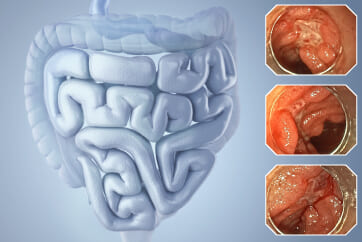
Colorectal Case 4
.jpg)
Prof. Yoji Takeuchi
Scope: CF-EZ1500DI
Case: Early rectal cancer, SM deep invasion carcinoma
Organ: Lower rectum
Patient information: F, 54
Medical history: Nothing worth noting
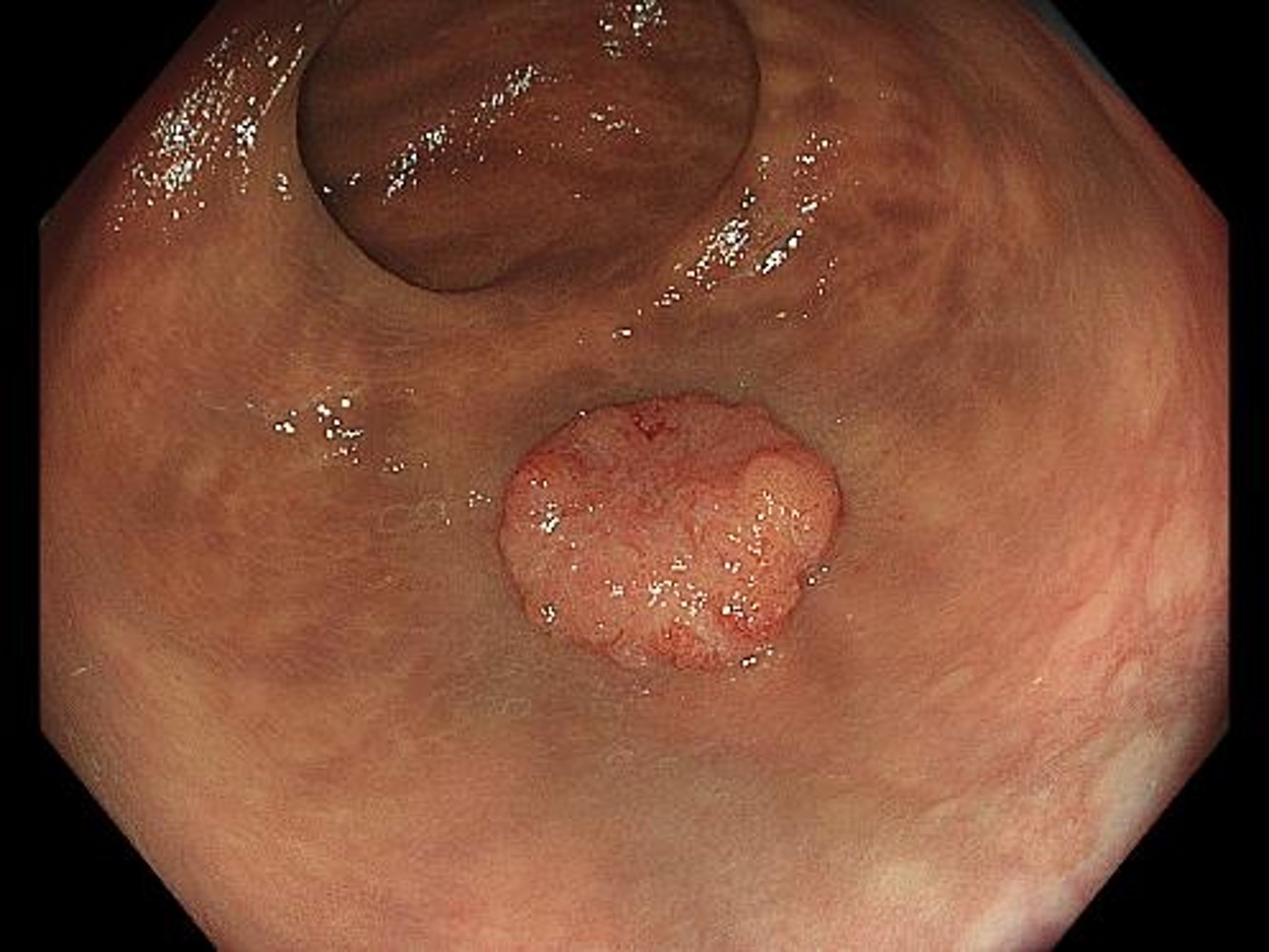
NBI non-magnifying observation
