Colorectal Case 19

Scope: CF-EZ1500
Organ: Transverse colon
Patient information: 69 years old, Male
Medical history: No related diseases
1. WLI Observation
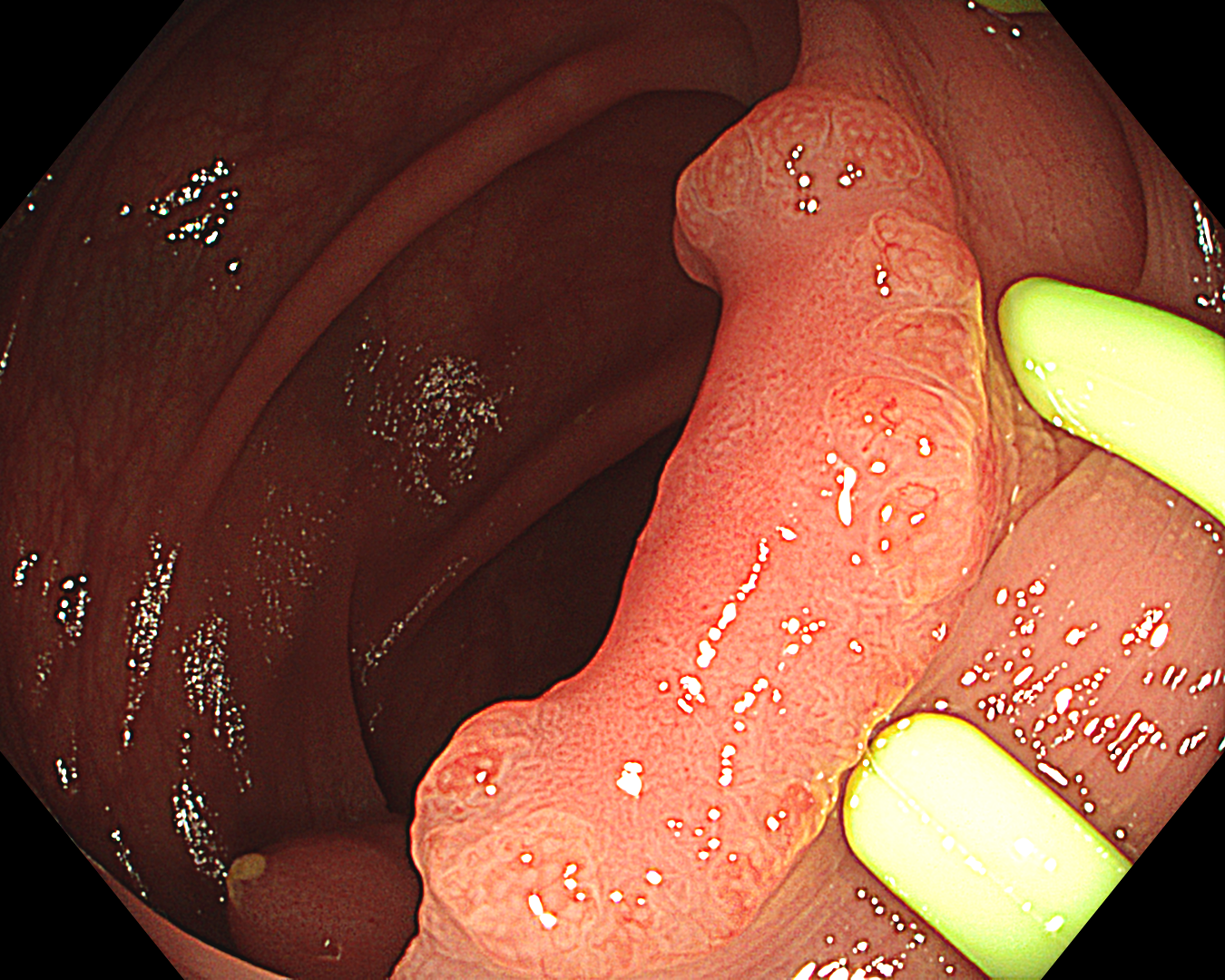
Enhancement: A8
WLI mode
TXI Mode: None
RDI Mode: None
BAI-MAC: On
2. NBI Observation
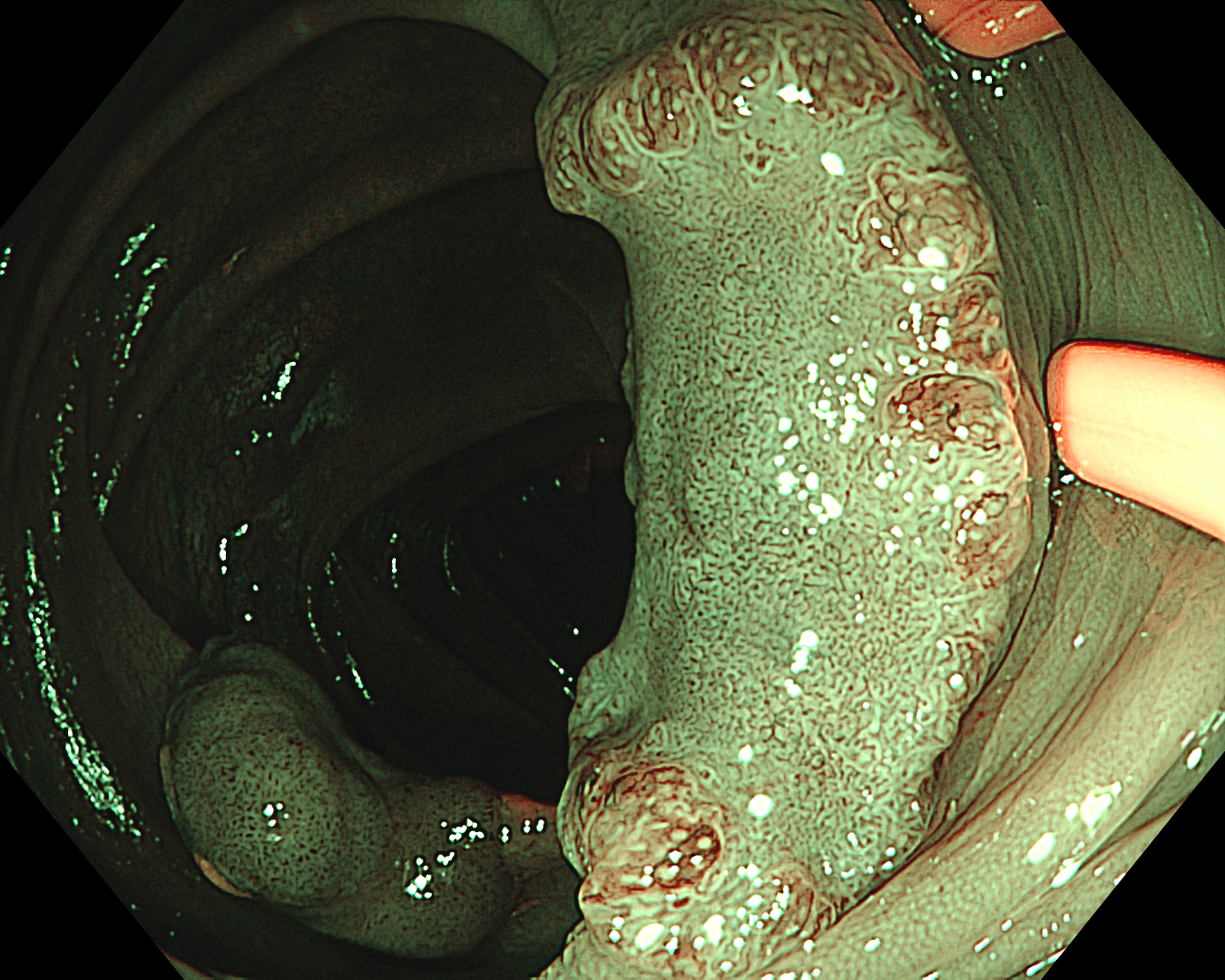
Enhancement: B8
