Case : Tumor in the bronchus intermedius

Kei Morikawa, MD
Division of Respiratory and Infectious Diseases
Department of Internal Medicine
St. Marianna University School of Medicine
Scope: BF-1TH1200
Location: Intermediate bronchial trunk
Patient information: Female in her 70s
Medical history: After removal of a thyroid tumor, coughed up blood accompanied by epigastric discomfort and saw a local doctor. No history of smoking. Chest X-ray showed a mass shadow in the right lower lobe, and she was referred to our institution for further examination.
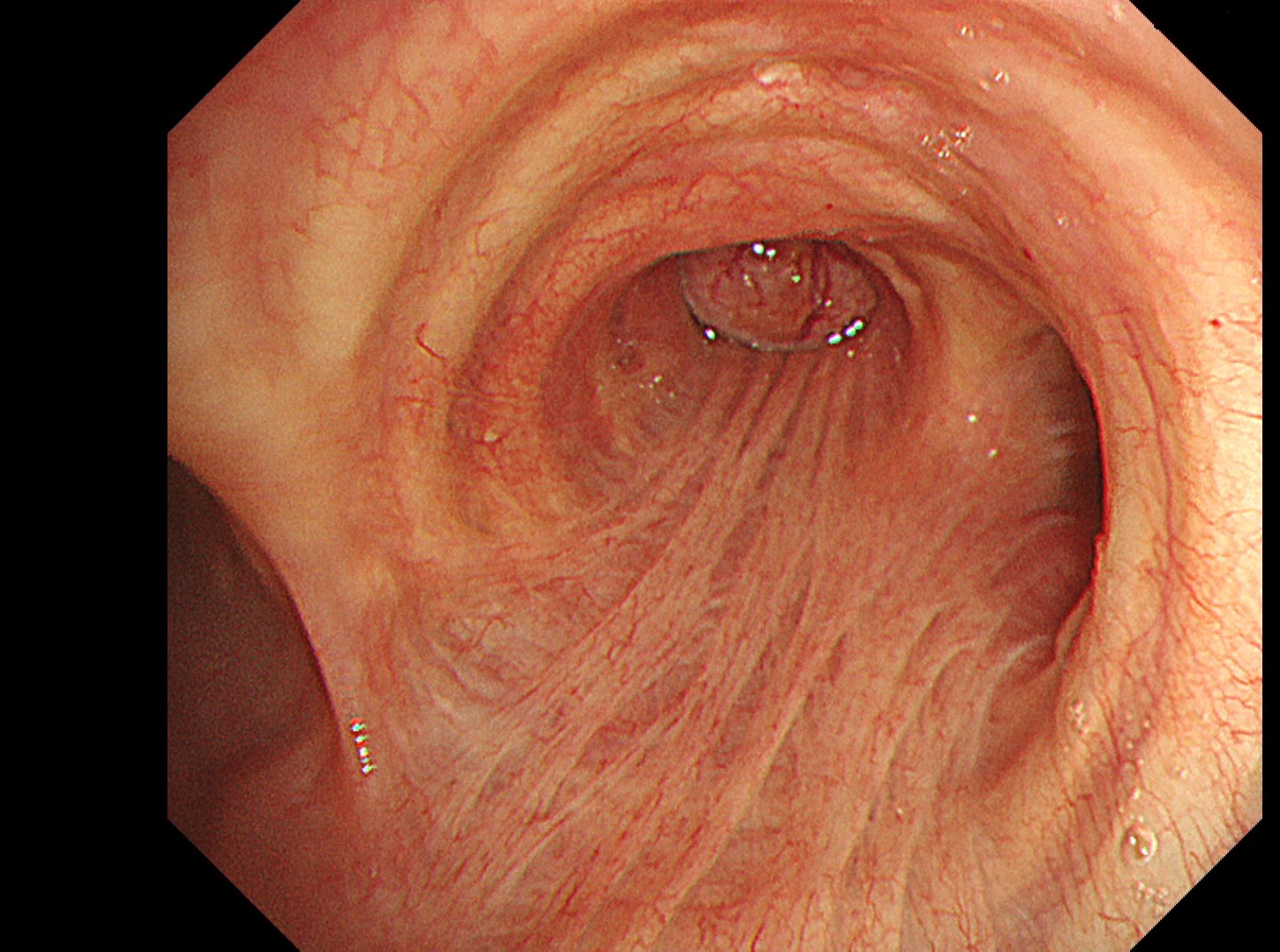
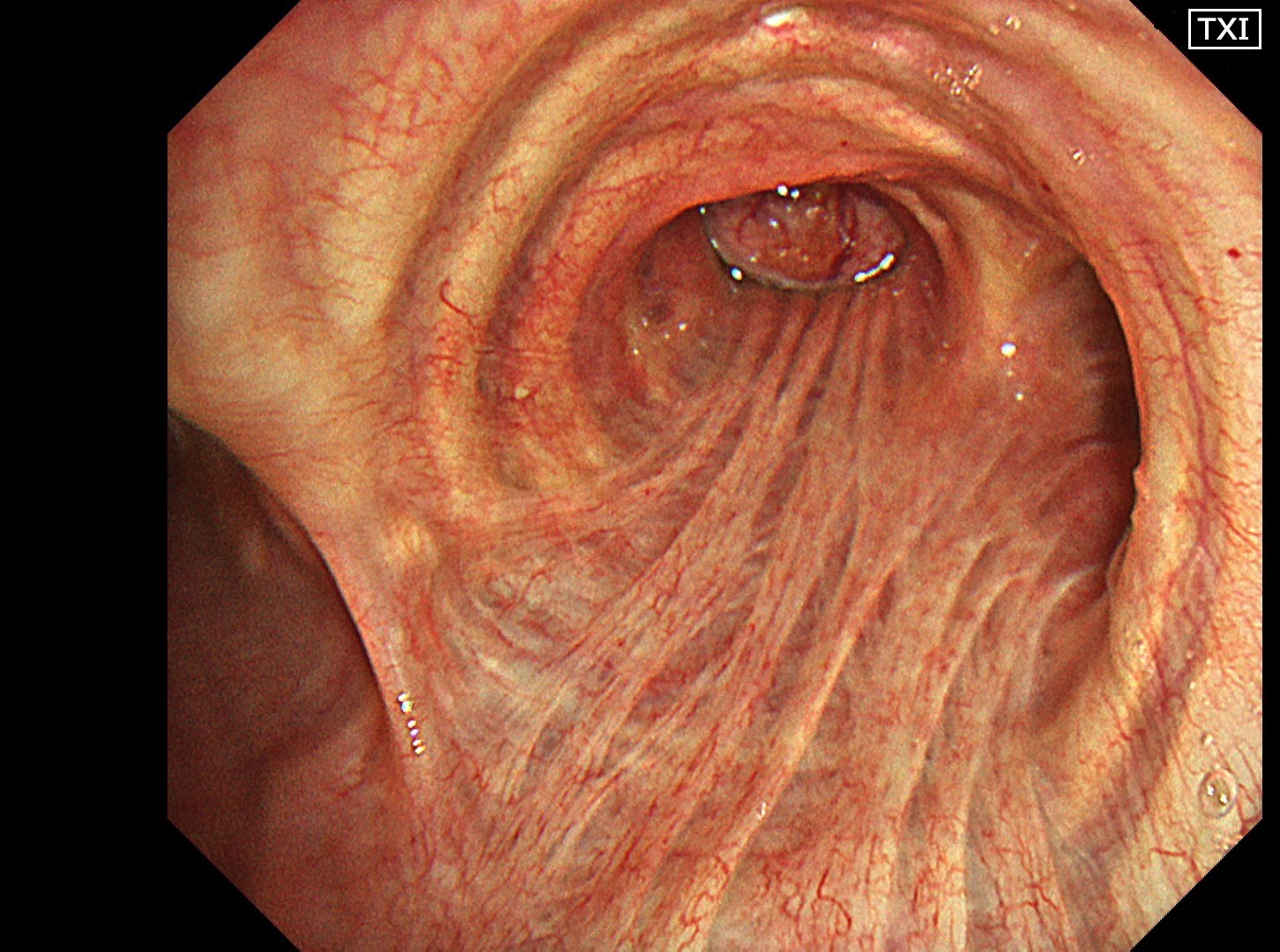
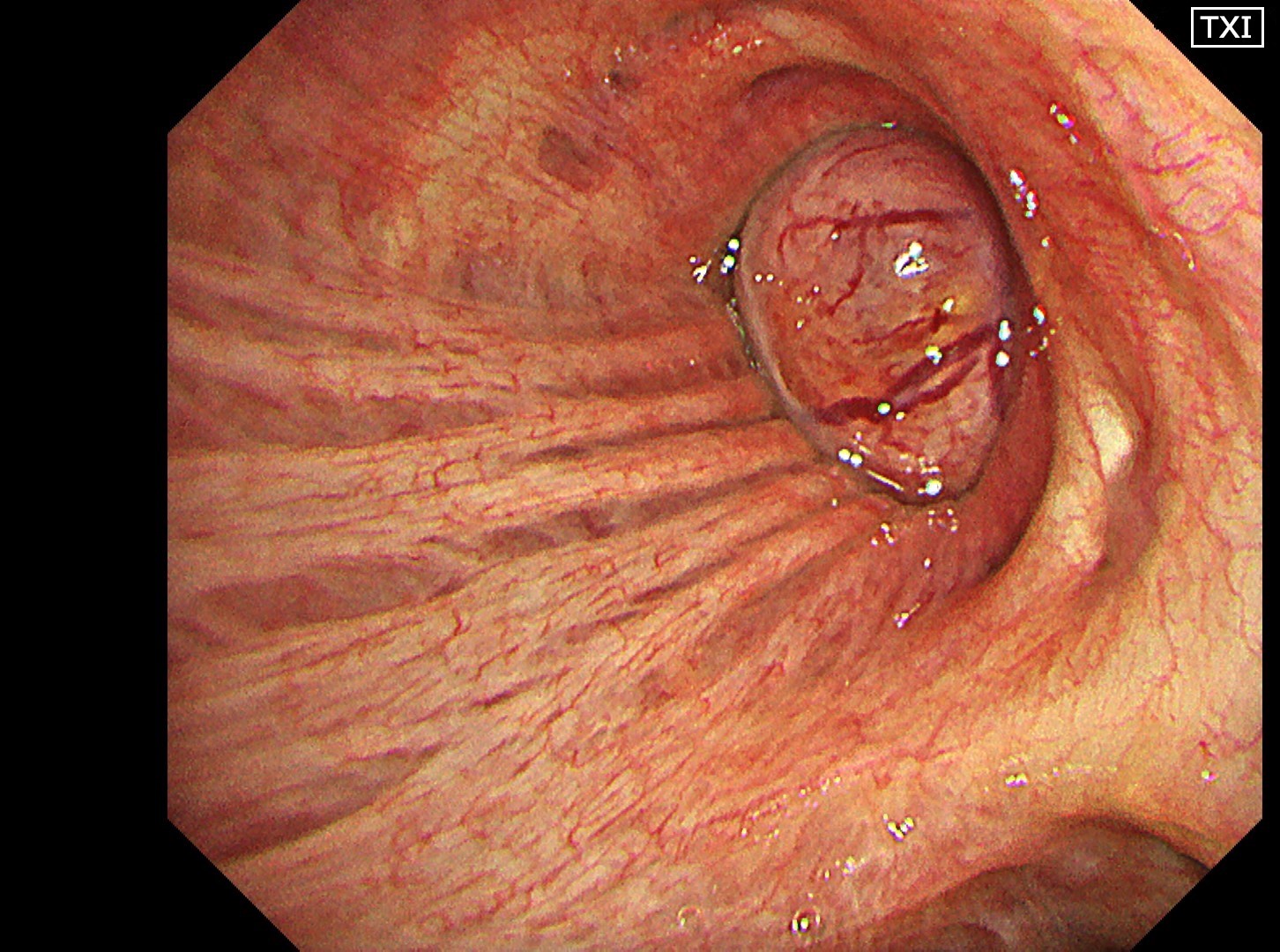
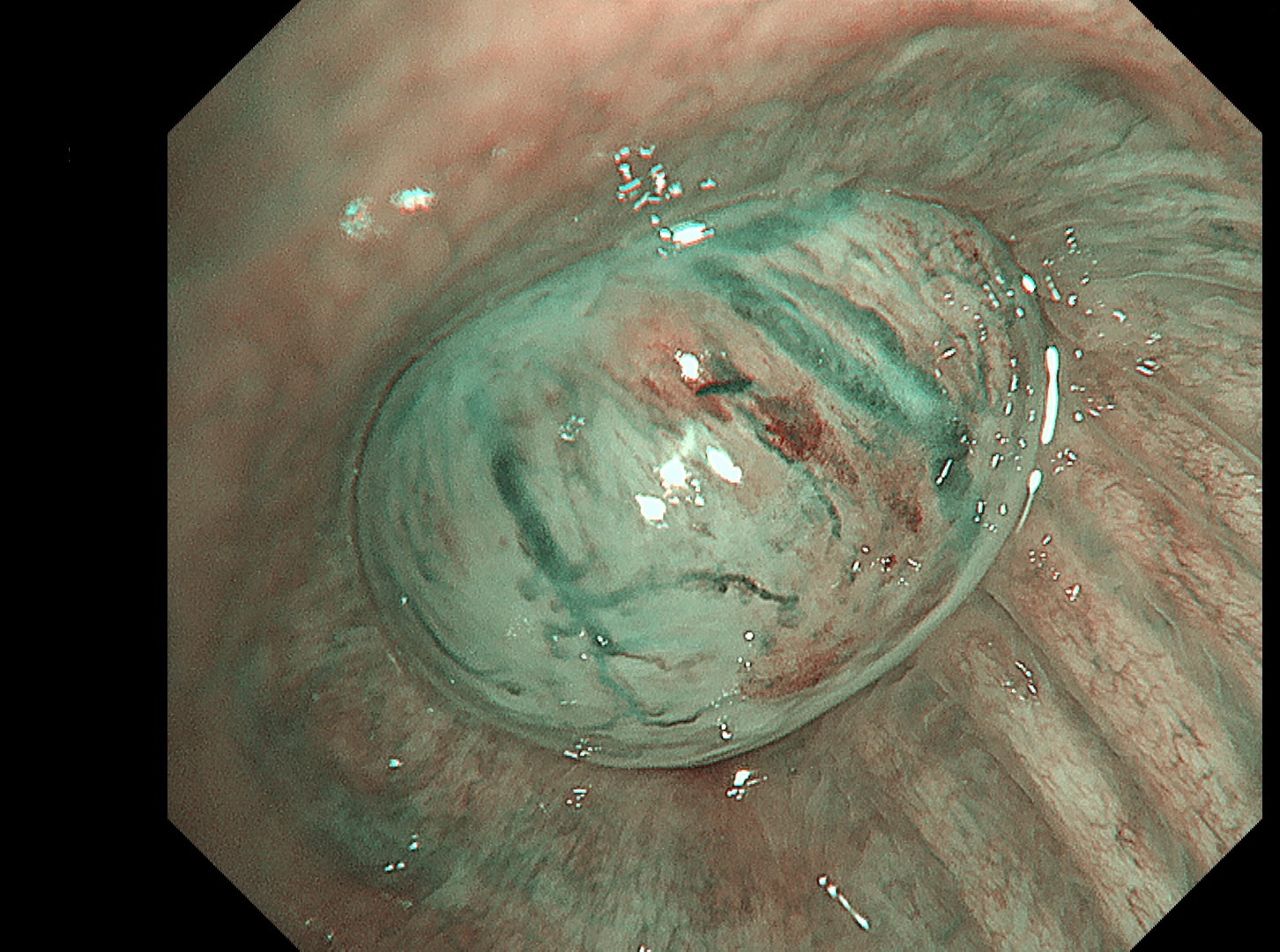
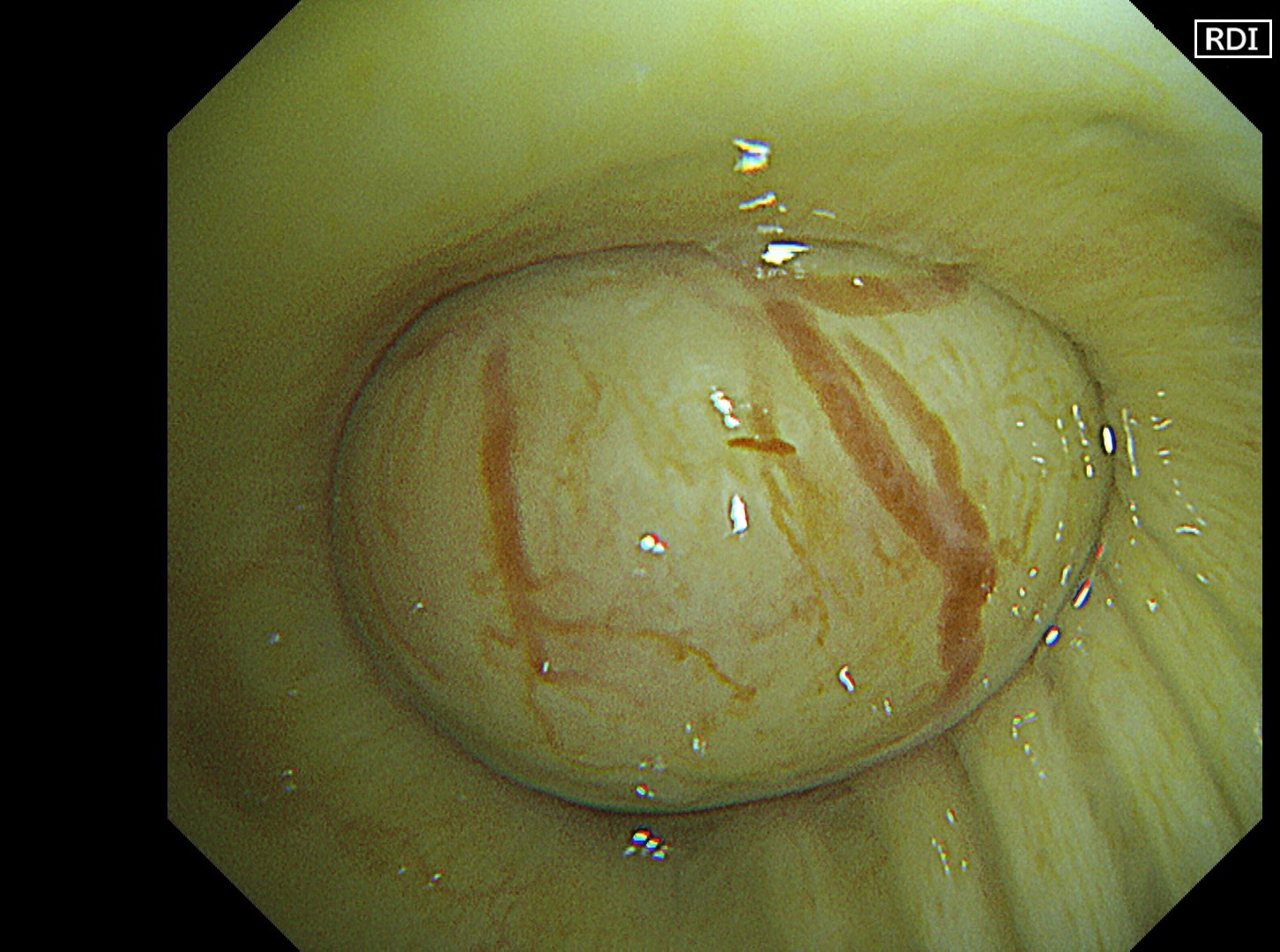
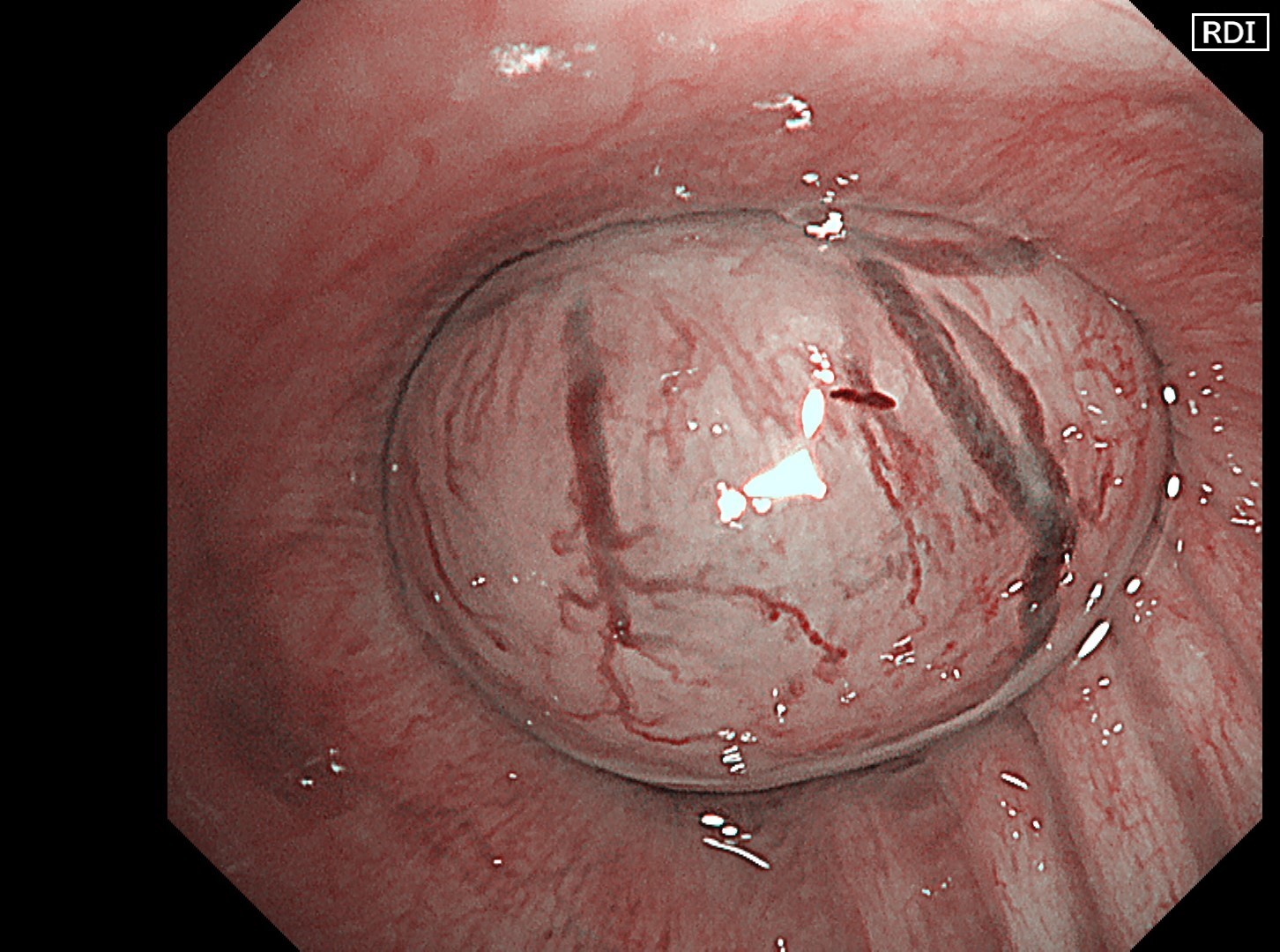
