Colorectal Case 23

Prof. Han-Mo Chiu
Clinical Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine,
National Taiwan University College of Medicine, Taiwan
Scope: Diagnosis: CF-HQ290ZI; ESD: PCF-H290TI
Organ: Colorectum
Patient information: 58 years old, Male
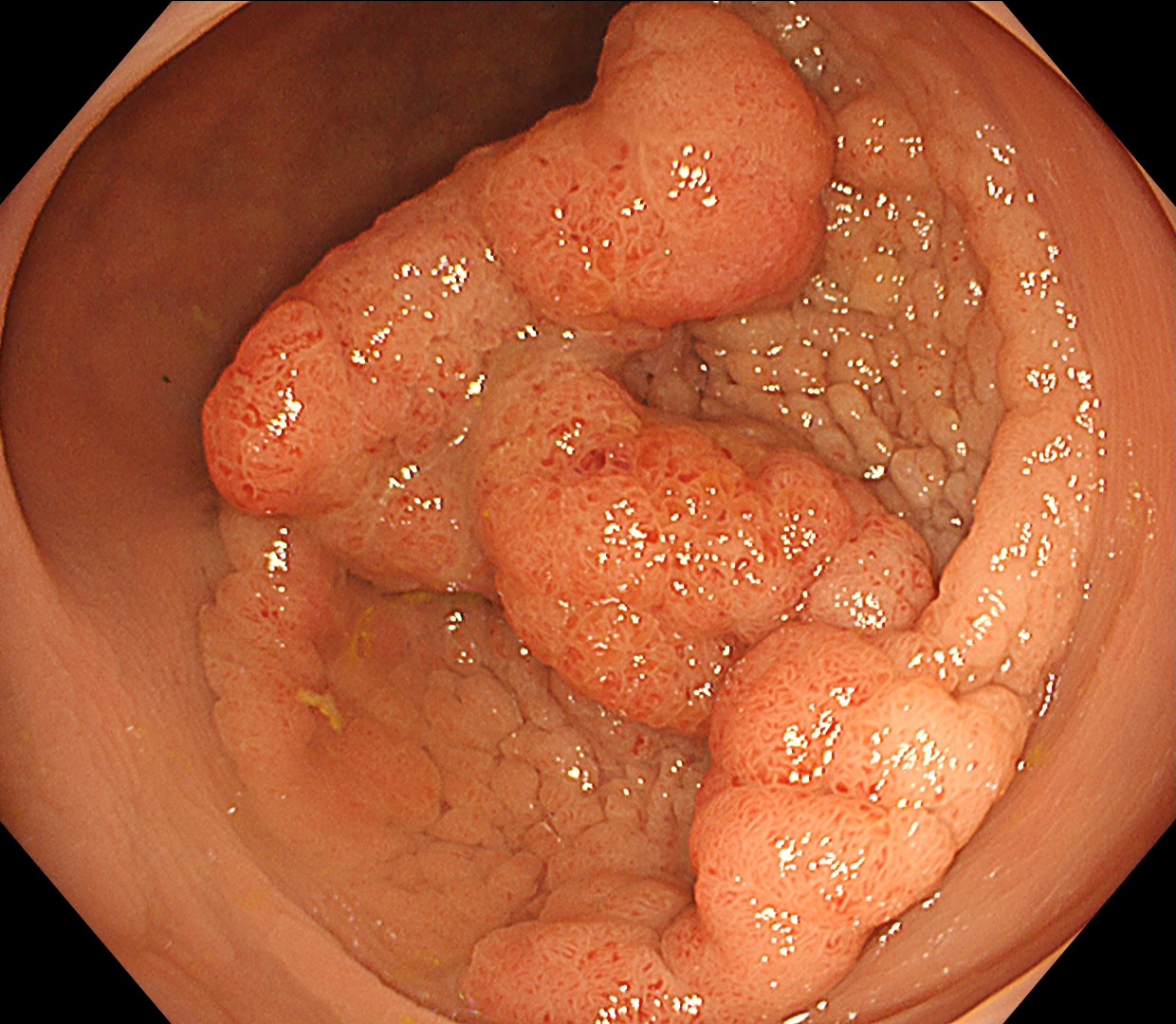
Rectal tumor found at colonoscopy after a positive FIT (fecal immunochemical test)