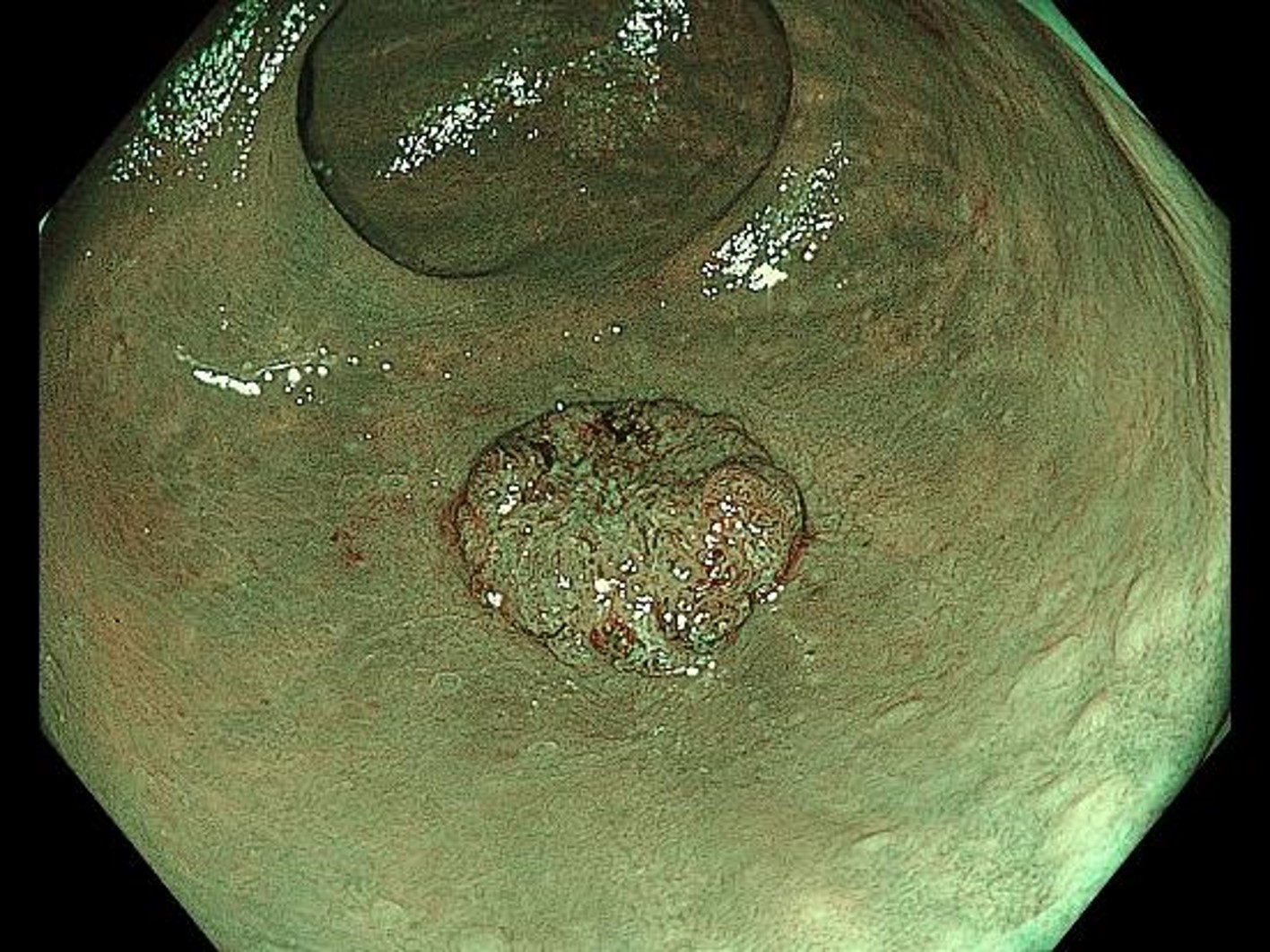
While the surface structure and vascular pattern in the margins of the lesion can be recognized even with relatively distant observation, they appear irregular and unclear in the center of the lesion. This lesion may be interpreted as Type 2 or 3 in the NICE classification, depending on the doctor.
