How PDD works
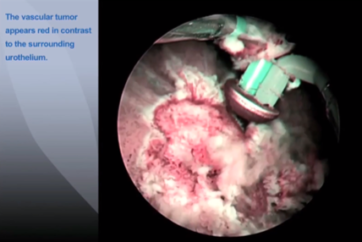
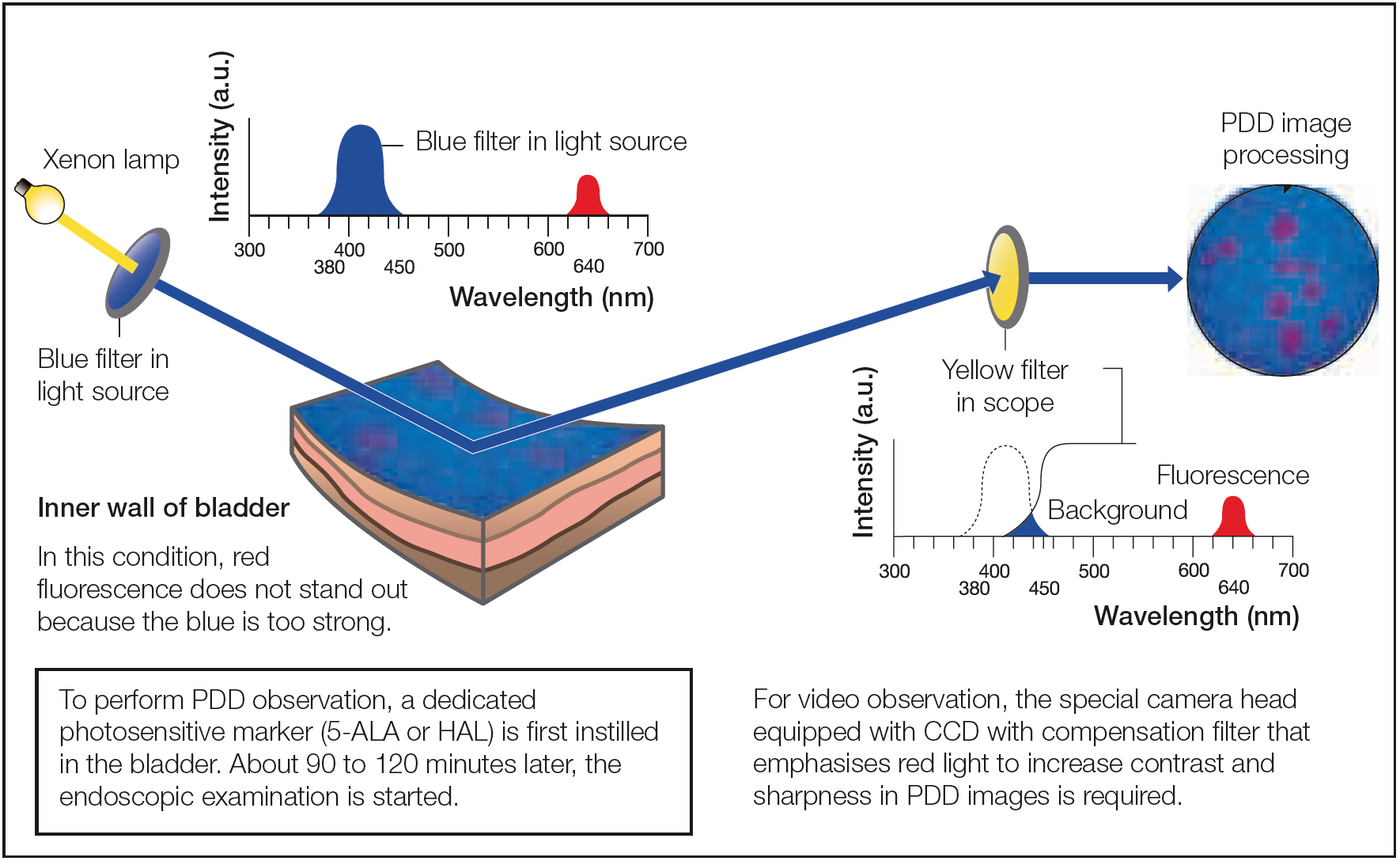
When a photosensitive marker1) has been introduced transurethrally into the bladder, the inner surface of the bladder absorbs the drug over a period of 90–120 minutes and converts it into an endogenous pigment called protoporphyrin IX. This pigment is then selectively deposited in a tumour and, under blue excitation light, will emit red fluorescence. Nevertheless, in this condition, a sufficient contrast of the red fluorescence against the blue background is hard to obain because the red fluorescence is too weak compared with the blue light. To emphasize this fluorescence, a yellow filter exclusively designed for PDD is built into the scope. As a result, the red fluorescence can be observed with excellent contrast.
- Content Type