Colorectal Case 27
.jpg)
Prof. Yoji Takeuchi
Gunma University Hospital, Japan
Scope: CF-EZ1500DI
Organ: Sigmoid Colon
Patient information: Female in Her 50s
Medical history: Colon Polypectomy (1 Year Prior)
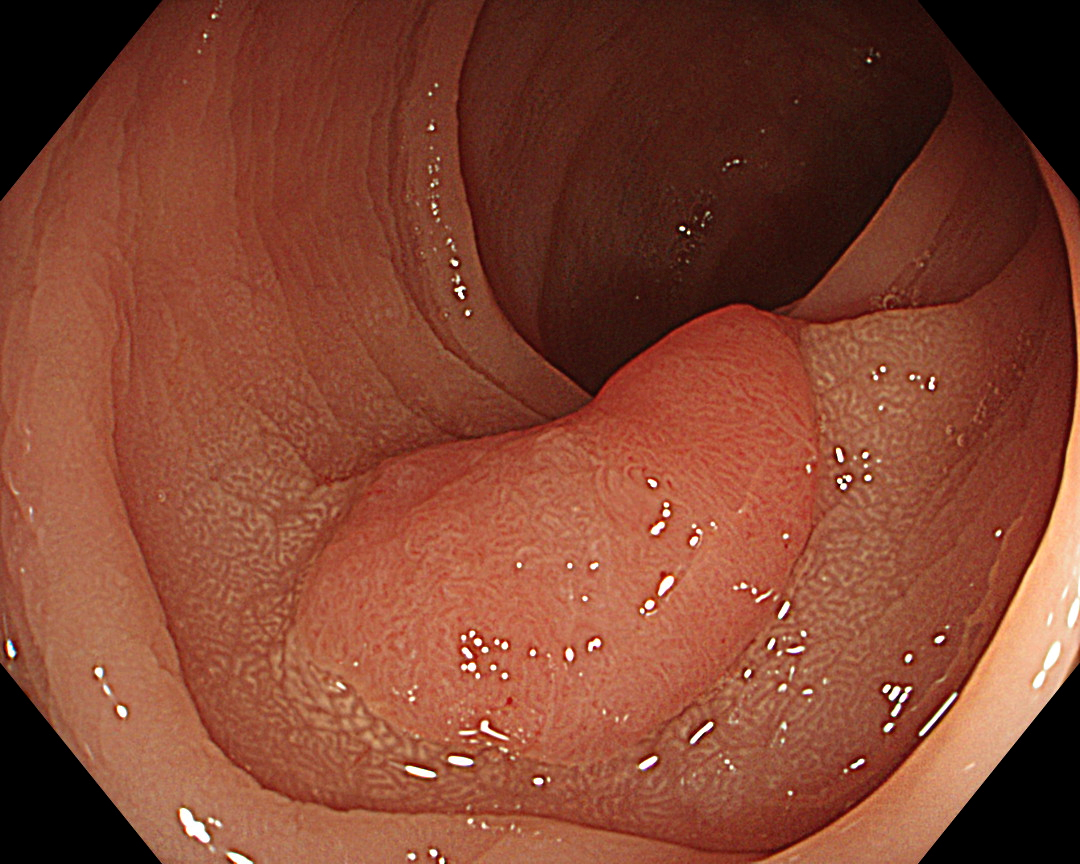
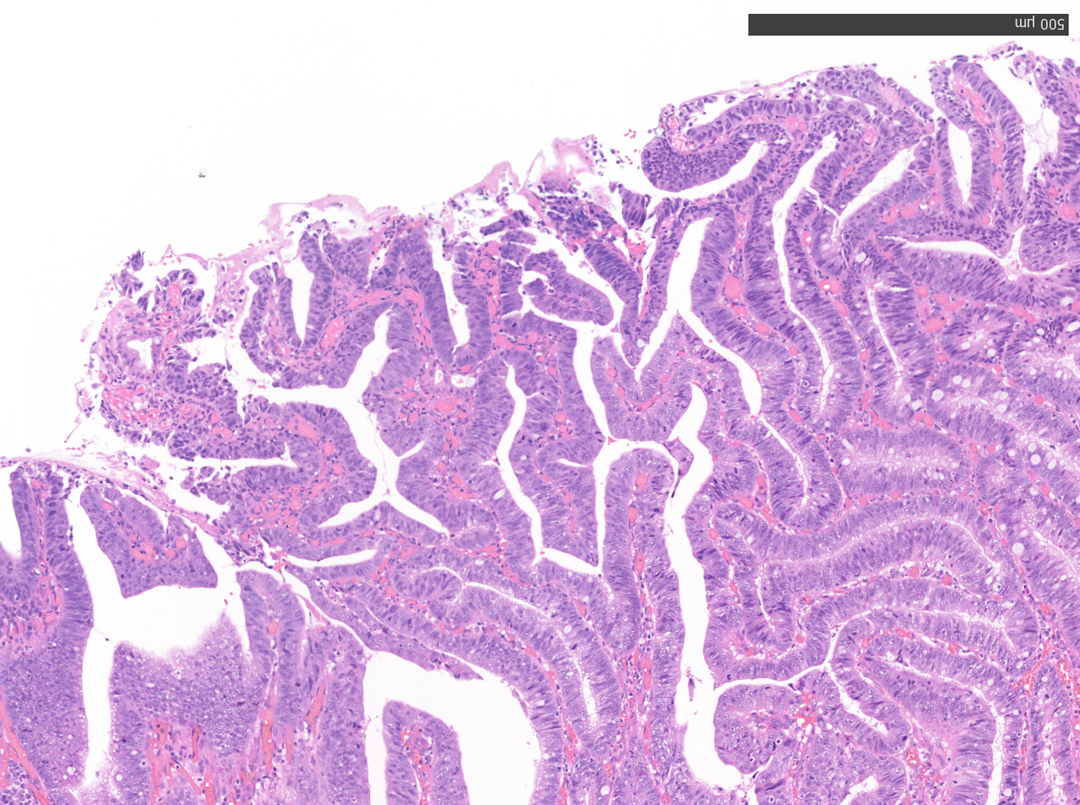
7. Narrow Band Imaging (Close Observation, without Near Focus)
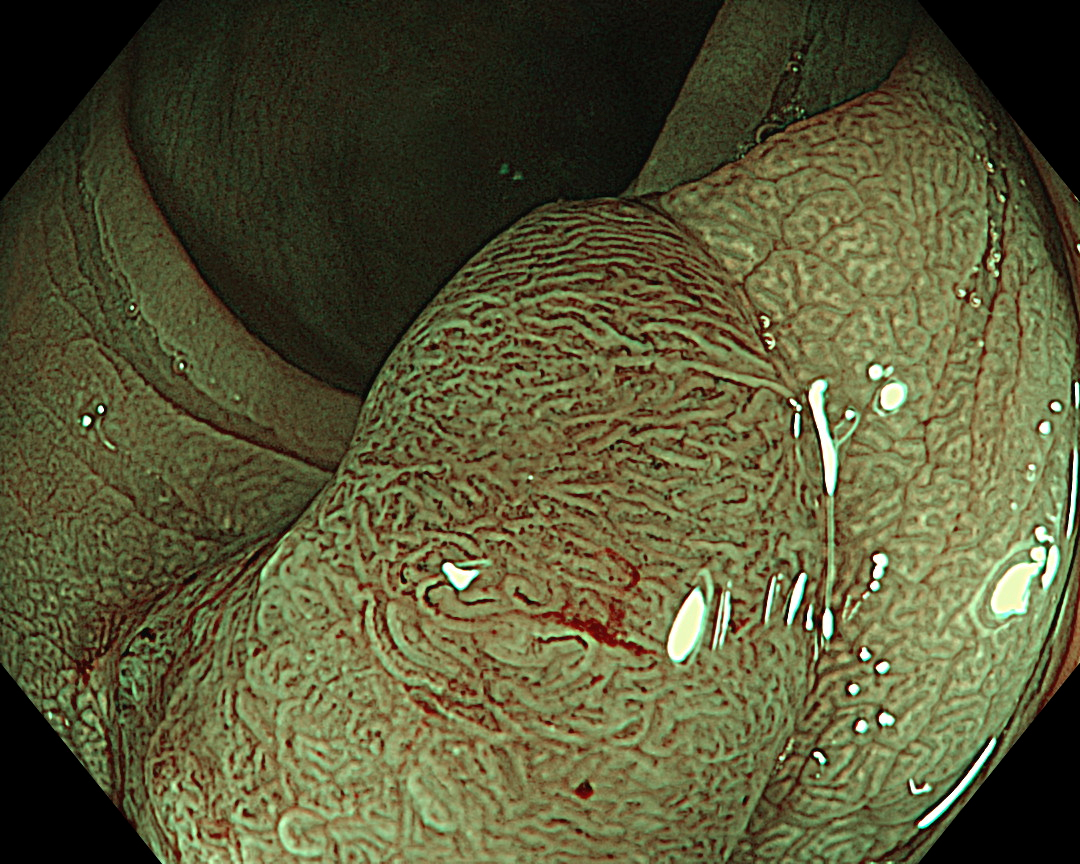
Enhancement: A8