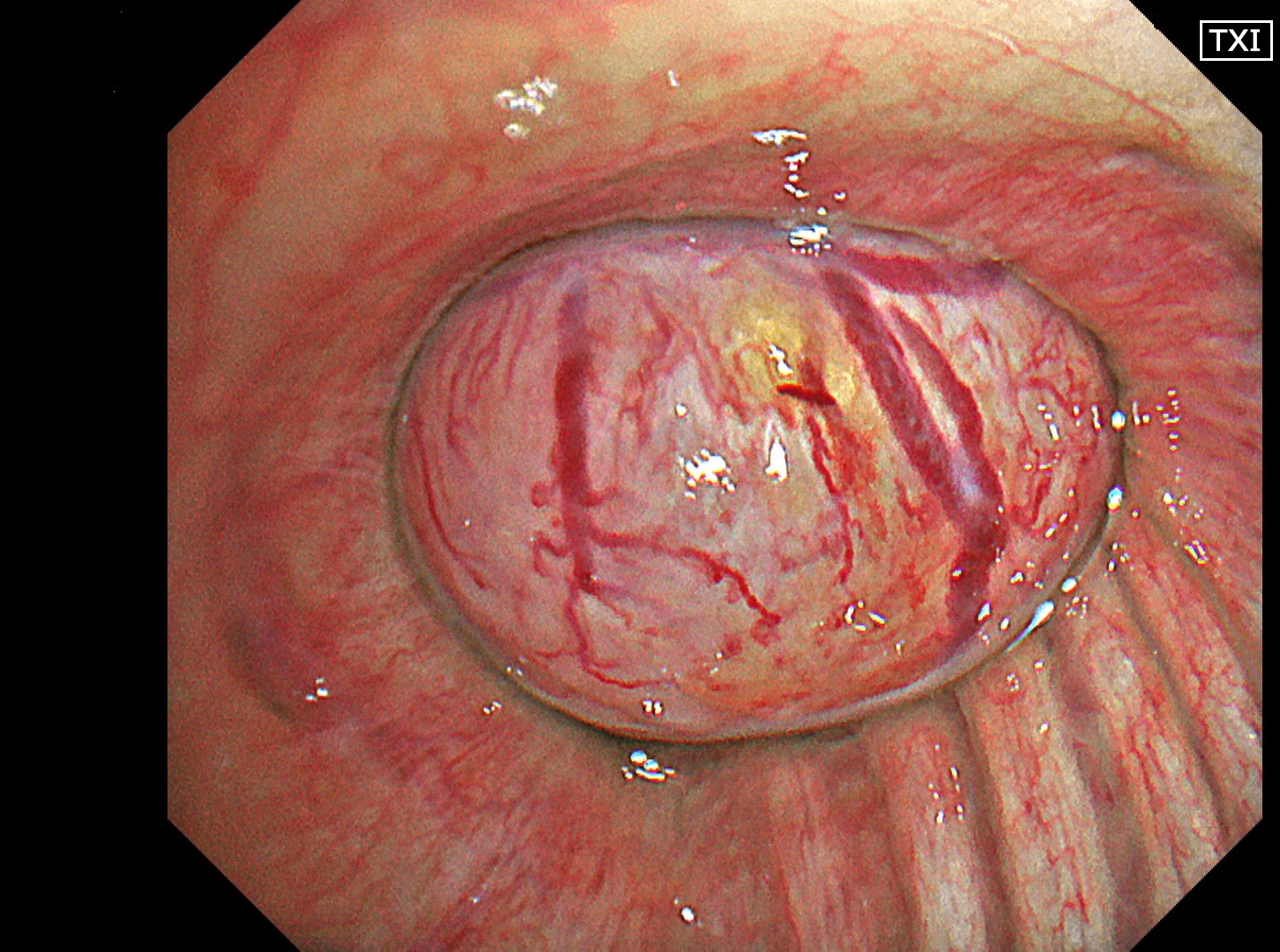
1-4 Intermediate trunk tumor(TXI 1)
Case Video
Normal structures in the vicinity of the tracheal bifurcation are observed in WLI and TXI for comparison, then the tumor in the right intermediate trunk is observed in detail in WLI, NBI, TXI, and RDI.
Pathological Findings
The tumor biopsy was performed using the peripheral approach to avoid bleeding.
