Duodenum Case 9

Prof. Dr. Fatih Aslan
Koc University Hospital
Istanbul, Turkey
Scope: GIF-XZ1200, GIF-EZ1500
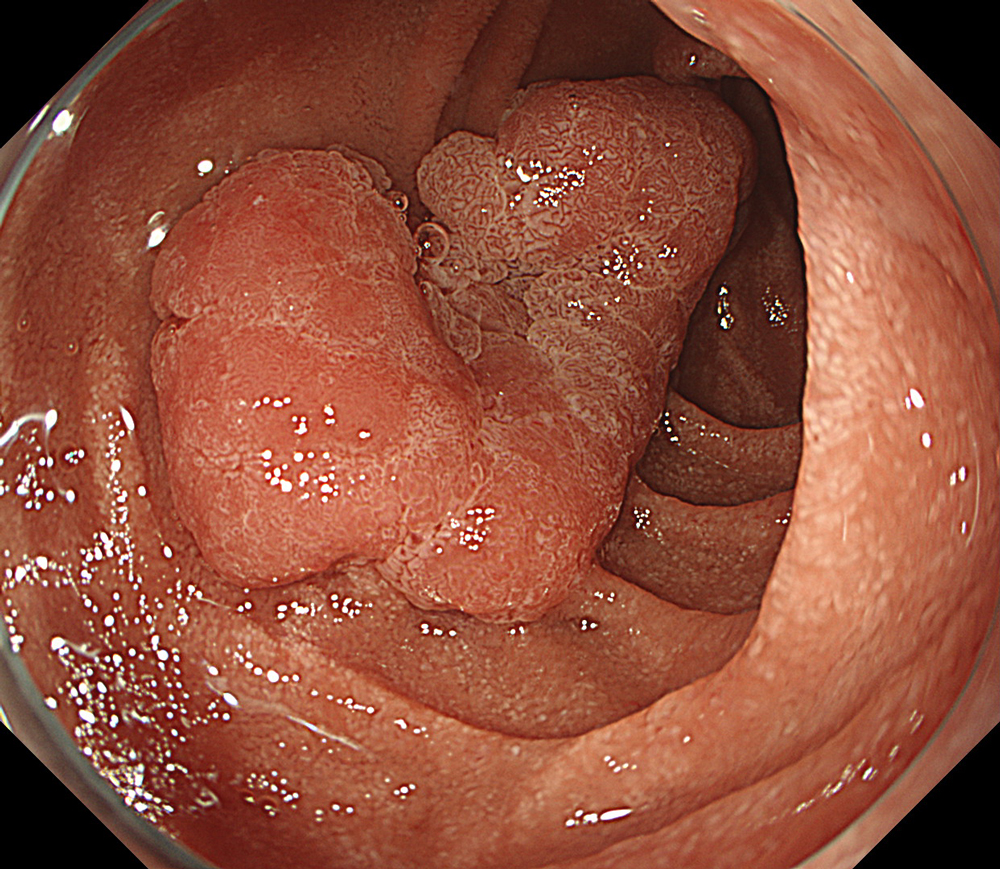
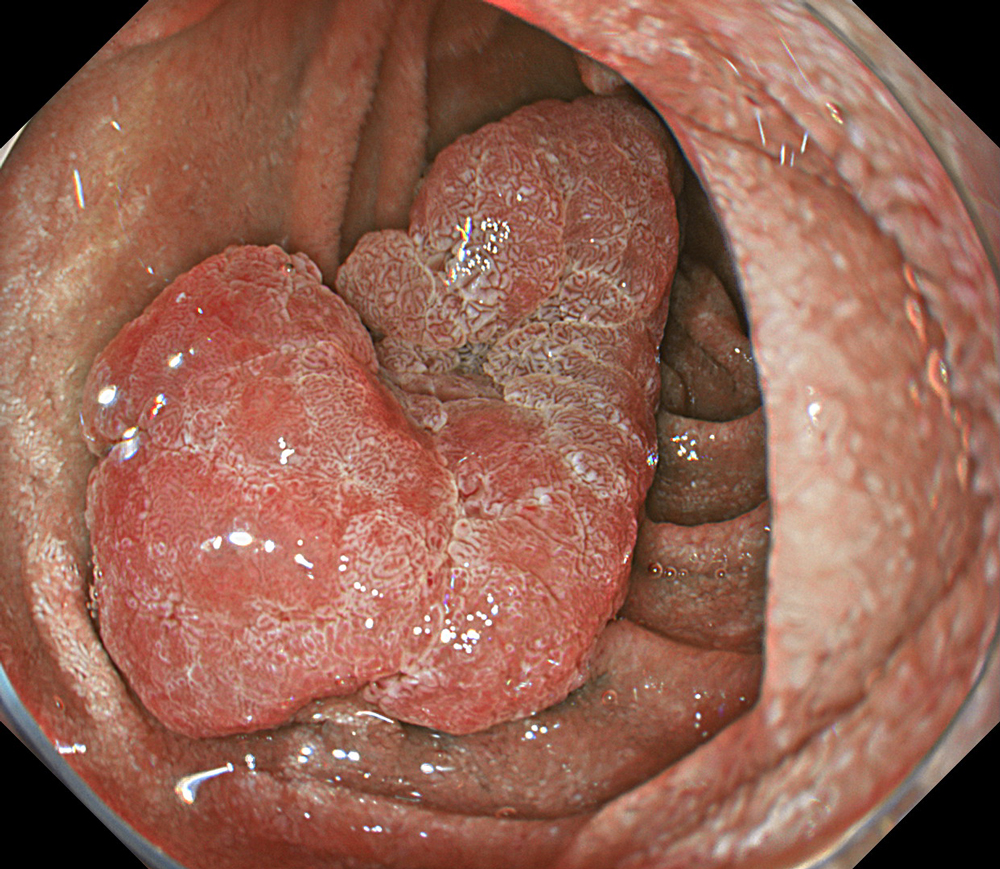
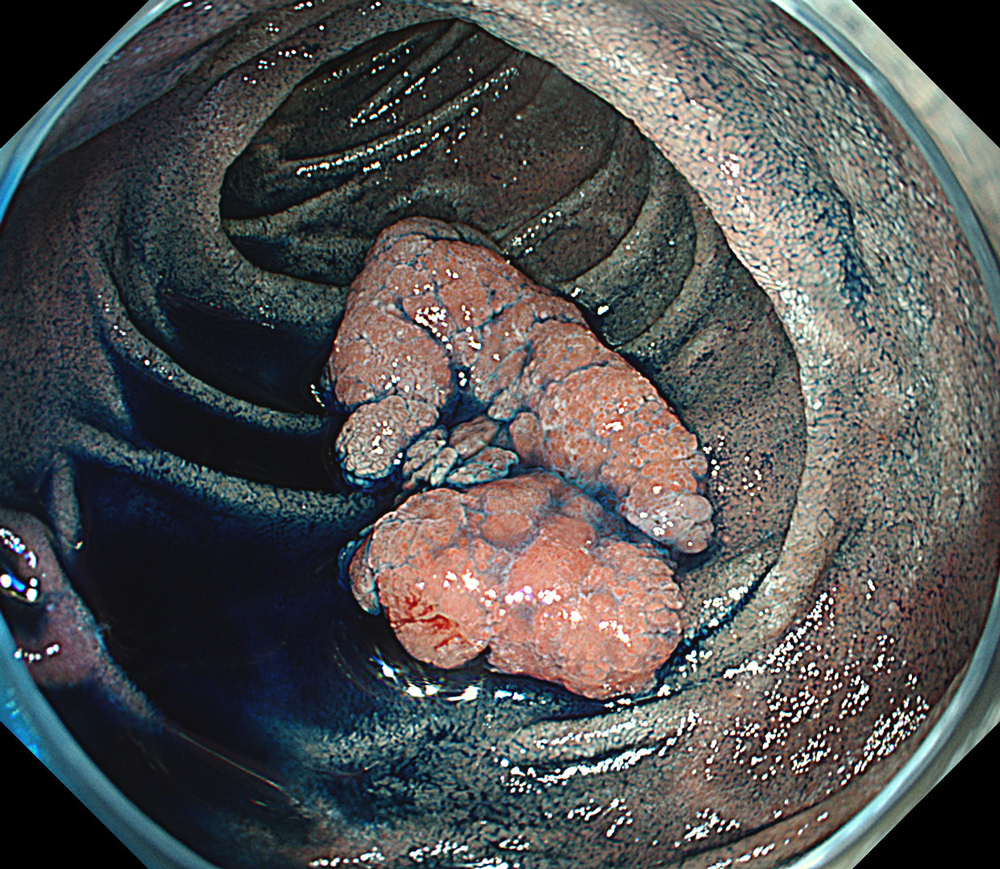
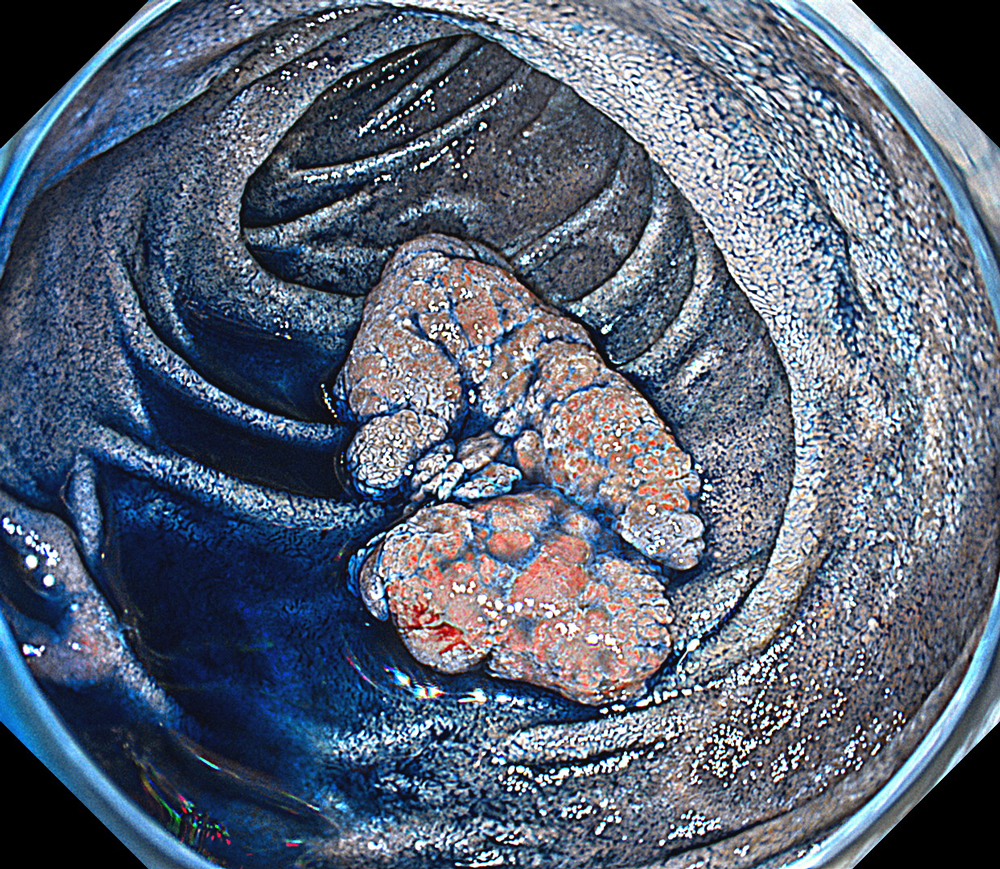
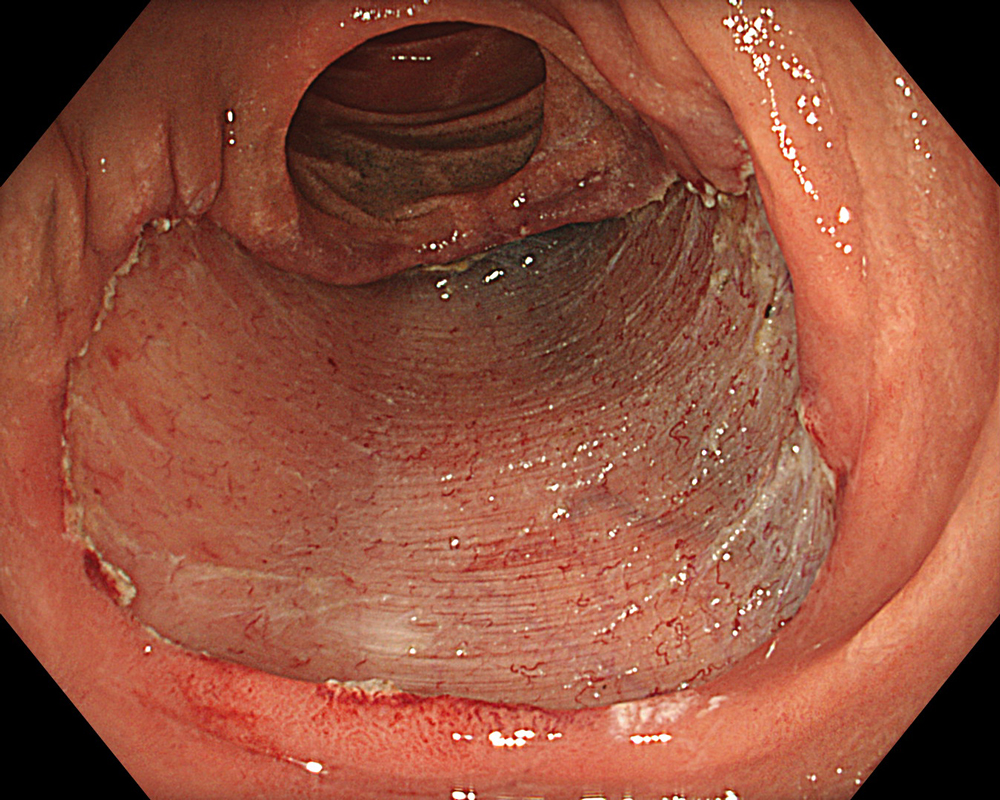
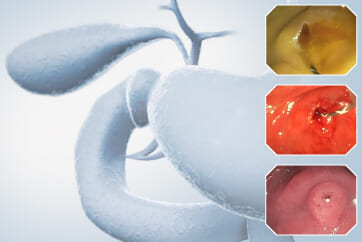