NBI Mode: On
BAI-MAC: On
Near Focus: Off
8. Narrow Band Imaging (Close Observation, without Near Focus)
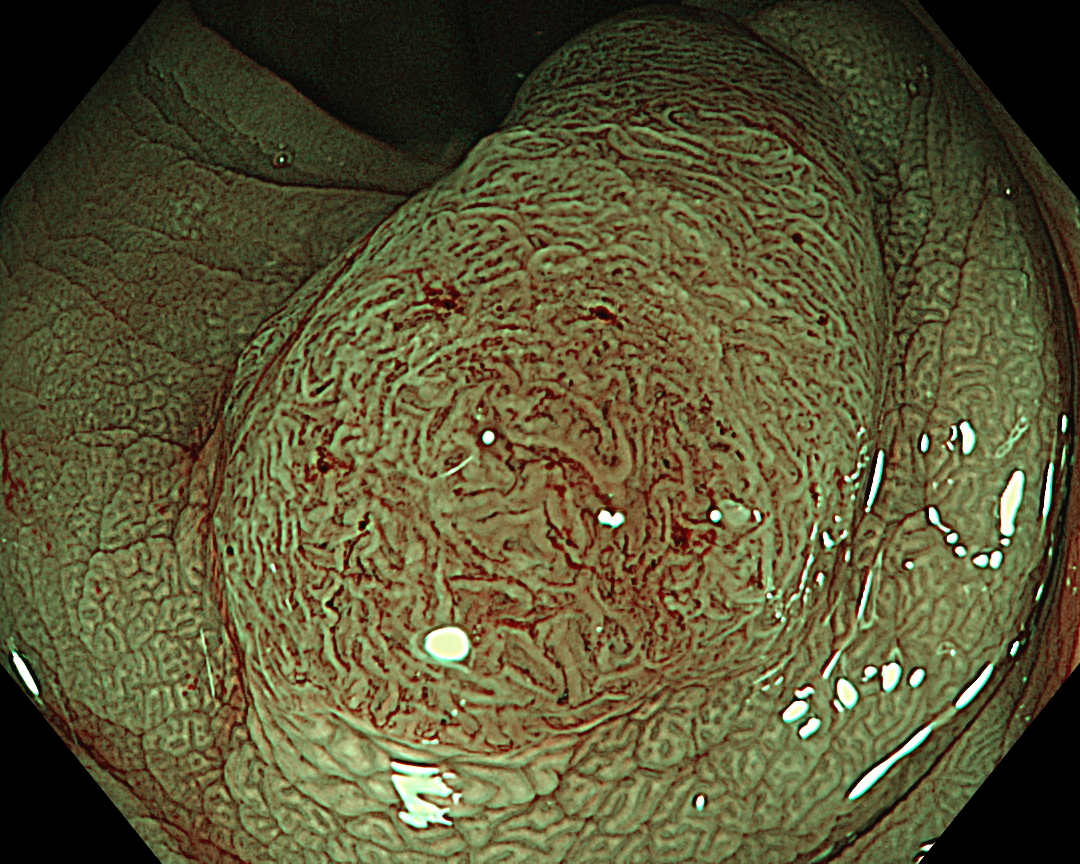
Enhancement: A8
NBI Mode: On
BAI-MAC: On
Near Focus: Off
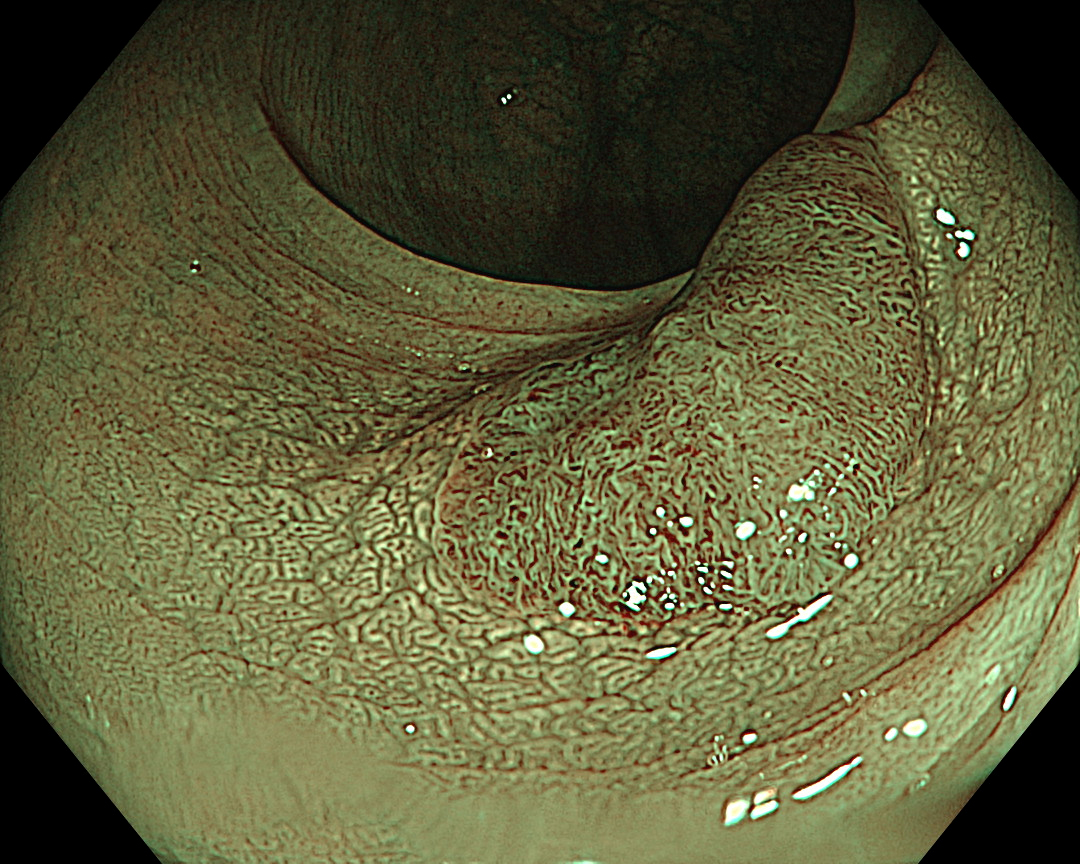
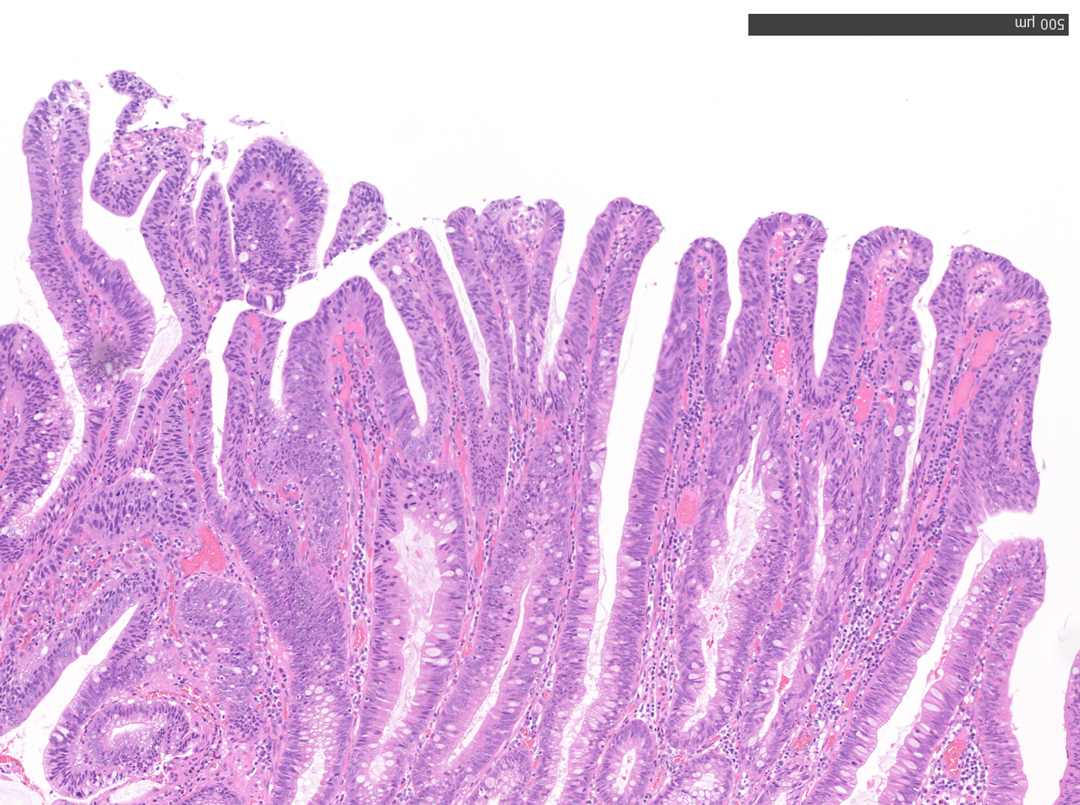
9. Narrow Band imaging (Near Focus Mode)
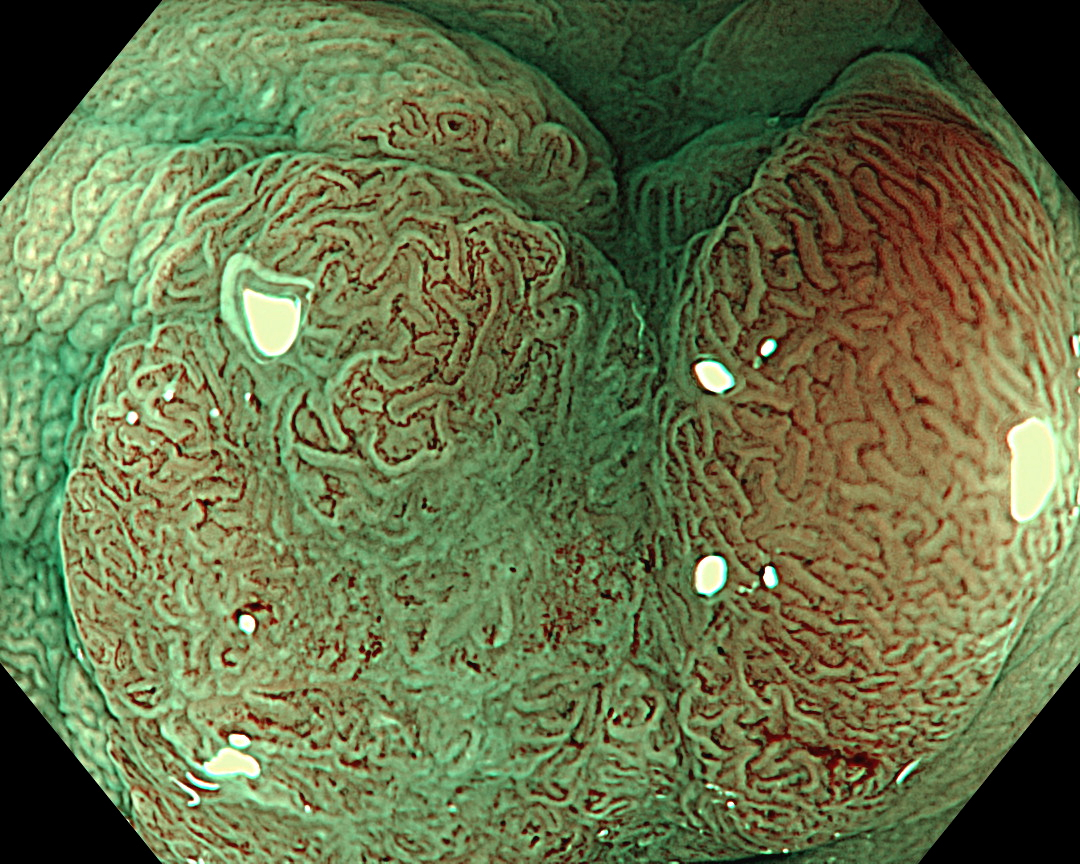
Enhancement: A8
NBI Mode: On