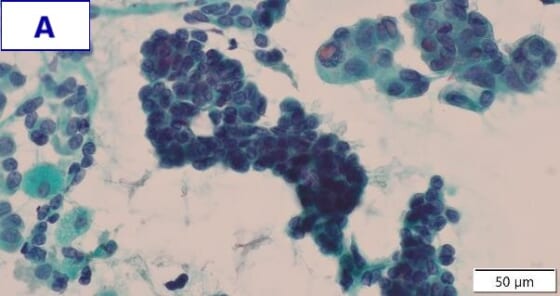
- Figure A (Papanicolaou staining): Clusters of glandular cells with atypical morphology can be seen. These feature a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, irregularly shaped nuclei, and increased nuclear chromatin.
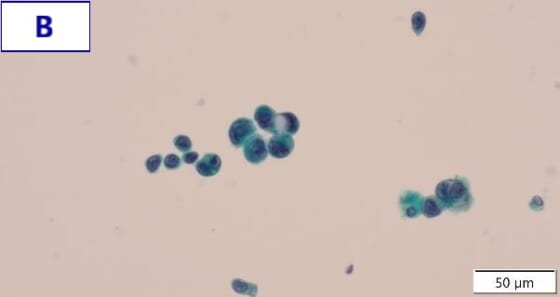
- Figure B (Papanicolaou staining): Glandular cells with atypical morphology are observed both in small clusters and scatterings. These feature unevenly distributed nuclei, a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, and nuclear hypertrophy and irregularity.
- EGRF genetic mutation was detected by a gene mutation search.
- Final diagnosis: Primary lung adenocarcinoma (EGFR exon 21 L858R)
Overall Comment
In the comparison between WLI and TXI viewed from above the tracheal bifurcation, the peripheral lesion could be recognized first with the BAI-MAC function, which made the lesion brighter than its surroundings. TXI observation increased the visibility not only of the lesion but also the normal structures in the trachea and bronchi. In this respect, the value of high-specification equipment has been proven. Subepithelial vessels characteristic of tumors were most clearly depicted with the TXI and RDI3 settings. Since there were no significant invasion findings, low-grade malignancy was taken into consideration and the lesion was designated as an EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Molecular-targeted medication demonstrated high efficacy.
Co-editor:
Dr. Nobuyuki Ohike
Department of Pathology, St. Marianna University School of Medicine
- Content Type