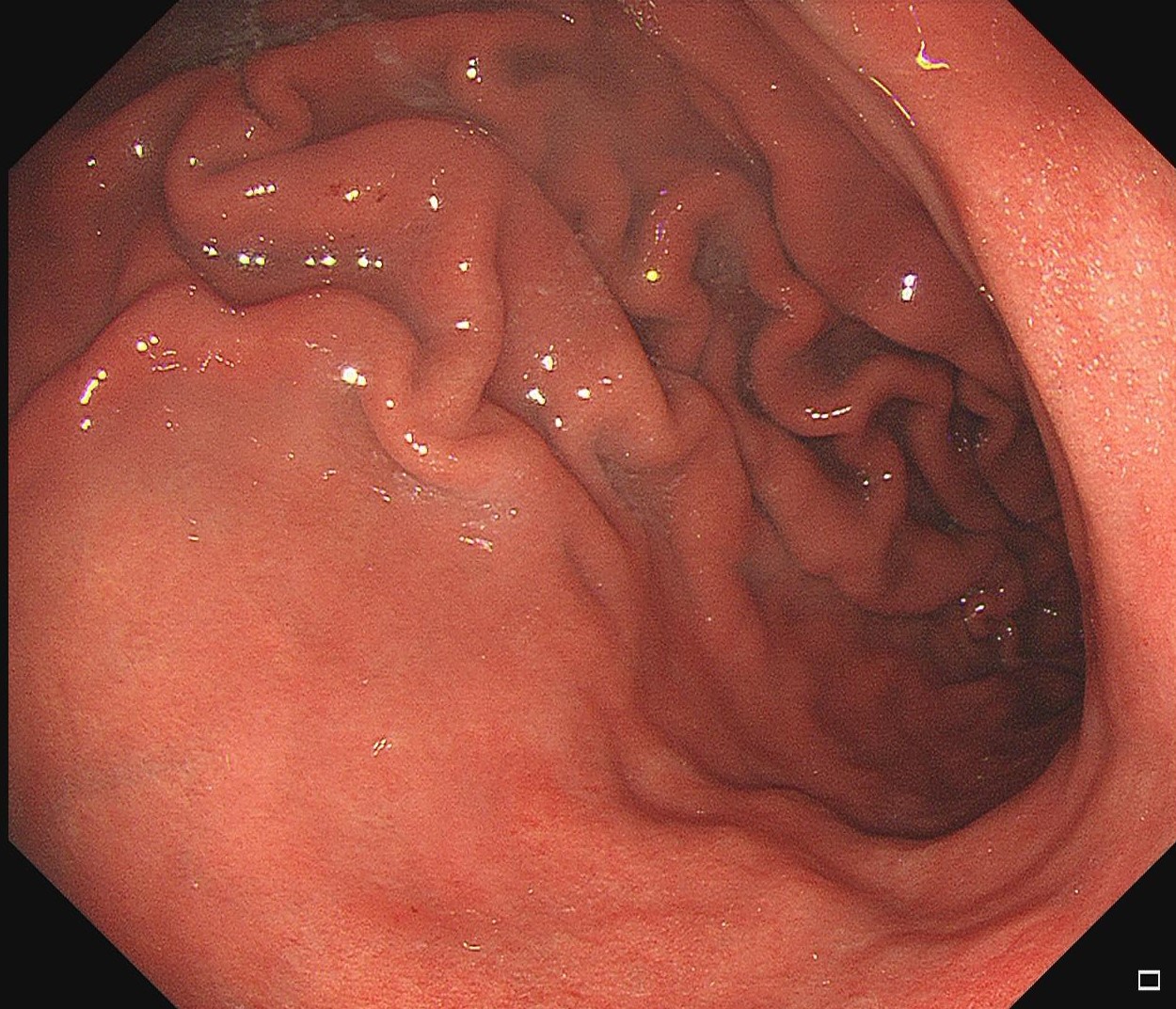
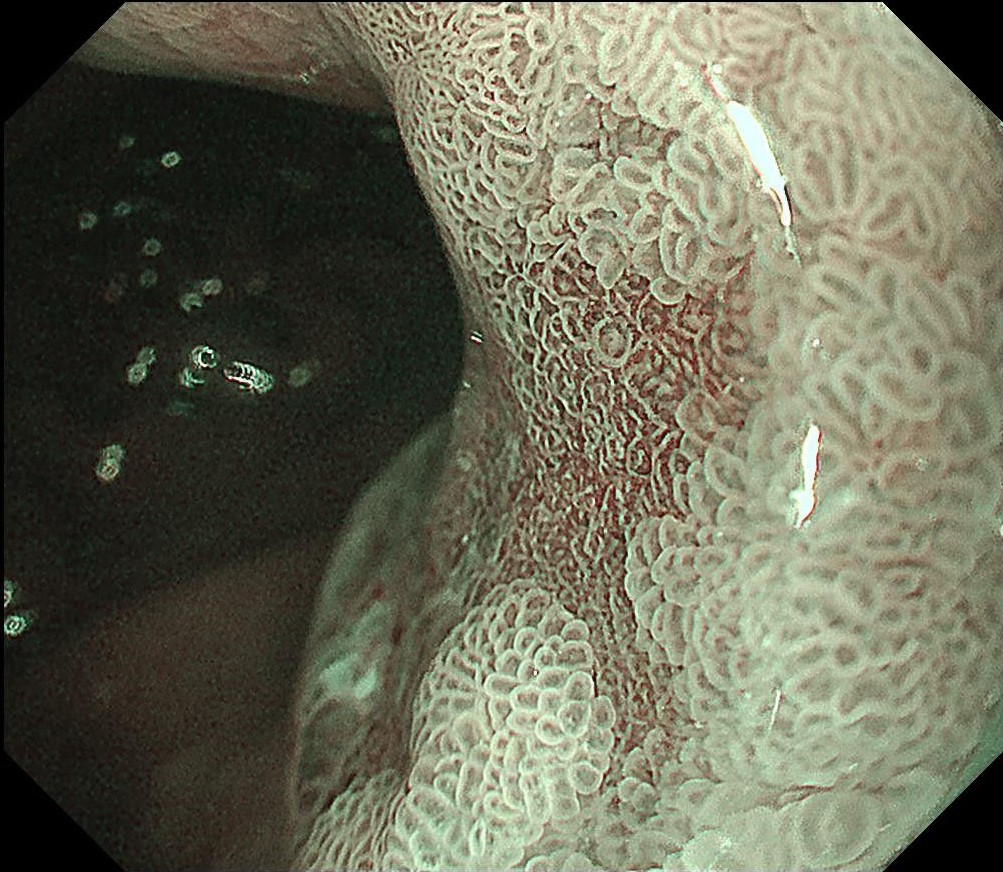
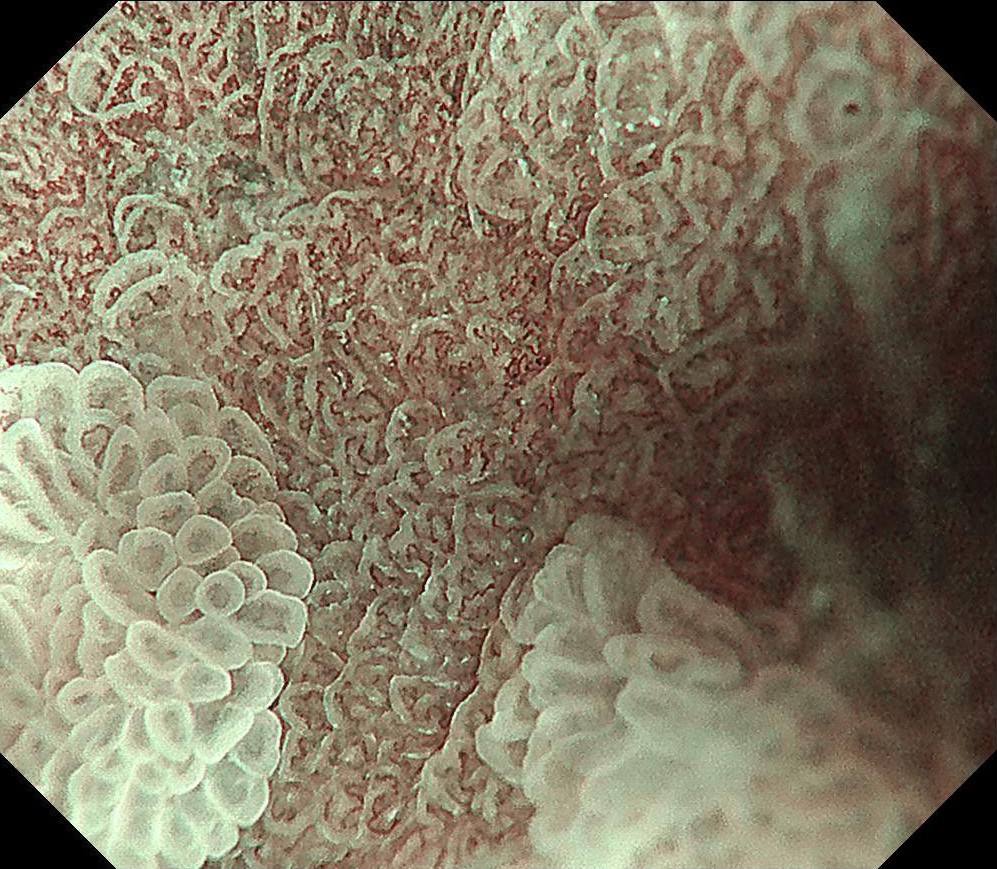
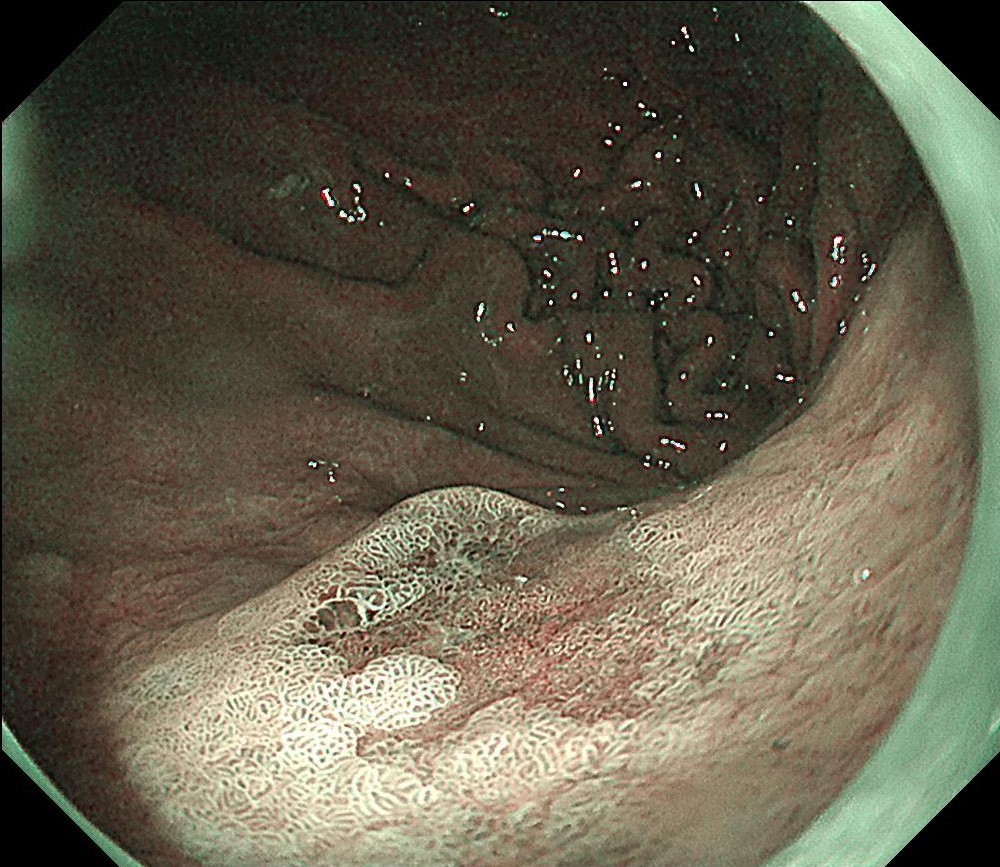
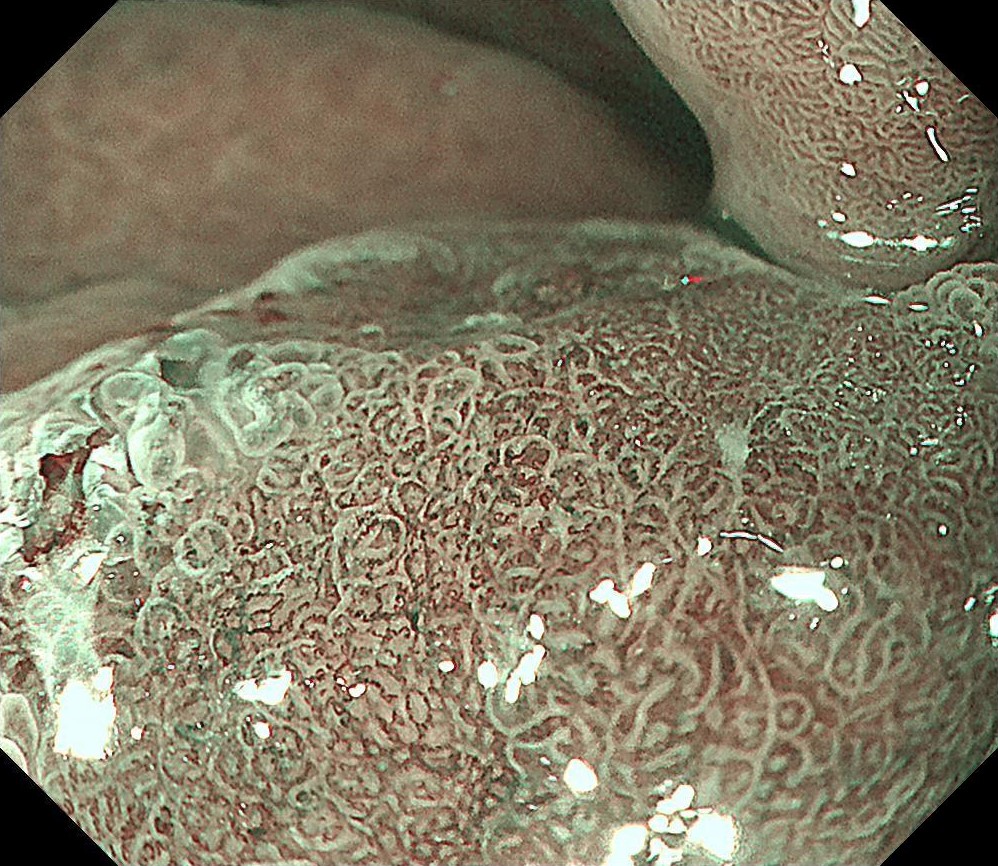
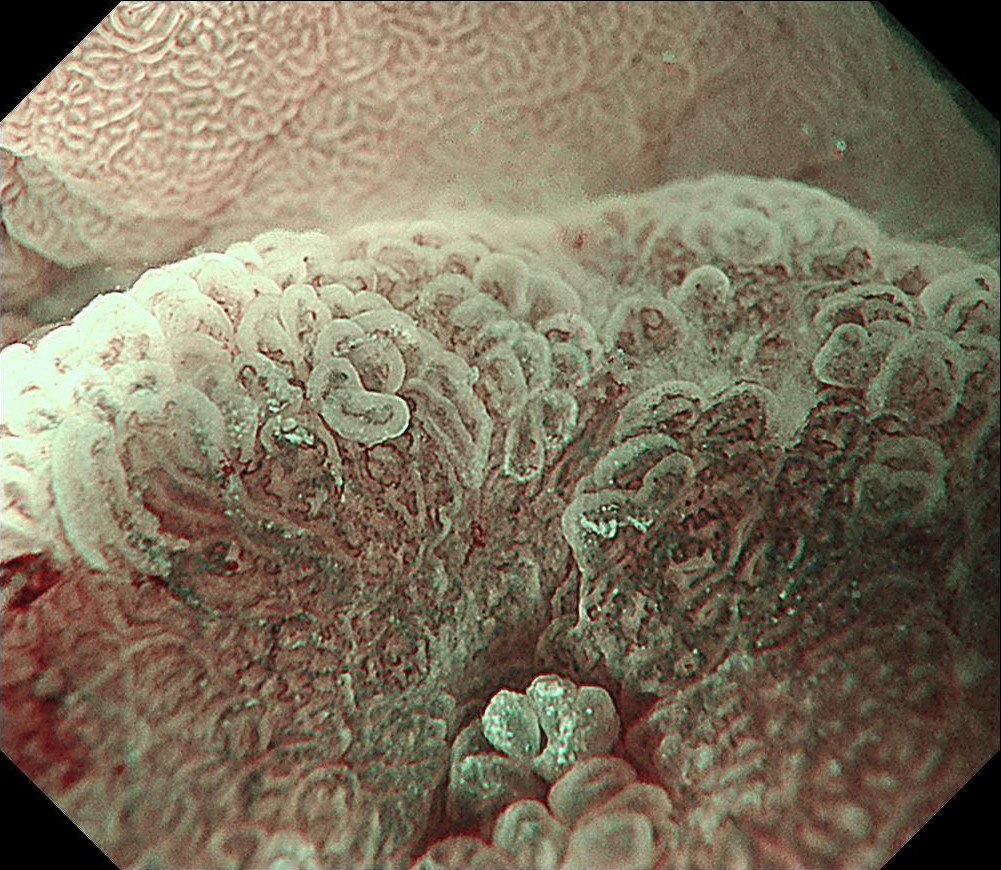
During the follow-up, breath test was negative, the level of pepsinogen