Standard Imaging Techniques
Summary of scanning routes
The standard convex EUS scanning routes are listed below.
Transgastric approach (aortic route)
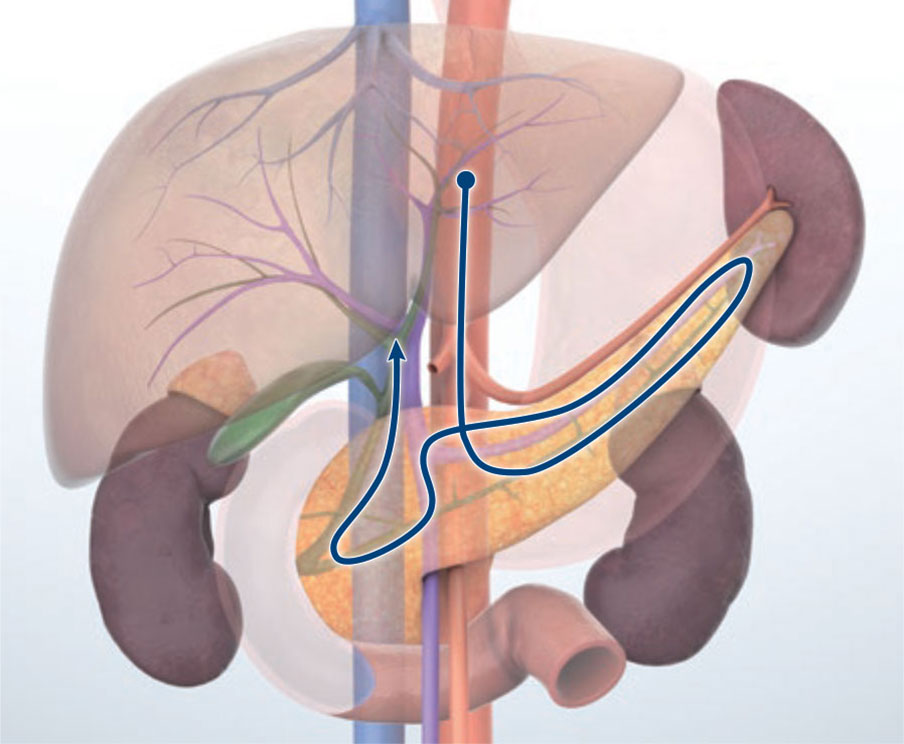
Transgastric approach (portal vein route)
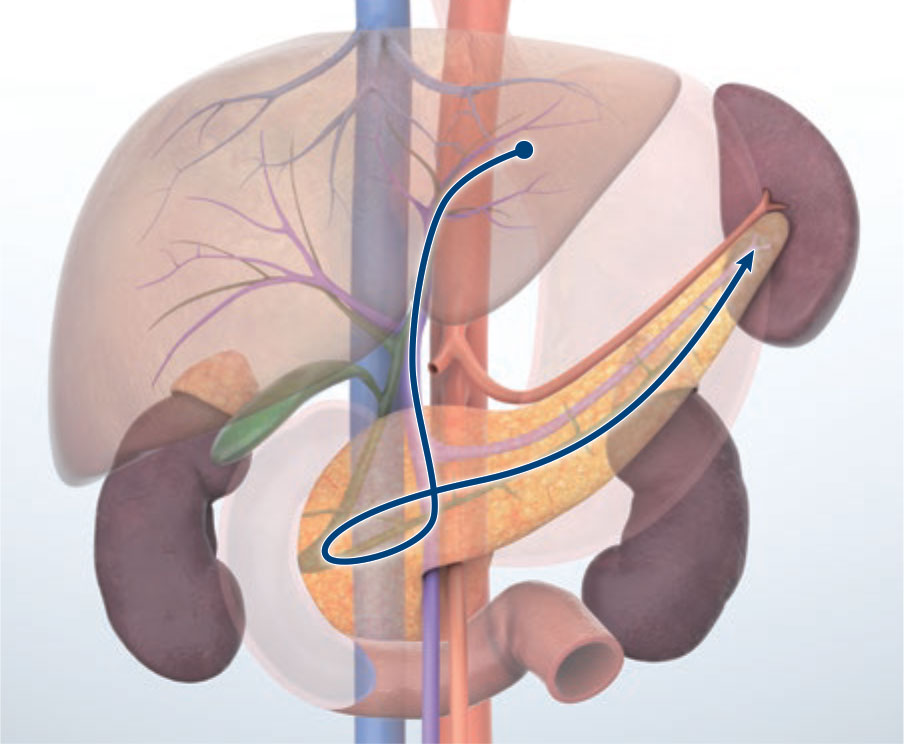
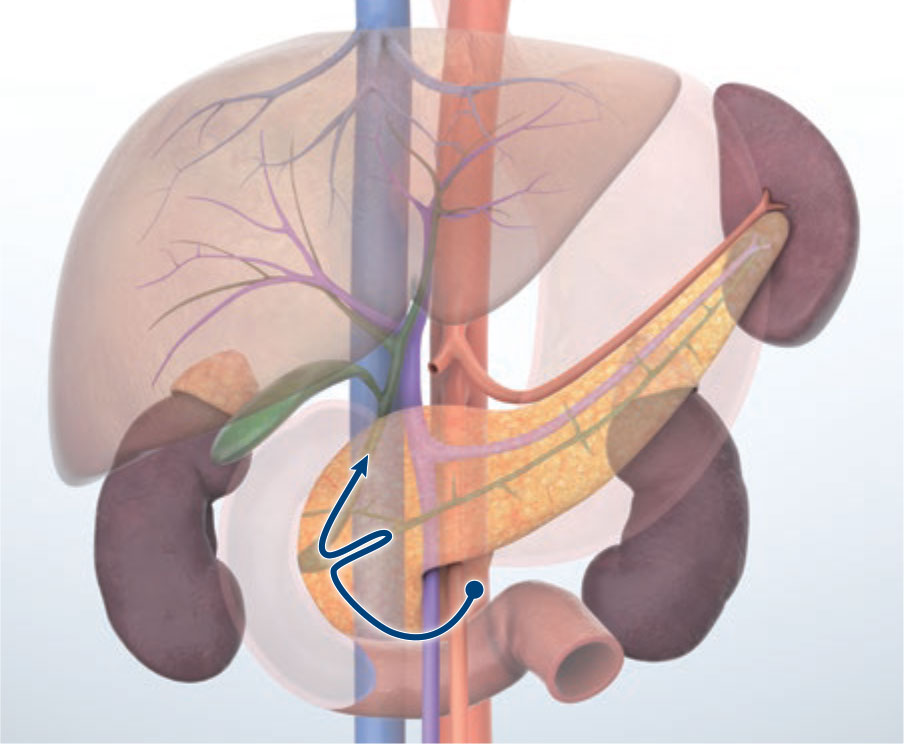
Transduodenal bulb approach