Case: Duodenal second part tubular adenoma with high grade dysplasia
Organ: Duodenum Second Part
Case Video
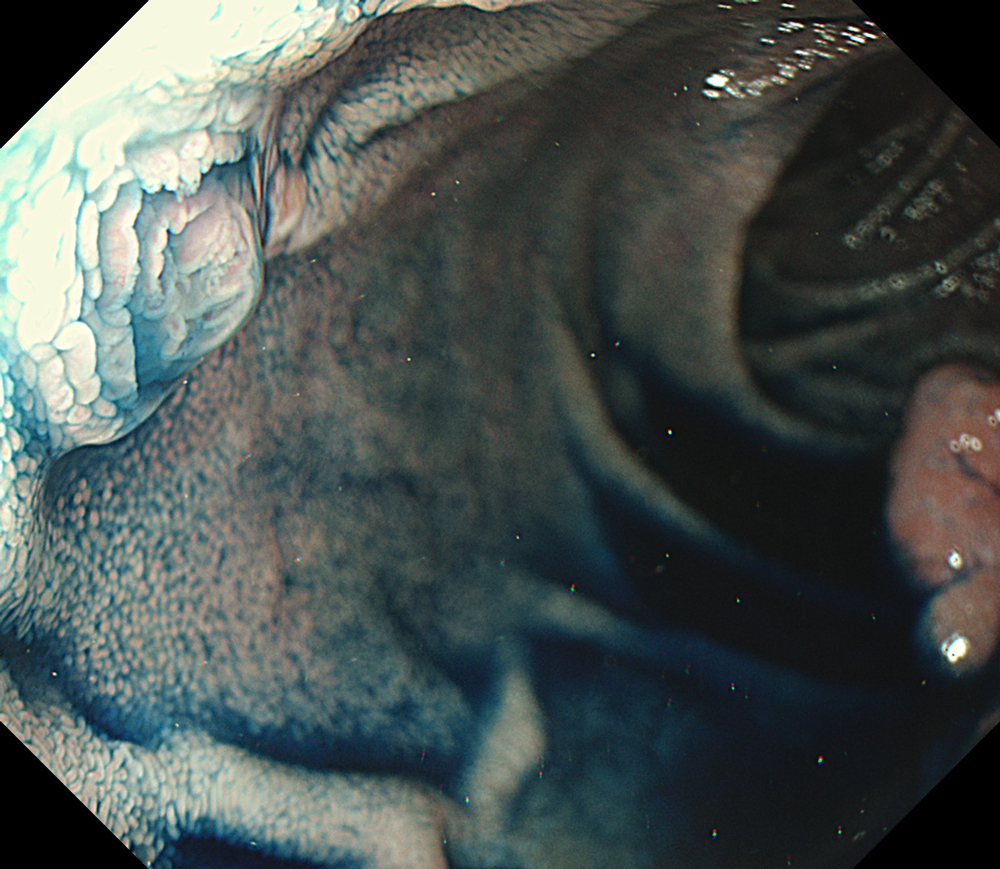
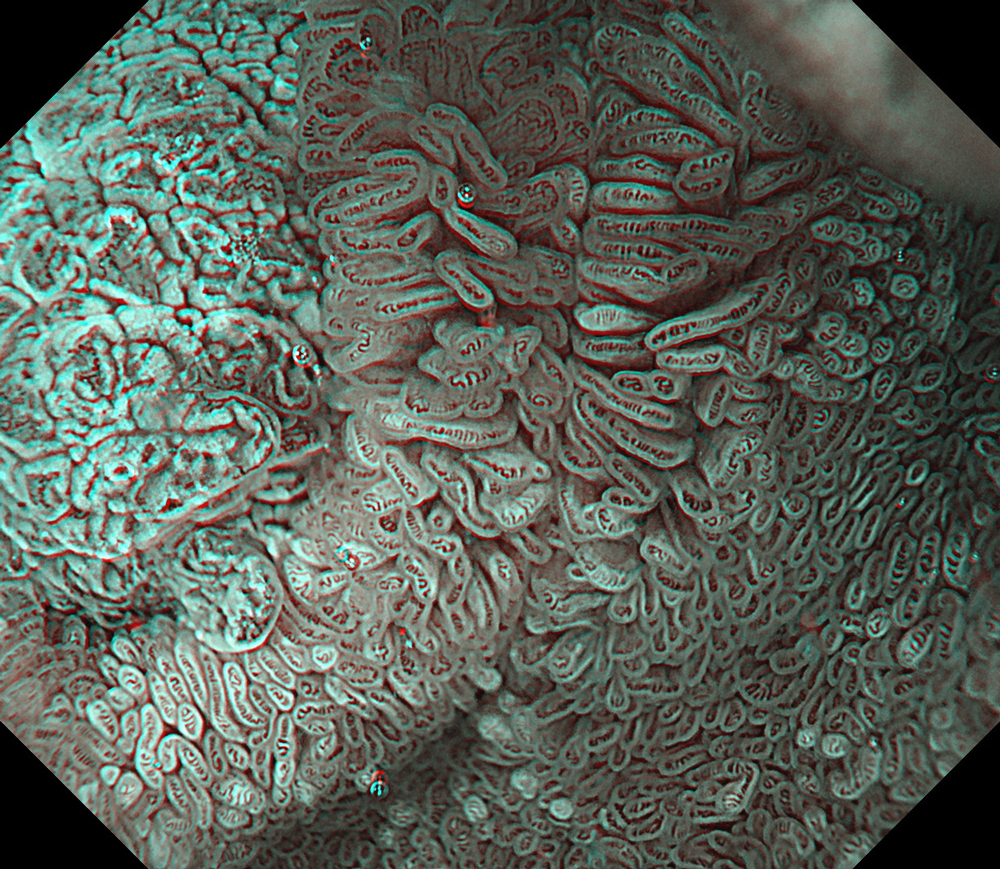
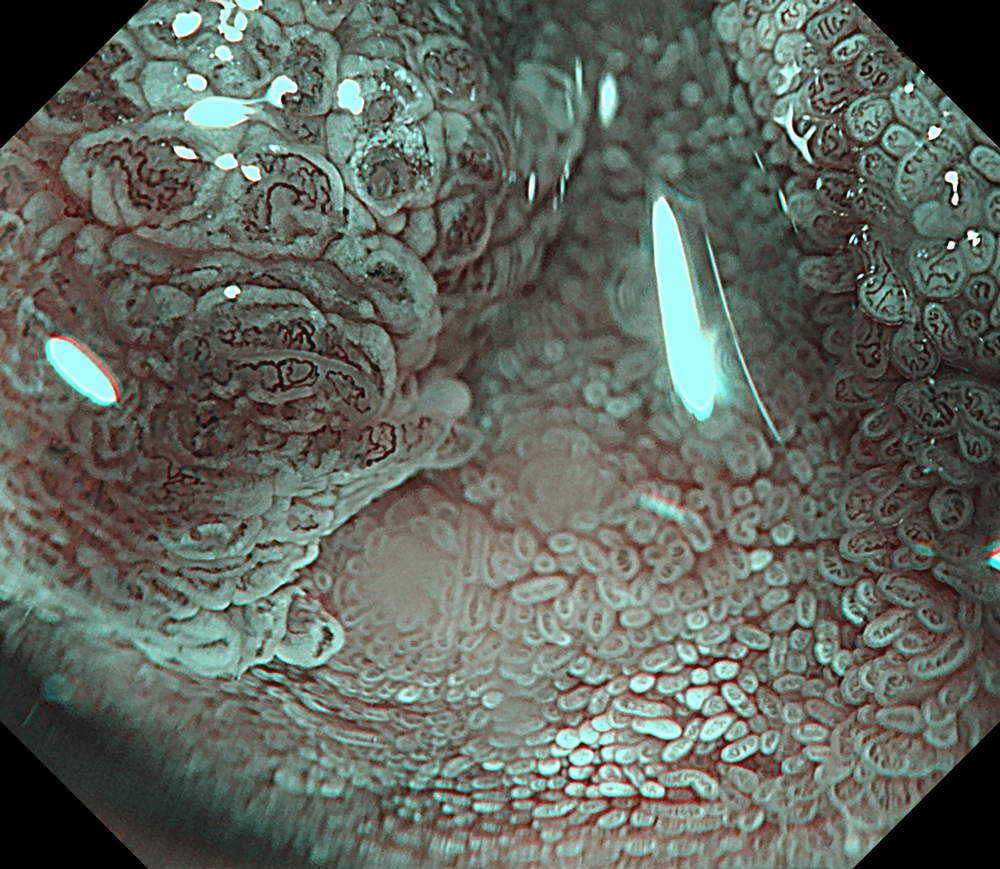
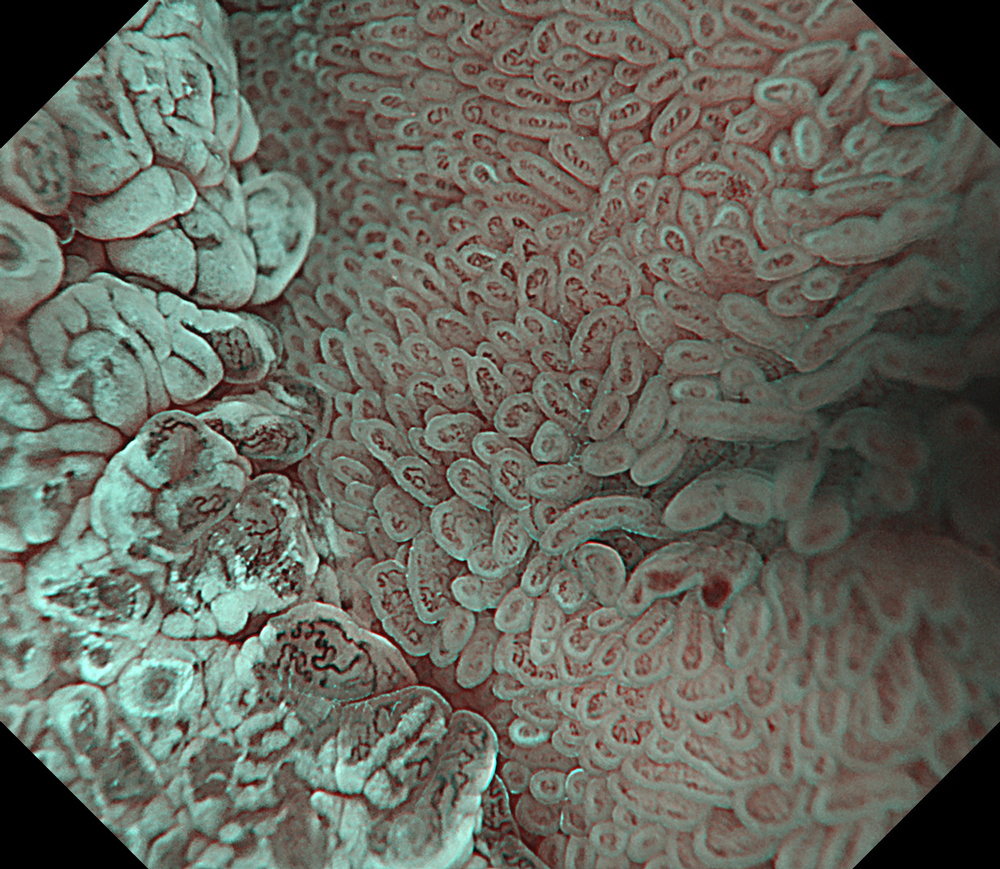
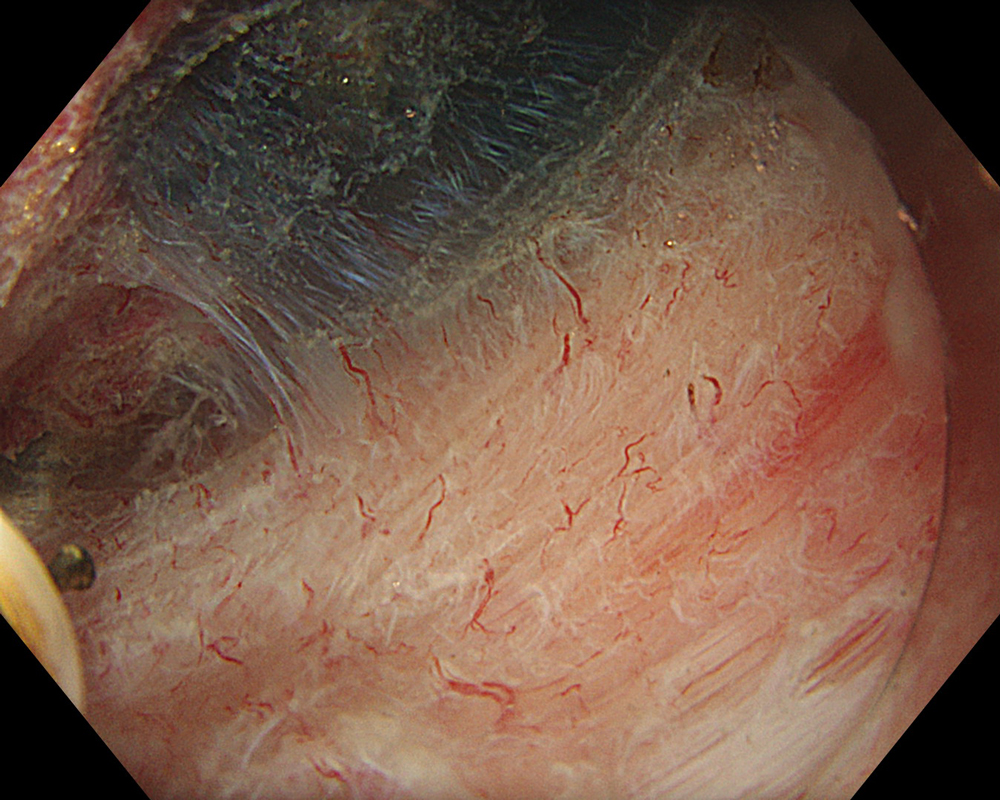
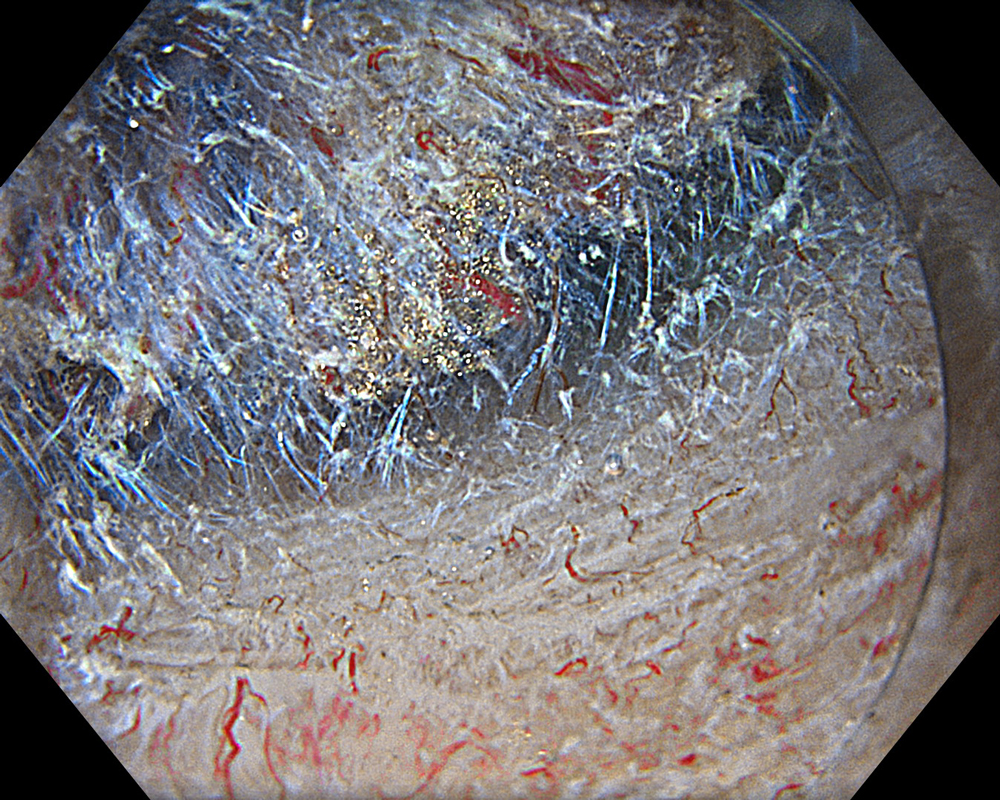
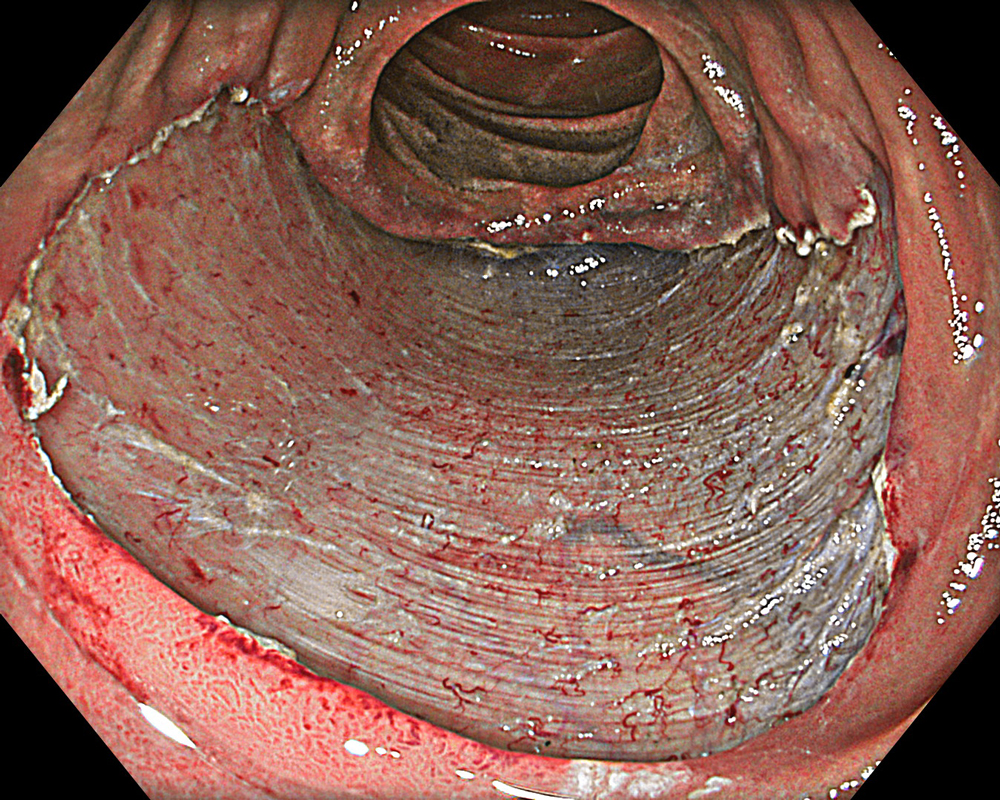
