Case 2 – SCLC extensive disease (T1bN3M1b)
Author: Felix Herth, MD and Ralf Eberhardt, MD, Thoraxklinik, University of Heidelberg, Germany
Source: DVD-ROM ‘Light & Sound – Diagnostic Training’, Olympus Europa SE & Co. KG, 2013
Patient History
58 years, male.
The patient received a Chest X-ray in order to clarify about a suspected pneumonia which resulted in discovery of a suspicious formation in the left upper lobe.
CT
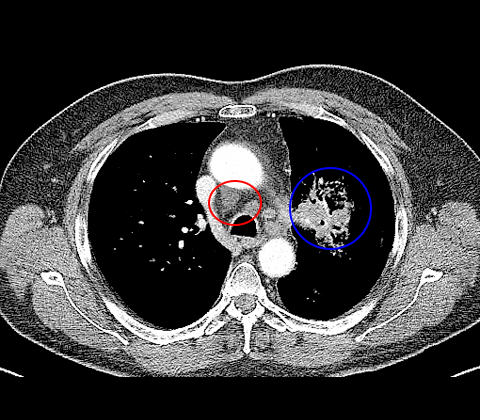
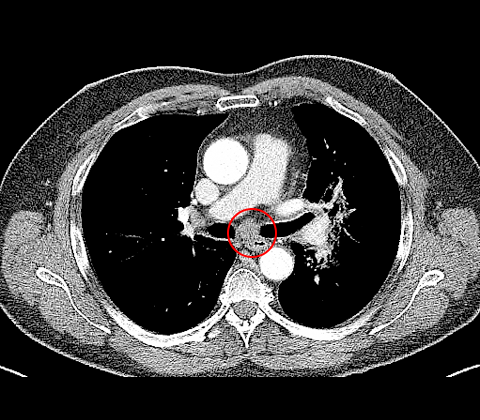
Consecutive imaging by CT reveals a suspicious mass in left upper lobe (fig. 1), furthermore enlarged lymph node station 7 (N2) (fig. 2) and lymph node station 4R (N3) (fig. 1).
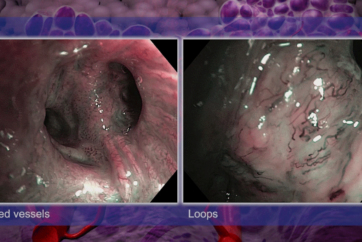
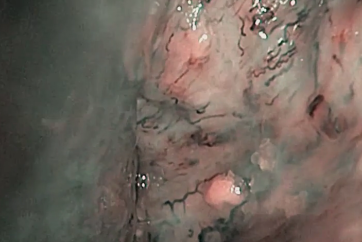
White light bronchoscopy
Thickened carina at the level of left upper lobe bronchus (fig. 3). Suspicious thickened carina and increased vessel formation at the carina of LUL S 1+2 (fig. 4).
3
4
Endobronchial ultrasound
Radial endobronchial miniature probe confirms distinct tumour formation around the left upper lobe bronchus, segment 1+2b (fig. 5).
5
Cytology and bronchial biopsy were performed(fig. 6-7)
6
7
Histology and Immunohistochemistry
The tissue sample confirmed Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC).
Nuclei prove TTF-1 positive, Cytoplasm positive for BerEp4, predominantly CD56 and partly NSE and synaptophysin.
An absence of a specific immune reaction to CK5/6, p63 and KL-1 and a proliferation rate above 80% (Ki67) were assessed.
Diagnosis
SCLC LUL, extensive disease (T1bN3M1b).
Treatment
Chemotherapy 4 cycles Cisplatin, partial remission.
PET-CT and switch to limited disease as adrenals were unsuspicious. Thoracic radiation therapy and PCI.
Follow-up after six months shows progressive thoracic and hepatic disease. 2nd-line-chemotherapy was offered.
- Content Type