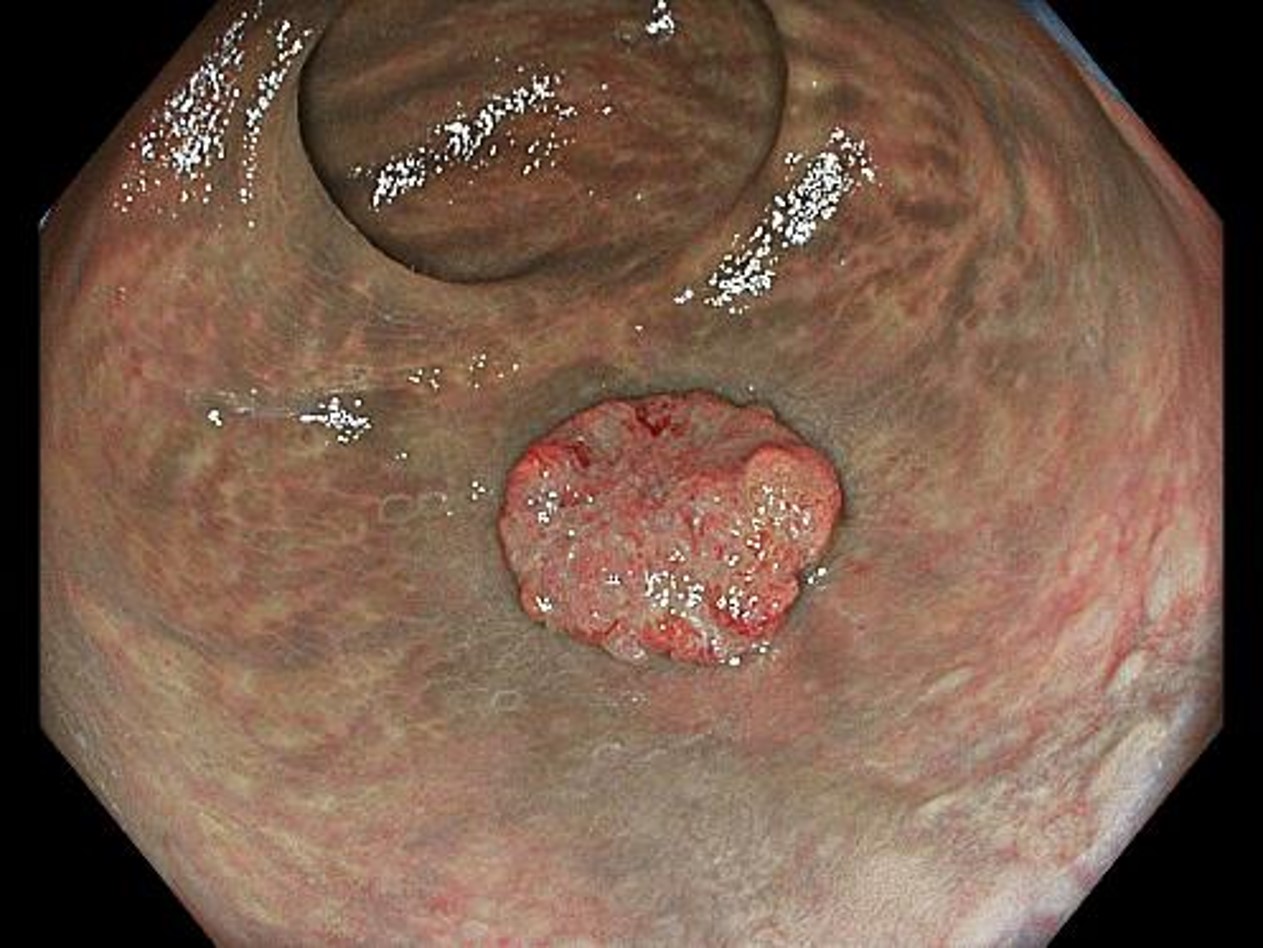
WLI non-magnifying chromoendoscopy (with indigo carmine staining)
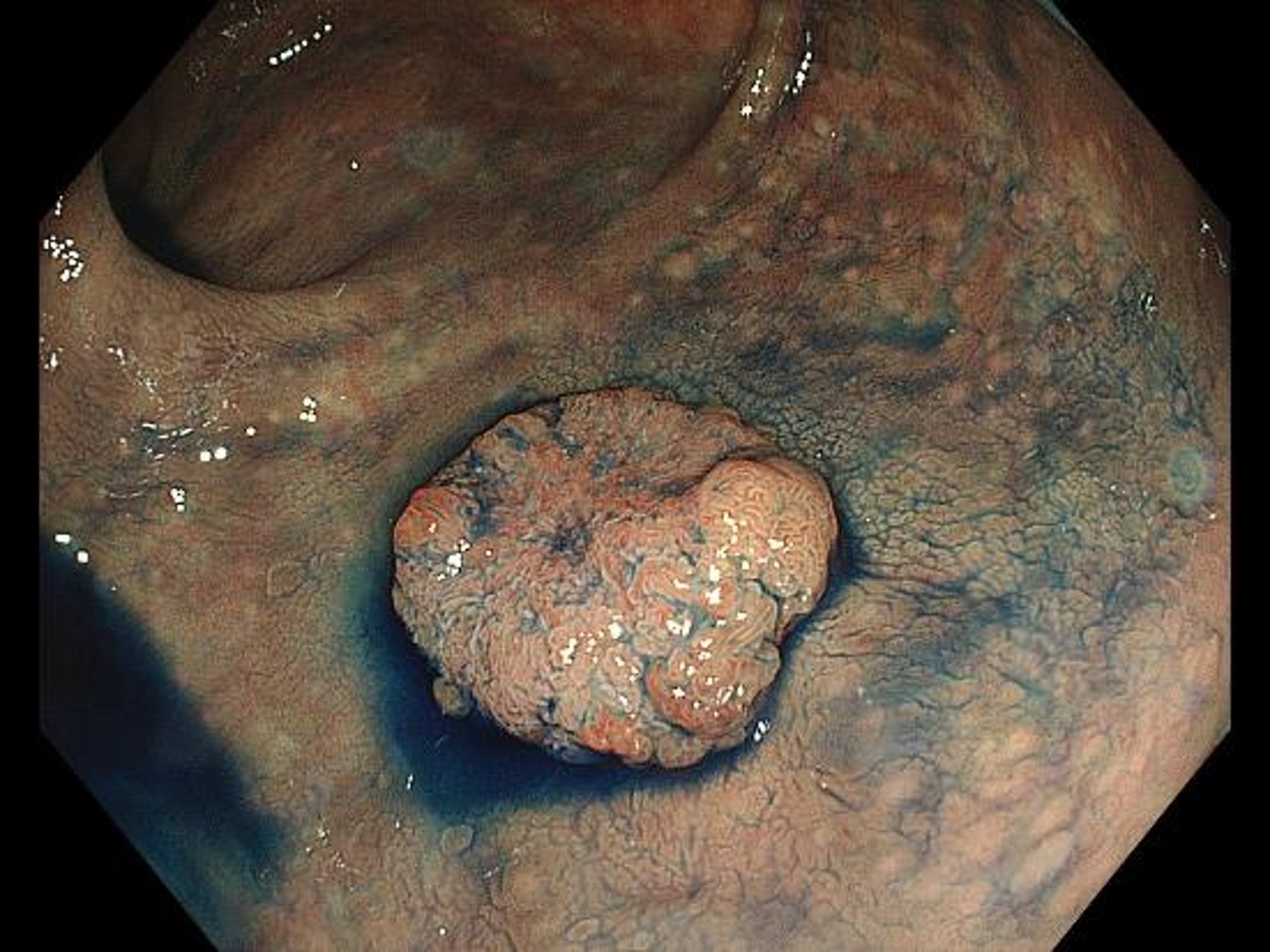
Pooling of indigo carmine in the grooves emphasizes the surface structure. The difference between the relatively inconspicuous irregularities in the margins and the dense yet unclear irregularities in the center is recognized more clearly.