BAI-MAC: On
Near Focus: On
Overall Comment
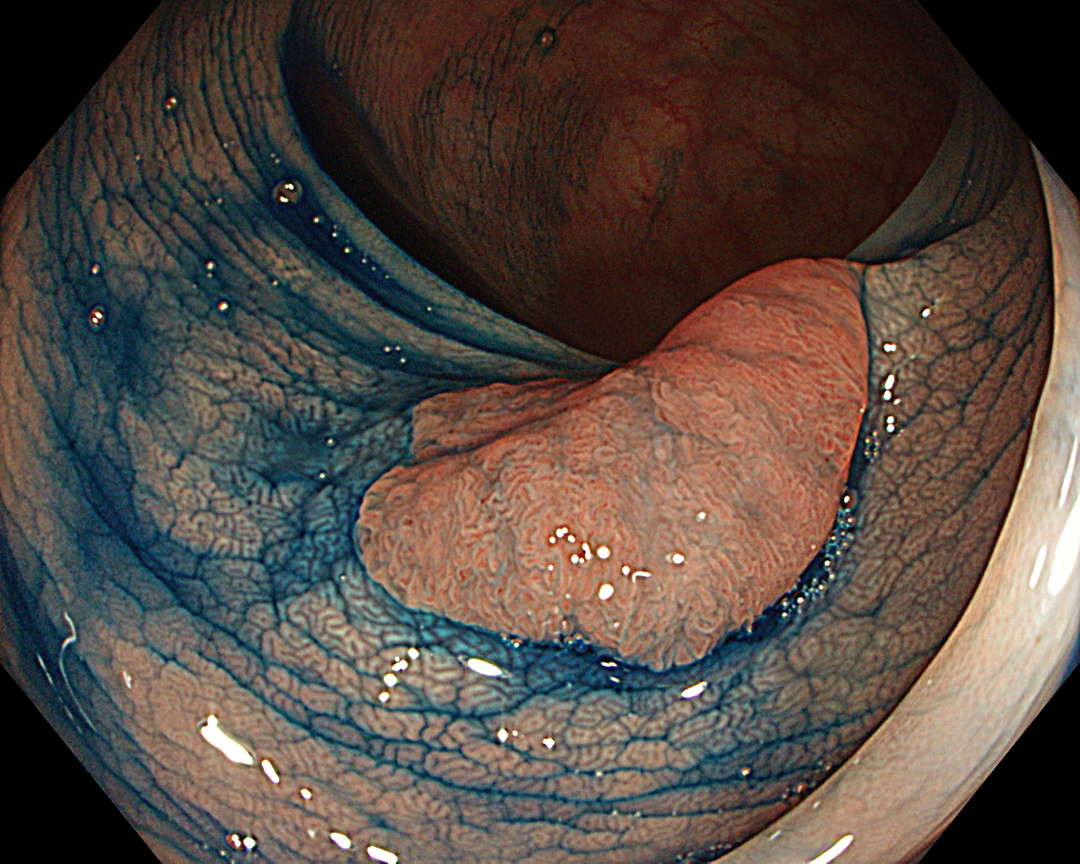
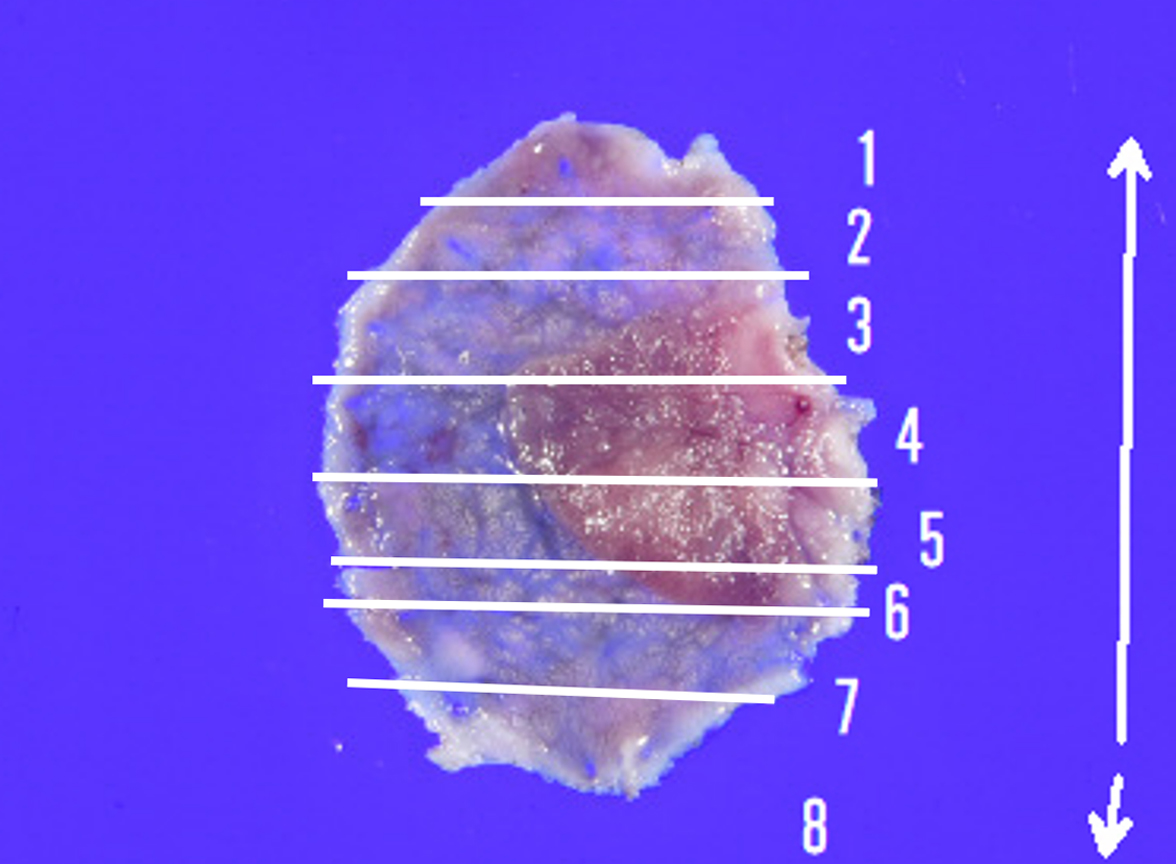
This case presented a 12 mm-sized carcinoma in adenoma in the sigmoid colon. As it was located near a previous polypectomy scar, it was diagnosed as a residual recurrent lesion. En bloc resection would have been the ideal option in this case; however, the presence of scarring meant there was a risk that the lesion could not be resected en bloc using conventional EMR. Therefore, ESD was chosen despite the small size of the lesion. Without comprehensive observation, it is likely that EMR — the inappropriate, but easier option — would have been selected. We believe that magnifying observation with the CF-EZ1500DI enabled us to select an appropriate treatment option.
White-light observation showed a reddish, flat elevated lesion with a notch near the center, which appeared to be slightly thicker. At this point, the lesion should not be considered a simple low-grade adenoma, but a more dysplastic lesion that requires close examination, including magnifying observation.
Indigo carmine and crystal violet are commonly available in Japan due to a long tradition of chromoendoscopy. However, these dyes are not widely used in Europe and North America, which may make it difficult for some endoscopy facilities to obtain them. Moreover, chromoendoscopy is typically time-consuming and cumbersome. NBI, on the other hand, is able to provide more information than white-light observation because microvessels and surface structures can be evaluated at the flick of a switch.