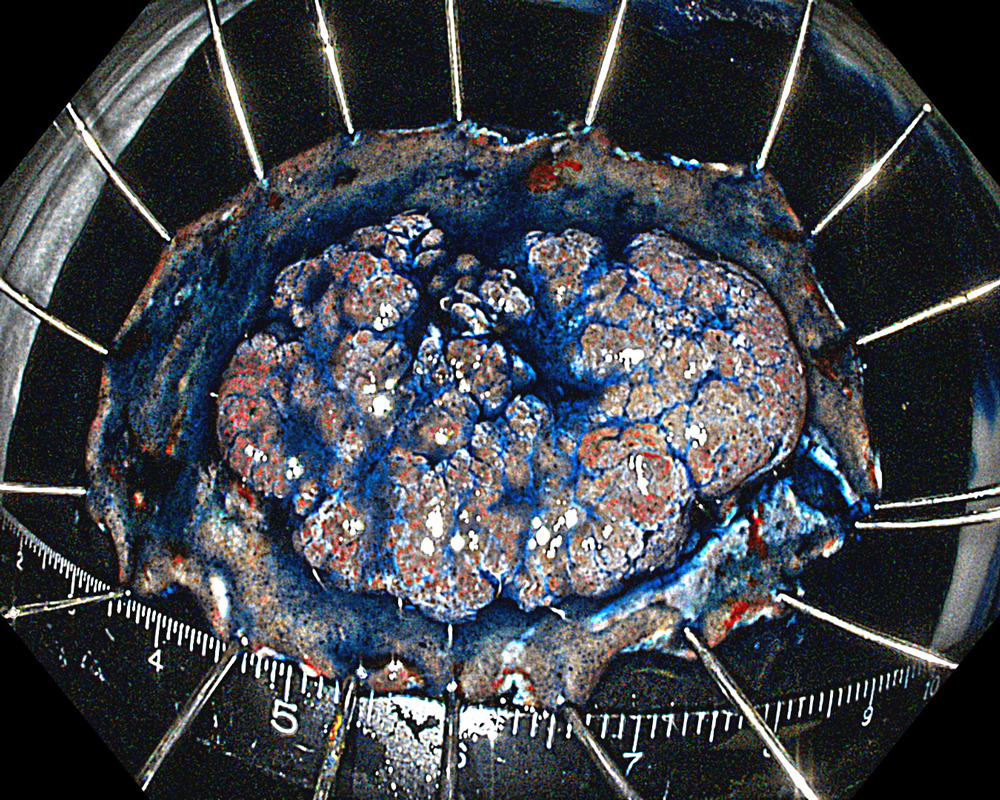
Pre-procedural assessment of the lesion was performed using the GIF-XZ1200 endoscope. Thanks to its manual optical magnification capability, the entire surface of the lesion was thoroughly examined, aided by the magnifying effect of water immersion. Subsequently, a standard Olympus straight hood was attached to the GIF-EZ1500 endoscope, and the ESD procedure