NBI mode
TXI Mode: None
RDI Mode: None
BAI-MAC: None
3. Near Focus mode with NBI
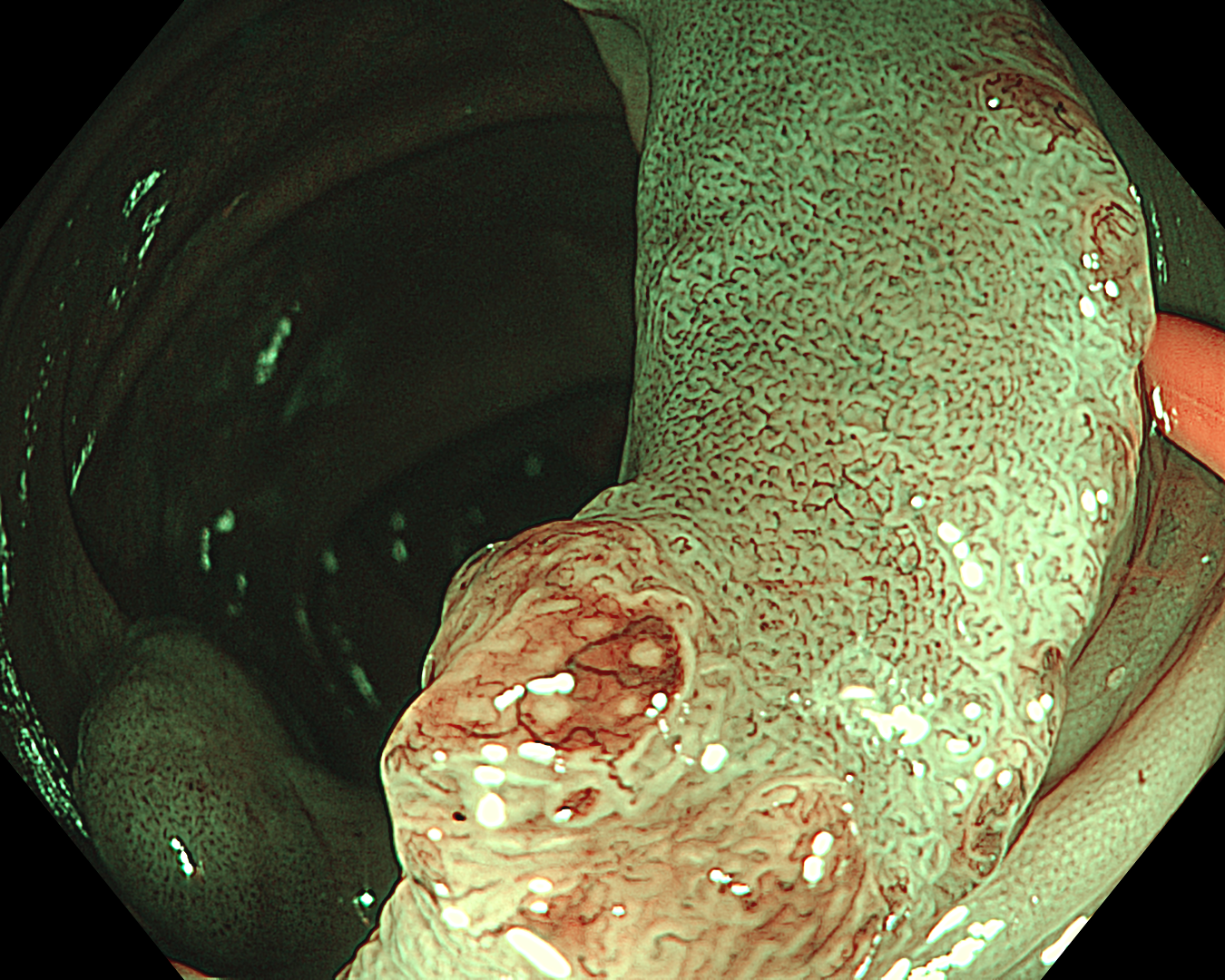
Enhancement: B8
NBI mode
TXI Mode: None
RDI Mode: None
BAI-MAC: None
4. Near Focus mode with NBI
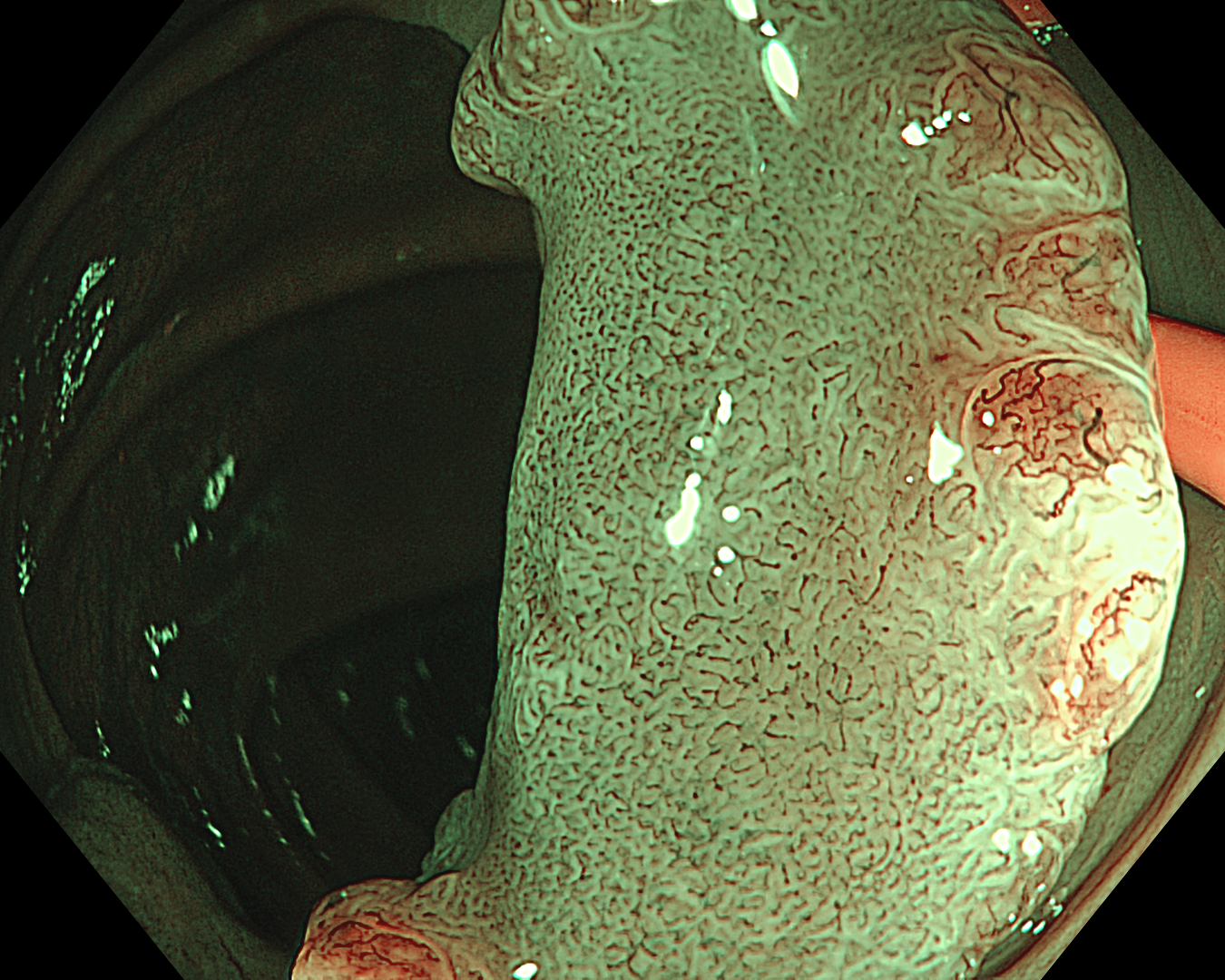
Enhancement: B8
NBI mode
TXI Mode: None
RDI Mode: None
BAI-MAC: None
6. TXI mode