NBI non-magnifying observation (close-up observation)
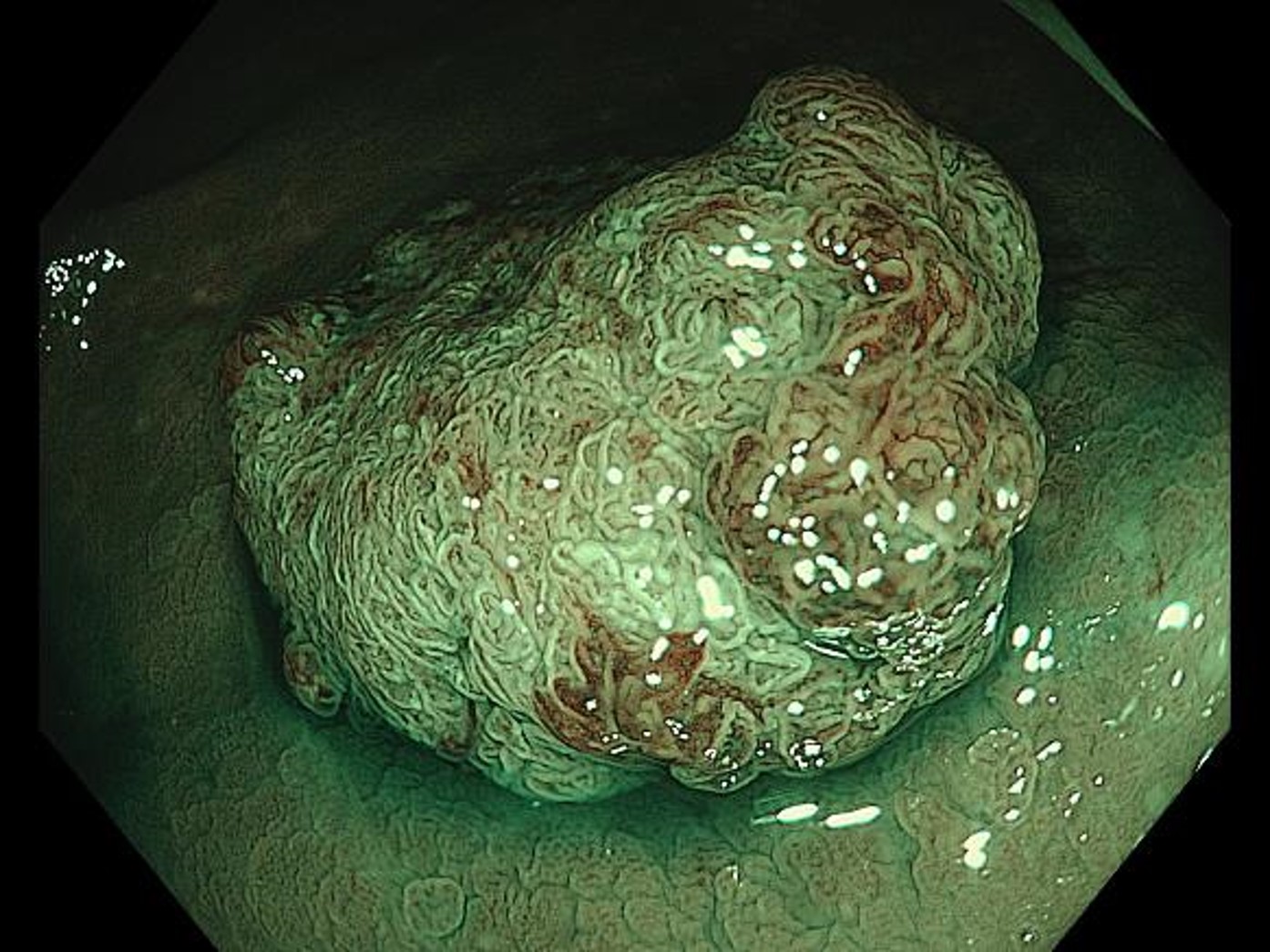
Bringing the scope tip close to the lesion makes it possible to clearly recognize surface microstructures and microvascular patterns without magnification. The image is in focus in both near and far areas, making it easier to tell which part of the entire image requires closer examination.
NBI magnifying chromoendoscopy (in Near Focus mode)
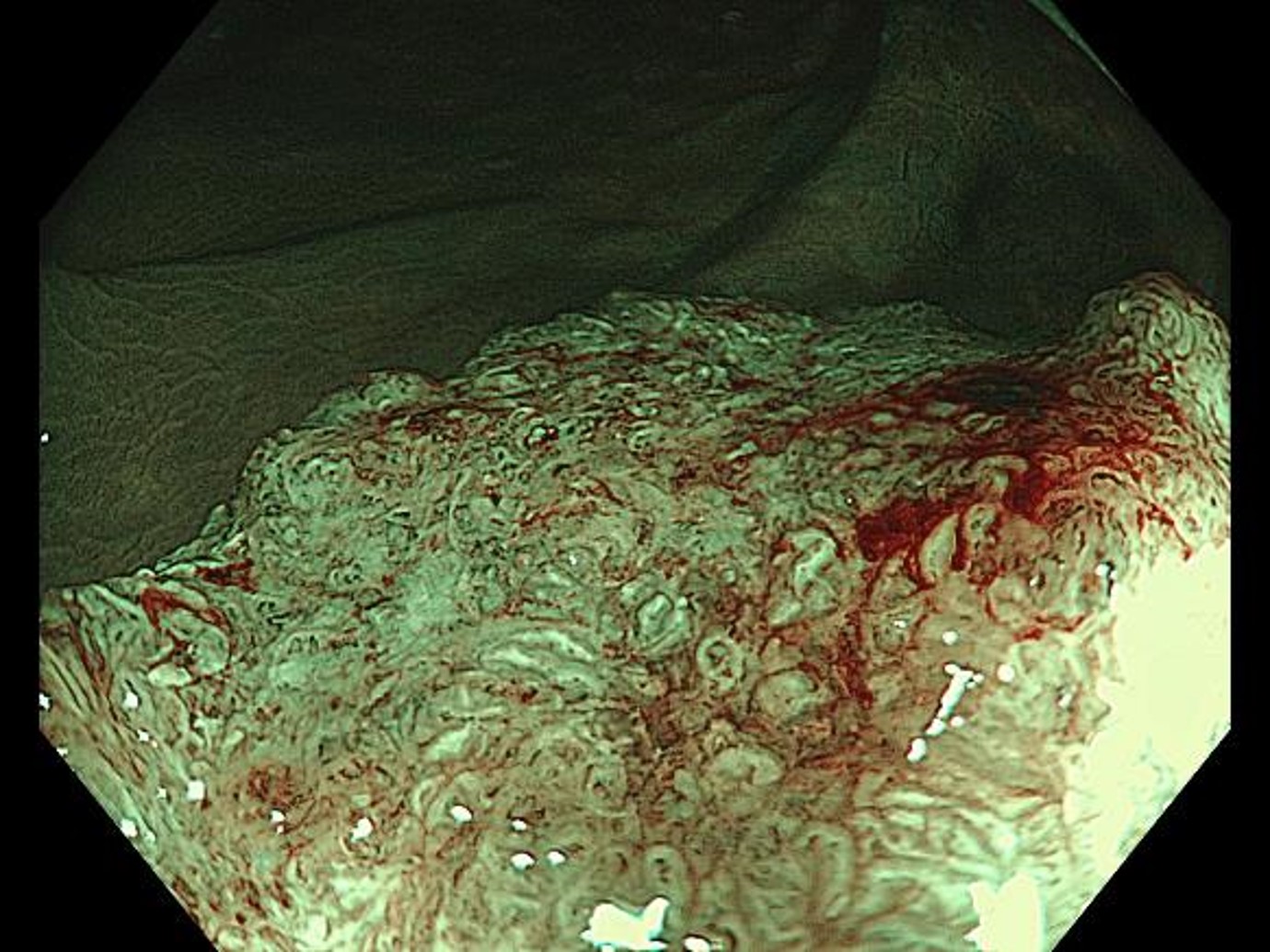
Disappearance of the surface structure and disruption of the microvascular network are recognized. The lesion can be diagnosed as type 2B-3 in the JNET classification. The image is mostly in focus at both near and far points, making it possible to comprehend the characteristics of the lesion in certain regions.
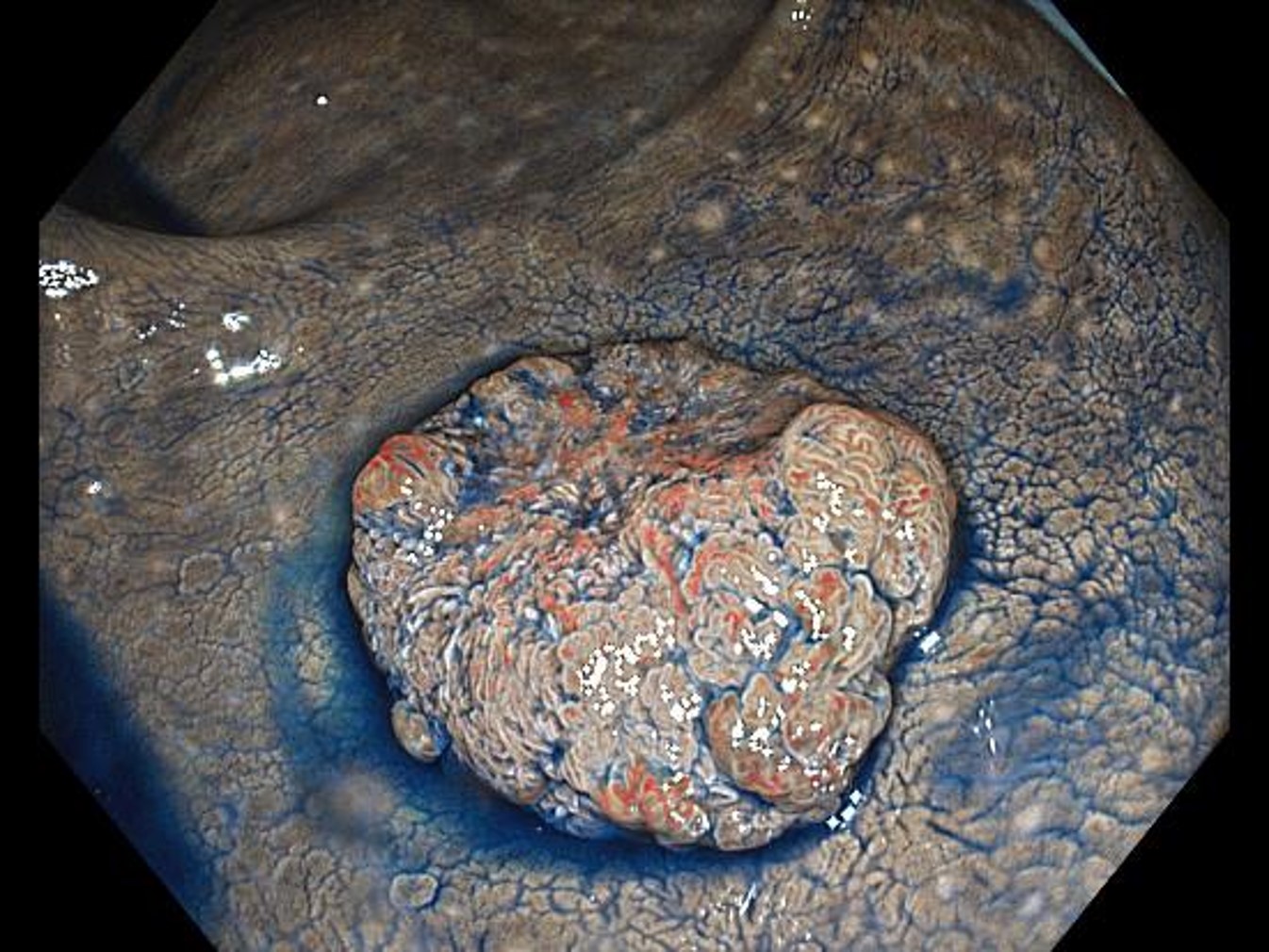
Magnifying chromoendoscopy (with crystal violet staining, in Near Focus mode)
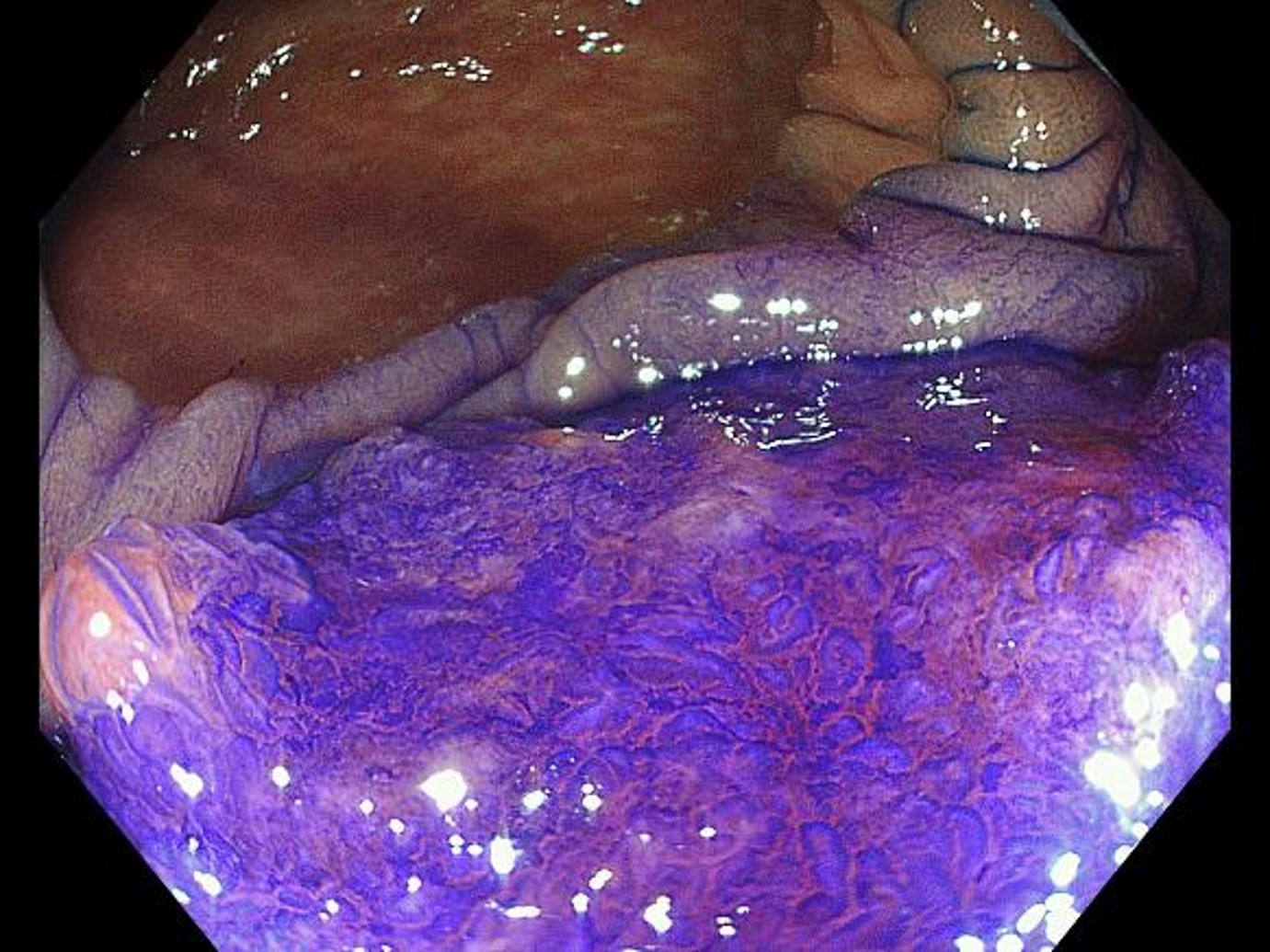
While a highly irregular surface structure is recognized on the right of the image, a surface structure so damaged that it can be called structureless is recognized on the left. Diagnosis of pits is possible even in the Near Focus mode.