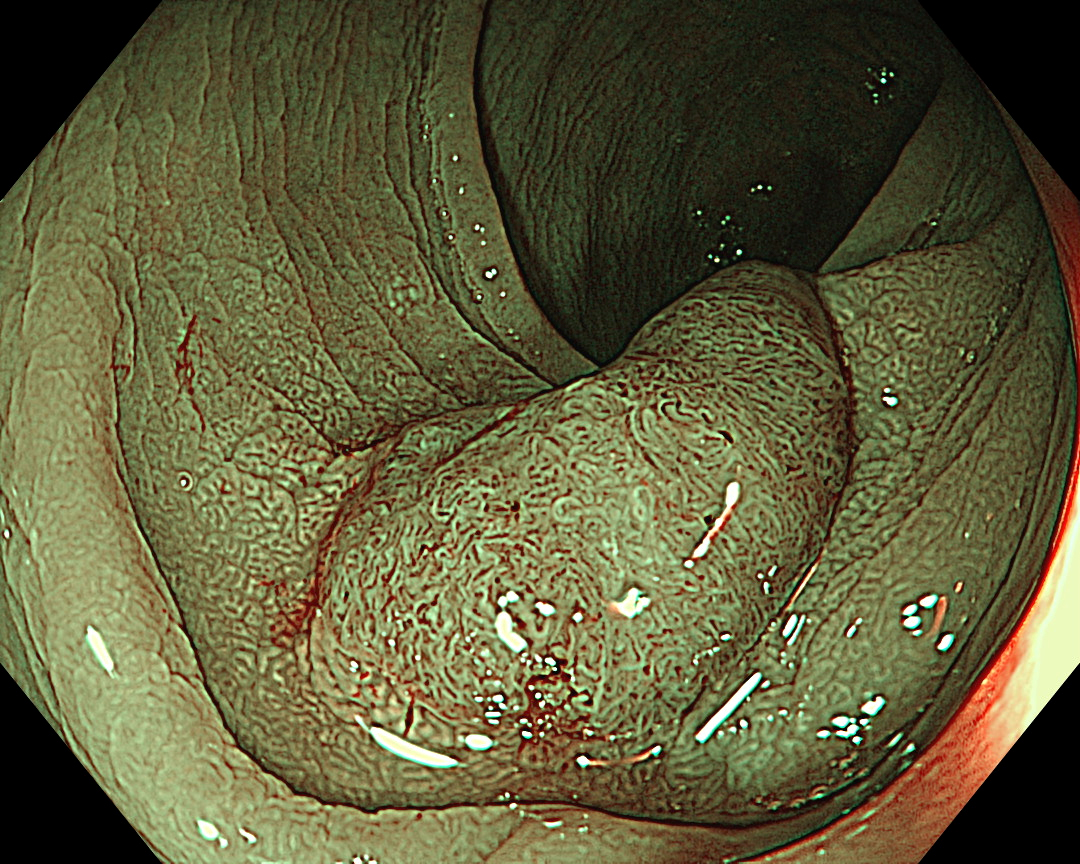
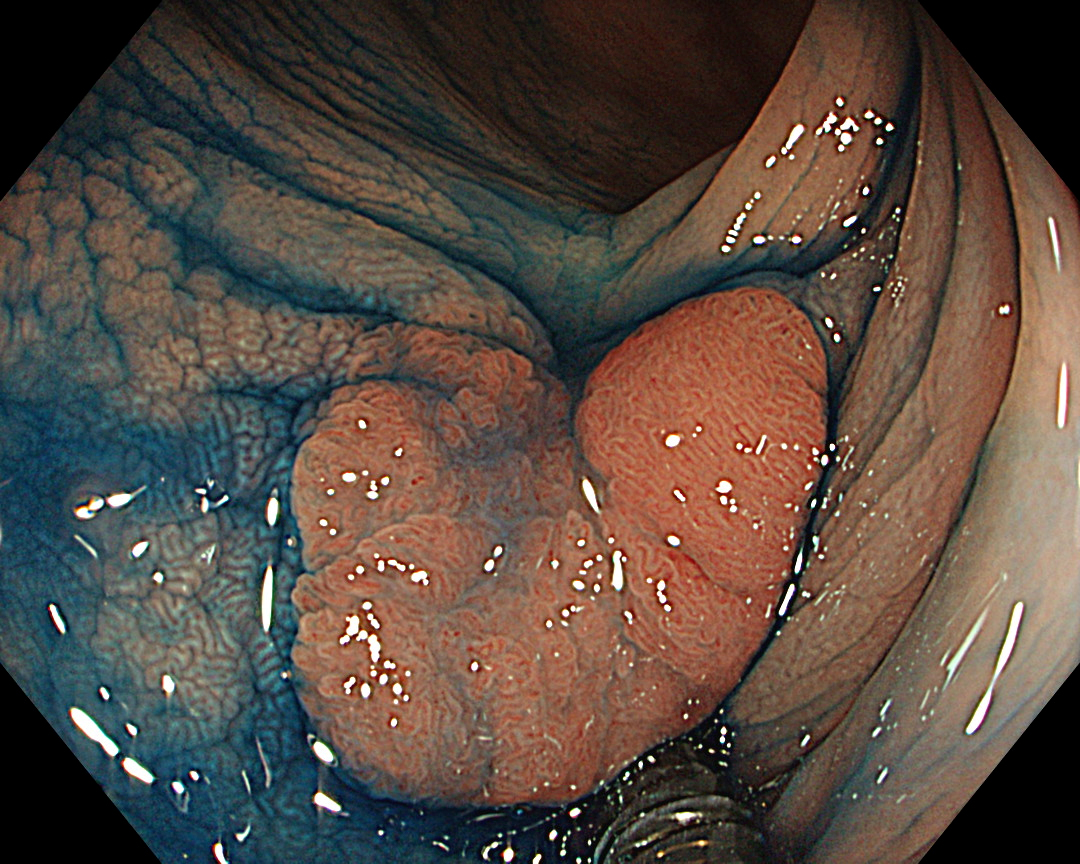
Non-magnifying NBI shows a uniform brown lesion, which can be classified as Type 2 in the NICE classification. However, the microvascular and surface structures are opaque and complex, especially near the center of the lesion, suggesting that further detailed observation should be performed. As magnifying endoscopes are not commonly used in Europe and North America, it seems that no further information could have been obtained.