Medical history: No systemic disease
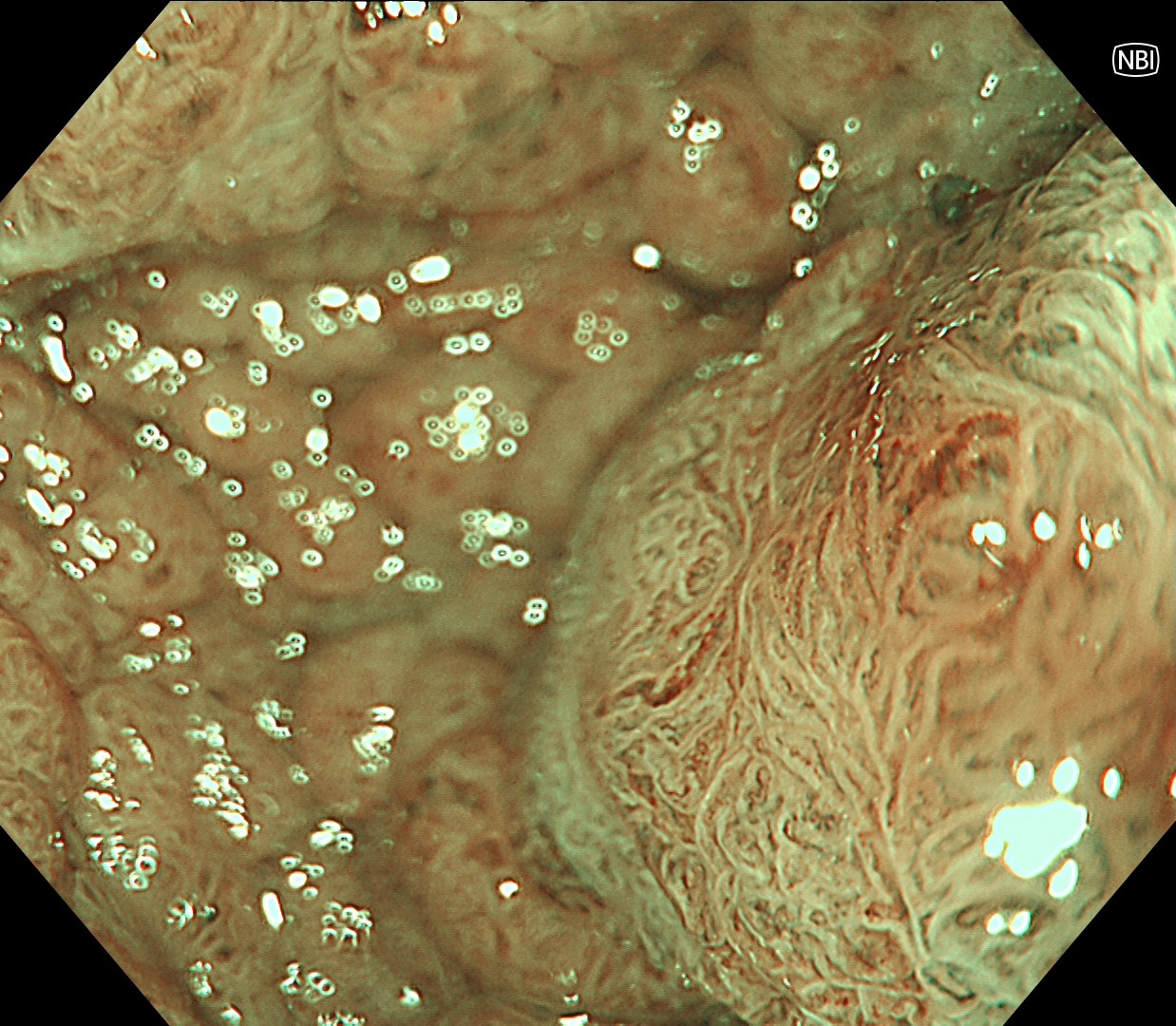
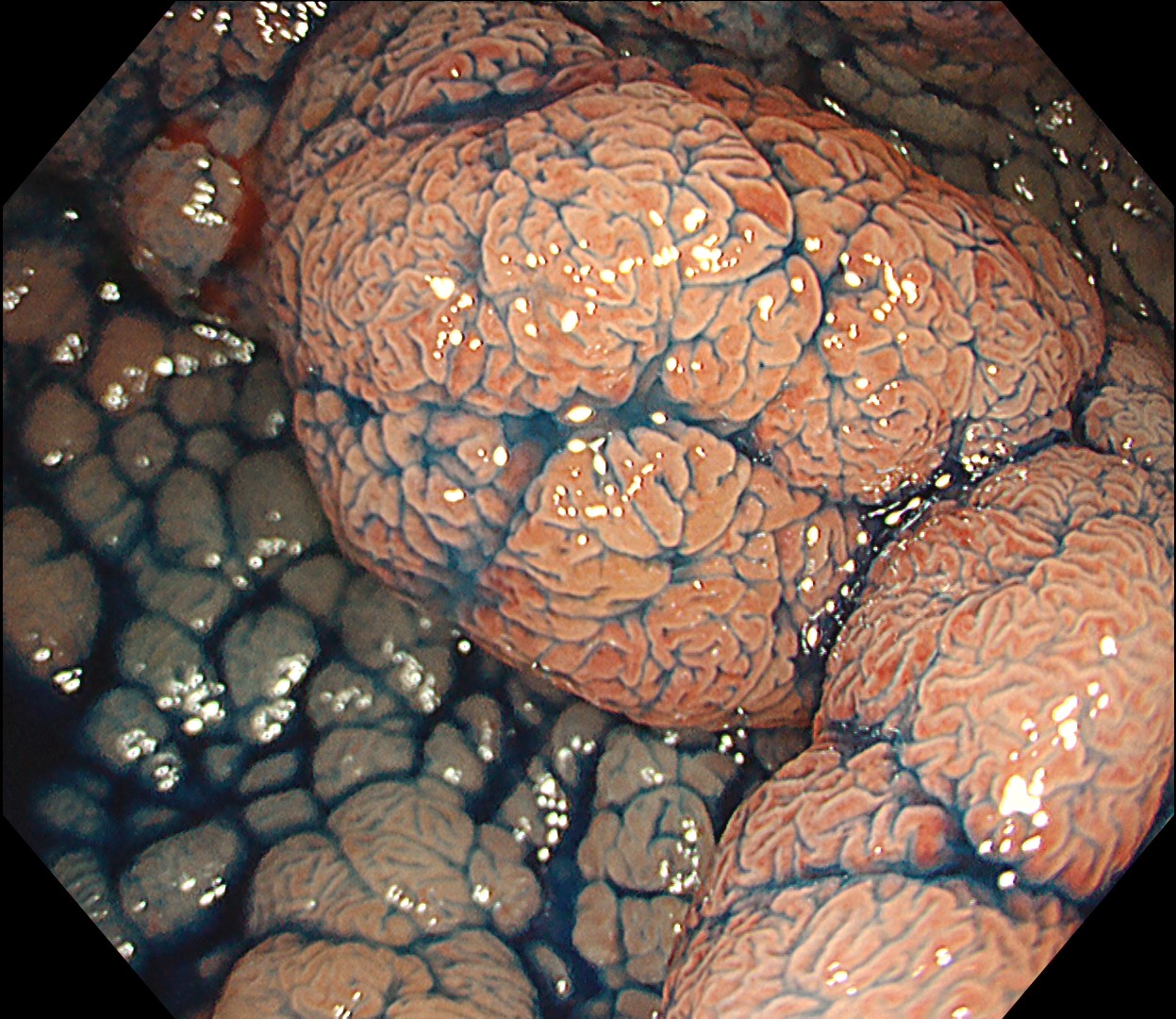
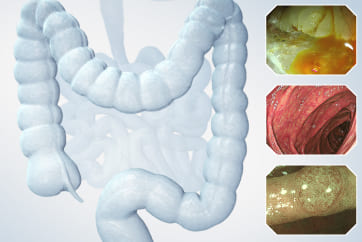
6. Chromoendoscopy

Enhancement : A7
NBI Mode : NA
TXI Mode : NA
RDI Mode : NA
BAI-MAC : On
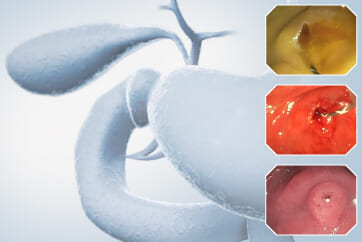
9. Chromoendoscopy

Enhancement : A7
NBI Mode : NA
TXI Mode : NA
RDI Mode : NA
BAI-MAC : On