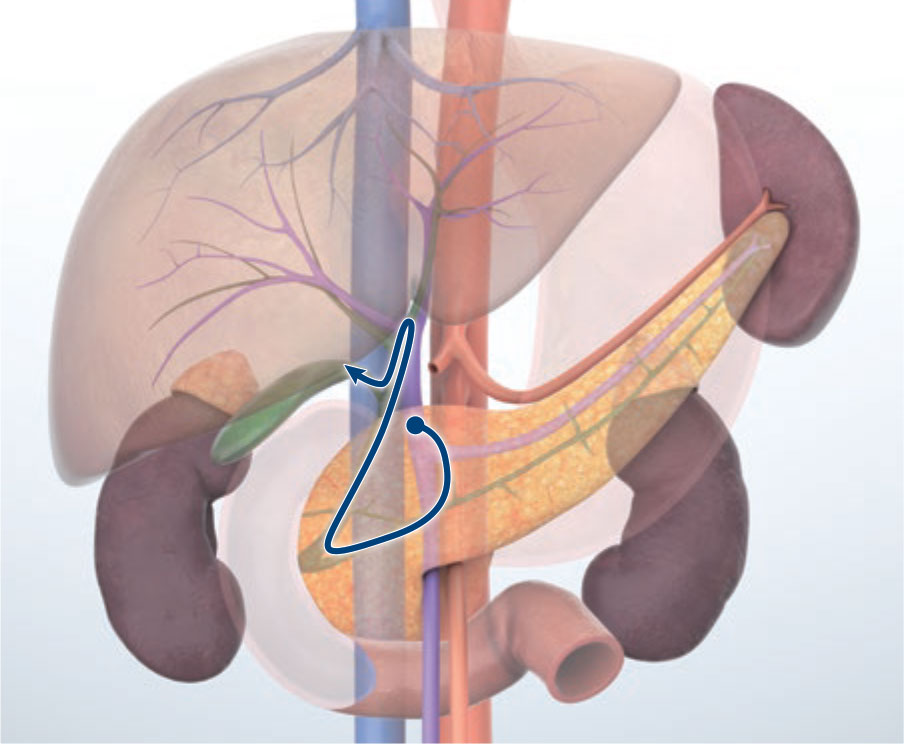
Transduodenal (descending part) approach
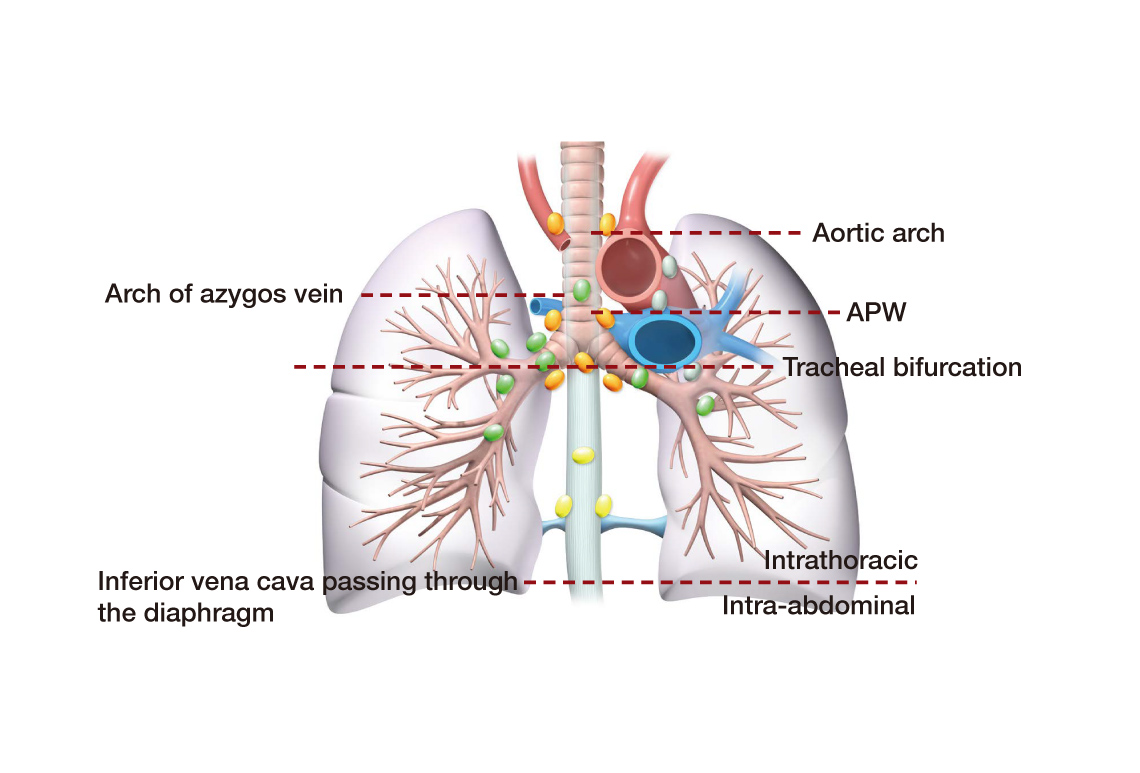
Anatomy around the esophagus
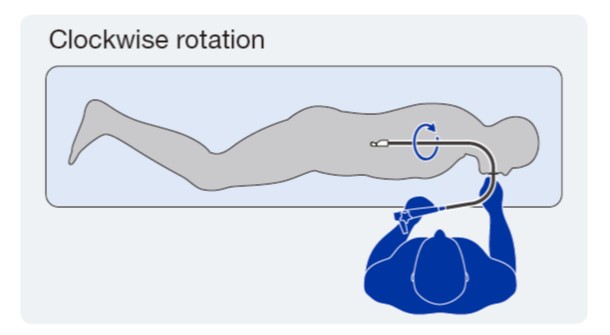
Orientation of the endosonographer and the control section and rotation of the endoscope
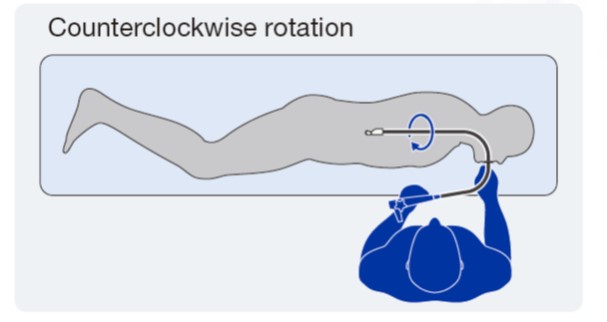
When imaging a target with convex EUS, torque operation of the endoscope is important. In this handbook, rightward rotation is referred to as “clockwise”, and leftward rotation as “counterclockwise”. When the transducer is pointing to the posterior side, the left side of the abdominal cavity is observed with clockwise rotation and the right side of the abdominal cavity is observed with counterclockwise rotation.