Case video
[Summary for this case]
This was an elevated-type, deeply invasive carcinoma in the lower rectum. In the distant view under non-magnifying observation (WLI, TXI, NBI, and chromoendoscopy), entire images were bright and in focus due to BAI-MAC, which enabled comprehension of the lesion’s irregular morphology, leading to the suspicion that the lesion represented an invasive carcinoma. In TXI observation, the surface structures were further enhanced after indigo carmine spraying.
Even when the magnification function was not used, rough surface structures and vascular architecture could be recognized in close-up NBI observation, enabling targeting of areas where further detailed examination using magnifying observation would be necessary. Focus adjustment — which, in conventional magnifying observation had to be precisely adjusted in minute increments — was switchable at the touch of the Near Focus button. EDOF made it easy to obtain clear, in-focus images, which should support the popularization of magnifying endoscopy.
Overall Comment
Colon tumors often exhibit elevated lesions. When observing an elevated lesion, it is often the case that only a part of the lesion is in focus because the distance between the lens and subject is not constant. But with EDOF both near and far points can be brought into focus, making possible observation with clear images in focus from edge to edge. Elevated lesions in the colon — especially invasive carcinomas — are often fragile and hemorrhagic and bleed when brought in contact, often resulting in hindered observation subsequently. EDOF can help minimize contact, limiting the dangers of hemorrhaging.
Magnifying observation of the upper digestive tract is usually for histological and extension diagnosis and requires close examination of the details of surface and vascular structures using full zoom. In the colon, however, pinpoint invasion does not occur, meaning that magnifying observation of colon tumors for invasion diagnosis is only necessary to evaluate the irregularities and disappearances of surface structures across a limited range, rather than to examine each specific structure.
The Near Focus mode’s magnification power is not as high as in conventional magnifying observation. However, a relatively wide area can be observed while keeping a distance between the lens and lesion. No contact is made with the lesion and bleeding does not occur. This allows you to make a high-quality diagnosis, which can be applied to decision making when determining the treatment policy.
Additionally, while in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy it is not unusual to perform detection and detailed examination on different days because fasting is required, in colonoscopy it is often the case that the procedure transitions directly to treatment when a lesion is detected because preparation for colonoscopy is stressful for patients. The CF-EZ1500 endoscope is well suited to diagnosis in the colon because lesions can be easily detected with the new TXI function and brighter NBI and close-up observation and magnifying observation can be performed seamlessly.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer.
- Content Type