Case Video
Overall Comment
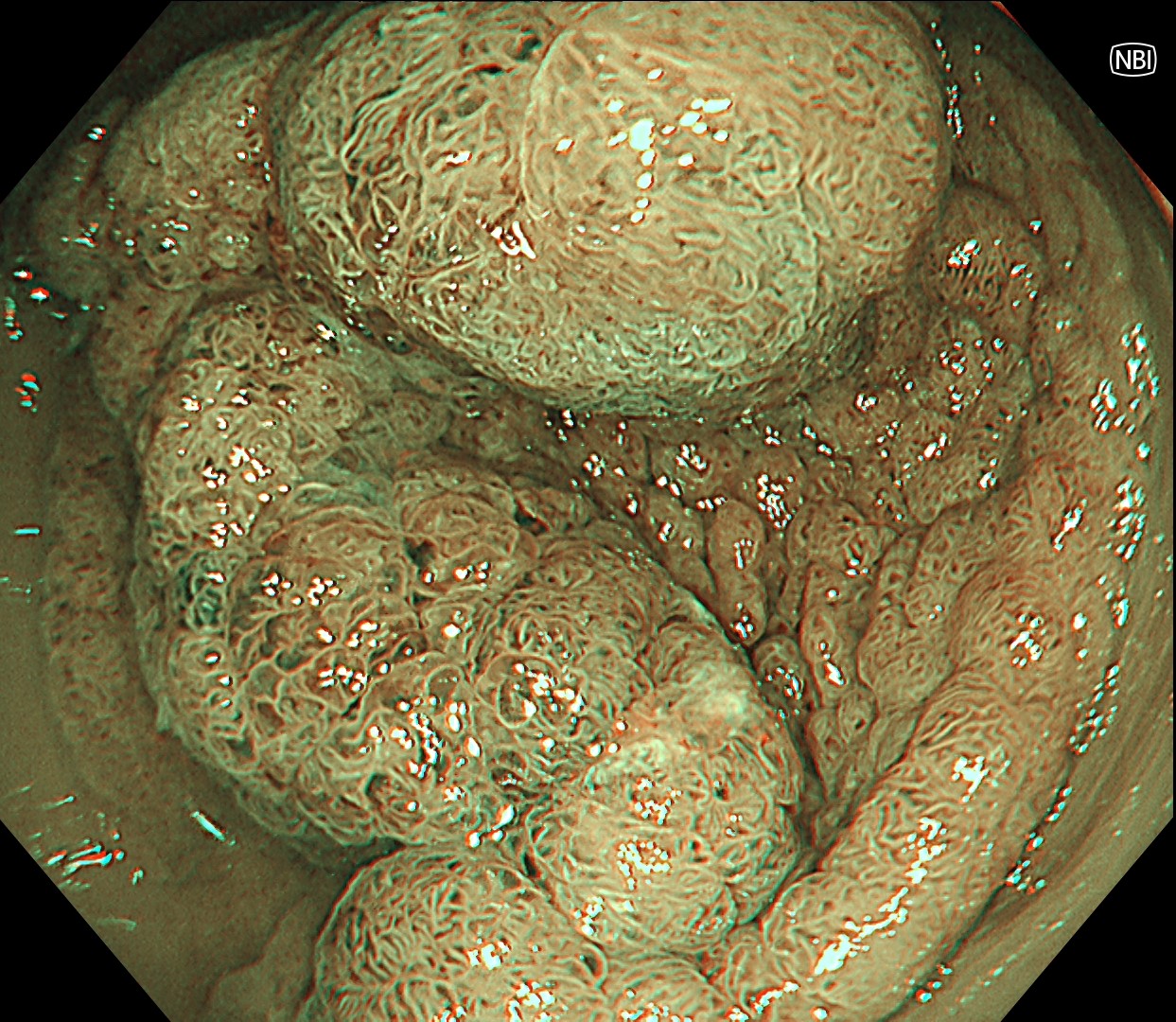
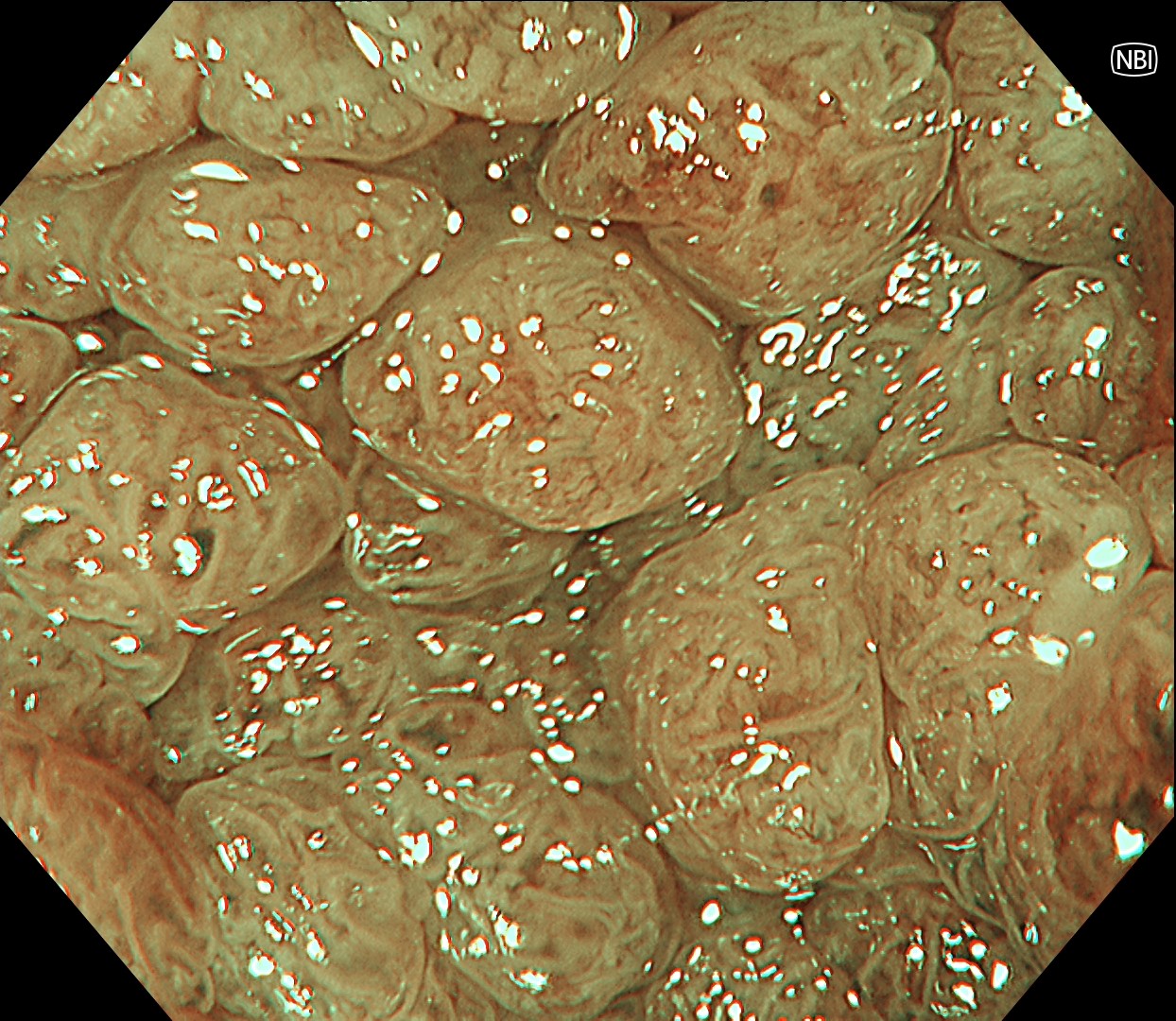
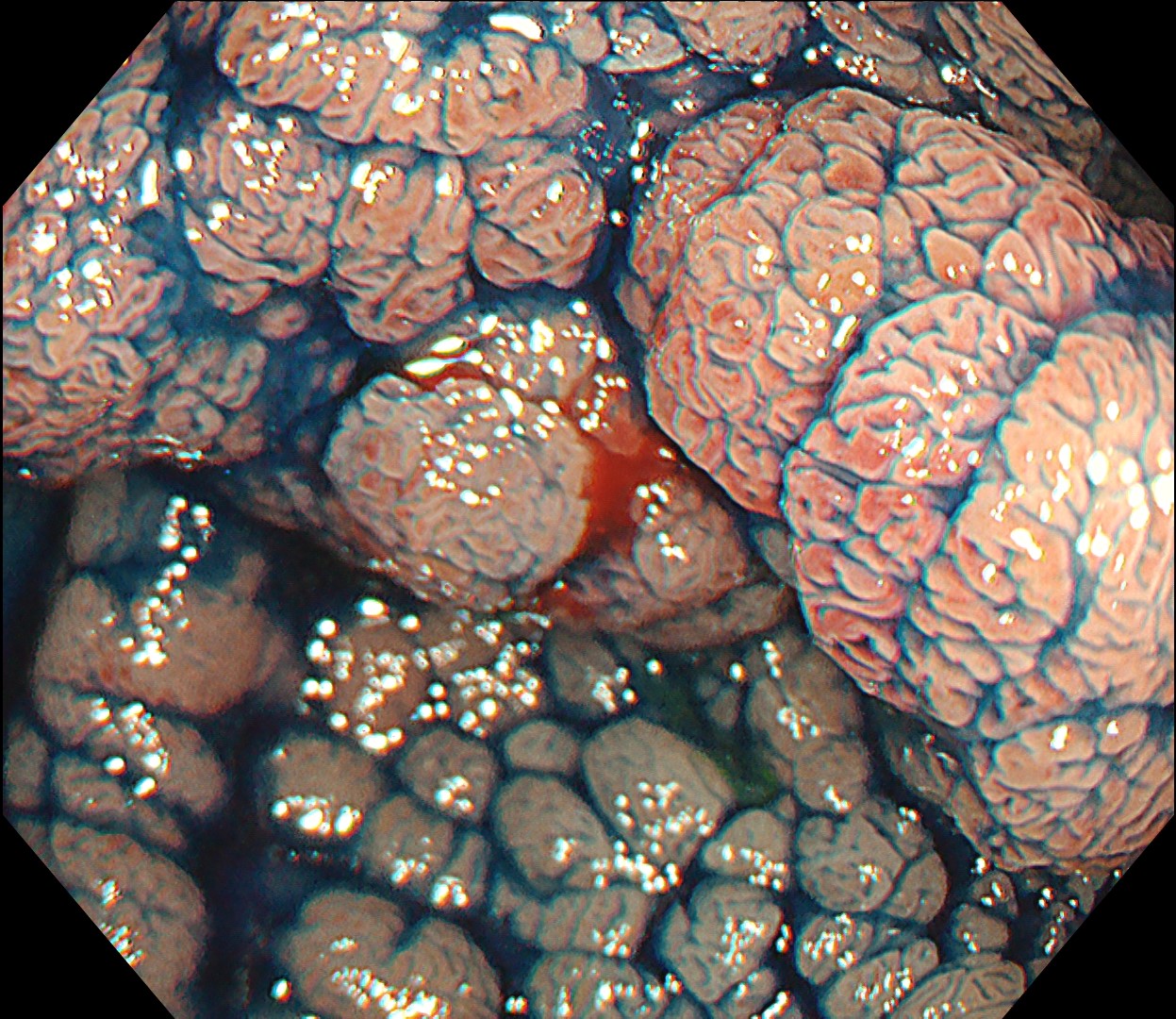
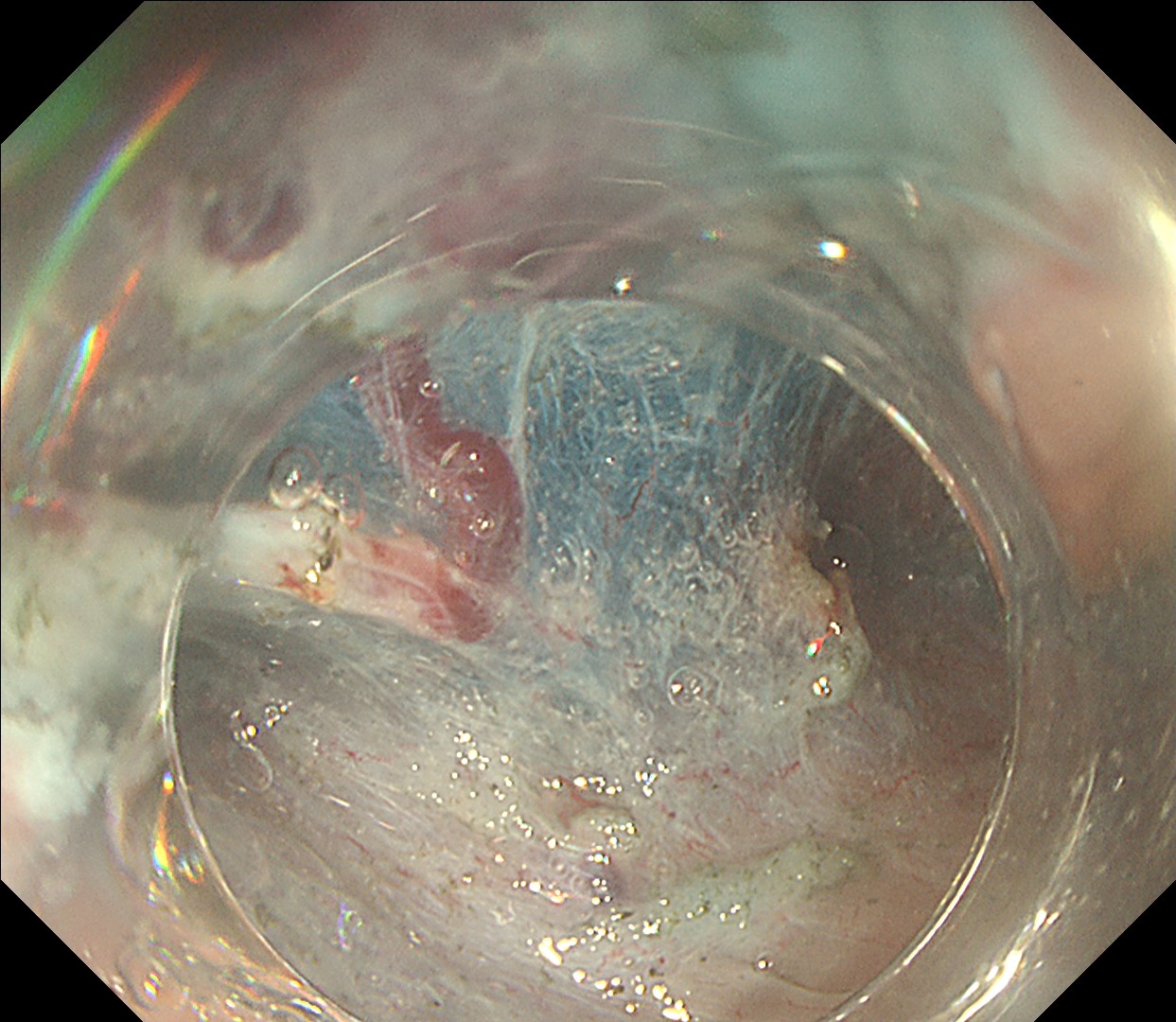
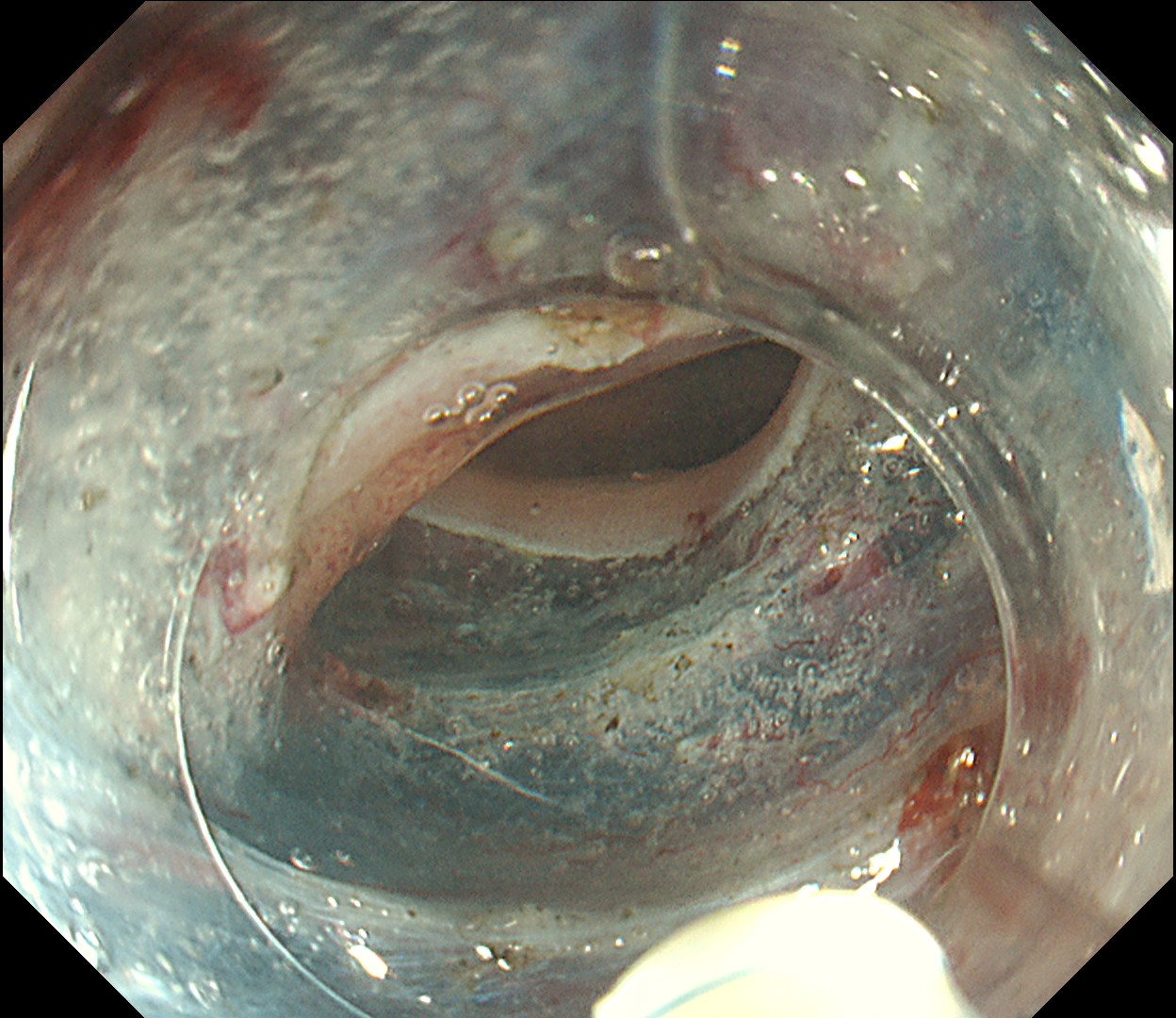
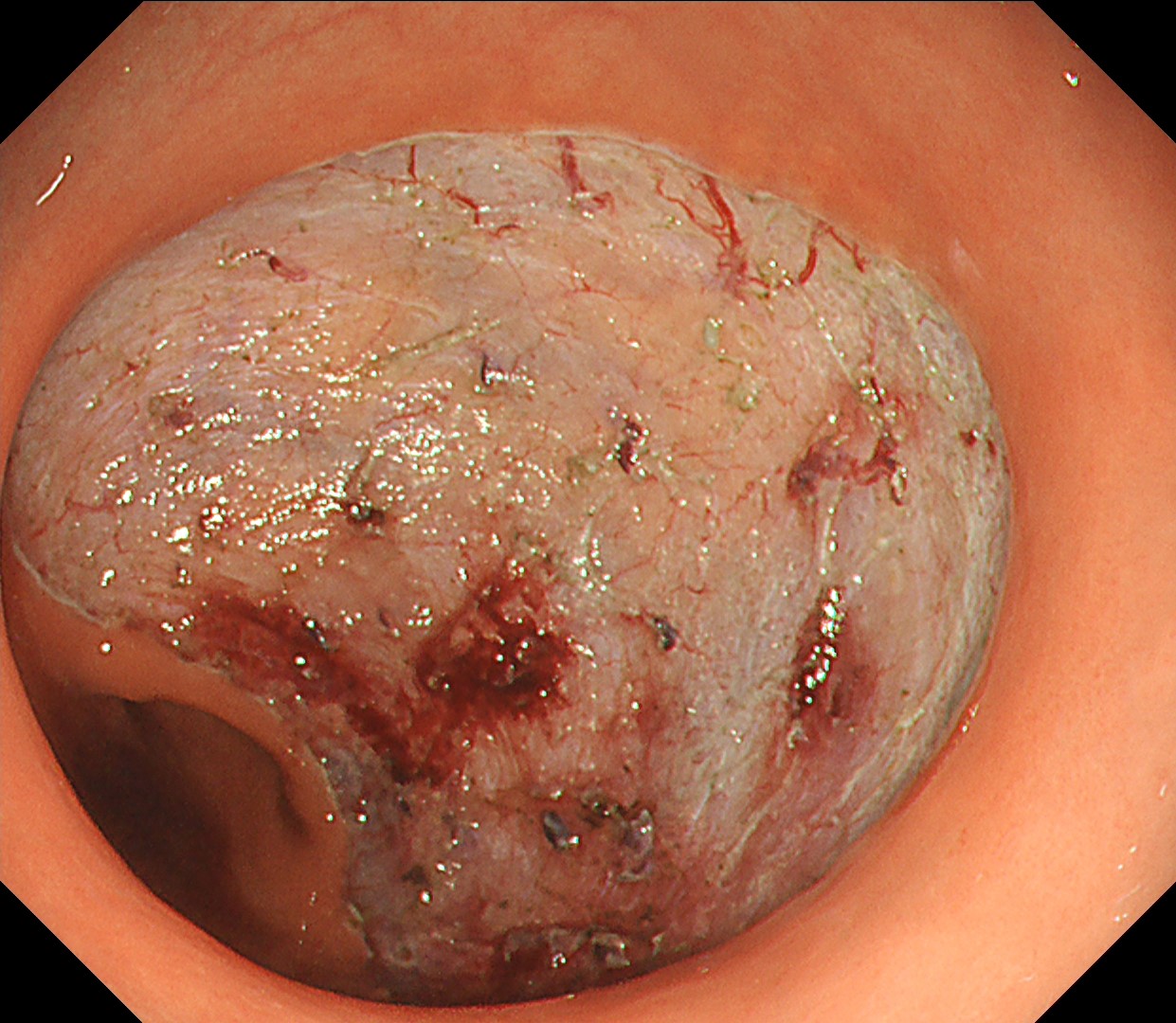
This is a large rectal tumor (7 cm in diameter) detected by FIT screening and subsequent colonoscopy. Initially, it