was carried out using the water pressure method with a Dual Knife (2.0 mm Knife Length). During the procedure, the contrast enhancement provided by TXI mode was found to be particularly useful for distinguishing the submucosa from the muscularis propria. In addition, the EDOF function of the scope was frequently utilized, enabling close and effective dissection throughout the procedure. These visual advantages are believed to contribute not only to procedural efficiency but also to the prevention of potential adverse events. To minimize the risk of delayed complications such as perforation or bleeding, the resection site was securely closed using absorbable barbed sutures.
Overall Comment
This case highlights the evaluation of an adenoma located in the second portion of the duodenum using various endoscopic imaging modalities, the ability to perform detailed anatomical distinction, and the safe closure of the post-resection defect using a minimally invasive suturing technique following advanced endoscopic resection. Imaging technologies such as TXI and NBI enabled clearer visualization of lesion margins and vascular patterns. During the ESD procedure, the enhanced contrast provided by TXI allowed for a clear distinction between the submucosa and muscularis propria layers. After resection, the defect was successfully closed using barbed sutures, thereby reducing the risk of complications. This case demonstrates how novel imaging modes facilitate precise preoperative assessment of duodenal lesions. Furthermore, it underscores how advances in endoscopic technology and instrumentation enable the minimally invasive treatment of premalignant lesions while also allowing for the effective prevention of potential adverse events.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer.
Prof. Dr. Liu Zhiguo Cases 10: Post-eradication gastric cancer screening
Dr. Kunihisa Uchita
- Keyword
- Content Type