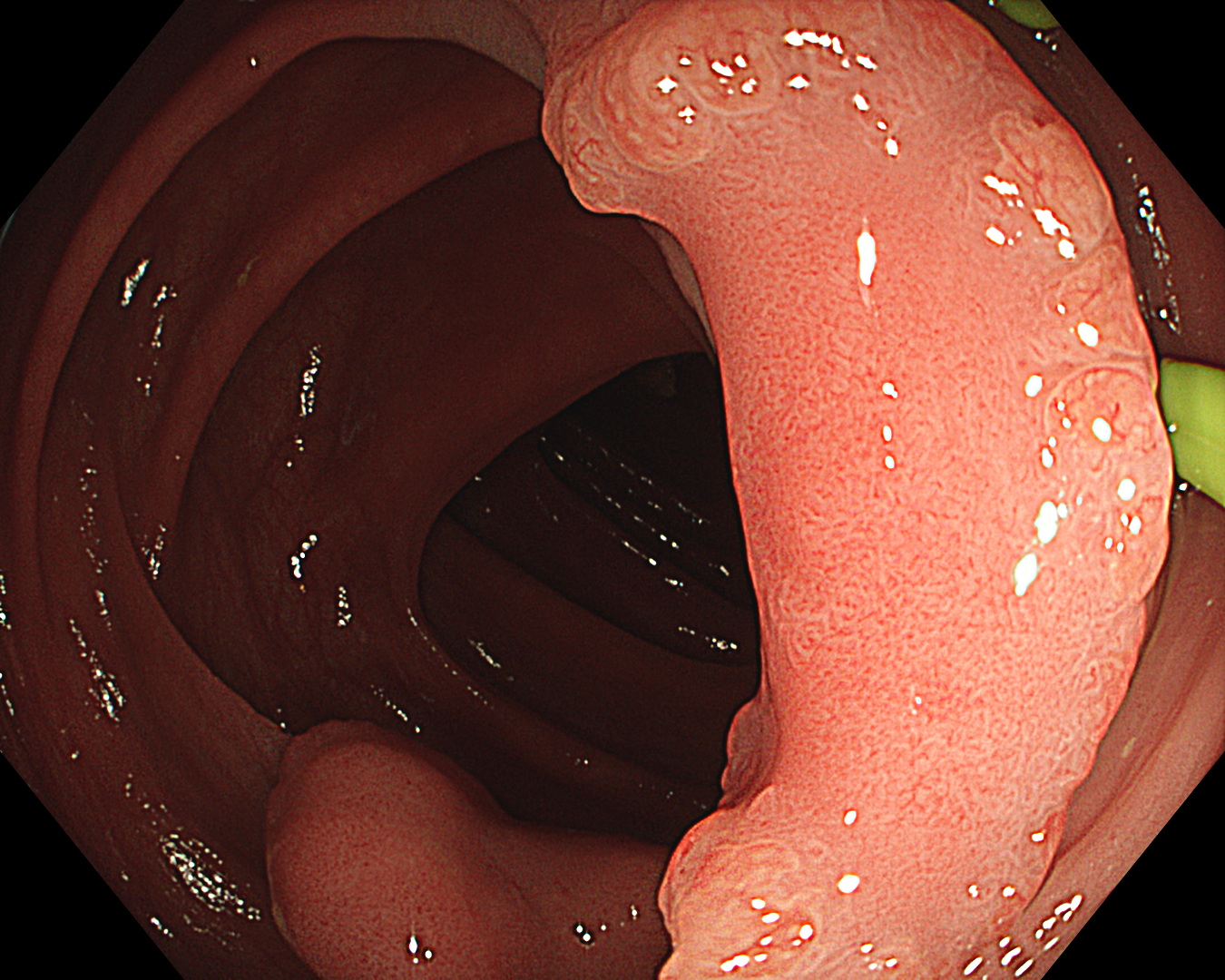
TXI Mode: 2
7. TXI mode + Near Focus mode
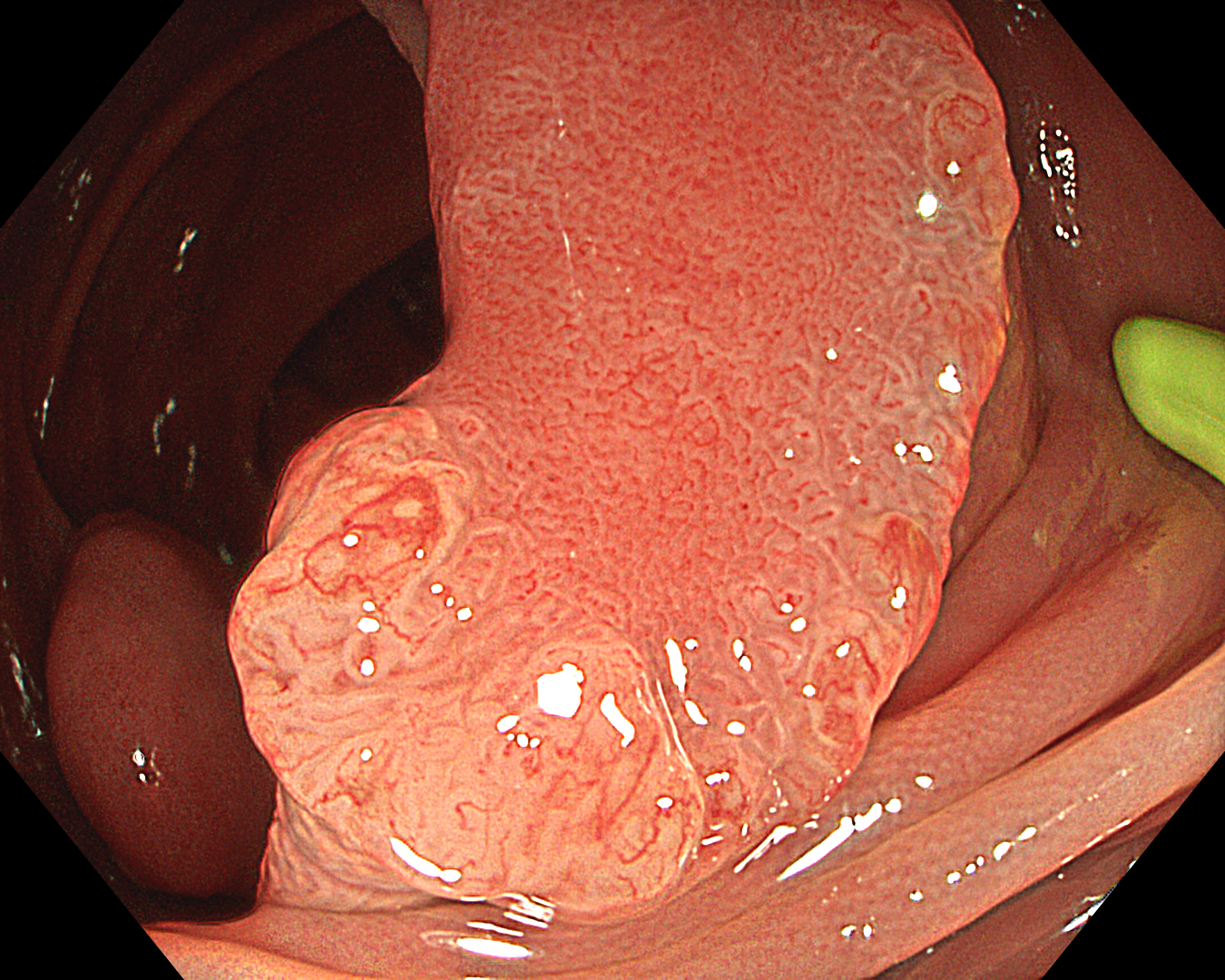
TXI Mode: 2
8. TXI mode + Near Focus mode
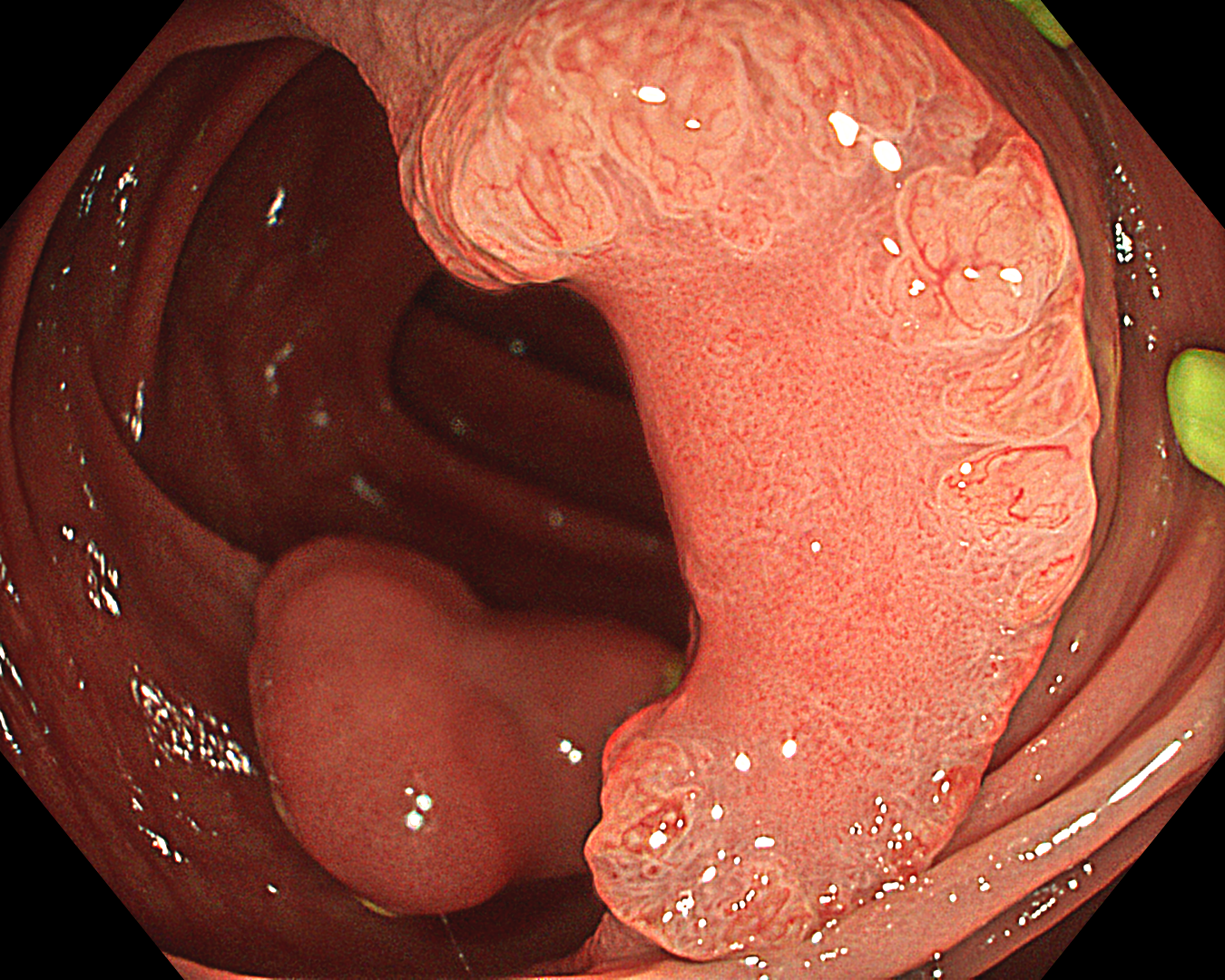
TXI Mode: 2
12. Underwater observation
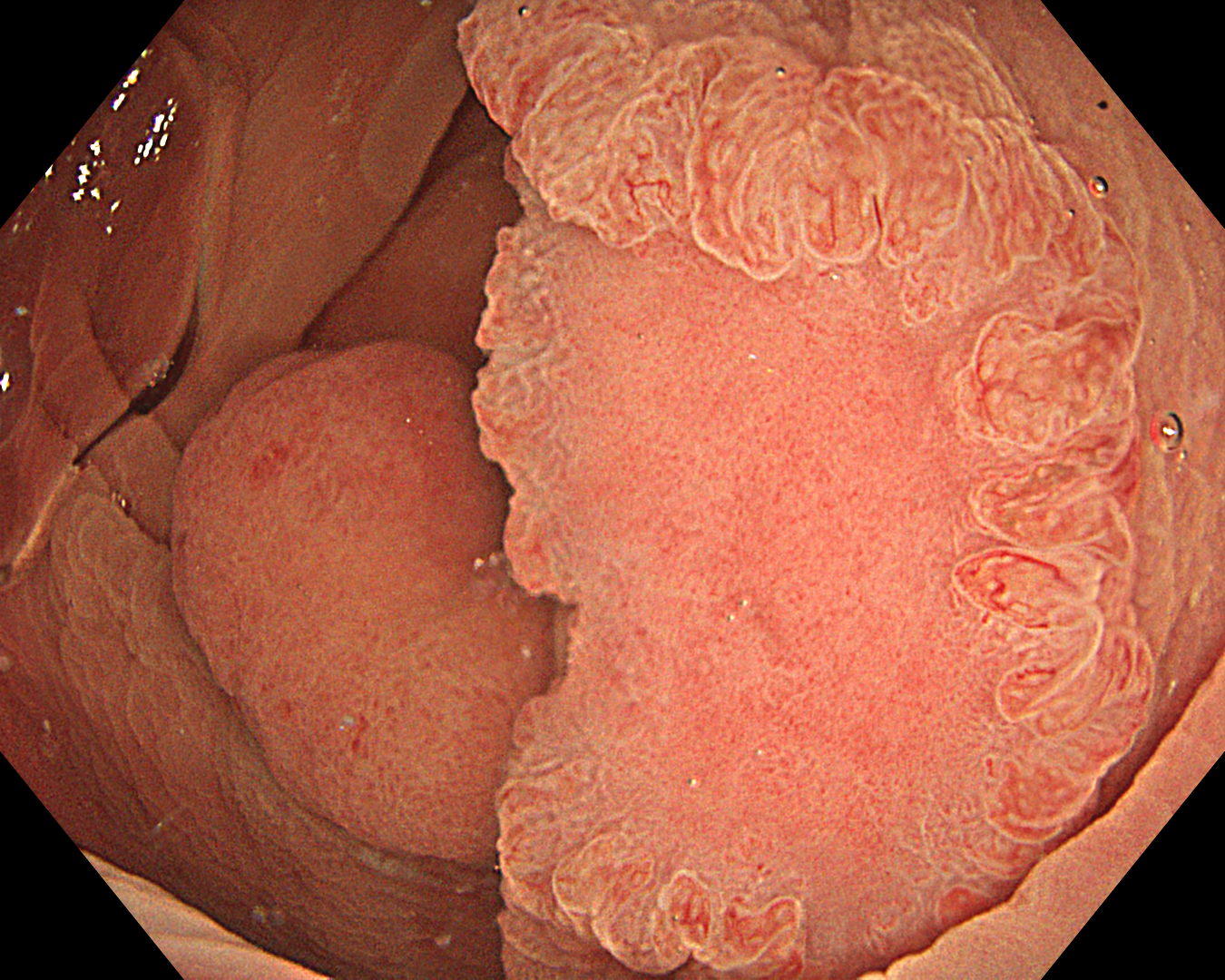
TXI Mode: 2
13. Underwater observation