I was significantly reduced (30-40ng/ml), and atrophy was graded as C3. One year before the ESD procedure, a reddish 0-IIc lesion was found below the cardia, and biopsy suggested atrophic gastritis, and another biopsy 1 month ago suggested epithelial neoplasia with low atypia, which was considered to be a neoplastic lesion. Elevation of anal side was clear after 1-year follow-up, and the lesion showed significant redness, so endoscopic resection was recommended. The possibility of submucosal infiltration was not excluded due to the macrotypic manifestion of the lesion.
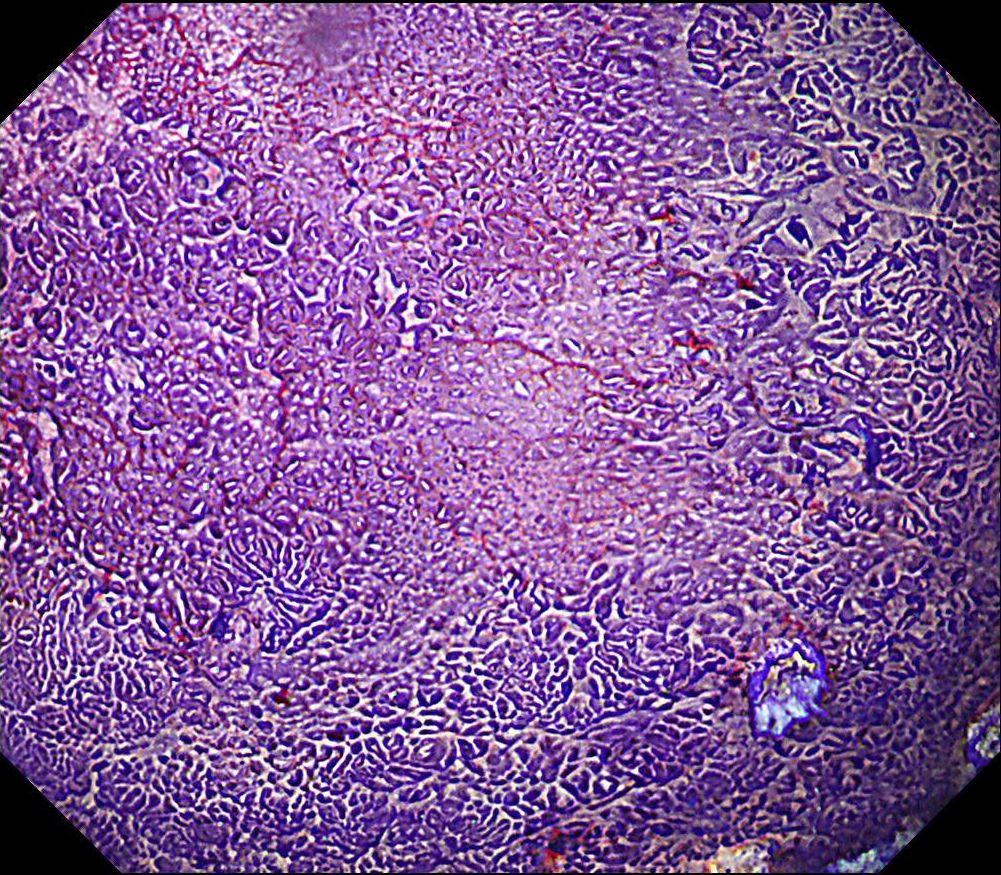