The CF-EZ1500DI’s short focal length enables clear images to be obtained even when the lesion is as close as 3 mm, and microvessels and surface structures can be assessed without magnification. As the complex lever operations required in conventional magnification are not necessary with the CF-EZ1500DI, simply approaching the lesion can increase the degree of magnification. It is possible to determine whether observation in Near Focus mode is required by pressing a button.
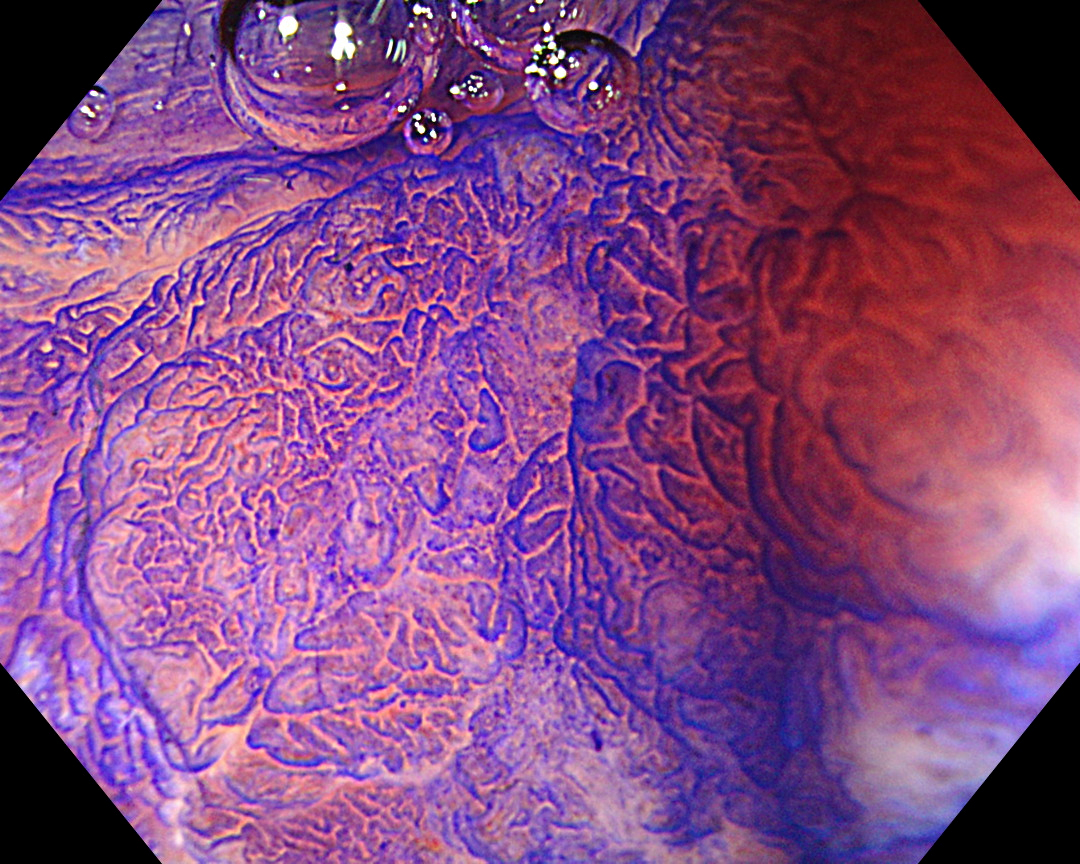
The Near Focus mode enables detailed observation with a magnification of approximately 80x, which is close to that of a conventional magnifying endoscope. The EDOF function widens the focal length and facilitates focusing, making it easy to obtain sharp images even when the area of interest is slightly concave, as in this case.
The CF-EZ1500DI, which allows almost seamless observation from normal to detailed magnification, is an excellent tool for providing more accurate and appropriate treatment, as it can easily magnify the lesion and increase the amount of information about the lesion.
* Specifications, design and accessories are subject to change without any notice or obligation on the part of the manufacturer
Dr. Shiaw-Hooi Ho Case 28: Pedunculated polyp
Mr. Peter Borch-Johnsen
- Keyword
- Content Type