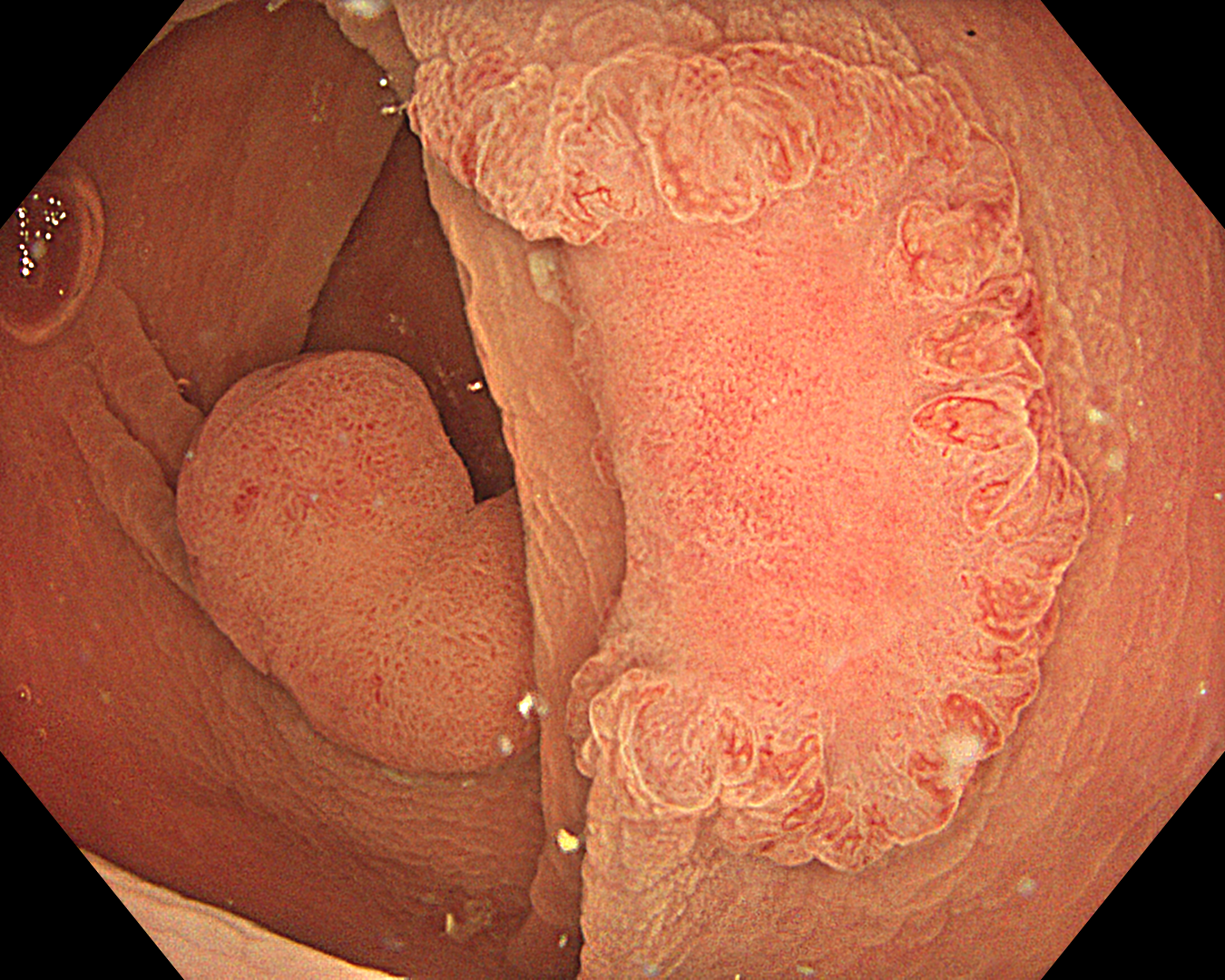
TXI Mode: 2
Case Video
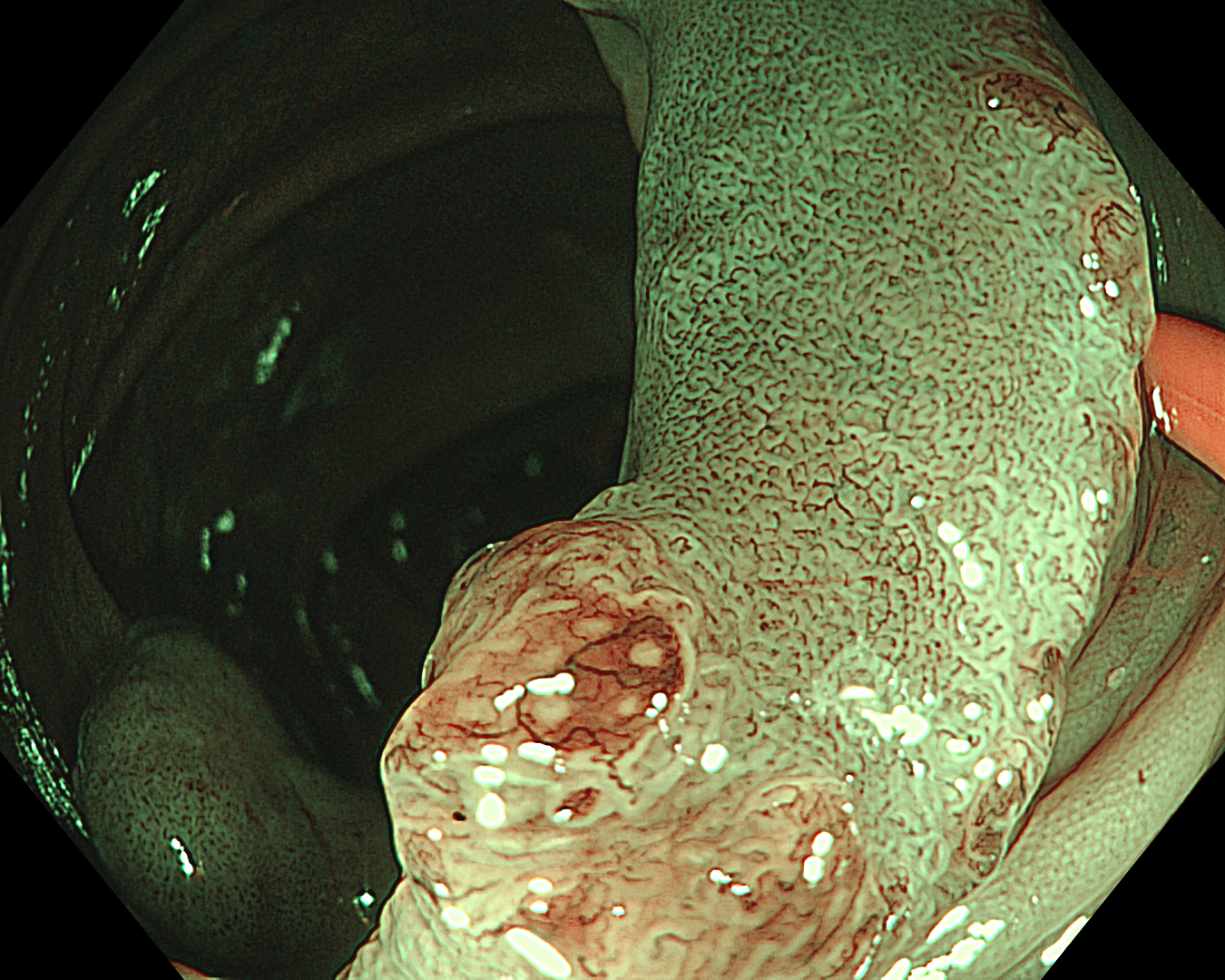
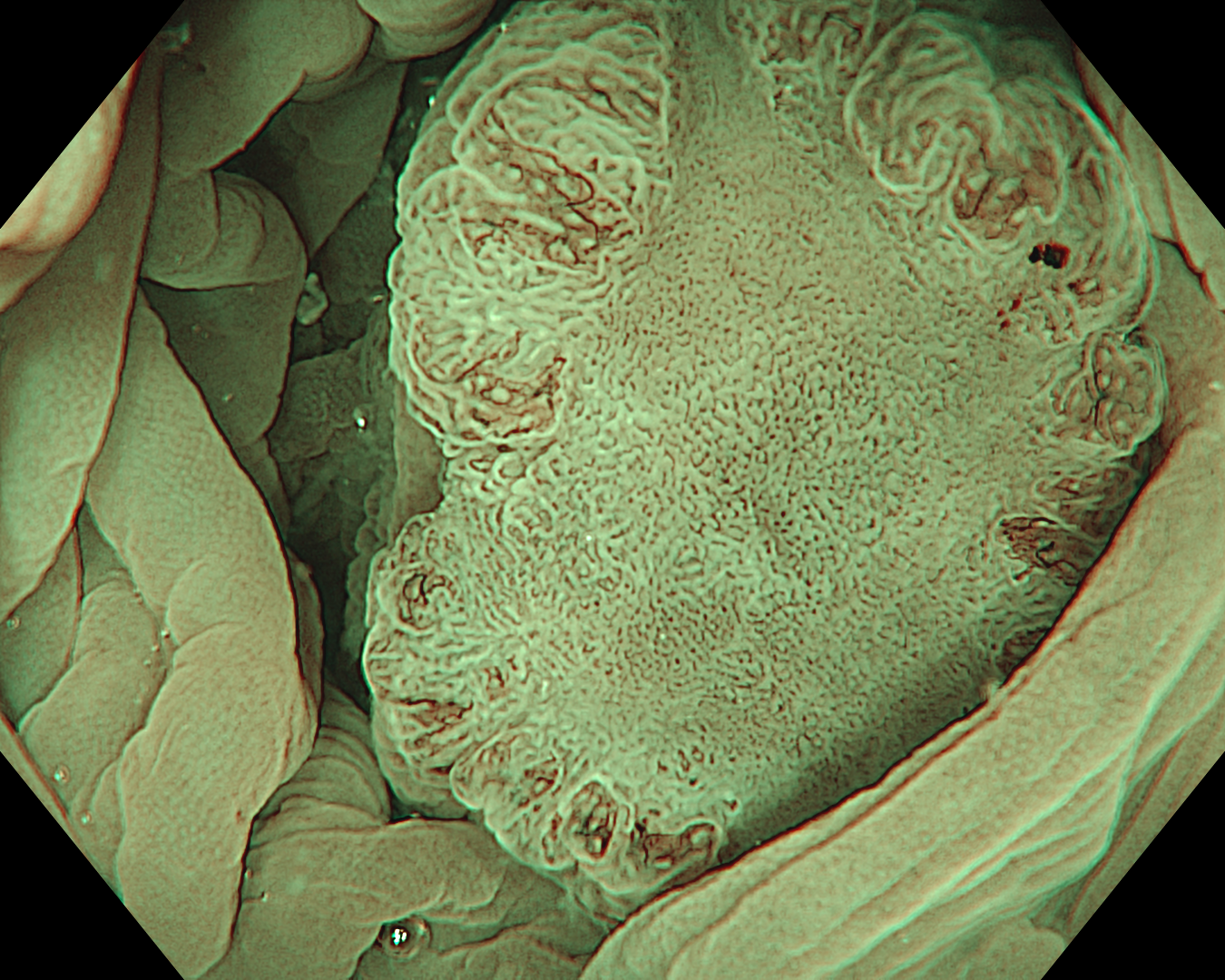
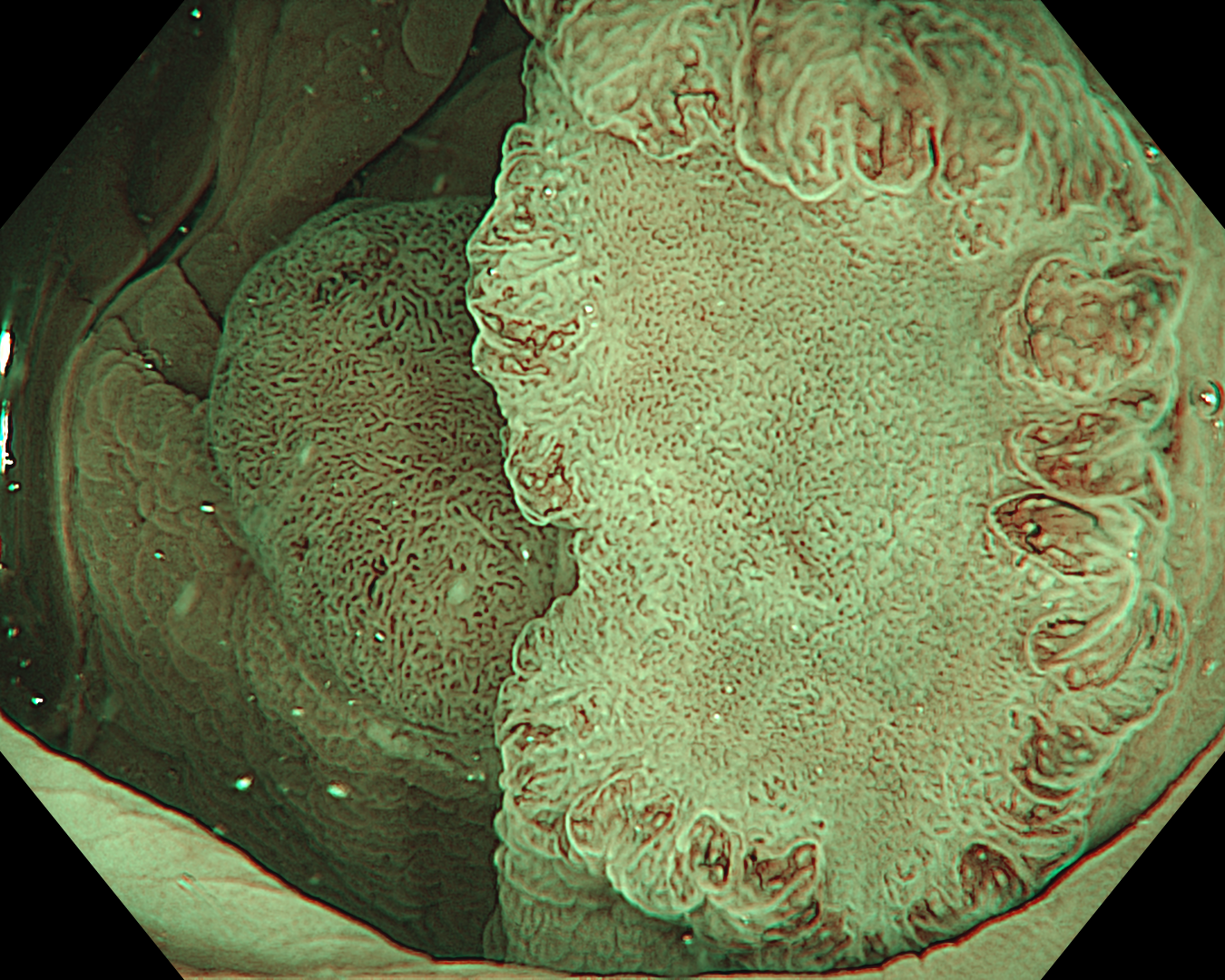
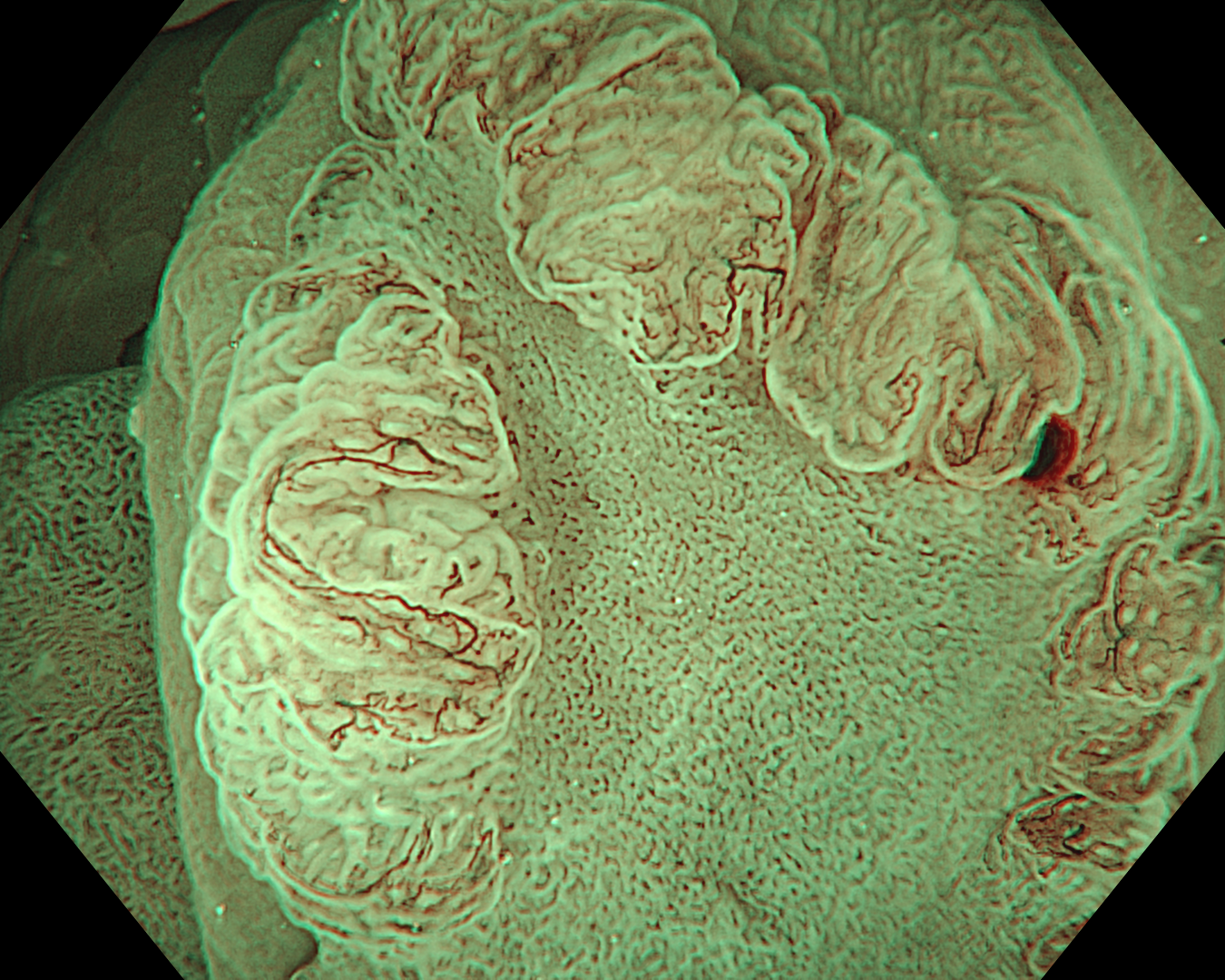
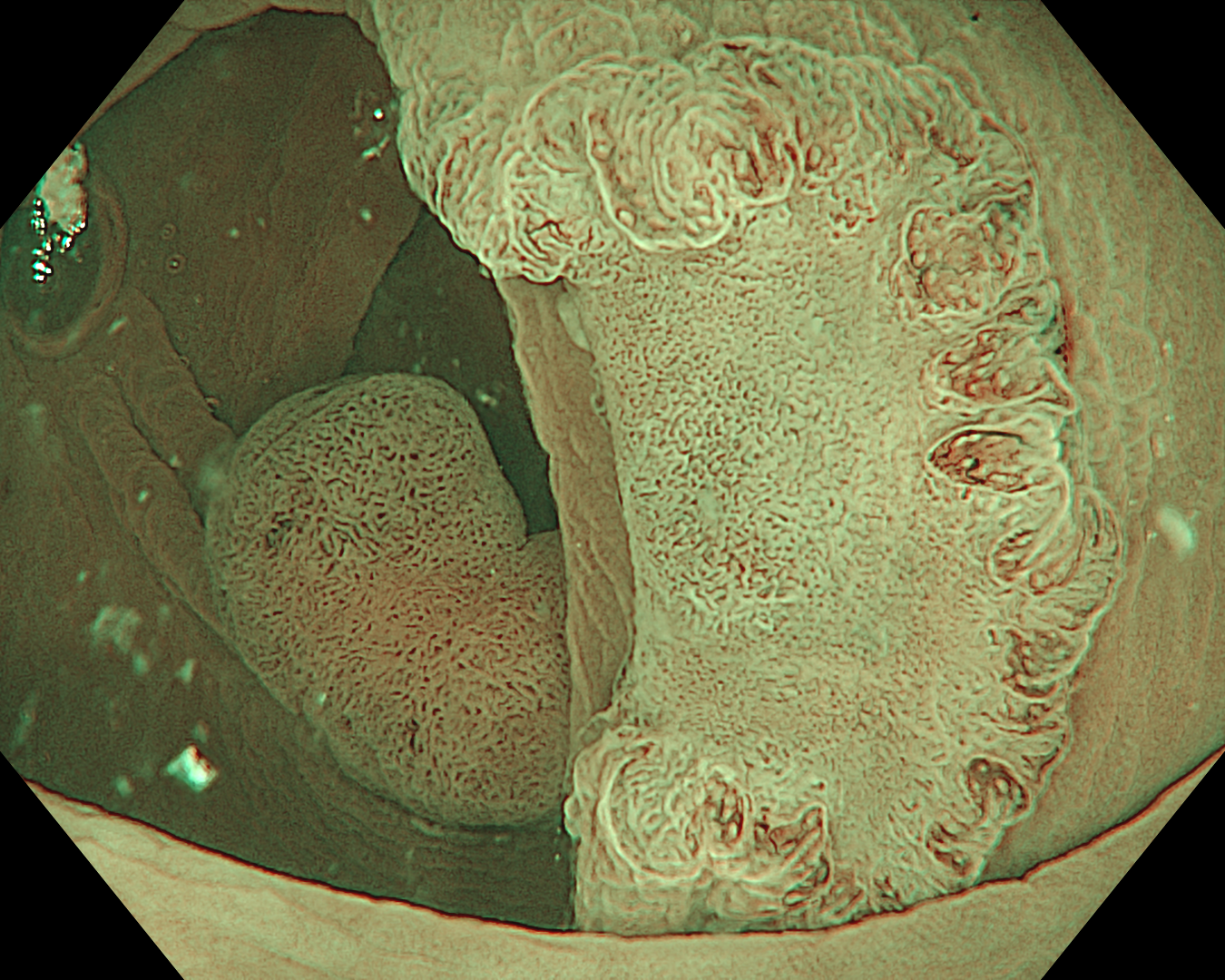
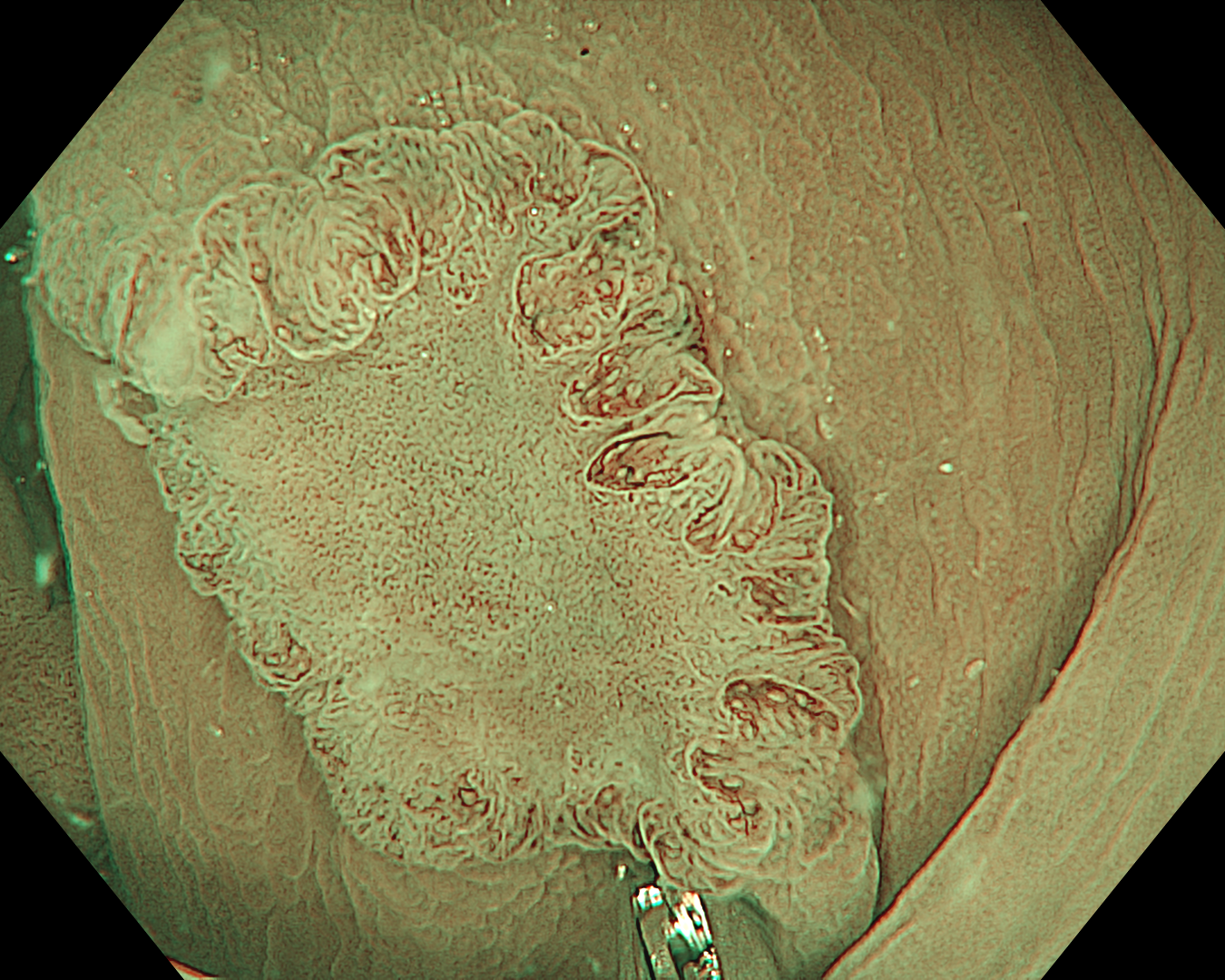
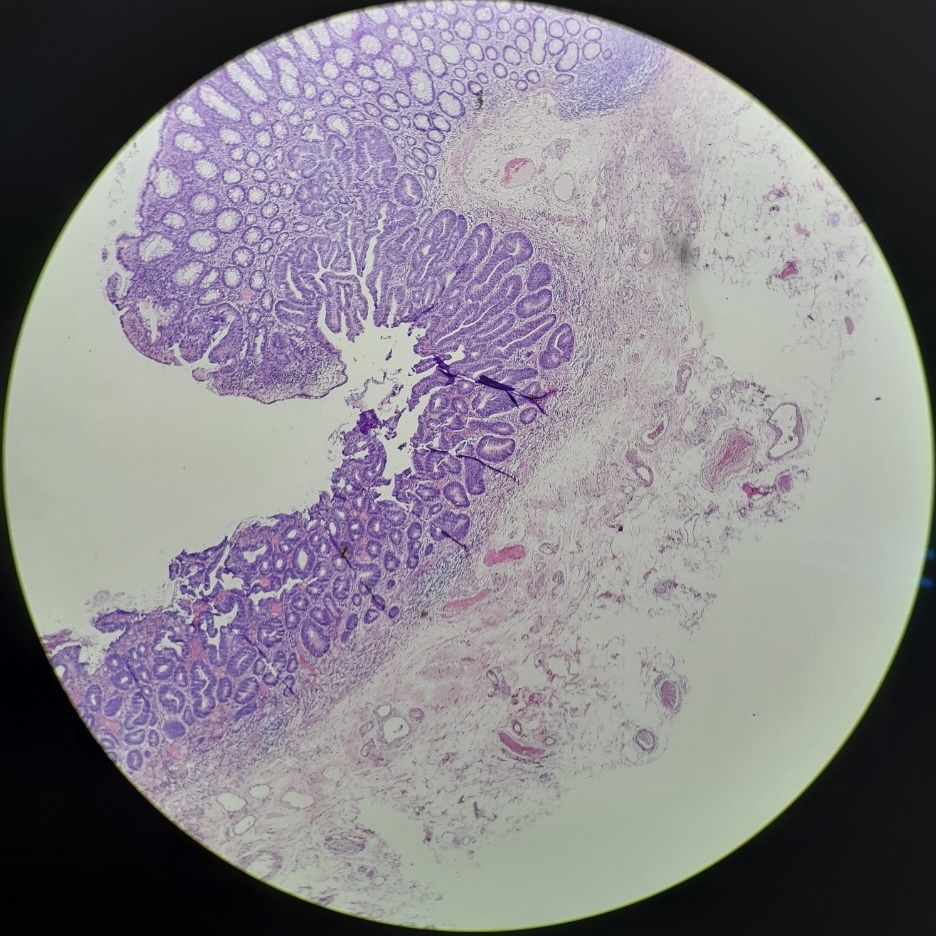
This was an LST-NG-PD-type mucosal cancer in the transverse colon. By using image enhancement modes (WLI, TXI, and NBI with or without magnification mode), surface and vessel abnormalities of the lesion are clearly observed, making an important contribution to the assessment and classification of the lesion. Underwater observation, visualization of the entire lesion is easier, while assessment of surface pattern and vessel pattern of the lesion is still very clear.
Overall Comment
Laterally spreading tumors (LSTs) were originally classified into four subtypes by Shin-ei Kudo et al., including LST-G and LST-NG. LST-G is subclassified into homogeneous (LST-G-H) and nodular mixed types (LST-G-M), and LST-NG is divided into flat elevated (LST-NG-F) and pseudo-depressed types (LST-NG-PD).
LST-G types tend to have less submucosal carcinoma, irrespective of the size of the lesion. However, the LST-NG types tend to be more aggressive, with a higher incidence of advanced carcinoma, especially the pseudo-depressed type.