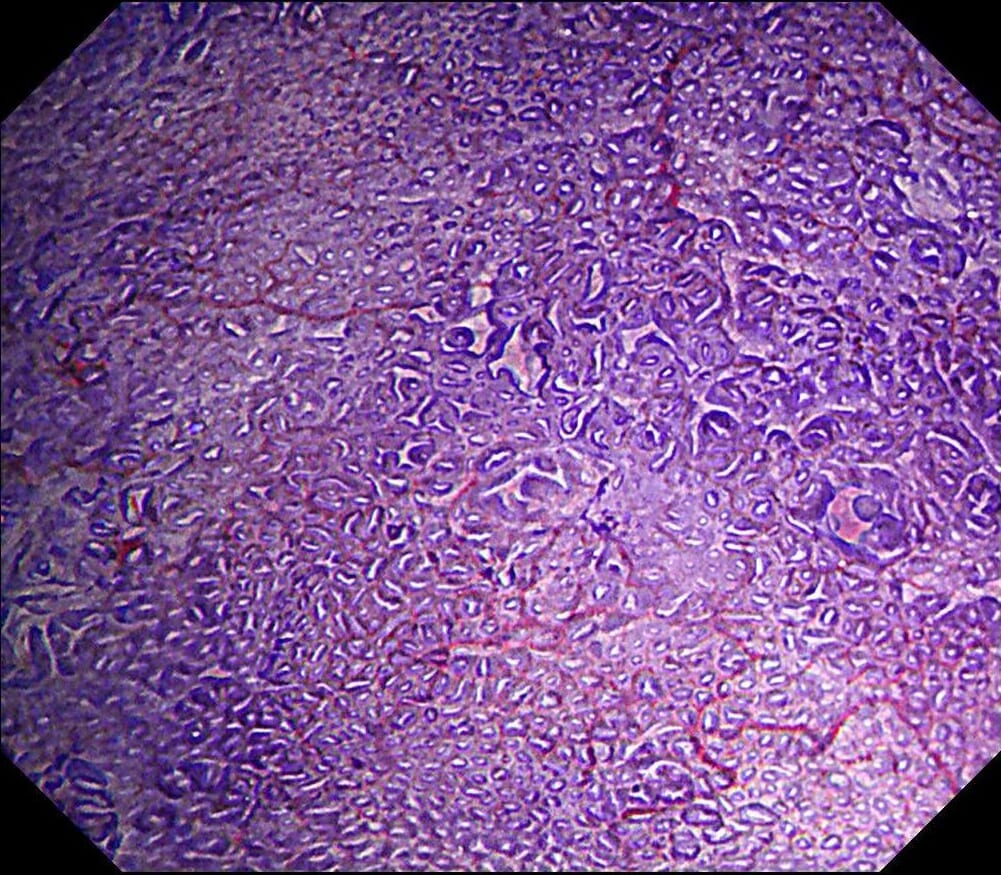
The pathology result of the resected lesion showed intramucosal carcinoma (tub1>pap, MM, pHM0, pVM0, UL-, ly-, v-, pT1aNx). The lesion was well demarcated under non-magnifying observation of resected specimen, but magnifying observation showed hyperplastic glands mixed with carcinoma, consistent with gastric cancer after Hp eradication. Elevation on the anal side was considered an artifact caused by the accumulation of adipose tissue and dilated submucosal blood vessels. Due to the rich vascularity of the lesion, massive bleeding occurred during resection, and RDI helped to distinguish the submucosal vessels, especially the bleeding point to facilitate better hemastatis in time.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
Dr. Khanh Do-Cong Pham Case 9: Duodenal second part tubular adenoma with high grade dysplasia
Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan
- Keyword
- Content Type