Clockwise rotation
Counterclockwise rotation
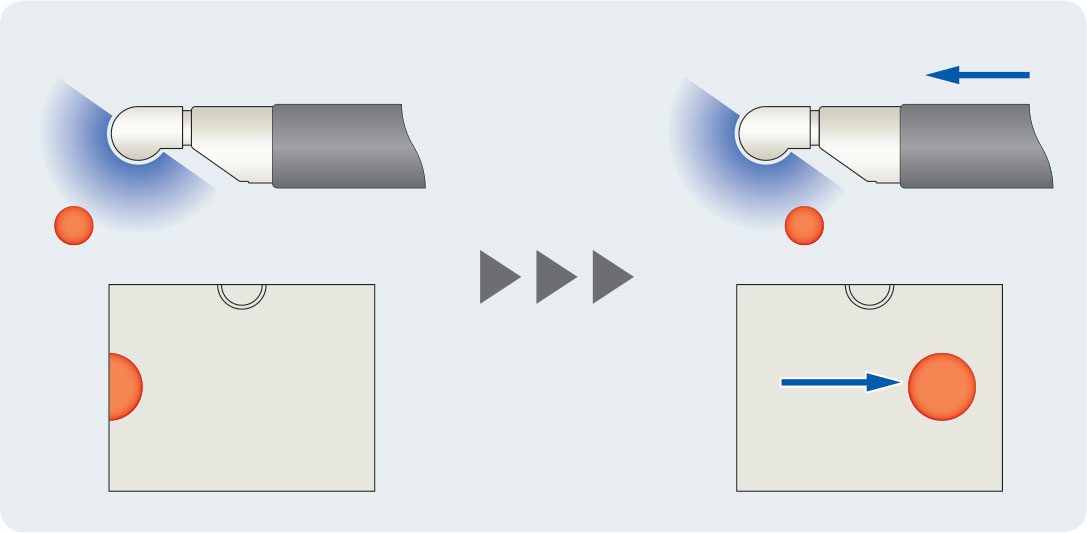
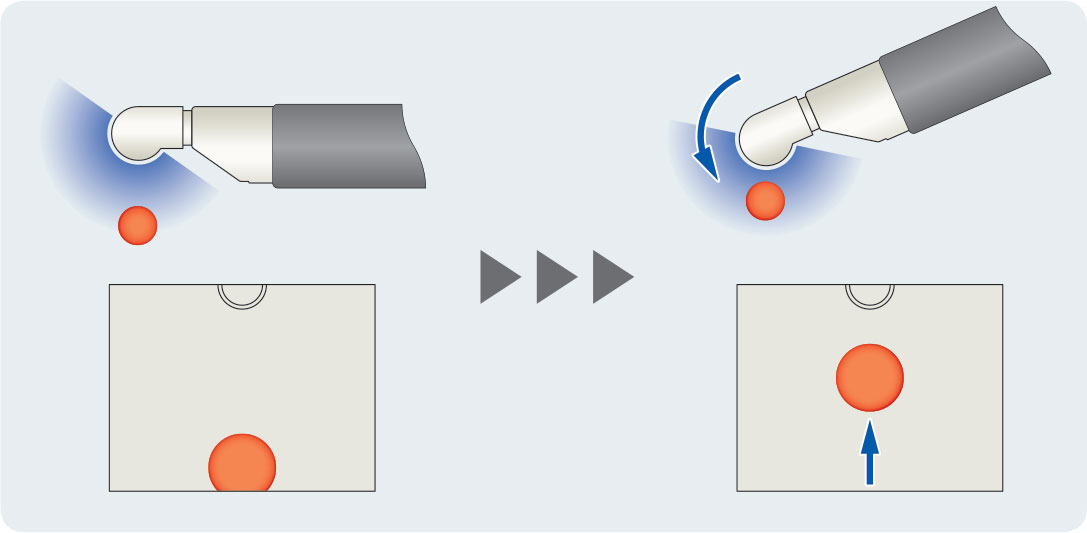
Relationship between the endoscope and target
As the scope is advanced, the target moves to the right on the ultrasound screen. Moreover, as the transducer is incorporated in the up angulation side of the scope tip, it moves closer to the target when the scope tip is bent upward, while the target moves upward on the ultrasound screen.
Abbreviations used in this handbook
| Ao | Aorta | SMV | Superior Mesenteric Vein |
| IVC | Inferior Vena Cava | IMA | Inferior Mesenteric Artery |
| PV | Portal Vein | GDA | Gastroduodenal Artery |
| UP | Umbilical Portion | Ph | Head of the Pancreas |
| CA | Celiac Artery | Pn | Neck of the Pancreas |
| SA | Splenic Artery | Pb | Body of the Pancreas |
| SV | Splenic Vein | Pt | Tail of the Pancreas |
| CHA | Common Hepatic Artery | MPD | Main Pancreatic Duct |
| PHA | Proper Hepatic Artery | BD | Bile Duct |
| RHA | Right Hepatic Artery | GB | Gallbladder |
| LHV | Left Hepatic Vein | CHD | Common Hepatic Duct |
| SMA | Superior Mesenteric Artery | APW | Aortopulmonary Window |
- Keyword
- Content Type