Case: Thermal Ablation of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Left Main Bronchus

Director Bai Chong
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,
the First Affiliated Hospital of Naval Military Medical University
(Shanghai Changhai Hospital)

Deputy Director, Huang Haidong
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,
the First Affiliated Hospital of Naval Military Medical University
(Shanghai Changhai Hospital)

Professor Shi Dongchen
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,
the First Affiliated Hospital of Naval Military Medical University
(Shanghai Changhai Hospital)
Scope: BF-Q290
Case: Left main bronchus
Patient information: 56 years old, Female
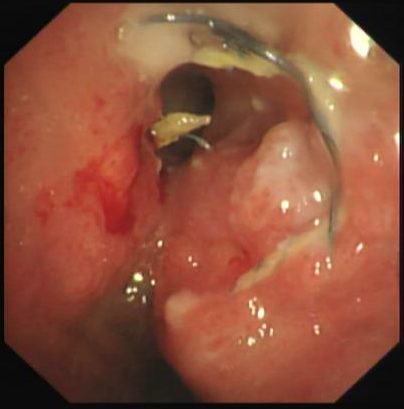
Medical history: The patient was diagnosed with adenoid cystic carcinoma of the left main bronchus with neoplastic stenosis for more than 10 years. After comprehensive treatment including placement of uncovered metallic stent in the left main bronchus, brachytherapy and radioactive seeds implantation for mediastinal lesions, her condition was stable. The patient had shortness of breath after activity in the past 2 weeks. Chest CT and bronchoscopy showed that tumor tissue growth in the left main bronchus stent had caused restenosis of the left main bronchus.
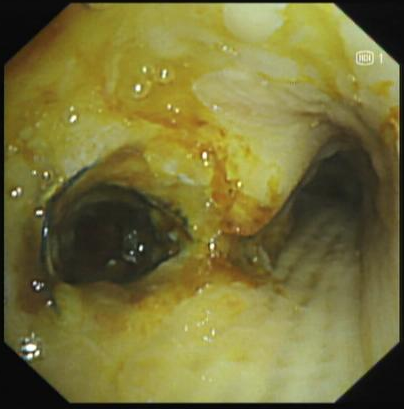
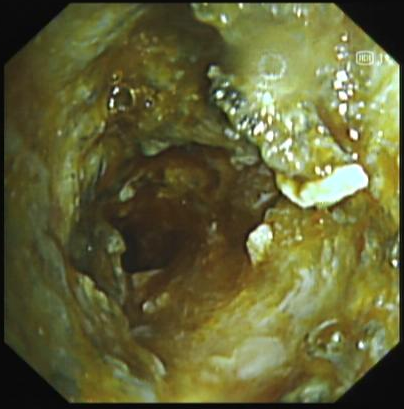
4. The lower trachea observed in WLI mode showed recanalization of the left main bronchus after thermal ablation and recanalization
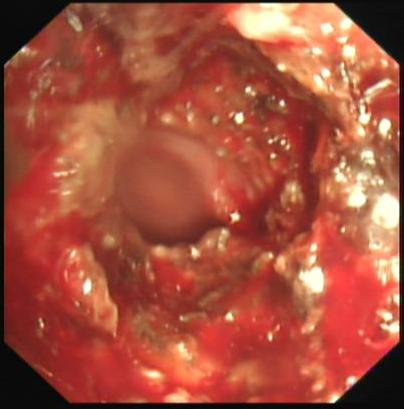
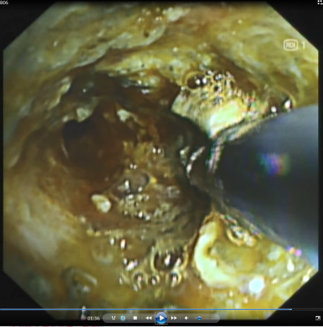
The tumor tissue invaded the stent in the lower trachea of the left main bronchus. After treatment, the lumen was more unobstructed than before. The tumor tissue was rich in capillaries and easily bled upon touch.
6. Endoscopic video
Endoscopy revealed that tumor tissue had invaded and blocked the lumen of the uncovered metal stent of the left main bronchus. The tumor tissue within the stent was rich in capillaries and easily bled upon touch. High-frequency electrocoagulation was given in RDI mode to repeatedly cauterize and ablate the tumor tissue. During the operation, the field of view was clear. After treatment, the lumen of the left main bronchus became more unobstructed.
Overall comment
Intraluminal thermal ablation of tracheal adenoid cystic carcinoma can effectively solve the problem of restenosis after stent placement. However, due to the abnormally rich capillaries in tumor tissue, the continuous bleeding of the bronchial mucosa caused by thermal ablation interferes with the field of view in WLI mode, affecting the accuracy and safety of the treatment and reducing the treatment efficiency. The RDI mode can effectively reduce the interference on the field of view caused by local bleeding, thereby improving the operational accuracy, efficiency and safety of thermal treatment and effectively avoiding thermal damage to normal mucosal tissue.
- Content Type