was examined using a high-definition colonoscope with magnification function. The lesion size exceeded half of the rectal circumference, and its macroscopic morphology was interpreted as 0-Is+IIa (LST-G-NM). According to a previous meta-analysis, lesions with such morphology carry a higher risk of submucosal invasion, estimated at around 10% (Bogie R et al. Endoscopy. 2018;50:263-282). While invasive cancer was reported to mainly occur in the large nodular part, a later study on a large ESD cohort revealed that invasive cancer may also be present in a multi-focal fashion and even in the non-nodular portion, justifying en bloc resection for such lesions (Yamada M et al. Endoscopy. 2016;48:456-64).
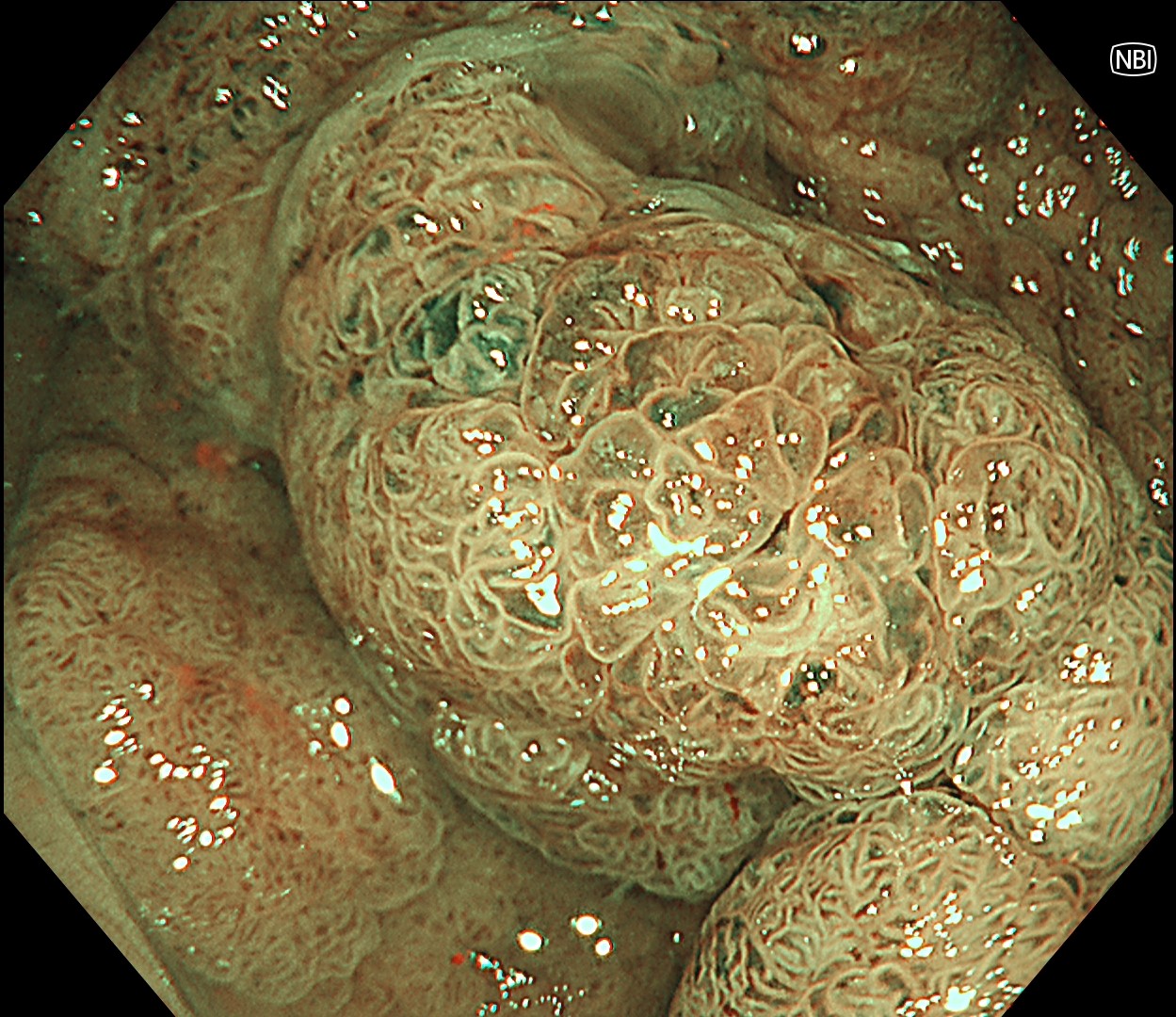
In this case, a focal JNET-2B capillary pattern was observed, indicative of advanced histology including high-grade dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, or even superficial invasive cancer. However, chromoendoscopy with crystal violet revealed a focal Kudo type Vi pit pattern without a demarcation line, indicating a non-invasive lesion and justifying endoluminal therapy.