Different classifications help predict the risk of submucosal invasion, such as the NICE classification and the JNET classification. Its subclass JNET2a is mostly comprised of intraepithelial lesions; JNET3 is composed mainly of deep submucosal invasive lesions; and JNET2b can be found in both intramucosal and submucosal invasive lesions.
When a part of the polyp is hidden behind a fold or clamshell wrapped around a fold, endoscopists encounter challenges in visualizing the entire surface area of the polyp. Underwater observation could help solve this issue.
This is a LST-NG-PD with a 16-mm diameter. The lesion has a red O-ring with a depressed area about 14mm in diameter. In “air” endoscopy and underwater endoscopy, the lesion has a “non-extension” or “sclerosis of the wall” sign. Observing in the “near focus” magnifying endoscopy, some areas had JNET type 2b, suggesting that this is either an intramucosal cancer lesion or a cancer lesion with submucosal invasion.
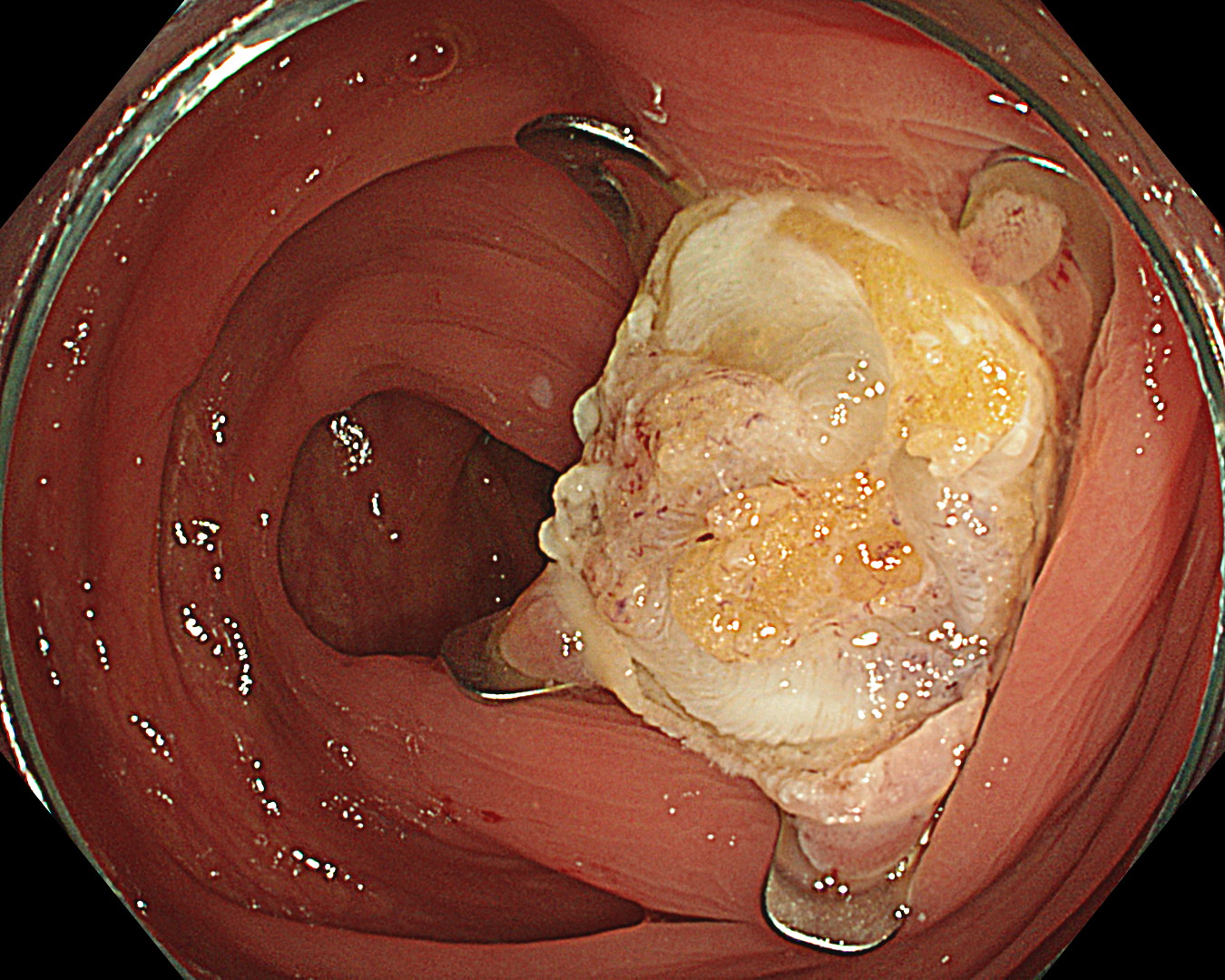
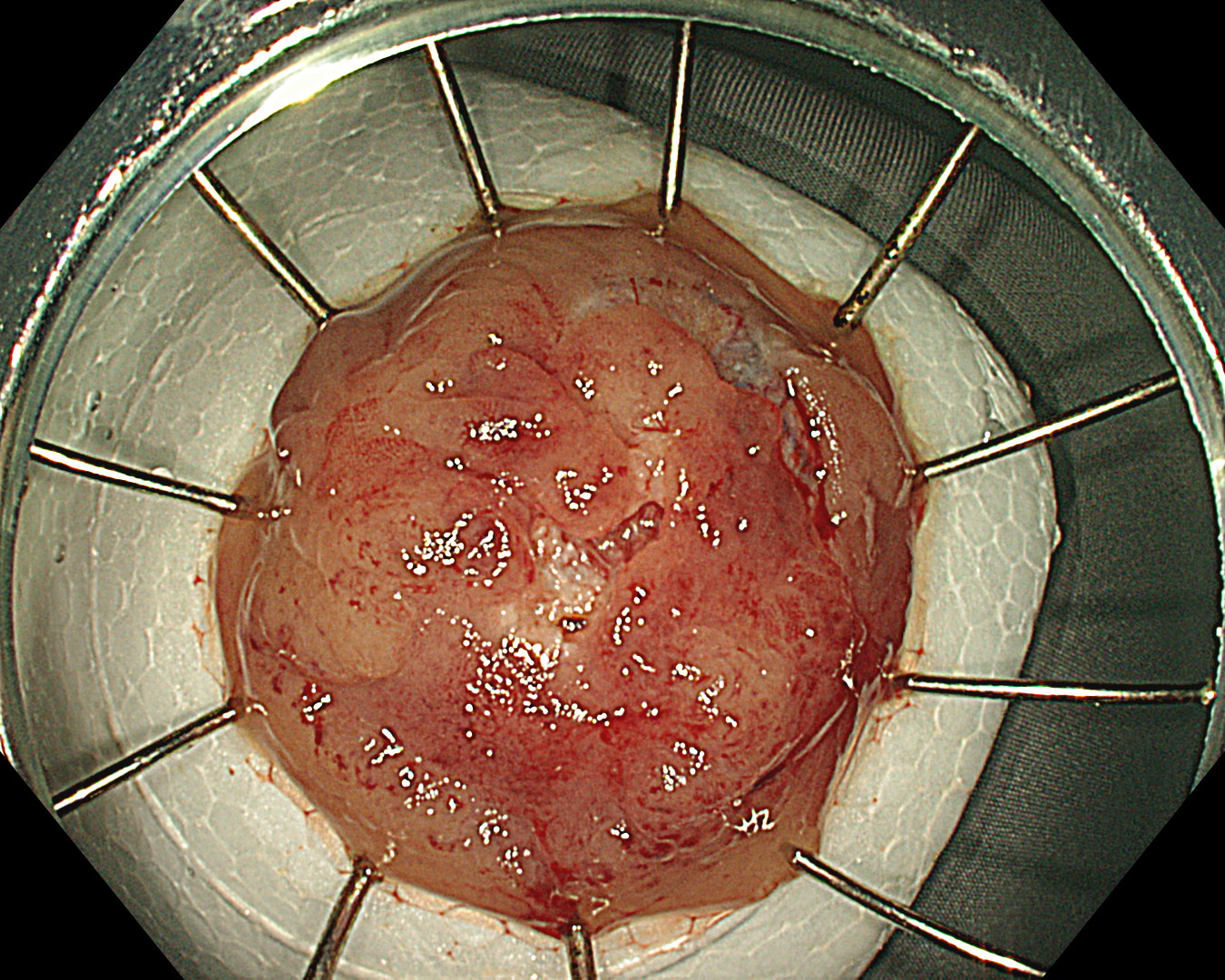
We resect the lesion by FTRD (Full-Thickness Resection Device) due to failure to resect the lesion by ESD.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
Dr. Serhii Polishchuk Case 20: 0-Is (LST-mixed type), 22mm, JNET 2A with fern-like pits
Prof. Yasushi Sano
- Keyword
- Content Type