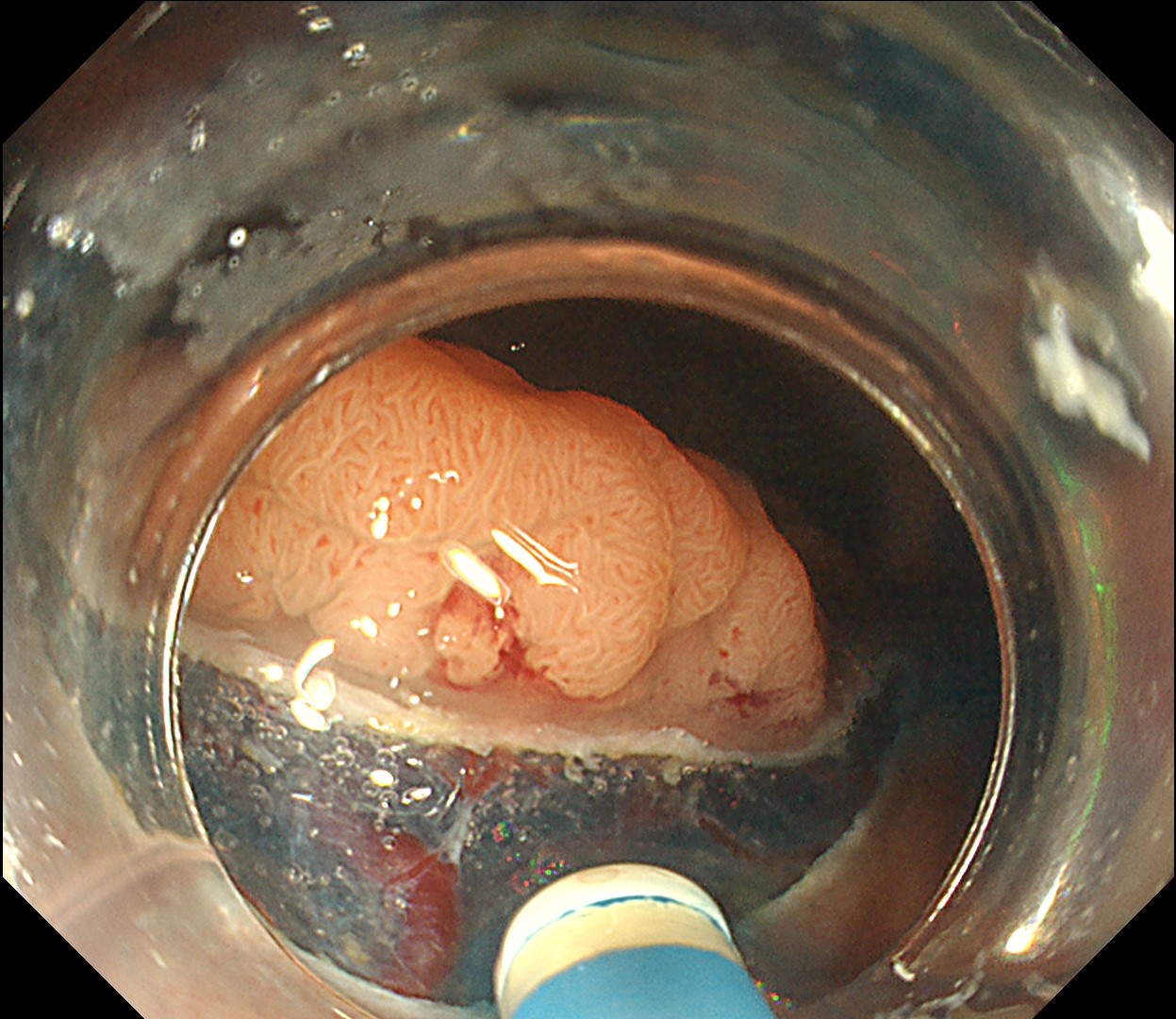
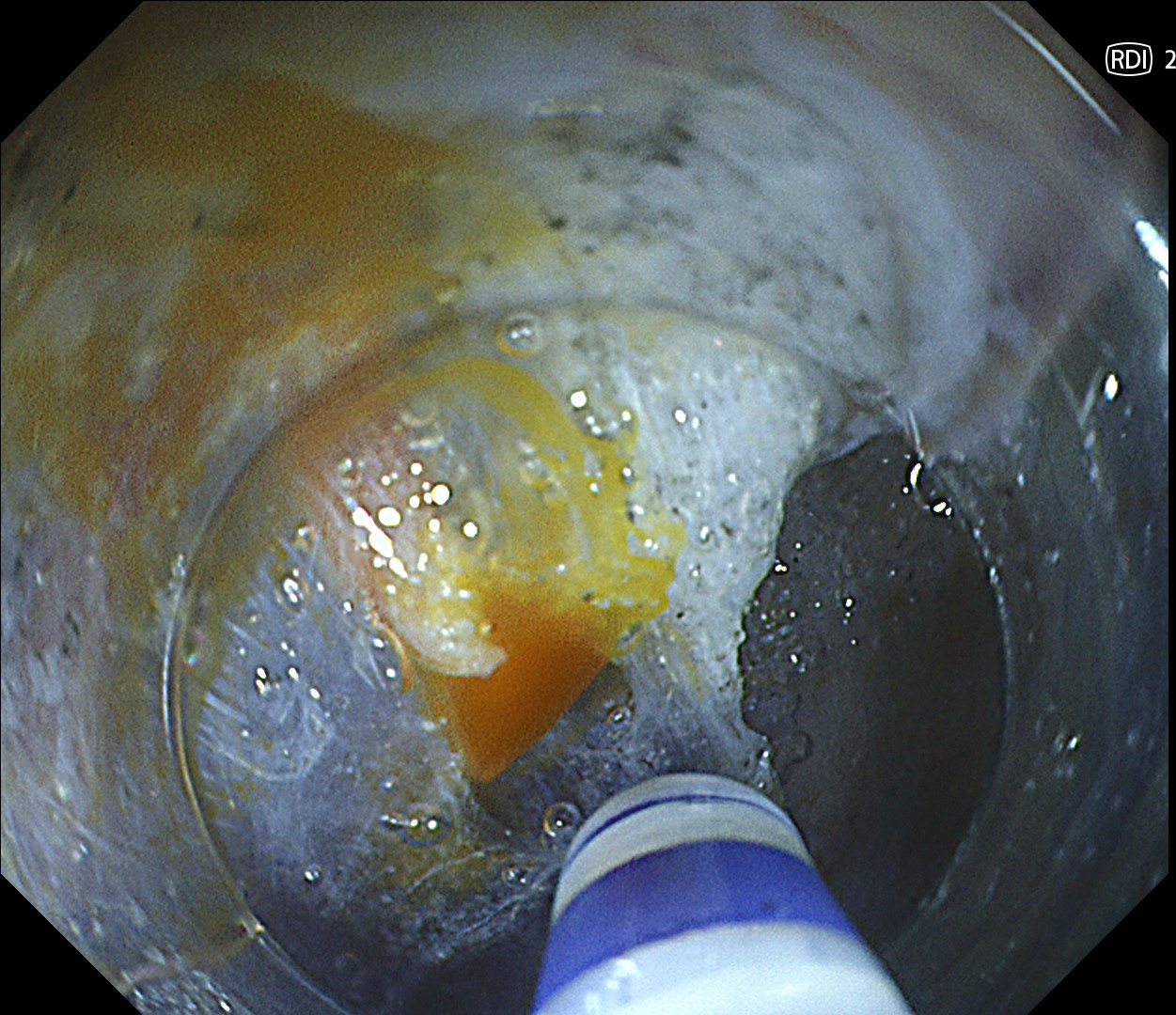
ESD was performed using the Olympus DualKnife J (KD-655U) with a therapeutic colonoscope (PCF-H290TI), featuring an up angulation of 210° and a short bending section, facilitating the ESD procedure.
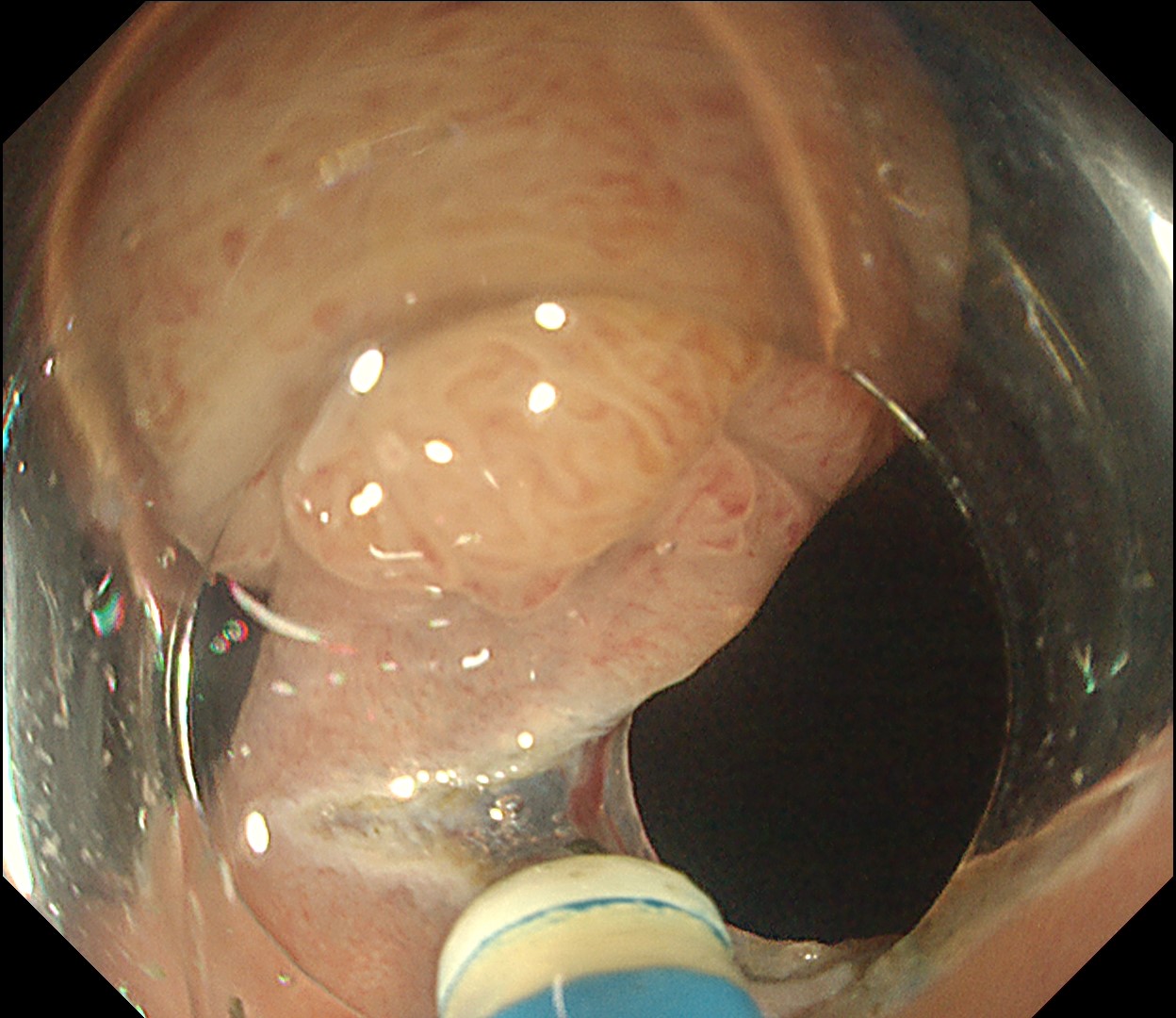
Histologically, this lesion was diagnosed as a tubulovillous adenoma with high-grade dysplasia, which was consistent with the area where the JNET 2B capillary pattern and Kudo type Vi pit pattern were observed.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
- Keyword
- Content Type